Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5680-5687.doi: 10.12307/2025.737
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha regulating bone homeostasis in oral and maxillofacial diseases
Li Zeming1, Zhang Yuntao1, Wang Maolin1, Hou Yudong2
- 1Binzhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-24Accepted:2024-11-05Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-28 -
Contact:Hou Yudong, MS, Professor, School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Zeming, Master’s candidate, Binzhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zeming, Zhang Yuntao, Wang Maolin, Hou Yudong. Role and mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha regulating bone homeostasis in oral and maxillofacial diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5680-5687.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
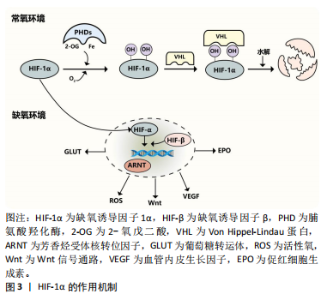
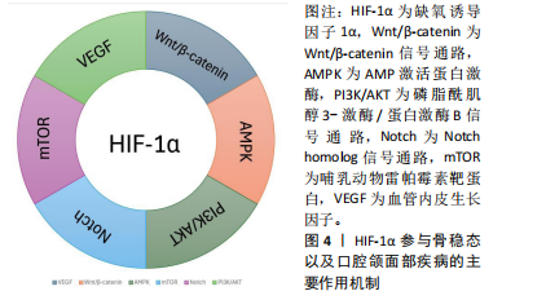
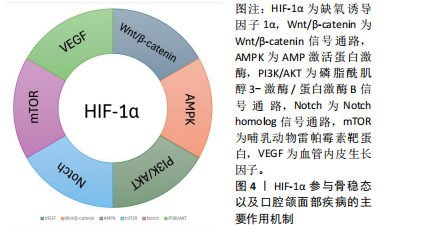
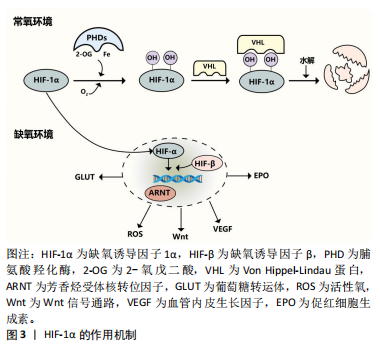
2.2 HIF-1α在骨稳态中的调节机制 2.2.1 HIF-1α HIF异二聚体由3个α亚基(HIF-1α、HIF-2α 和 HIF-3α)和1个β亚基组成。HIF-1α可与 HIF-1β异二聚化,是一种受缺氧调节的转录因子[23],见图3。在常氧条件下,HIF-1α 被羟基化并与 von Hippel-Lindau蛋白相互作用进行泛素化和蛋白酶体降解。HIF-1α几乎在所有细胞类型中都有表达,而 HIF-2α的分布则有限。在缺氧条件下,HIF-1α对人体的代谢和功能适应起着至关重要的作用[24]。在常氧环境下,脯氨酸羟化酶羟基化HIF-1α的氧敏感α亚基,von Hippel-Lindau蛋白识别羟基化的HIF-1α,然后泛素化并被泛素酶水解,而缺氧环境下脯氨酸羟化酶的活性被抑制,导致HIF-1α积累后进入细胞核,与HIF-β和芳烃受体核转位因子形成转录复合物,然后与缺氧反应元件结合,从而调节许多下游基因(葡萄糖转运蛋白、促红细胞生成素、血管内皮生长因子、Wnt等)以及活性氧的产生,见图4。"

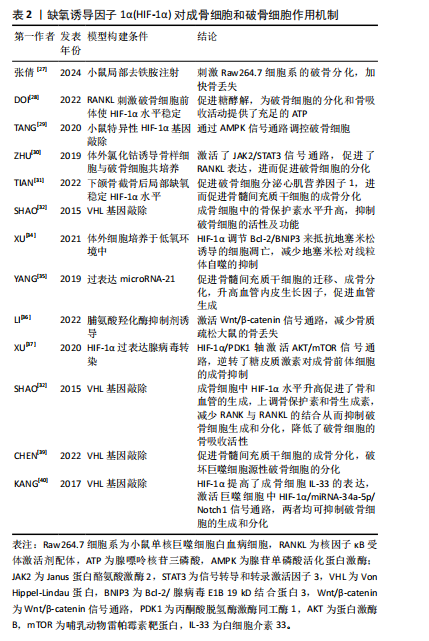
2.2.2 HIF-1α调节破骨细胞的增殖和分化 破骨细胞是由CD14+单核细胞或巨噬细胞在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的作用下形成巨噬细胞集落单位,在核因子κB受体激活因子配体存在下融合,形成直径20-100 μm、含有2-20个紧密堆积细胞核的多核破骨细胞,破骨细胞的胞质富含线粒体、溶酶体、核糖体和高尔基体等细胞器,是迄今为止唯一被发现具有骨吸收功能的细胞[25]。当炎症、激素或者创伤刺激时,成熟的破骨细胞会首先附着到骨表面上,在细胞-骨界面酸化细胞外环境,在蛋白激酶K、基质金属蛋白酶等共同作用下,破骨细胞最终降解骨组织中的有机物和无机矿物质,产生大量的钙、磷和胶原片段,这些片段通过内吞作用释放[26] 。 去铁胺是一种螯合剂,能够与非蛋白质结合的铁螯合,并抑制铁离子依赖性脯氨酸羟化酶活性,从而抑制HIF-1α的羟基化和降解,稳定HIF-1α的水平。在小鼠上颌骨中,去铁胺可能通过升高HIF-1α的途径促进破骨细胞分化和牙槽骨改建过程[27]。破骨细胞的形成和骨吸收都是对ATP需求很高的过程,在破骨细胞生成过程中,葡萄糖转运蛋白表达升高、糖酵解增加,而HIF-1α 是糖酵解的强诱导剂,DOI等[28]发现抑制HIF-1α蛋白表达,能通过促进糖酵解的方式来促进破骨细胞分化。TANG等[29]发现敲除HIF-1α基因能使小鼠的腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)的表达减弱,小鼠髁部的破骨细胞数量显著减少,出现下颌髁部畸形,表明HIF-1α 可以通过影响 AMPK 信号传导来调控破骨细胞。不仅如此,使用氯化钴诱导或者在体积分数2%氧气中模拟缺氧环境,将小鼠骨样细胞与破骨细胞共培养,骨样细胞的HIF-1α水平升高并通过激活JAK2/STAT3通路来促进核因子κB受体激活剂配体的表达,增强骨样细胞介导的破骨细胞分化[30]。 但HIF-1α对破骨细胞的影响并不是单一方向的,下颌骨截骨后破骨细胞被募集,破骨细胞分泌心肌营养因子1刺激骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,而局部缺氧环境导致HIF-1α水平升高,可以促进破骨细胞分泌更多的心肌营养因子1,进一步促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨反应,促进骨重建[31]。骨保护素又叫破骨细胞抑制因子,是核因子κB受体激活剂配体的诱导受体,两者结合可以减少破骨细胞的产生,SHAO等[32]发现成骨细胞中的骨保护素可以被HIF-1α上调,进而下调破骨细胞的活性及功能,减少骨吸收。 目前的研究发现HIF-1α对破骨细胞的影响是复杂和多向的,局部组织炎症、损伤时发生缺氧稳定了HIF-1α水平,可以通过多种信号通路促进破骨细胞的增殖、迁移和分化,首先进行骨吸收,但随后又促进更多成骨细胞的迁移和分化进行骨形成,并抑制破骨细胞的活动。 2.2.3 HIF-1α增强成骨细胞的成骨能力,参与成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的偶联 成骨细胞来源于多能骨髓基质的间充质细胞,首先分化为前体成骨细胞,并在 Runt相关转录因子2和成骨相关转录因子的作用下分化为成熟的可形成骨基质的成骨细胞。这些细胞具有不同的转归:细胞凋亡、骨表面细胞或骨细胞。成熟成骨细胞的亚群被未矿化的类骨质包围,并进一步分化为骨细胞,即矿化骨中的终末分化骨细胞[33]。 XU等[34]研究发现缺氧环境中 HIF-1α稳定表达,调节其下游标记物Bcl-2/BNIP3,抵抗地塞米松诱导的细胞凋亡,并减少了地塞米松对线粒体自噬的抑制。HIF-1α还可以通过非编码RNA调节骨髓间充质干细胞,miRNA-21通过升高HIF-1α活性,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移,增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力,还通过血管内皮生长因子来促进血管生成[35]。Li等[36]研究发现脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂罗沙司他可以激活HIF-1α并通过Wnt/β-catenin通路来促进骨形成和抑制骨吸收,改善去卵巢大鼠的骨微结构恶化,从而减少骨丢失。糖皮质激素作为免疫抑制和抗炎药物,广泛应用于各种疾病的治疗,但长期和高剂量的激素治疗会影响成骨细胞的存活和成骨能力,甚至出现骨质疏松和骨坏死,XU等[37]研究发现HIF-1α/PDK1轴通过激活AKT/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路能够逆转糖皮质激素诱导的成骨前体细胞的成骨抑制。 成骨细胞除了直接参与骨生成,还能产生细胞因子调节破骨细胞的分化和成熟。成骨细胞既可以表达巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子κB受体激活剂配体以促进破骨细胞的存活、分化,还可以分泌骨保护素抑制破骨细胞的分化[38],HIF-1α能够调节成骨细胞与破骨细胞之间的这种偶联机制。在成骨细胞与破骨细胞共培养时,敲除von Hippel-Lindau基因后HIF-1α在成熟的成骨细胞中过表达,可能通过直接激活骨保护素的转录,使核因子κB受体激活剂配体与核因子κB受体激活因子的结合减少,抑制破骨细胞的生成,降低破骨细胞的骨吸收活性,从而抑制骨吸收[32]。CHEN等[39]敲除骨细胞中的von Hippel-Lindau基因使HIF-1α稳定表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,抑制骨髓源性巨噬细胞来源的破骨细胞分化,破坏成骨细胞的骨形成和破骨细胞的骨吸收之间的平衡,使骨量增加。成骨细胞中 HIF-1α还可以通过与白细胞介素 33 启动子上的-1 504/-1 500 bp 位点结合致其表达增加,而白细胞介素33可以作用于骨髓来源单核细胞以减少其破骨细胞方向的分化;此外,HIF-1α还激活了巨噬细胞中的白细胞介素 33/miRNA-34a-5p/Notch1通路,抑制了破骨细胞的生成和破骨分化[40]。这些研究一致表明在成骨过程中,HIF-1α不仅能够通过多种信号通路减少骨髓间充质干细胞的凋亡,促进其增殖和迁移,还能通过多种细胞因子来调节成骨细胞与破骨细胞的偶联。 文章总结了HIF-1α对成骨细胞和破骨细胞作用机制的研究,见表2。"

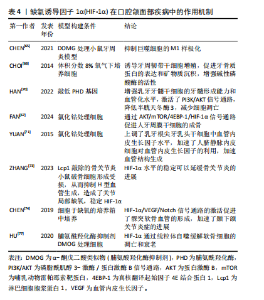
2.2.4 HIF-1α调节成骨-血管生成偶联 HIF-1α的靶基因血管内皮生长因子在血管生成和骨重塑中发挥重要作用[41-42]。HIF-1α是干骺端H型血管形成的关键启动子,HIF-1α/VEGF通路参与骨稳态的调节也得到了广泛研究,如血管生成-成骨偶联[43]。在血管生成素1和血管生成素2的相互调节下,HIF-1α刺激骨髓间充质干细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子,并抑制血管内皮生长因子受体的内源性竞争性抑制剂——金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂3的表达,介导成骨和血管生成,这种相互调节关系被称为“HIF-1α/VEGF/Ang-1轴”[44–46]。ZHANG等[47]采用超滤法获得脐带间充质干细胞外泌体,并联合水凝胶移植到骨折大鼠模型的骨折部位,可以显著促进骨折大鼠的血管生成和骨愈合,同时发现移植外泌体后上调了HIF-1α水平,并进一步证实HIF-1α在脐带间充质干细胞外泌体诱导的血管内皮生长因子表达、促血管生成和增强骨折修复中发挥了重要作用。LIU等[48]发现miRNA-210促进骨髓间充质干细胞中HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达,上调碱性磷酸酶和成骨相关转录因子Osterix的表达,并抑制过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体的表达,诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞,改善绝经后因雌激素缺乏所引起的骨质疏松症。谢冰颖等[49]对卵巢摘除大鼠进行续苓健骨方灌胃的预防性治疗,发现HIF-1α/VEGF信号通路相关因子的表达升高,促进了血管生成,改善了骨微结构,缓解了骨代谢失调。 2.2.5 HIF-1α缓解骨组织的氧化应激 细胞中的活性氧主要来源于线粒体中的电子传递链、内质网和还原烟酰胺二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶[50],可以作为第二信使激活多种信号通路,因此适当浓度的活性氧对于细胞正常功能至关重要。然而,线粒体功能障碍或氧化酶的上调等都会导致活性氧过量,过量的活性氧会损伤细胞甚至导致细胞凋亡。以往的研究中,性激素减少被认为是衰老过程中骨质流失的首要外在原因,但有证据表明性类固醇减少之前骨丢失就已经开始[51],ALMEIDA等[52]研究表明在氧化应激条件下,即使性类固醇充足,小鼠的骨量仍然会减少,并且相较于年轻个体,衰老个体中细胞的活性氧显著增加,高水平的活性氧会损害成骨细胞的寿命。这些研究表明氧化应激可能是老年骨质疏松的重要诱导因素,而性激素水平下降会加速这一过程。 HIF-1α是一种内源性抗氧化应激调节剂,当局部组织发生氧化应激时 HIF-1α通路激活,活性氧水平也随之升高[53],活性氧会损伤细胞中的DNA,而增殖细胞核抗原可以通过多种方式修复受损的DNA,以减轻DNA损伤引起的细胞凋亡[54]。WANG等[55]用脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂DMOG预先处理小鼠前体成骨细胞,随后对预处理的细胞进行过氧化氢处理模拟短期氧化应激,研究发现细胞中HIF-1α上调会显著增加细胞内活性氧水平,HIF-1α可以通过增加增殖细胞核抗原的表达来促进过氧化氢诱导的DNA损伤的修复,从而减少细胞凋亡。WANG等[55]研究还发现HIF-1α可以通过抑制促凋亡蛋白和促进抗凋亡蛋白表达,减少过氧化氢诱导的细胞凋亡。Bcl-2蛋白家族是一种与细胞凋亡密切相关的蛋白质,可分为2组:一组抑制细胞凋亡,包括Bcl-2和Bcl-xl;而另一组促进细胞凋亡,包括Bax和Bak。HIF-1α的增加拮抗了过氧化氢对Bax、Bak的抑制,并增加了Bcl-2和Bcl-xl的含量,减少氧化应激对细胞造成的损伤[56-57]。此外,ZHENG等[58]发现在缺氧条件下,稳定HIF-1α水平可以通过糖酵解途径动态调节葡萄糖水解,以防止线粒体产生过量活性氧,并减少细胞凋亡。综合以上研究,HIF-1α水平的增加可以修复由活性氧导致的DNA损伤,减少氧化应激造成的细胞凋亡,还能影响糖酵解途径来提高细胞保护作用和减少细胞凋亡,为未来预防骨组织氧化应激的方法提供新的思路。 文章总结了HIF-1α促进成骨-成血管偶联和缓解氧化应激的作用机制,见表3。 2.3 HIF-1α在口腔颌面部疾病中的作用机制 2.3.1 HIF-1α在牙周炎中的作用 牙周组织是支撑和容纳牙列的组织,包括牙骨质、牙周韧带和牙槽骨,牙骨质通"

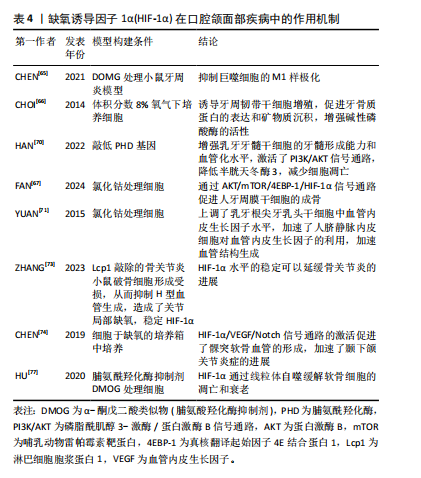
过牙周韧带与牙齿周围的牙槽骨紧密附着。牙周炎的特点是牙周组织出现病理性不可逆的损伤,最终导致牙齿脱落,牙周治疗的目的是控制感染并重建牙周组织的结构和功能,因此牙周组织的再生包括牙骨质、牙周韧带以及牙槽骨的再生[59-60]。HIF-1α在巨噬细胞分化过程中起到了重要的作用,巨噬细胞是牙周炎中对抗病原体的关键防御者,参与炎症反应[61], M1样促炎巨噬细胞的分化促进牙槽骨的吸收[62],M2样巨噬细胞的分化会产生精氨酸酶1促进胶原沉积,并促进牙龈组织中的纤维生成[63],巨噬细胞表现出高度的功能性组织可塑性,M1/M2巨噬细胞比例的变化可以改变牙周炎的结局,从而控制组织的修复和重塑[64]。脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂DMOG可以稳定HIF-1α水平来抑制牙周炎小鼠模型中的M1巨噬细胞极化,降低小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞的M1/M2值,还发现其通过抑制牙周炎小鼠模型的核因子κB活化来抑制破骨细胞分化,减少牙周炎导致的骨质丧失[65]。CHOI等[66]体外培养人牙周膜干细胞,发现缺氧可以通过升高HIF-1α水平来促进牙骨质蛋白1的表达,促进矿物质沉积和增强碱性磷酸酶的活性,当 HIF-1α沉默时, 牙骨质蛋白1的表达则不会增加,这表明HIF-1α有促进牙骨质再生的潜力。FAN等[67]观察到氯化钴处理人牙周膜干细胞48 h后,成骨效果最佳,并发现可能通过AKT/mTOR/4EBP-1/HIF-1α信号传导促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化和修复牙槽骨缺损。以上结果表明HIF-1α能够控制局部炎症,促进牙骨质和牙槽骨的再生,但仍需继续研究如何长期作用于局部牙周组织而减小对全身组织的影响。 2.3.2 HIF-1α在牙髓再生中的作用 目前牙髓炎和根尖周炎的治疗方法大多为根管治疗术和牙髓血运重建术,尽管有临床完全康复和组织学重建的迹象,但牙髓组织的真正再生远未实现。而基于干细胞的疗法是牙髓再生中一种很有前途的策略,特别是当牙髓组织损伤范围太广而无法自我再生时,需要将干细胞源输送到宿主中,以使牙髓组织再生到原始状态或接近原始状态[68-69]。HAN等[70]将人乳牙牙髓干细胞预处理到缺氧状态,并通过敲低含有脯氨酰羟化酶结构域蛋白 2基因来稳定HIF-1α的表达,然后将HIF-1α稳定的乳牙牙髓干细胞包封在PuraMatrix水凝胶中,注射到人牙齿的根管中,植入免疫缺陷小鼠皮下,28 d后与对照组相比观察到牙髓样组织形成增强,血管化水平显著升高。通过实验发现缺氧条件下乳牙牙髓干细胞中HIF-1α稳定,PI3K/AKT 通路激活,半胱天冬酶3表达降低,细胞凋亡减少,细胞存活率显著提高。研究团队还发现HIF-1α在激肽释放酶2和葡萄糖转运蛋白1上调中起重要作用,这有助于维持缺氧时活性氧稳态和代谢适应,增强乳牙牙髓干细胞的存活率,为牙髓干细胞疗法提供了有利的证据。HIF-1α也参与了牙髓再生中的血管生成,YUAN等[71]将根尖牙乳头干细胞与脐静脉内皮细胞共同培养,并使用氯化钴来诱导缺氧环境,发现根尖牙乳头干细胞中的HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子水平均显著增加,有趣的是,当共培养根尖牙乳头干细胞和脐静脉内皮细胞时,发现上清液中血管内皮生长因子浓度非常低,推测根尖牙乳头干细胞分泌的血管内皮生长因子可能被脐静脉内皮细胞代谢,用于加速血管生成。综上,低氧预适应或使用缺氧模拟剂在提高干细胞存活率、促进血管生成和调节成牙本质细胞的牙本质形成能力方面均显示出较大的潜能,有待深入研究。 2.3.3 HIF-1α在颞下颌骨关节炎中的作用 近年来,HIF-1α 被认为是维持正常软骨细胞功能的保护因子,主要是通过促进软骨细胞代谢、分化和基质分泌等发挥作用。正常情况下,软骨下骨和软骨严重缺氧,软骨中的氧体积分数为1%-5%,软骨下骨中的氧体积分数为7%[72],因此HIF-1α水平较稳定。但ZHANG等[73]认为在骨关节炎中,软骨下骨中破骨细胞活化,诱导H型血管生成,H型血管会带来大量的氧气,从而泛素化软骨细胞中HIF-1α并导致软骨变性,然后使用破骨细胞形成受损的淋巴细胞胞质蛋白1基因敲除小鼠进行研究,发现小鼠的H型血管难以生成,从而维持了关节的缺氧环境,稳定了HIF-1α水平,延缓了骨关节炎的进展。在此基础上将HIF-1α敲除则不能减缓软骨变性,证明了淋巴细胞胞质蛋白1基因敲除小鼠是通过稳定HIF-1α途径来延缓骨关节炎进展的。也有其他研究人员给出了不同的结论,CHEN等[74]在大鼠颞下颌关节中提取出髁突软骨细胞,将细胞置于低氧浓度培养箱中培养,发现低氧激活了HIF-1α/VEGF/Notch信号通路,该通路在髁突软骨的血管生成中起着至关重要的作用,并加速了颞下颌关节炎症的发展,因此推测HIF-1和Notch可能被用作早期颞下颌关节炎抗血管生成治疗的靶点。但LI等[75]则认为虽然血管生成可以促进关节炎,但它也是颞下颌关节重塑的关键步骤,可以缓解髁突软骨的组织病理学变化。 线粒体自噬通过降解无用的蛋白质和细胞器或功能失调的细胞器来维持细胞功能,是病理条件下细胞的一种自我保护机制[76]。自噬在防止软骨细胞凋亡和衰老以推迟关节炎发展方面发挥了重要作用,HU等[77]研究使用脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂DMOG稳定HIF-1α水平能够显著抑制软骨细胞的凋亡和衰老,HIF-1α不仅在转录水平上增强了细胞外基质的合成,而且通过增强线粒体自噬抑制了缺氧诱导的细胞外基质降解,并发现HIF-1α介导的线粒体自噬机制可能与BNIP3有关,因此,HIF-1α可能是缓解关节炎的潜在靶点。 文章总结了HIF-1α在口腔颌面部疾病中作用机制,见表4。"

2.4 通过支架材料修复骨缺损过程中HIF-1α的作用机制 传统通过去铁胺螯合铁离子激活HIF-1α通路的方法难以解决其突释的问题,可能造成生物安全风险,因此GAO等[78]采取了数字光处理打印技术制备了一种结构良好、生物相容性的甲基丙烯酸酯明胶/聚甲基丙烯酸(GelMA/PMAA)水凝胶,GelMA在骨组织再生方面表现出了一定的促进作用[79-80],PMAA的羧基官能团可有效螯合铁离子,持续激活HIF-1α信号通路,通过HIF-1α/SOX9显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞的软骨分化,并通过HIF-1α/VEGF促进血管的再生。NAGAI等[81]利用搭载脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂1,4-DPCA的可注射水凝胶来处理牙周炎小鼠以及前体成骨细胞,使其HIF-1α水平稳定,证明了1,4-DPCA/水凝胶可以降低牙周炎小鼠的促炎因子表达,并在牙周愈合后期(第15天)上调了多种成骨基因和成骨转录因子,包括Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素,表明1,4-DPCA/水凝胶不仅有助于炎症的消退,而且增强了成骨基因的表达,促进骨再生。同样,为了达到控释的目的,CHEN等[82]将脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂DMOG和甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白(PTHrP)制备聚乳酸-聚乙醇酸共聚微球,并将微球掺入纳米纤维结构的聚左旋乳酸支架上,以构建基于微球的支架输送系统,这个材料植入裸鼠皮下,DMOG和甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白的时空控制释放有效地模拟了缺氧微环境,升高了HIF-1α水平,促进了体内软骨的形成。成骨和血管生成特性是骨移植材料的两个最有价值的因素,镁涂层的钛支架可以通过JAK1/STAT1/HIF-1α信号通路显著刺激前体成骨细胞的增殖、黏附、细胞外基质矿化以及碱性磷酸酶活性,Mg2+ 离子通过上调人脐静脉内皮细胞中镁转运蛋白 1的表达来增加Mg2+ 的流入量,进而通过激活HIF-1α刺激血管内皮生长因子的转录,从而诱导血管生成,并改善人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、黏附、细胞迁移能力[83-84]。"

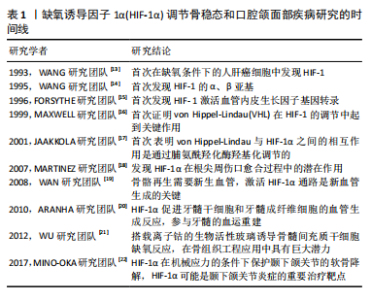
| [1] PALUMBO C, FERRETTI M. The Osteocyte: From “Prisoner” to “Orchestrator”. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2021;6(1):28. [2] CHEN W, WU P, YU F, et al. HIF-1α Regulates Bone Homeostasis and Angiogenesis, Participating in the Occurrence of Bone Metabolic Diseases. Cells. 2022;11(22):3552. [3] ZHAO Y, XING C, DENG Y, et al. HIF-1α signaling: Essential roles in tumorigenesis and implications in targeted therapies. Genes Dis. 2023;11(1):234-251. [4] SATO T, TAKEDA N. The roles of HIF-1α signaling in cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiol. 2023;81(2):202-208. [5] SEMENZA GL. Pharmacologic Targeting of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019;59:379-403. [6] ZHANG FJ, LUO W, LEI GH. Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82(3):144-147. [7] FAYED HA, BARAKAT BM, ELSHAER SS, et al. Antiosteoporotic activities of isoquercitrin in ovariectomized rats: Role of inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;865:172785. [8] CHEN C, YAN S, GENG Z DR, et al. Fracture repair by IOX2: Regulation of the hypoxia inducible factor-1α signaling pathway and BMSCs. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;921:174864. [9] LI D, HU Q, TAN G, et al. Erythropoietin Enhances Bone Repair Effects via the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Signal Pathway in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Am J Med Sci. 2018;355(6):597-606. [10] YOU J, LIU M, LI M, et al. The Role of HIF-1α in Bone Regeneration: A New Direction and Challenge in Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):8029. [11] HOLZER LA, KRAIGER M, TALAKIC E, et al. Microstructural analysis of subchondral bone in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(10):2037-2045. [12] ZHANG J, HU Y, WANG Z, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor expression is related to apoptosis and cartilage degradation in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):583. [13] WANG GL, SEMENZA GL. General involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in transcriptional response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(9):4304-4308. [14] WANG GL, JIANG BH, RUE EA, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(12):5510-5514. [15] FORSYTHE JA, JIANG BH, IYER NV, et al. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16(9): 4604-4613. [16] MAXWELL PH, WIESENER MS, CHANG GW, et al. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature. 1999;399(6733):271-275. [17] JAAKKOLA P, MOLE DR, TIAN YM, et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292(5516):468-472. [18] MARTINEZ ZR, NARUISHI K, YAMASHIRO K, et al. Gene profiles during root canal treatment in experimental rat periapical lesions. J Endod. 2007;33(8):936-943. [19] WAN C, GILBERT SR, WANG Y, et al. Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway accelerates bone regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(2):686-691.
[20] ARANHA AM, ZHANG Z, NEIVA KG, et al. Hypoxia enhances the angiogenic potential of human dental pulp cells. J Endod. 2010;36(10):1633-1637. [21] WU C, ZHOU Y, FAN W, et al. Hypoxia-mimicking mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with controllable cobalt ion release for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2076-2085. [22] MINO-OKA A, IZAWA T, SHINOHARA T, et al. Roles of hypoxia inducible factor-1α in the temporomandibular joint. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;73:274-281. [23] YIN CL, MA YJ. The Regulatory Mechanism of Hypoxia-inducible Factor 1 and its Clinical Significance. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024;17:e18761429266116. [24] HUANG X, ZHANG Y, QI B, et al. HIF‑1α: Its notable role in the maintenance of oxygen, bone and iron homeostasis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2022;50(6):141. [25] KNOWLES HJ. Hypoxic regulation of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity. Hypoxia (Auckl). 2015;3:73-82. [26] TAKITO J, INOUE S, NAKAMURA M. The Sealing Zone in Osteoclasts: A Self-Organized Structure on the Bone. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):984. [27] 张倩,康非吾.去铁胺局部注射对小鼠牙槽骨骨改建的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2024,34(2):87-93. [28] DOI K, MURATA K, ITO S, et al. Role of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 in Metabolically Integrating Osteoclast Differentiation and Inflammatory Bone Resorption Through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α and E2F1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(6):948-960. [29] TANG Y, HONG C, CAI Y, et al. HIF-1α Mediates Osteoclast-Induced Mandibular Condyle Growth via AMPK Signaling. J Dent Res. 2020;99(12):1377-1386. [30] ZHU J, TANG Y, WU Q, et al. HIF-1α facilitates osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis by activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(11):21182-21192. [31] TIAN Y, SHAO Q, TANG Y, et al. HIF-1α regulates osteoclast activation and mediates osteogenesis during mandibular bone repair via CT-1. Oral Dis. 2022;28(2):428-441. [32] SHAO J, ZHANG Y, YANG T, et al. HIF-1α disturbs osteoblasts and osteoclasts coupling in bone remodeling by up-regulating OPG expression. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(8):808-814. [33] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2073. [34] XU K, LU C, REN X, et al. Overexpression of HIF-1α enhances the protective effect of mitophagy on steroid-induced osteocytes apoptosis. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36(11):2123-2137. [35] YANG C, LIU X, ZHAO K, et al. miRNA-21 promotes osteogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway and enhances bone regeneration in critical size defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):65. [36] LI L, LI A, ZHU L, et al. Roxadustat promotes osteoblast differentiation and prevents estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss by stabilizing HIF-1α and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022; 17(1):286. [37] XU WN, ZHENG HL, YANG RZ, et al. HIF-1α Regulates Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Through PDK1/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;10:922. [38] KASSEM A, LINDHOLM C, LERNER UH. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Stimulation of Osteoblasts Mediates Staphylococcus Aureus Induced Bone Resorption and Osteoclastogenesis through Enhanced RANKL. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156708. [39] CHEN K, ZHAO J, QIU M, et al. Osteocytic HIF-1α Pathway Manipulates Bone Micro-structure and Remodeling via Regulating Osteocyte Terminal Differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:721561. [40] KANG H, YANG K, XIAO L, et al. Osteoblast Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Pathway Activation Restrains Osteoclastogenesis via the Interleukin-33-MicroRNA-34a-Notch1 Pathway. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1312. [41] RUBIO RG, ADAMIS AP. Ocular Angiogenesis: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Other Factors. Dev Ophthalmol. 2016;55:28-37. [42] RIVERA JC, MADAAN A, ZHOU TE, et al. Review of the mechanisms and therapeutic avenues for retinal and choroidal vascular dysfunctions in retinopathy of prematurity. Acta Paediatr. 2016;105(12):1421-1433. [43] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328. [44] WESTRA J, MOLEMA G, KALLENBERG CG. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 as regulator of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis - therapeutic implications. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(3):254-263. [45] CHEN YY, BROWN NJ, JONES R, et al. A peptide derived from TIMP-3 inhibits multiple angiogenic growth factor receptors and tumour growth and inflammatory arthritis in mice. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(1):207-219. [46] CHAI M, GU C, SHEN Q, et al. Hypoxia alleviates dexamethasone-induced inhibition of angiogenesis in cocultures of HUVECs and rBMSCs via HIF-1α. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):343. [47] ZHANG Y, HAO Z, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019; 52(2):e12570. [48] LIU XD, CAI F, LIU L, et al. MicroRNA-210 is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal osteoporosis through promotion of VEGF expression and osteoblast differentiation. Biol Chem. 2015;396(4):339-347. [49] 谢冰颖,李生强,林若慧,等.基于HIF-1α/VEGF通路探讨续苓健骨方对去卵巢大鼠骨代谢和局部血管生成的影响[J].福建中医药,2024,55(1):21-24+31. [50] ARANDA-RIVERA AK, CRUZ-GREGORIO A, APARICIO-TREJO OE, et al. Redox signaling pathways in unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;172:65-81. [51] RIGGS BL, MELTON LJ, ROBB RA, et al. A population-based assessment of rates of bone loss at multiple skeletal sites: evidence for substantial trabecular bone loss in young adult women and men. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(2):205-214. [52] ALMEIDA M, HAN L, MARTIN-MILLAN M, et al. Skeletal involution by age-associated oxidative stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):27285-27297. [53] JIANG L, ZENG H, NI L, et al. HIF-1α Preconditioning Potentiates Antioxidant Activity in Ischemic Injury: The Role of Sequential Administration of Dihydrotanshinone I and Protocatechuic Aldehyde in Cardioprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019;31(3):227-242. [54] LU S, DONG Z. Additive effects of a small molecular PCNA inhibitor PCNA-I1S and DNA damaging agents on growth inhibition and DNA damage in prostate and lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0223894. [55] WANG X, WEI L, LI Q, et al. HIF-1α protects osteoblasts from ROS-induced apoptosis. Free Radic Res. 2022;56(2):143-153. [56] ZHOU F, YANG Y, XING D. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. FEBS J. 2011;278(3):403-413. [57] DELBRIDGE AR, GRABOW S, STRASSER A, et al. Thirty years of BCL-2: translating cell death discoveries into novel cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(2):99-109. [58] ZHENG X, NARAYANAN S, XU C, et al. Repression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 contributes to increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in diabetes. Elife. 2022;11:e70714. [59] SAYGIN NE, GIANNOBILE WV, SOMERMAN MJ. Molecular and cell biology of cementum. Periodontol 2000. 2000;24:73-98. [60] LIU J, RUAN J, WEIR MD, et al. Periodontal Bone-Ligament-Cementum Regeneration via Scaffolds and Stem Cells. Cells. 2019;8(6):537. [61] MANTOVANI A, BISWAS SK, GALDIERO MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 2013;229(2):176-185. [62] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(9):6425-6440. [63] GALVÁN-PEÑA S, O’NEILL LA. Metabolic reprograming in macrophage polarization. Front Immunol. 2014;5:420. [64] LEE S, KI CS. Inflammatory responses of macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells in a 3D hydrogel matrix to ultrasonicated schizophyllan. Carbohydr Polym. 2020; 229:115555. [65] CHEN MH, WANG YH, SUN BJ, et al. HIF-1α activator DMOG inhibits alveolar bone resorption in murine periodontitis by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:107901. [66] CHOI H, JIN H, KIM JY, et al. Hypoxia promotes CEMP1 expression and induces cementoblastic differentiation of human dental stem cells in an HIF-1-dependent manner. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(1-2):410-423. [67] FAN Z, LIU Y, LAN Y, et al. CoCl2-Induced hypoxia promotes hPDLSCs osteogenic differentiation through AKT/mTOR/4EBP-1/HIF-1α signaling and facilitates the repair of alveolar bone defects. Cell Biol Int. 2024;48(6):808-820. [68] LIN LM, HUANG GT, SIGURDSSON A, et al. Clinical cell-based versus cell-free regenerative endodontics: clarification of concept and term. Int Endod J. 2021; 54(6):887-901. [69] XIE Z, SHEN Z, ZHAN P, et al. Functional Dental Pulp Regeneration: Basic Research and Clinical Translation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8991. [70] HAN Y, KOOHI-MOGHADAM M, CHEN Q, et al. HIF-1α Stabilization Boosts Pulp Regeneration by Modulating Cell Metabolism. J Dent Res. 2022;101(10):1214-1226. [71] YUAN C, WANG P, ZHU L, et al. Coculture of stem cells from apical papilla and human umbilical vein endothelial cell under hypoxia increases the formation of three-dimensional vessel-like structures in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(5-6): 1163-1172. [72] LAFONT JE. Lack of oxygen in articular cartilage: consequences for chondrocyte biology. Int J Exp Pathol. 2010;91(2):99-106. [73] ZHANG H, WANG L, CUI J, et al. Maintaining hypoxia environment of subchondral bone alleviates osteoarthritis progression. Sci Adv. 2023;9(14):eabo7868. [74] CHEN Y, ZHAO B, ZHU Y, et al. HIF-1-VEGF-Notch mediates angiogenesis in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(5):2969-2982. [75] LI QF, RABIE AB. A new approach to control condylar growth by regulating angiogenesis. Arch Oral Biol. 2007;52(11):1009-1017. [76] DUTTA D, XU J, KIM JS, et al. Upregulated autophagy protects cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress-induced toxicity. Autophagy. 2013;9(3):328-344. [77] HU S, ZHANG C, NI L, et al. Stabilization of HIF-1α alleviates osteoarthritis via enhancing mitophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(6):481. [78] GAO J, WANG H, LI M, et al. DLP-printed GelMA-PMAA scaffold for bone regeneration through endochondral ossification. Int J Bioprint. 2023;9(5):754. [79] HONG Y, ZHOU F, HUA Y, et al. A strongly adhesive hemostatic hydrogel for the repair of arterial and heart bleeds. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2060. [80] RATHEESH G, VAQUETTE C, XIAO Y. Patient-Specific Bone Particles Bioprinting for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(23):e2001323. [81] NAGAI K, IDEGUCHI H, KAJIKAWA T, et al. An injectable hydrogel-formulated inhibitor of prolyl-4-hydroxylase promotes T regulatory cell recruitment and enhances alveolar bone regeneration during resolution of experimental periodontitis. FASEB J. 2020;34(10):13726-13740. [82] CHEN L, HUANG X, CHEN H, et al. Hypoxia-mimicking scaffolds with controlled release of DMOG and PTHrP to promote cartilage regeneration via the HIF-1α/YAP signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;226:716-729. [83] GAO P, FAN B, YU X, et al. Biofunctional magnesium coated Ti6Al4V scaffold enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo for orthopedic application. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):680-693. [84] YU Y, JIN G, XUE Y, et al. Multifunctions of dual Zn/Mg ion co-implanted titanium on osteogenesis, angiogenesis and bacteria inhibition for dental implants. Acta Biomater. 2017;49:590-603. |
| [1] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [4] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [5] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [6] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [7] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [8] | Zhao Zengbo, Li Chenxi, Dou Chenlei, Ma Na, Zhou Guanjun. Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/leonurine hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [9] | Lu Xiuli, Xu Huazhen, Chen Yuxing, Yao Nan, Hu Zixuan, Huang Dane. Mechanism of Jiangu Formula in treating osteoporosis based on osteoclast-osteoblast coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6828-6835. |
| [10] | Yao Wenxin, Wang Yi, Cai Lin, Feng Xiaobo. Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblasts, inhibit osteoclasts, and promote osteogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6765-6771. |
| [11] | Deng Guanghui, Xiang Wei, Su Qifan, Chen Xiaoyu, Wang Liangwei, Wan Zhihong, Wu Jiaqi, Chen Xiaojun. Preparation of osteoporotic femoral condylar bone defect model in rabbits and its critical value [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6426-6433. |
| [12] | Zhu Menghan, Yang Xuetao, Sun Yimin, Wang Chenglin. Anti-inflammatory peptides for oral inflammatory diseases: regulation of inflammatory response to reduce tissue destruction and structural loss [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6529-6537. |
| [13] | Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Ran Dongcheng, Xu Jiamu, Wu Wangxiang, Xu Jiafu, Chen Jingjing, Jiang Guangfu, Wang Chunqing. Ferroptosis and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 554-562. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Wu Wangxiang, Ran Dongcheng, Xu Jiamu, Xu Jiafu, Chen Jingjing, Wang Chunqing. Long noncoding RNAs related to osteoporosis: current research status and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6360-6368. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||