Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (25): 5486-5500.doi: 10.12307/2025.505
Transcriptomic analysis and drug prediction of basement membrane-related genes in different traditional Chinese medicine patterns of rheumatoid arthritis
Liu Yuan1, Qu Yuan1, Wan Yakun2, Guo Jingyu3, Jiang Ping1, 4
- 1First Clinical Medical College, 2College of Rehabilitation, 3College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 4Affiliated Hospital, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-12Accepted:2024-04-22Online:2025-09-08Published:2024-12-30 -
Contact:Jiang Ping, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; Affiliated Hospital, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Yuan, Doctoral candidate, First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82274481, 81874449 (to JP); National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Department Jointly Constructed Science and Technology Project, No. GZY-KJS-SD-2023-041 (to JP); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2022LZY004 (to JP); Qilu Zhang’s Rheumatoid Bone Disease Traditional Chinese Medicine Specialty Technology Project, No. Luweihan [2022] 93 (to JP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yuan, Qu Yuan, Wan Yakun, Guo Jingyu, Jiang Ping. Transcriptomic analysis and drug prediction of basement membrane-related genes in different traditional Chinese medicine patterns of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5486-5500.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
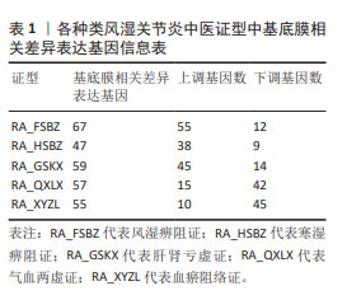
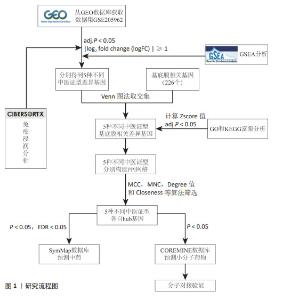
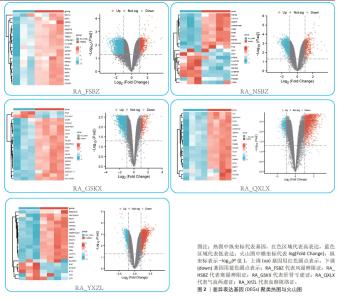
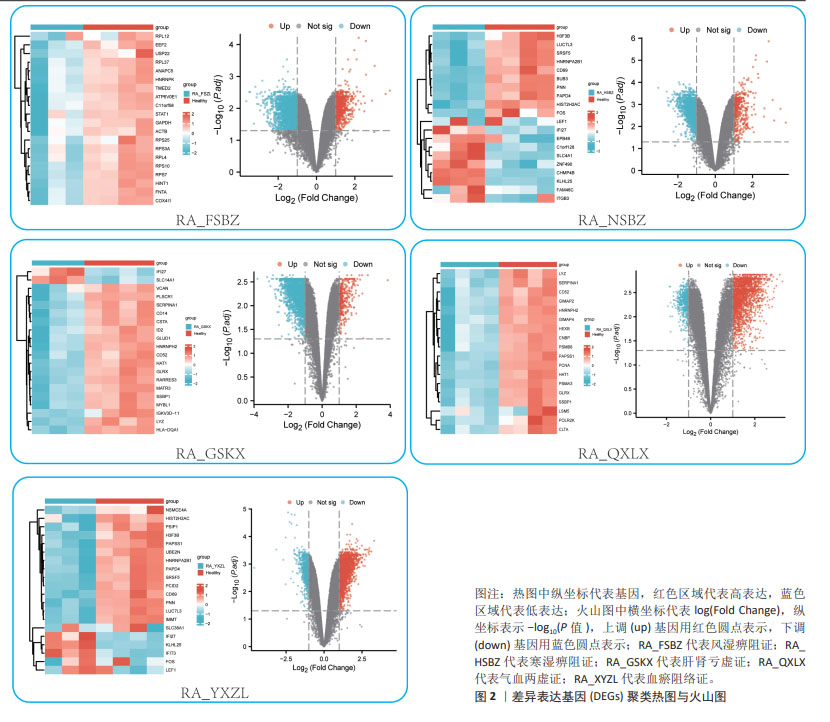
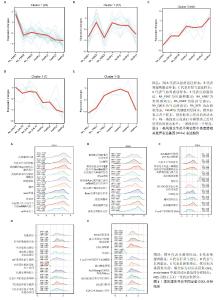
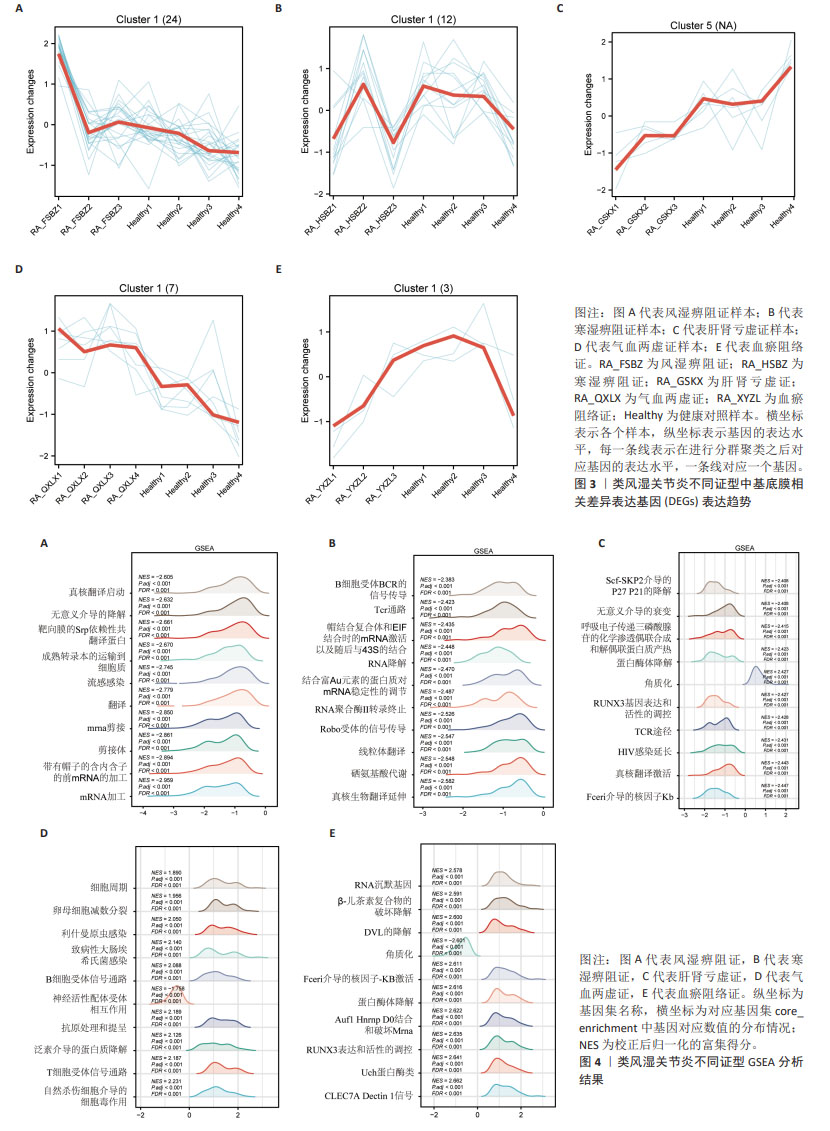
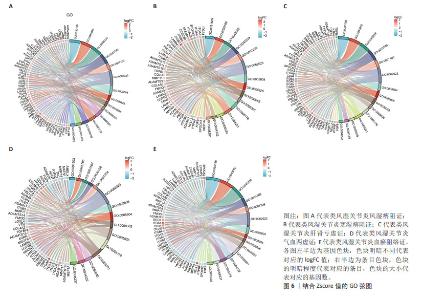
2.1 数据预处理及筛选基底膜相关DEGs 通过文献共获得基底膜相关基因226个,与GSE205962数据集中5种类风湿关节炎中医证型筛选出的DEGs分别取交集,共获得67(RA_FSBZ),47(RA_HSBZ),59(RA_GSKX),57(RA_QXLX)及55(RA_XYZL)个基底膜相关DEGs,具体DEGs信息见表1。研究流程见图1。相关差异基因聚类图见图2。 对基底膜相关的DEGs在各证型中的表达趋势进行了预测分析,结果发现在RA_FSBZ,RA_GSKX及RA_QXLX中与健康对照组相比,其基底膜相关DEGs的表达呈现高表达趋势,而在RA_XYZL中呈现低表达趋势,而RA_HSBZ中表达趋势不明显,见图3。 2.2 GSEA与富集分析结果 运用R语言进行GSEA分析,结果以adj.P < 0.05,FDR(qvalue) < 0.25为条件筛选显著富集条目,并将富集显著条目以山峦图进行可视化。RA_FSBZ相关基因集主要富集在mRNA剪接、ROBO受体信号传导等反应途径;RA_HSBZ相关基因集主要富集在B细胞受体信号传导、线粒体翻译等反应途径;RA_GSKX相关基因集主要富集在FCERI介导的和转录因子κB激活反应途径及TCR等信号通路;RA_QXLX相关基因集主要富集在自然杀伤细胞介导的细胞毒作用、T细胞受体等信号通路;RA_XYZL相关基因集主要富集在FcεRI介导的核转录因子κB激活、RUNX3表达和活性的调控等。综合各证型结果发现,5种不同证型的类风湿关节炎基因集主要集中于免疫调控、炎症细胞反应和信号转导等反应途径及通路,见图4。 "
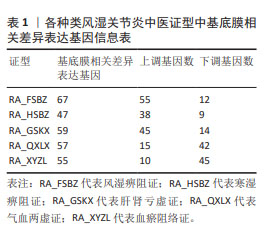
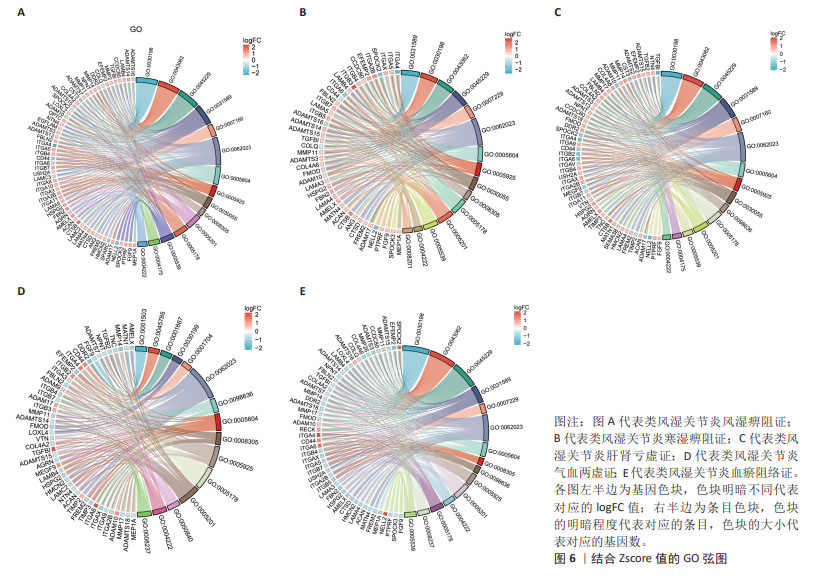
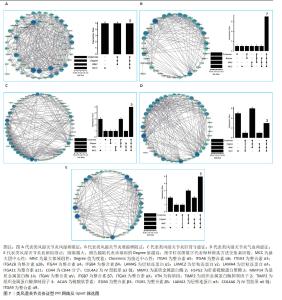
GO富集分析结果显示,5种类风湿关节炎中医证型分别筛选出(adj.P < 0.05)227(RA_FSBZ),104(RA_HSBZ),109(RA_GSKX),185(RA_QXLX)及66(RA_XYZL)条生物学过程(biological processes,BP),基底膜相关DEGs大多富集于细胞基质黏附、免疫细胞迁移及胶原代谢等生物学过程。KEGG富集结果显示(adj.P < 0.05),基底膜相关DEGs主要富集于ECM受体相互作用、PI3K-Akt、局灶性粘连和Rap1等免疫相关信号通路。其中RA_FSBZ共获得21条KEGG通路,RA_HSBZ共获得36条KEGG通路,RA_GSKX共获得16条KEGG通路,RA_QXLX共获得43条KEGG通路,RA_XYZL共获得22条KEGG通路。选取富集倍数前15的条目绘制聚类树,并计算Zscore值以弦图可视化,见图5,6。 "

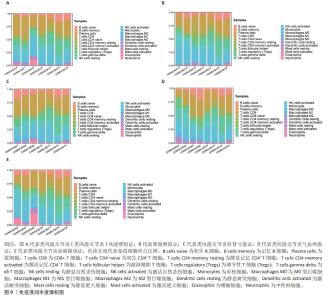
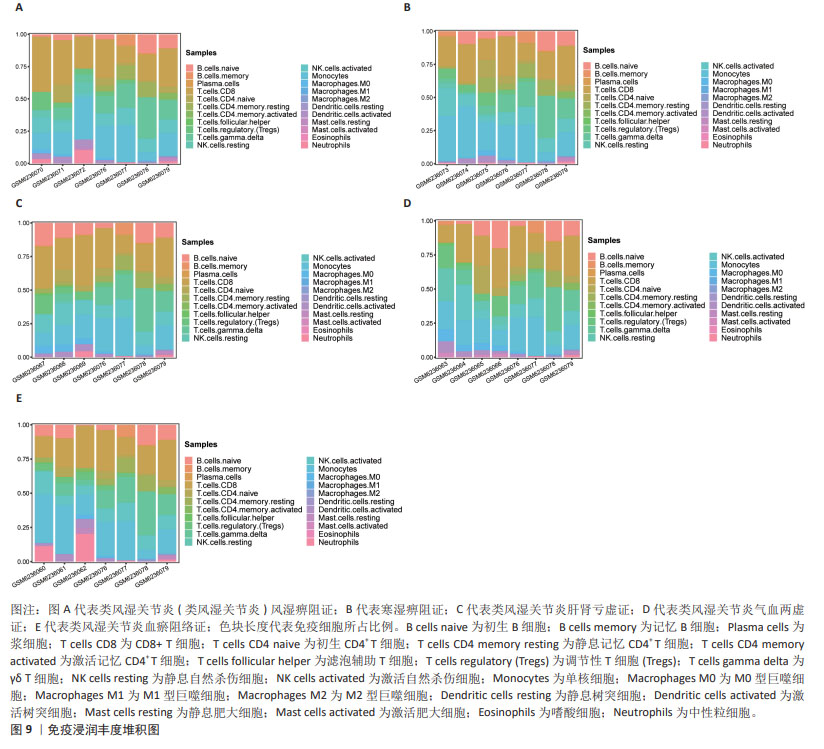
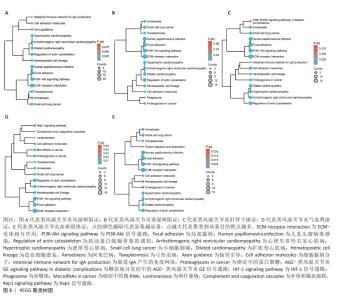
2.4 免疫浸润与ROC分析结果 免疫浸润分析显示,与健康人相比,类风湿关节炎风湿痹阻证患者外周全血中调节性T细胞、CD8+T细胞、静息状态的自然杀伤细胞、M0巨噬细胞、激活的树突状细胞和中性粒细胞显著升高(P < 0.01);类风湿关节炎寒湿痹阻证患者外周全血中CD4+T细胞、调节性T细胞、激活的自然杀伤细胞、M0巨噬细胞和激活的树突状细胞较健康人相比显著升高(P < 0.01);类风湿关节炎肝肾亏虚证患者外周全血中CD8+T细胞、调节性T细胞、激活的自然杀伤细胞、静息状态的自然杀伤细胞和激活的树突状细胞较健康人相比显著升高(P < 0.01);类风湿关节炎气血两虚证患者外周全血中辅助性T细胞、CD4+T细胞、调节性T细胞、静息状态的自然杀伤细胞及激活的肥大细胞较健康人相比显著升高(P < 0.01);类风湿关节炎瘀血阻络证患者外周全血中单核细胞、激活的树突状细胞及中性粒细胞较健康人相比显著升高(P < 0.01)。综合分析发现,调节性T细胞、激活的树突状细胞、自然杀伤细胞是类风湿关节炎患者外周血中较为活跃的免疫细胞,见图8,9。"

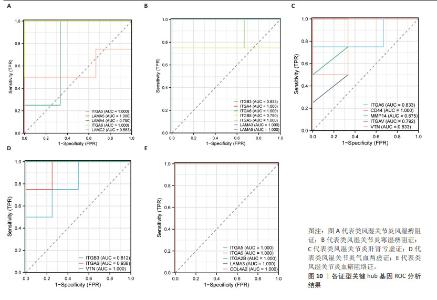
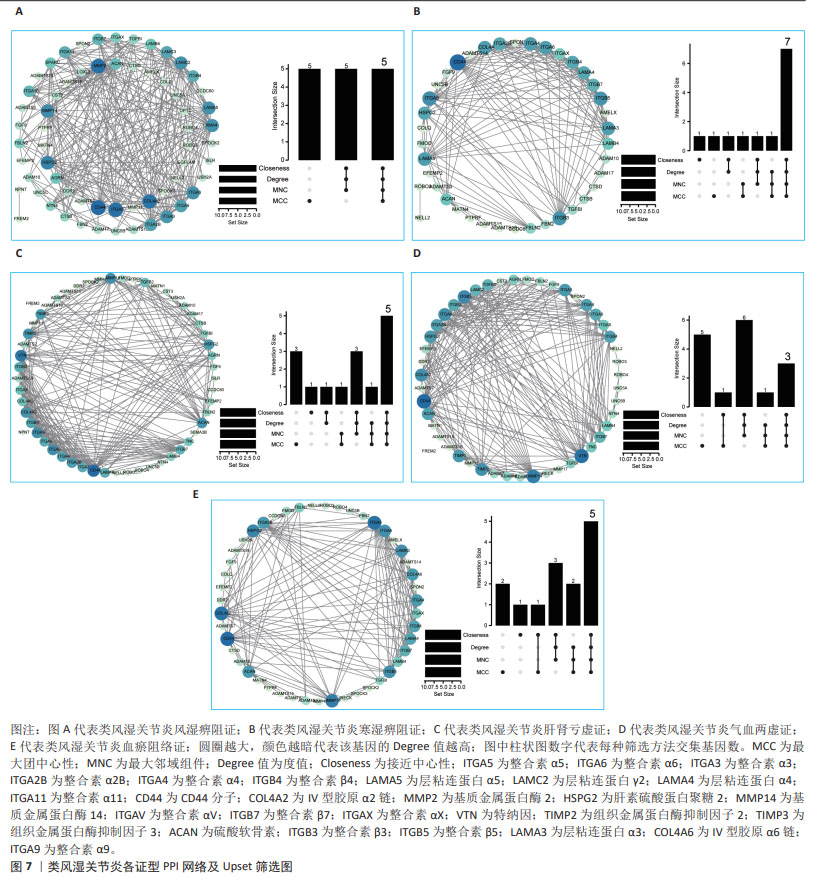
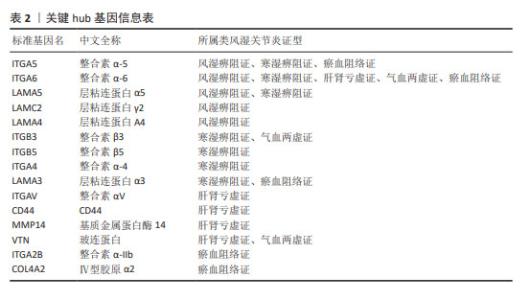
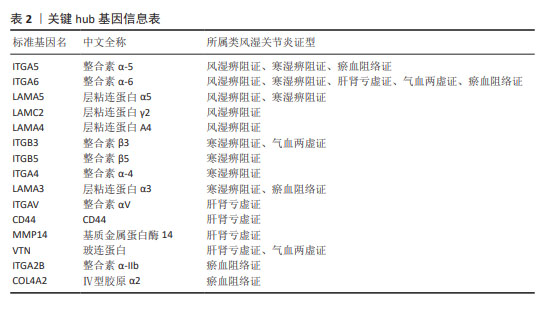
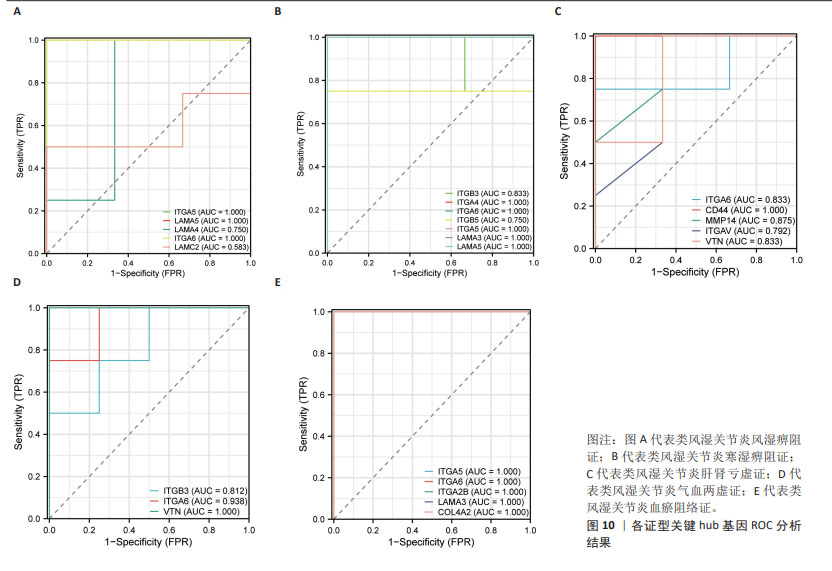
文章对5种类风湿关节炎中医证型中各自筛选出的关键hub基因进行ROC分析,以此来评估hub基因对类风湿关节炎各证型潜在的诊断价值。AUC越接近于1,说明该变量在预测结局上诊断效果越好,目前普遍认为AUC值> 0.7时,该靶标存在诊断价值;AUC值> 0.85时,该靶标存在较高诊断价值[13]。ROC结果见图10,RA_FSBZ中有4个关键hub基因AUC值> 0.7,其中整合素α5(ITGA5;AUC值=1.000)、整合素α6(ITGA6;AUC值=1.000)、层粘连蛋白A5(LAMA5;AUC值=1.000)对该证型具有较高潜在诊断价值;RA_HSBZ中有7个关键hub基因AUC值> 0.7,其中ITGA5(AUC值=1.000),ITGA6(AUC值=1.000),ITGB5(AUC值=1.000),ITGA4(AUC值=1.000),LAMA5(AUC值=1.000)及LAMA3(AUC值=1.000)对该证型具有较高潜在诊断价值;RA_GSKX中有5个关键hub基因AUC值> 0.7,其中CD44(AUC值=1.000)和MMP14(AUC值=0.875)对该证型具有较高潜在诊断价值;RA_QXLX中有3个关键hub基因AUC值> 0.7,其中ITGA6(AUC值=0.938)和VTN(AUC值=0.875)对该证型具有较高潜在诊断价值;ERA_YXZL中有5个关键hub基因AUC值> 0.85,关键hub基因均对该证型具有较高潜在诊断价值。综合分析发现,各证型关键hub中均有ITGA6存在,且AUC值均大于0.7,说明ITGA6可作为类风湿关节炎诊断的新型潜在生物标志物。 "
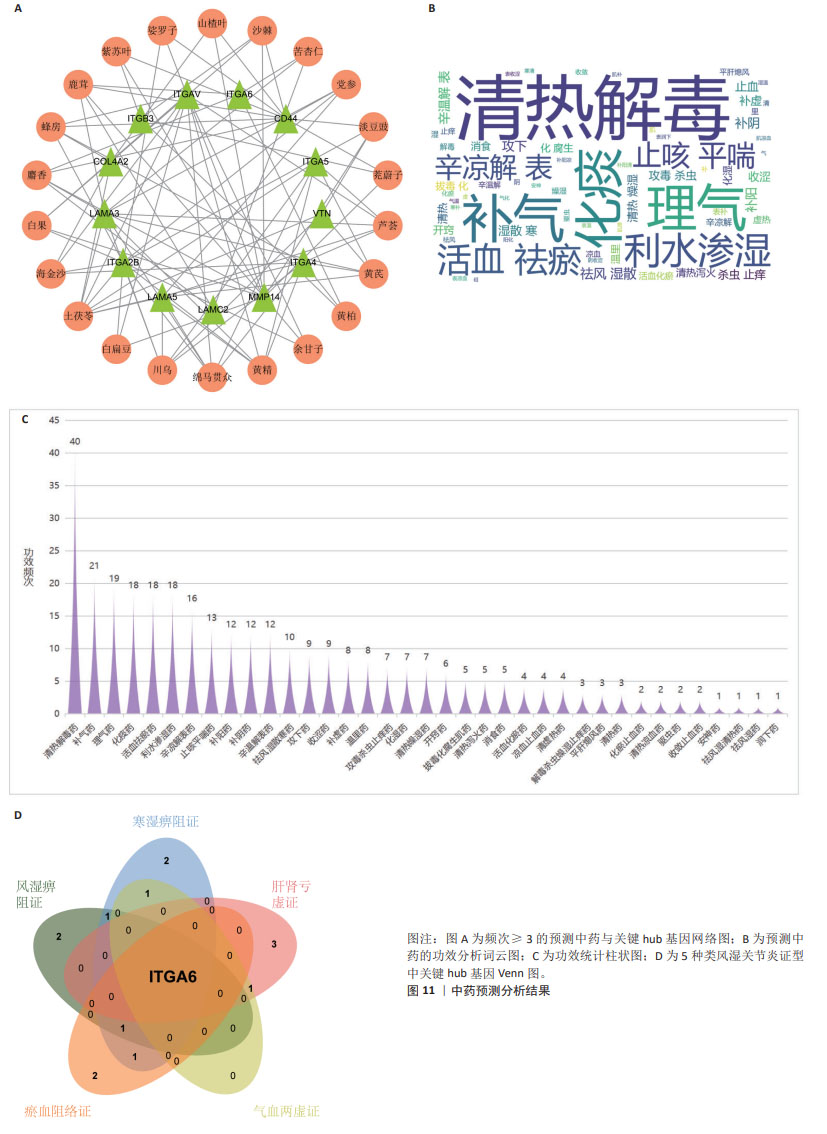
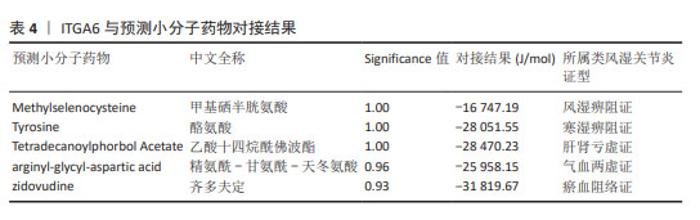
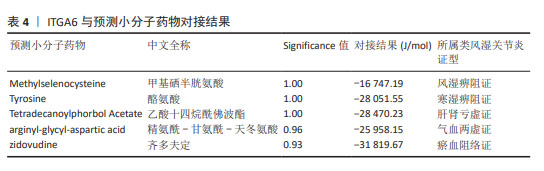
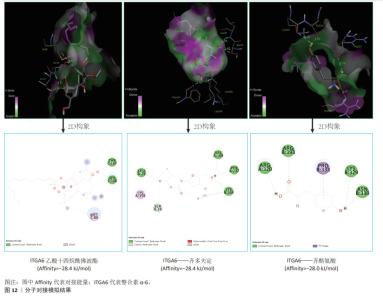
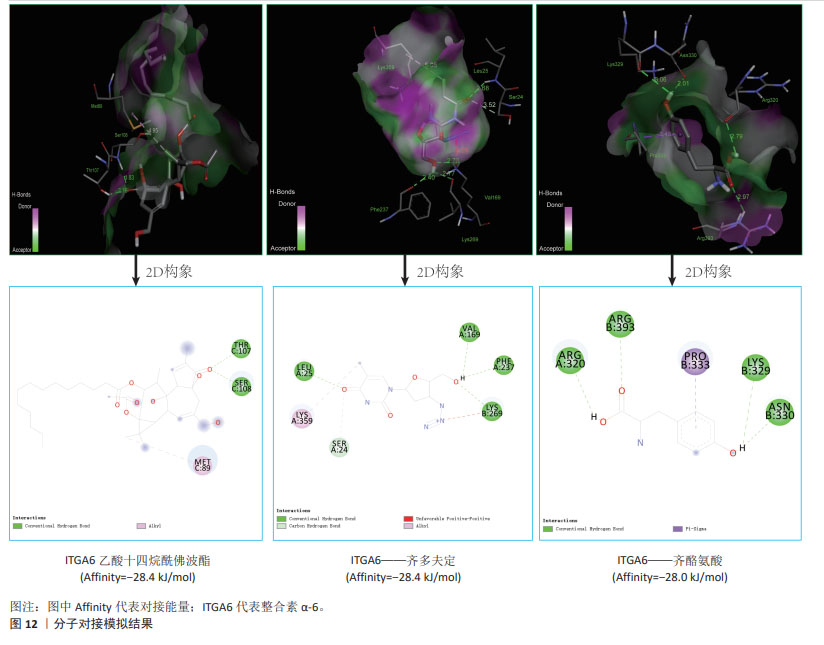
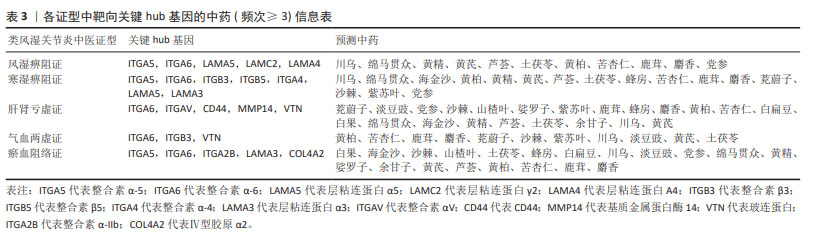
2.5 类风湿关节炎不同中医证型中靶向基底膜相关基因的潜在治疗药物预测与小分子验证结果 将5种类风湿关节炎中医证型中各自关键hub基因以此输入到SymMap数据库中,共计预测出207味相关中药。其中频次≥3的中药共计23味,各证型详细药物信息见表3。综合频次≥3的中药及关键hub基因,绘制关系网络图,见图11。拓扑分析发现,网络中频次前5位的中药为土茯苓、川乌、绵马贯众、黄精及黄芪,可分别靶向8,6,6,6,5个基底膜相关类风湿关节炎关键hub基因,是能够靶向调控基底膜相关基因治疗类风湿关节炎最有潜力的中药。通过对207味中药功效的分析统计,发现对于治疗不同类风湿关节炎证型的潜在预测中药,主要以清热解毒药为主。因此推测清热解毒类中药可能是类风湿关节炎不同证型治疗中可以贯穿始终的潜在有效药物,见图11。 通过COREMINE数据库分别对5种类风湿关节炎证型的关键hub基因联合预测,共筛选得到209种小分子药物(P < 0.05),选取每种证型中预测得到的显著性最高的小分子与类风湿关节炎潜在生物标志物ITGA6进行分子对接模拟,结果见表4。除 Methylselenocysteine(甲基硒半胱氨酸)外,其余小分子与ITGA6均显示出良好的对接效果(结合热能均小于-20 933.99 J/mol),具有稳定的氢键结构形成,见图12。使用Discovery Studio (v4.5)软件进行对接模式构象。"
| [1] RADU AF, BUNGAU SG. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857. [2] HUANG J, FU X, CHEN X, et al. Promising therapeutic targets for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:686155. [3] FOSTER MH. Basement membranes and autoimmune diseases. Matrix Biol. 2017; 57-58:149-168. [4] TöPFERU. Basement membrane dynamics and mechanics in tissue morphogenesis. Biol Open. 2023;12(8): bio059980. [5] UESAKA K, OKA H, KATO R, et al. Bioinformatics in bioscience and bioengineering: recent advances, applications, and perspectives. J Biosci Bioeng. 2022;134(5):363-373. [6] DING Z, CHEN W, WU H et al. Integrative network fusion-based multi-omics study for biomarker identification and patient classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin Med. 2023;18(1):48. [7] ALBARADEI S, THAFAR M, ALSAEDI A, et al. Machine learning and deep learning methods that use omics data for metastasis prediction. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:5008-5018. [8] JAYADEV R, MORAIS MRPT, ELLINGFORD JM, et al. A basement membrane discovery pipeline uncovers network complexity, regulators, and human disease associations. Sci Adv. 2022;8(20): eabn2265. [9] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012; 16(5):284-287. [10] GUSTAVSSON EK, ZHANG D, REYNOLDS RH, et al. ggtranscript: an R package for the visualization and interpretation of transcript isoforms using ggplot2. Bioinformatics. 2022;38(15):3844-3846. [11] ROBIN X, TURCK N, HAINARD A, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:77. [12] WU Y, ZHANG F, YANG K, et al. SymMap: an integrative database of traditional Chinese medicine enhanced by symptom mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1): D1110-D1117. [13] 宋哲,劳慧敏,王晓,等.铁死亡基因在儿童川崎病中的生物信息学分析及中药预测研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2023, 38(5):2286-2291. [14] HALFTER W, OERTLE P, MONNIER CA, et al. New concepts in basement membrane biology. FEBS J. 2015;282(23): 4466-4479. [15] GUDMANN NS, JUNKER P, JUHL P, et al. Type IV collagen metabolism is associated with disease activity, radiographic progression and response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(5):829-835. [16] GUDMANN NS, HIRATA S, KARSDAL MA, et al. Increased remodelling of interstitial collagens and basement membrane is suppressed by treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: serological evaluation of a one-year prospective study of 149 Japanese patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(3):462-470. [17] KHALILGHARIBI N, MAO Y. To form and function: on the role of basement membrane mechanics in tissue development, homeostasis and disease. Open Biol. 2021;11(2):200360. [18] DINESH P, RASOOL M. uPA/uPAR signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: shedding light on its mechanism of action. Pharmacol Res. 2018;134:31-39. [19] BOUDKO SP, ASPIRNAUTS PEDCHENKO VK, POKIDYSHEVA EN, et al. Collagen IV of basement membranes: III. Chloride pressure is a primordial innovation that drives and maintains the assembly of scaffolds. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(11):105318. [20] ONG S, ZHANG J, SU Q, et al. Downregulation of ITGA6 confers to the invasion of multiple myeloma and promotes progression to plasma cell leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2021;124(11):1843-1853. [21] TANSATHITAYA V, SARASIN W, PHAKHAM T, et al. Regulation of mi-RNAs target cancer genes between exercise and non-exercise in rat rheumatoid arthritis induction: pilot study. Epigenet Insights. 2022;15:25168657221110485. [22] TU Y, MA T, WEN T, et al. MicroRNA-377-3p alleviates IL-1β-caused chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis in part by downregulating ITGA6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(1):46-53. [23] HUANG JM, PANG ZY, QI GB, et al. Association of ITGAV polymorphisms and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence from a meta-analysis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16(6):631-640. [24] HOLLIS-MOFFATT JE, ROWLEY KA, PHIPPS-GREEN AJ, et al. The ITGAV rs3738919 variant and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in four Caucasian sample sets. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11(5):R152. [25] SHAKIBA E, TAVILANI H, GOODARZI MT, et al. The ITGAV-rs3911238 polymorphism is associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014;13(5):356-363. [26] KOCA SS, KARA M, OZGEN M, et al. The rs3768777-G allele of ITGAV gene is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(5):693-698. [27] KANE BA, AN H, RAJASEKARIAH P, et al. Differential expression and regulation of the non-integrin 37/67-kDa laminin receptor on peripheral blood leukocytes of healthy individuals and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1149. [28] WANG J, LIU C, WANG T, et al. Single-cell communication patterns and their intracellular information flow in synovial fibroblastic osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Lett. 2023;263:1-13. [29] WANG G, CHEN S, XIE Z, et al. TGFβ attenuates cartilage extracellular matrix degradation via enhancing FBXO6-mediated MMP14 ubiquitination. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(8):1111-1120. [30] CHEN Z, WANG H, XIA Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol. 2018;201(8):2472-2482. [31] XIA XD, GILL G, LIN H, et al. Global, but not chondrocyte-specific, MT1-MMP deficiency in adult mice causes inflammatory arthritis. Matrix Biol. 2023;122:10-17. [32] QADRI MM. Targeting CD44 receptor pathways in degenerative joint diseases: involvement of proteoglycan-4 (PRG4). Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(10): 1425. [33] SÁNCHEZ-ZUNO GA, BUCALA R, HERNÁNDEZ-BELLO J, et al. Canonical (CD74/CD44) and non-canonical (CXCR2, 4 and 7) MIF receptors are differentially expressed in rheumatoid arthritis patients evaluated by DAS28-ESR. J Clin Med. 2021; 11(1):120. [34] HERNÁNDEZ DAZ, CHAGOLLÁN MG, ZUNO GAS, et al. Expression of transcriptional factors of T helper differentiation (T-bet, GATA-3, RORγt, and FOXP3), MIF receptors (CD44, CD74, CXCR2, 4, 7), and Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in PBMC from control subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Curr Mol Med. 2023. doi: 10.2174/0115665240260976230925095330. [35] PARADOWSKA-GORYCKA A, WAJDA A, ROMANOWSKA-PRÓCHNICKA K, et al. Th17/Treg-related transcriptional factor expression and cytokine profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:572858. [36] WEHR P, PURVIS H, LAW SC, et al. Dendritic cells, T cells and their interaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019;196(1):12-27. [37] KUCUKSEZER UC, AKTAS CETIN E, ESEN F, et al. The role of natural killer cells in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:622306. [38] 李慧,张林.土茯苓治疗类风湿关节炎的网络药理学研究[J].时珍国医国药, 2020,31(12):2854-2857. [39] CHEN Q, WU C, WANG S, et al. Glycyrrhizic acid modified Poria cocos polyscaccharide carbon dots dissolving microneedles for methotrexate delivery to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Front Chem. 2023;11:1181159. [40] LIU X, TAO H, TIAN R, et al. Hezi inhibits Tiebangchui-induced cardiotoxicity and preserves its anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects by regulating the pharmacokinetics of aconitine and deoxyaconitine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;302(Pt A):115915. [41] HE YN, OU SP, XIONG X, et al. Stems and leaves of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. as potential herbal resources for treating rheumatoid arthritis: chemical analysis, toxicity and activity evaluation. Chin J Nat Med. 2018;16(9):644-652. [42] QI Y, GAO F, HOU L,et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunostimulatory activities of astragalosides. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(6): 1157-1167. [43] WANG Y, LIU Y, XI Z, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwutang granule in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(11):e14888. [44] 曹培晨,付新利.张鸣鹤教授清热解毒法论治类风湿关节炎[J].吉林中医药, 2022,42(11):1269-1272. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [5] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [6] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [7] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [8] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [9] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [10] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [11] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [12] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [13] | Xie Yizi, Lin Xueying, Zhang Xinxin, Huang Xiufang, Zhan Shaofeng, Jiang Yong, Cai Yan. Biological mechanism of mitophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6708-6716. |
| [14] | Cui Yuena, Chen Xiaoyu, Liang Meiting, Chen Wujin, He Yi, Dilinur·Ekpa, Du Manxi, Zhu Yuqiu, Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Sun Yuping. Differences of calorie restriction and time-restricted feeding on metabolic indices and gut microbiota of mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6449-6456. |
| [15] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||