Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6416-6425.doi: 10.12307/2025.785
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dynamic stress analysis of maxillary sinus lifting without bone grafting and with immediate loading after bone grafting
Akliya·Anwar, Nafisa·Gupur, Baibugafu·Yelisi, Zilalai·Gulaiti, Guzalnur·Emrayim, Nijat·Tursun
- Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-07-27Accepted:2024-10-11Online:2025-10-28Published:2025-03-27 -
Contact:Nijat·Tursun, MS, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Akliya·Anwar, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2021D01C362 (to NT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Akliya·Anwar, Nafisa·Gupur, Baibugafu·Yelisi, Zilalai·Gulaiti, Guzalnur·Emrayim, Nijat·Tursun. Dynamic stress analysis of maxillary sinus lifting without bone grafting and with immediate loading after bone grafting[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6416-6425.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

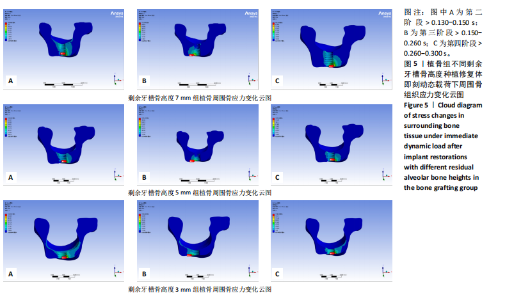
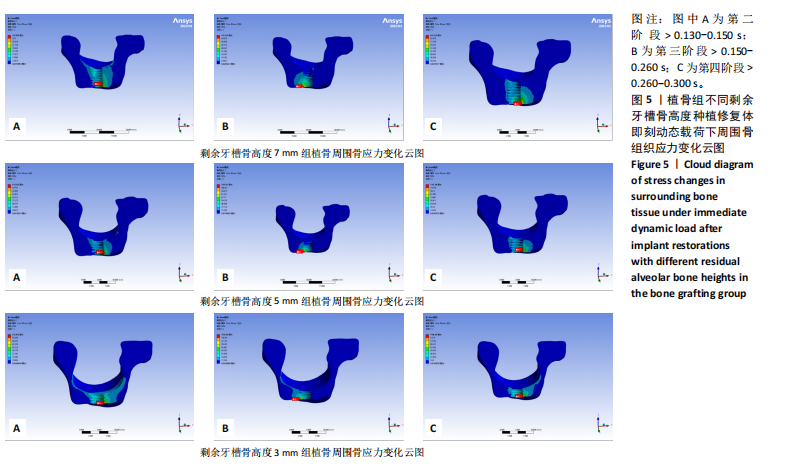
2.1 10 mm常规牙槽骨高度组应力分布情况 10 mm常规牙槽骨高度组即刻动态载荷下的应力分布云图,见图4。在不同咬合阶段应力分布集中区域均位于种植体颈部骨组织,种植体颈部骨组织应力均大于根方骨组织。种植体修复体受力时周围骨组织应力从第二咬合阶段开始增高,到达第三咬合阶段前增长幅度最大,在第四咬合阶段达到最高等效应力值,见表4。 2.2 植骨组即刻动态加载时周围骨组织应力分布情况 多种剩余骨高度下,植骨组种植修复体在动态加载过程中周围骨组织的应力变化云图,见图5。植骨组无论骨高度如何,各咬合阶段种植体颈部骨组织均为应力最大区域,骨高度和植骨的多少都无法避免颈部骨组织应力高于种植体根部填充材料的应力水平。"
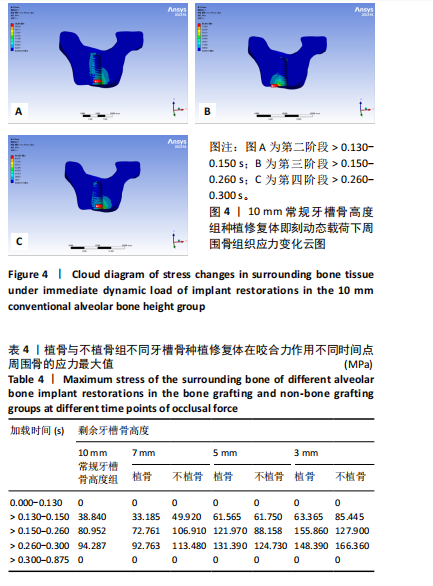
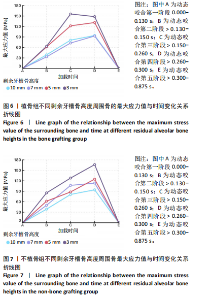
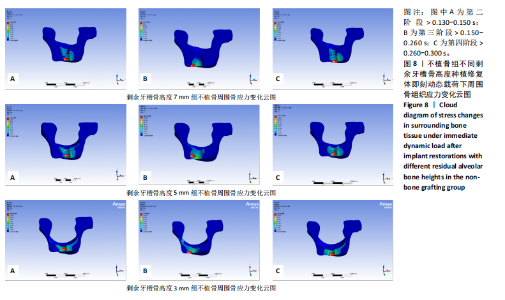
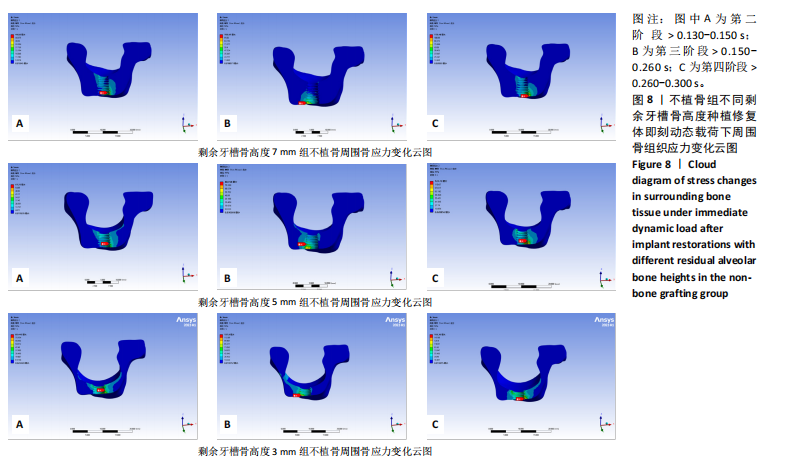
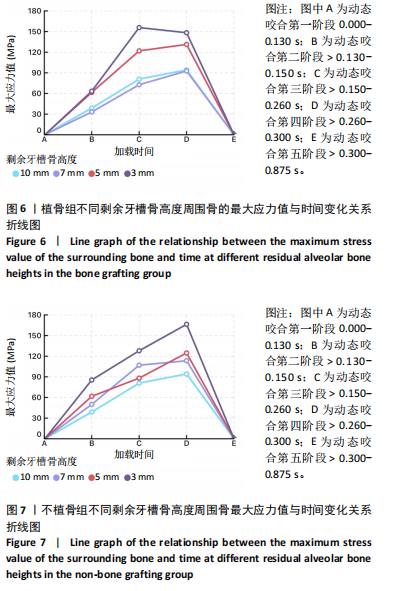
在剩余牙槽骨高度3,5,7 mm植骨条件下,第二及第四咬合阶段虽以种植体颈部骨组织为主要受力点,但上颌窦底部骨组织亦出现了应力分布区域的扩大,其应力集中区域及受力范围的扩大依次为3 mm > 5 mm > 7 mm。不同剩余骨高度种植修复体受力时种植体周围骨应力上升增长幅度均在第二咬合阶段(> 0.130-0.150 s)至第三咬合阶段(> 0.150-0.260 s)内最大,当加载力到第三阶段时3 mm周围骨应力上升幅度达到最大值,当加载力至第四阶段(> 0.260-0.300 s)时,5,7 mm组周围骨等效应力峰值均达到最大值。见表4,图6。 2.3 不植骨组动态加载时周围骨组织应力分布情况 不植骨组在动态载荷过程中周围骨应力分布变化,见图7,8。不植骨组3种剩余牙槽骨高度种植修复体在咀嚼过程各时间节点上,种植体颈部骨组织仍然是最大应力集中区,最大应力范围相对于植骨组更为集中,不植骨组应力分布范围大于植骨组,尤其在剩余牙槽骨高度为3 mm及5 mm时扩展至上颌窦底部周围的骨组织,形成了更为广泛的应力分布网络。 在不植骨组内3,5,7 mm剩余牙槽骨高度条件下,应力增长幅度最大的还是在第二咬合阶段至第三咬合阶段,在第四咬合阶段达到高峰,剩余牙槽骨高度3 mm时在第四咬合阶段应力值达到最高。见表4,图7,8。 2.4 总结 无论是否进行骨充填,不同剩余牙槽骨高度种植修复体在受咬合力时,通过应力分布云图一致观察到种植体应力集中区域位于颈缘部。不同剩余牙槽骨高度"
| [1] 陈浚,徐光宙.上颌窦底提升技术的研究现状[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2023,21(3):291-300. [2] DENG Y, TONG C, GAO K, et al. Modified internal sinus elevation for patients with low residual bone height: A retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2023;25(3):458-472. [3] CHAUSHU L, CHAUSHU G, KOLERMAN R, et al. Histomorphometrical Assessment of Sinus Augmentation Using Allograft (Particles or Block) and Simultaneous Implant Placement. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9046. [4] LYU M, XU D, ZHANG X, et al. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation: a review of current evidence on anatomical factors and a decision tree. Int J Oral Sci. 2023;15(1):41. [5] 解孟佳,周志霖,张雅彤,等.剩余骨高度< 3 mm时联合CGF与Bio-Oss骨粉行液压法上颌窦内提升术并同期种植一例[J].海南医学,2023,34(20):3008-3011. [6] MANSO MC, WASSAL T. A 10-year longitudinal study of 160 implants simultaneously installed in severely atrophic posterior maxillas grafted with autogenous bone and a synthetic bioactive resorbable graft. Implant Dent. 2010;19(4):351-360. [7] 罗宝,黄咏瑜,刘伟,等.上颌窦内提升术同期种植内提3 mm以内植入骨粉与不植入骨粉的研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022, 38(10):614-617. [8] BOK S, GREENBLATT MB. Shaping the sinuses: a novel Krt14+Ctsk+ cell lineage driving regenerative bone formation. Cell Res. 2022;32(9):791-792. [9] 刘佳怡,何雨桐,汪振华.有限元分析法在口腔修复学中的应用进展[J].医学综述,2019,25(16):3248-3252. [10] 罗宇,江青松.口腔生物力学的研究方法[J].北京口腔医学,2023, 31(3):217-221. [11] GAO X, MA S, HUANG B, et al. Effect of Age on Transalveolar Sinus Floor Elevation with Simultaneous Placement of Dental Implants: A Retrospective Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2023;38(4):811-819. [12] LEKHOLM U. Surgical considerations and possible shortcomings of host sites. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;79(1):43-48. [13] JAMCOSKI VH, FAOT F, MARCELLO-MACHADO RM, et al. 15-Year Retrospective Study on the Success Rate of Maxillary Sinus Augmentation and Implants: Influence of Bone Substitute Type, Presurgical Bone Height, and Membrane Perforation during Sinus Lift. Biomed Res Int. 2023;2023:9144661. [14] 中华口腔医学会口腔种植专业委员会.上颌窦底提升专家共识:上颌窦间隔[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2024,29(2):103-108.
[15] 杜军,万哲.植入位点及轴向对上颌中切牙即刻种植即刻负重应力影响的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2023,38(2):353-359. [16] 孙江伟,王俊祥,白布加甫·叶力思,等.不同光滑颈圈种植体修复时应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(7):1004-1011. [17] 徐大鹏,景捷,马璐,等.上颌窦内提升术最佳二期修复时间的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(11):1647-1652. [18] 陈新民,赵云凤.口腔生物力学[M].北京:科学出版社,2010:225-234. [19] 王谜,刘定坤,邹俊东,等.有限元法模拟下颌磨牙咀嚼载荷的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2020,40(7):673-676. [20] 姜姗.不同角度基台在上颌第一磨牙区种植修复的三维有限元动态载荷分析[D].锦州:锦州医科大学,2023. [21] CORONEL ZABALBU B, CÁCERES OA, VERGARA-BUENAVENTURA A. Levantamiento del seno maxilar sin injerto óseo e implante simultáneo: un reporte de caso [Graftless maxillary sinus lift with simultaneous implant placement: a case report. Rev Cient Odontol (Lima). 2024; 12(2):e202. [22] 何添荣,陈玉英,许香娜,等.上颌窦内外侧宽度对不植骨上颌窦内提升的成骨影响[J].口腔生物医学,2021,12(4):257-261. [23] 胡宁,李凤丹,江银华.植骨与否对上颌窦底内提升同期种植术临床疗效的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2023,32(1):101-104. [24] 夏海斌,徐珺怡.上颌窦底内提升同期植入种植体的研究现状[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2024,29(2):109-117. [25] LIU L, YU WH, LI XT, et al. Clinical application study of immediate implantation without bone grafting in maxillary molars: a clinical study with one-year follow up. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;60(3):332-336. [26] 薄湛南,何冬冬.不用骨移植材对穿牙槽嵴顶上颌窦底提升术疗效的影响[J].辽宁医学杂志,2024,38(3):74-76. [27] SONG DS, KIM CH, KIM BJ, et al. Tenting effect of dental implant on maxillary sinus lift without grafting. J Dent Sci. 2020;15(3):278-285. [28] PRAMSTRALLER M, FARINA R, FRANCESCHETTI G, et al. Ridge dimensions of the edentulous posterior maxilla: a retrospective analysis of a cohort of 127 patients using computerized tomography data. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(1):54-61. [29] KOPECKA D, SIMUNEK A, BRAZDA T, et al. Relationship between subsinus bone height and bone volume requirements for dental implants: a human radiographic study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(1):48-54. [30] JADACH R, ASA’AD F, RASPERINI G, et al. Classifying Maxillary Sinuses of Polish Patients for Sinus Lift: A Pilot Study. Dent J (Basel). 2024;12(2):35. [31] 马犇,朱佳栋,郑泽光,等.即刻种植和延期种植及植骨后延期种植的疗效比较[J].当代医学,2021,27(19):171-172. [32] 邓大贵.即刻种植与延期种植在后牙区义齿种植中的应用效果分析[J].中国社区医师,2024,40(6):35-37. [33] EINI E, YOUSEFIMANESH H, ASHTIANI AH, et al. Comparing success of immediate versus delay loading of implants in fresh sockets: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;26(2): 185-194. [34] 詹红伟,王倩,移植,等.机械应力下骨细胞行为变化的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(2):250-256. [35] 梅冰馨,刘克华,张太阳.即刻负重对前牙种植后骨量的影响[J].医疗装备,2022,35(3):90-92. [36] GLAUSER R, LUNDGREN AK, GOTTLOW J, et al. Immediate occlusal loading of Brånemark TiUnite implants placed predominantly in soft bone: 1-year results of a prospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5 Suppl 1:47-56. [37] ESPOSITO M, GRUFFERTY B, PAPAVASILIOU G, et al. Immediate loading of occluding definitive partial fixed prostheses vs non-occluding provisional restorations - 3-year post-loading results from a pragmatic multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2018; 11(3):309-320. [38] MORRIS GA, STEINBERG MJ, DRAGO C. Full arch immediate occlusal loading using site specific implants: A clinical series of 10 patients (13 arches). J Prosthodont. 2023;32(3):204-213. [39] ZANINOVICH M, DRAGO C. Prosthodontic criteria for maxillary immediate occlusal loading, surgical classifications of atrophic maxillae, and presentation of a new implant/anatomic classification system for immediate maxillary rehabilitation. J Prosthodont. 2024. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13898. [40] MELLO CC, LEMOS CAA, VERRI FR, et al. Immediate implant placement into fresh extraction sockets versus delayed implants into healed sockets: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;46(9):1162-1177. [41] LANG NP, PUN L, LAU KY, et al. A systematic review on survival and success rates of implants placed immediately into fresh extraction sockets after at least 1 year. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23 Suppl 5: 39-66. [42] WIPAWIN R, AMORNSETTACHAI P, PANYAYONG W, et al. Clinical outcomes of 3-5 years follow-up of immediate implant placement in posterior teeth: a prospective study. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):312. [43] CRICCHIO G, IMBURGIA M, SENNERBY L, et al. Immediate loading of implants placed simultaneously with sinus membrane elevation in the posterior atrophic maxilla: a two-year follow-up study on 10 patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2014;16(4):609-617. [44] 吴越琳,刘加荣.三维有限元分析在口腔医学领域的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2021,41(7):659-663. [45] 张孟婷,高岚.三维有限元下后牙牙体缺损修复的研究现状[J].河北医药,2024,46(8):1239-1243. [46] 郭海涛,邓引昕,马攀,等.上颌窦底提升术后不同骨吸收高度种植体周围应力的三维有限元分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2023, 24(3):174-179. [47] 王俊祥,孙江伟,白布加甫·叶力思,等.动态加载下3种基台材料对上颌角度植入种植修复体周围骨应力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(3):398-405. [48] 张兴,刘英,陈松龄,等.上颌窦内提升不植骨同期种植术:3年临床回顾性研究[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(1):46-49. [49] BARROS F, FERNANDES CMDS, KUHNEN B, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of the maxillary sinus according to sex, age, skin color, and nutritional status: A study with live Brazilian subjects using cone-beam computed tomography. Arch Oral Biol. 2022;139:105435. [50] DENG Y, MA R, HE Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the maxillary sinus floor membrane during internal sinus floor elevation with implants at different angles of the maxillary sinus angles. Int J Implant Dent. 2024;10(1):11. [51] 罗宇,江青松.口腔生物力学的研究方法[J].北京口腔医学,2023, 31(3):217-221. |
| [1] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [4] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [7] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [8] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [9] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [10] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [11] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [12] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [13] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [14] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [15] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||