Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5757-5764.doi: 10.12307/2025.816
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of biomechanical characteristics of superior and inferior pubic ramus fractures fixed with different internal fixation methods
Rao Xin1, 2, 3, Jiang Daixiang1, 2, 3, Lu Hui3, Luo Yangxing3, Li Meng4, Liu Dingxi4, Wu Qimei5, Liu Rong1, 2, 3, 5
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; 2School of Medicine, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 3Institute of Medical Innovation and Transformation, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; 4School of Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430080, Hubei Province, China; 5Wuhan Liu Sanwu Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopedic Hospital, Wuhan 430200, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-22Accepted:2024-07-10Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-04 -
Contact:Liu Rong, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; School of Medicine, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; Institute of Medical Innovation and Transformation, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; Wuhan Liu Sanwu Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopedic Hospital, Wuhan 430200, Hubei Province, China Co-corresponding author: Wu Qimei, MS, Chief physician, Wuhan Liu Sanwu Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopedic Hospital, Wuhan 430200, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Rao Xin, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; School of Medicine, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; Institute of Medical Innovation and Transformation, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China Jiang Daixiang, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; School of Medicine, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; Institute of Medical Innovation and Transformation, Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China Rao Xin and Jiang Daixiang contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:2023 Joint Fund for Occupational Hazard Identification and Control in Hubei Key Laboratory, No. JF2023-K01 (to LR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Rao Xin, Jiang Daixiang, Lu Hui Luo Yangxing, Li Meng, Liu Dingxi, Wu Qimei, Liu Rong. Comparison of biomechanical characteristics of superior and inferior pubic ramus fractures fixed with different internal fixation methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5757-5764.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
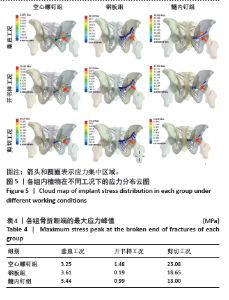
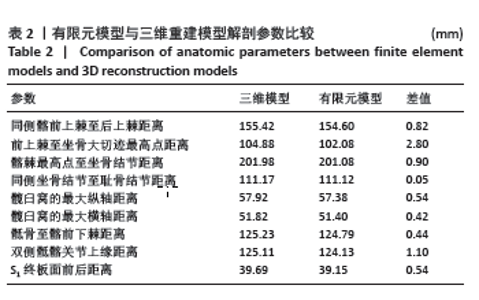
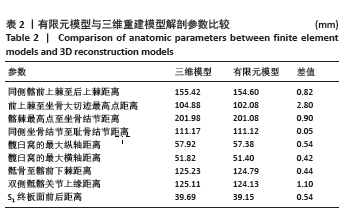
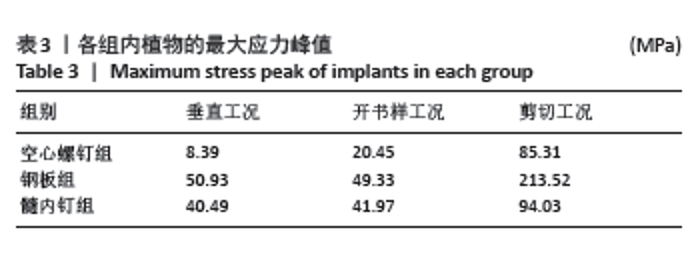
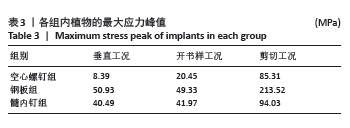
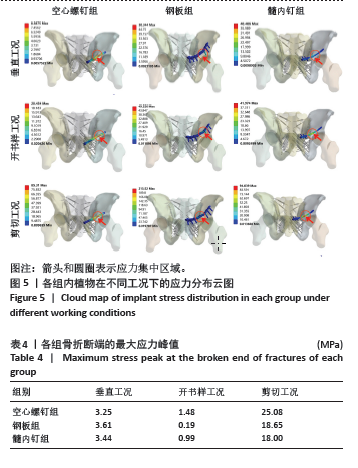
内植物的应力分布见图5,在垂直、开书样、剪切3种工况下,空心螺钉的应力都集中于耻骨上支骨折线附近的钉体部,其应力范围分别为3.731-8.39 MPa、9.10-20.45 MPa、37.92-85.31 MPa。在垂直、开书样、剪切3种工况下,髓内钉的应力集中相似,集中于耻骨上支骨折线附近的钉体部,其应力范围分别为18.00-31.49 MPa、18.66-32.64 MPa、41.80-94.03 MPa。在垂直、开书样、剪切3种工况下,钢板应力集中于钢板中间部与靠近骨折线的固定髂骨的第1根螺钉,其应力范围分别为22.37-50.34 MPa、21.93-49.33 MPa、94.91-213.52 MPa。 2.3 骨折断端应力分布与峰值 比较耻骨骨折上支耻骨端最大应力,见表4。在垂直工况下,钢板组耻骨骨折上支耻骨端应力峰值最大,其次是髓内钉组,耻骨骨折上支耻骨端应力最小的是空心螺钉,其峰值分别为3.61,3.44和3.25 MPa,3组断端应力峰值没有明显差异;在开书样工况下,空心螺钉组的耻骨骨折上支耻骨端的应力峰值最大,其次是髓内钉组,耻骨骨折上支耻骨端应力最小的是钢板组,其峰值分别为1.48,0.99和0.19 MPa;在剪切工况下,空心螺钉组的耻骨骨折上支耻骨端的应力峰值最大,其次是钢板组,耻骨骨折上支耻骨端应力最小的是髓内钉组,其峰值分别为25.08,18.65,18.00 MPa,从数值来看空心螺钉明显高于其他两组。"
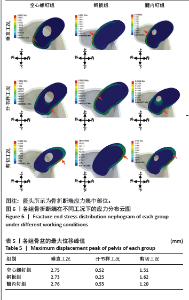
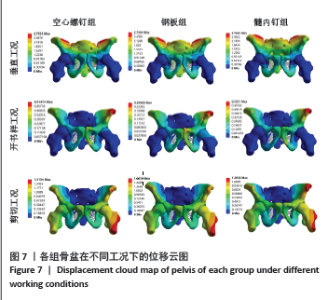
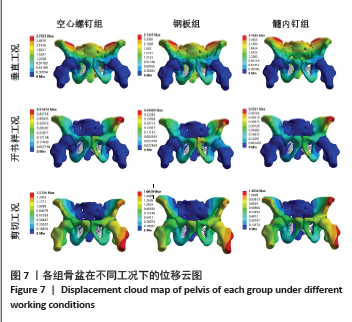
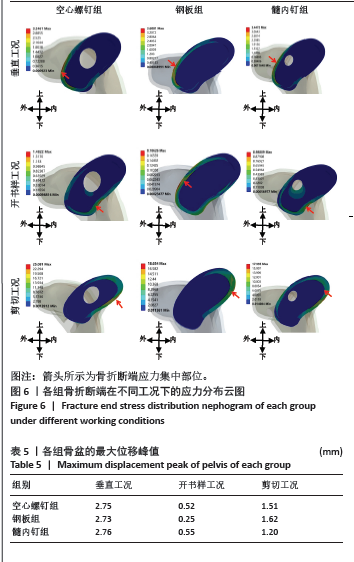
耻骨上支骨折断端应力分布见图6,在垂直工况下,3组的耻骨骨折上端断面应力集中于断面的外上方边缘处;在开书样工况下,空心螺钉组与髓内钉组的断面应力集中于耻骨上支骨折断端的外下侧边缘处;钢板组断面的应力集中于耻骨上支骨折耻骨端的应力集中于断端外上方的边缘处;在剪切工况下,空心螺钉组、钢板组、髓内钉组应力分布相似:耻骨上支骨折的耻骨端应力集中于断端内上方的边缘处。 2.4 骨盆的整体位移 骨盆整体位移见表5。在垂直工况下,髓内钉组骨盆整体的位移峰值最大,其次是空心螺钉组,骨盆整体位移最小的是钢板,其峰值分别为2.76,2.75,2.73 mm,从数值来看没有明显的区别。在开书样工况下,髓内钉组骨盆整体的位移峰值最大,其次为空心螺钉组,最小的骨盆整体位移是钢板组,其位移峰值分别为0.55,0.52,0.25 mm,从结果来看钢板组骨盆位移明显低于空心螺钉组与髓内钉组,然而髓内钉组与钢板组没有明显的差异。在剪切工况下,钢板组的骨盆整体位移峰值最大,其次空心螺钉组,最小的是髓内钉组,其位移峰值分为1.62,1.51,1.20 mm,从骨盆的位移峰值来看髓内钉组骨盆位移明显小于钢板组和空心螺钉组。见图7。"
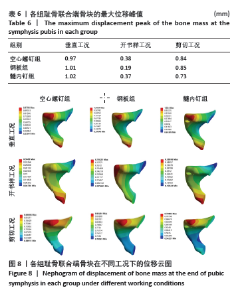
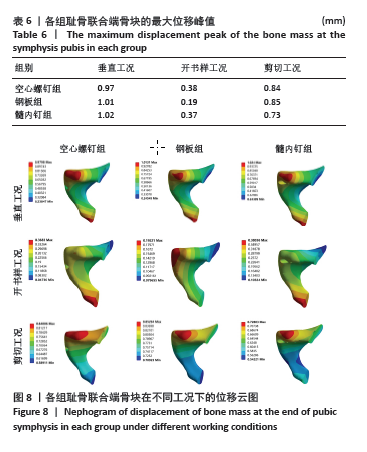
2.5 耻骨联合端骨块整体的位移 比较耻骨联合端骨块的位移,骨块位移见表6。在垂直工况下,髓内钉组的骨折块位移最大,其次是钢板组,最小骨块位移最小的是空心螺钉,其骨块位移峰值分别为1.02,1.01,0.97 mm,从位移的数字来看其实没有明显的差异。在开书工况下,空心螺钉组的骨折块位移最大,其次是髓内钉组,骨折块位移最小的是钢板,其位移峰值分为0.38,0.37, 0.19 mm,从数值来看钢板的位移明显小于髓内钉组与空心螺钉组。在剪切工况下,钢板组骨块的位移最大,其次是空心螺钉组,最小的骨块位移是髓内钉,其骨块位移峰值分别为0.85,0.84,0.73 mm,骨块位移峰值显示,髓内钉组的骨块位移明显小于钢板组和空心螺钉组,但是钢板组和空心螺钉组的骨块位移没有明显差别。见图8。"
| [1] COCCOLINI F, STAHEL PF, MONTORI G, et al. Pelvic trauma: WSES classification and guidelines. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12(1):1-18. [2] HU S, GUO J, ZHU B, et al. Epidemiology and burden of pelvic fractures: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Injury. 2023; 54(2):589-597. [3] FLANAGAN CD, FAIRCHILD R, MCCASKEY M, et al. Union and displacement characteristics following percutaneous screw fixation of superior pubic rami fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s00590-023-03681-0. [4] ROMMENS PM, GRAAFEN M, ARAND C, et al. Minimal-invasive stabilization of anterior pelvic ring fractures with retrograde transpubic screws. Injury. 2020;51(2):340-346. [5] 刘敏,周晓赛,王俊诚,等. 不同方法治疗不稳定骨盆骨折中前环损伤的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2019,32(2):156-160. [6] 王伟斌,袁欣华,郑轶,等. 经皮桥接钢板与逆行耻骨上支髓内螺钉固定骨盆前环骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国骨伤,2020,33(1):47-52. [7] 成凯,聂博渊,杨朝晖. 微创手术治疗骨盆前环骨折的研究进展[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2023,26(1):146-150. [8] 尹恩志,罗杨兴,袁雪峰,等. 逆行耻骨上支髓内钉固定治疗骨盆前环骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2023,25(6):491-497. [9] WELCH-PHILLIPS A, GIBBONS D, AHERN DP, et al. What Is Finite Element Analysis? Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(8):323-324. [10] 陈钵,秦大平,张晓刚,等.有限元分析法在脊柱生物力学中的研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2020,26(3):208-211,216. [11] 赵勇,马玉鹏,邹德鑫,等.三种微创内固定治疗骨盆前环双侧骨折的生物力学比较[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(11):2110-2113. [12] 鲁辉,徐玲,蒋代翔,等. 经皮逆向螺钉模拟治疗耻骨上支骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):1999-2004. [13] 蒋代翔,鲁辉,马玲,等. 基于三维骨折地图技术的跟骨骨折线分布研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18):2842-2847. [14] ZHAO Y, MA Y, ZOU D, et al. Biomechanical comparison of three minimally invasive fixations for unilateral pubic rami fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):594. [15] XU L, CAO X, LU H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of percutaneous anterograde and retrograde screw implantation for superior ramus pubis fractures: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(12): 8676-8685. [16] SONG Y, SHAO C, YANG X, et al. Biomechanical study of anterior and posterior pelvic rings using pedicle screw fixation for Tile C1 pelvic fractures: Finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2022;17(8):e0273351. [17] STARR AJ, NAKATANI T, REINERT CM, et al. Superior pubic ramus fractures fixed with percutaneous screws: what predicts fixation failure? J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(2):81-87. [18] HU P, WU T, WANG HZ, et al. Influence of Different Boundary Conditions in Finite Element Analysis on Pelvic Biomechanical Load Transmission. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):115-122. [19] 郭东鸿,童凯,王钢. 五种内固定方式固定髋臼后柱骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(6):529-535. [20] 王叙进,方诗元,徐磊,等. 有限元法分析不同内固定方法治疗复杂性骨盆骨折的力学稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(27):4354-4358. [21] 张永强,章莹,夏远军,等. 髋臼部T形骨折四种不同内固定方式的生物力学有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2017,35(3): 312-317. [22] HU P, WU T, WANG HZ, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Three Internal Fixation Techniques for Stabilizing Posterior Pelvic Ring Disruption: A 3D Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2): 195-203. [23] HUNG CC, WU JL, LI YT, et al. Minimally invasive treatment for anterior pelvic ring injuries with modified pedicle screw-rod fixation: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):238. [24] 张建,吴克俭,张伟佳,等.全螺纹加压无头空心螺钉经皮固定骨盆骨折[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(1):91-96. [25] TIMMER RA, MOSTERT CQB, KRIJNEN P, et al. The relation between surgical approaches for pelvic ring and acetabular fractures and postoperative complications: a systematic review. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023;49(2):709-722. [26] LIU L, FAN S, ZENG D, et al. Identification of safe channels for screws in the anterior pelvic ring fixation system. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):312. [27] THAUNAT M, LAUDE F, PAILLARD P, et al. Transcondylar traction as a closed reduction technique in vertically unstable pelvic ring disruption. Int Orthop. 2008;32(1):7-12. [28] JARRAGH A, LARI A, SHAIKH M. A computed tomography (CT) based morphometric study of superior pubic ramus anatomy among Arabs to determine safe intramedullary pubic rami screw insertion. Surg Radiol Anat. 2023;45(5):603-609. [29] KIM CH, KIM JW. Plate versus sacroiliac screw fixation for treating posterior pelvic ring fracture: a Systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury. 2020;51(10):2259-2266. [30] PERANDINI S, PERANDINI A, PUNTEL G, et al. Corona mortis variant of the obturator artery: a systematic study of 300 hemipelvises by means of computed tomography angiography. Pol J Radiol. 2018;83: e519-e523. [31] 陶岳峰,江兵,朱炳斌,等.微创经皮钢板内固定治疗骨盆前环骨折临床观察[J]. 山东医药,2023,63(1):62-64. [32] 张功林,师富贵,赵来绪,等.重建钢板微创内固定治疗骨盆前环骨折[J]. 中华卫生应急电子杂志,2020,6(1):57-59. [33] GUO HZ, TANG YC, GUO DQ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of four different posterior instrumentation techniques for single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(10):6160-6169. [34] 李祖涛,翁友林,郭彬,等. 髓内钉系统与空心螺钉治疗骨盆前环骨折的疗效[J]. 实用医学杂志,2023,39(2):244-248. [35] ABDELFATTAH A, MOED BR. Ligamentous contributions to pelvic stability in a rotationally unstable open-book injury: a cadaver study. Injury. 2014;45(10):1599-1603. [36] HE Y, LU Y, YIN B, et al. Numerical Investigation on the Biomechanical Performance of Laparoscopic-Assisted Plate Used for Fixing Pelvic Anterior Ring Fracture. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017:9261037. [37] GUO HZ, TANG YC, GUO DQ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of four different posterior instrumentation techniques for single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(10):6160-6169. [38] ZHENG YQ, CHEN LL, SHEN JZ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of seven fixation methods to treat pubic symphysis diastasis using finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):189. |
| [1] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [2] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [3] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [4] | Wu Hongxu, Liu Xuanyu, Wang Taoyu, Wang Shiyao, Cheng Jingyi, Zhang Mingwen, Zhang Yinxia, Liu Zhihua, Wang Xiaojie. Finite element simulation of scoliosis with muscle unit introduction: verification of correction effect under bidirectional load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2172-2181. |
| [5] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [6] | Zhou Daobin, Wang Kehao, Xie Yang, Ning Rende. Biomechanical characteristics of volar locking plate only versus combined dorsal mini-plate fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal ulnar fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2255-2261. |
| [7] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [8] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [9] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [10] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [11] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [12] | Yan Xiangning, Chen Lei, Chen Yonghuan, Wang Chao, Li Xiaosheng. Influence of different depths and loads on knee joint mechanics and peripheral muscle force characteristics during squatting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2236-2247. |
| [13] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [14] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Mechanical effect of mechanical wear of abutment screws on the Morse taper connection implant system: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1375-1383. |
| [15] | Zhong Caihong, Xiao Xiaoge, Li Ming, Lin Jianhong, Hong Jing. Biomechanical mechanism of sports-related patellar tendinitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1417-1423. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||