Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (25): 5478-5485.doi: 10.12307/2025.522
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of the sirtuins in pyroptosis
Li Wenjie, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Zeng Xiao, Sun Jinyi, Luo Yuncai, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Dong Qiang
- School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University/Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-09Accepted:2024-06-07Online:2025-09-08Published:2024-12-30 -
Contact:Dong Qiang, PhD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University/Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Wenjie, Master candidate, School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University/Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Wenjie, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Zeng Xiao, Sun Jinyi, Luo Yuncai, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Dong Qiang . Role of the sirtuins in pyroptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5478-5485.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
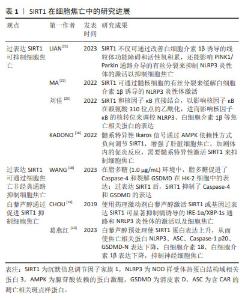
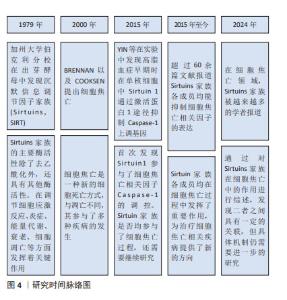
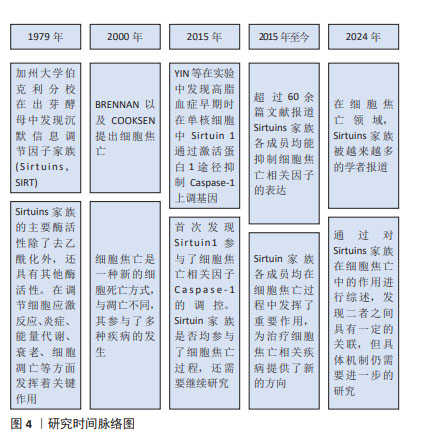
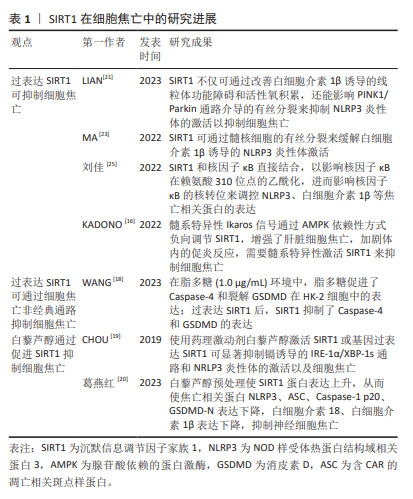
2.2 SIRT1与细胞焦亡 SIRT1是组蛋白去乙酰化酶(histone deacetylase,HDAC)中依赖于NAD+的Sirtuins家族成员之一。目前,在Sirtuins家族中SIRT1的研究报道最多、最深入。 SIRT1在抑制细胞凋亡、保护线粒体功能、抵抗氧化应激和减轻炎症反应方面发挥着重要作用[12]。其中,减轻炎症反应主要表现在抑制了炎症相关因子NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白 3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)的表达。NLRP3是一种多蛋白复合物,有3个蛋白结构域,分别是NLRP3、含CAR的凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD,ASC)和Caspase-1,当细胞受到损伤相关分子模式分子刺激时,NLRP3蛋白寡聚并招募ASC和Caspase-1前体(Procaspase-1),形成NLRP3炎性体,从而导致Procaspase-1的活化[13-15],引起细胞焦亡。因此,调节SIRT1水平可成为对抗细胞焦亡的一种方式。有研究表明,髓系特异性Ikaros家族锌指蛋白1(Ikaros family zinc finger protein 1,IKZF1/Ikaros)通过AMP激活蛋白激酶[Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase,AMPK)负向调节SIRT1,增强了肝脏细胞焦亡,从而加剧体内的促炎反应[16]。因此,在这项研究中,学者通过髓系特异性激活SIRT1后发现其抑制了细胞焦亡。此外,SIRT1可通过调控AMPK信号通路活性,降低焦亡相关因子的蛋白表达,缓解心肌缺血再灌注损伤[17]。WANG等[18]发现,不同浓度的SIRT1激活剂SRT1720促进SIRT1 mRNA在人肾小管上皮细胞系(human renal tubular epithelial cell line,HK-2)细胞中的表达,可抑制HK-2细胞中Caspase-1、Caspase-4、NLRP3和GSDMD的mRNA表达,呈剂量依赖性抑制作用。研究结果显示在脂多糖(1.0 μg/mL)环境下,HK-2细胞中的Caspase-4和GSDMD表达上升。研究人员促进SIRT1表达后发现,Caspase-4和GSDMD的表达受到抑制。上述研究证明,促进SIRT1的表达可以抑制NLRP3/Caspase-1经典细胞焦亡途径和抑制Caspase-4非经典细胞焦亡途径。 白藜芦醇是存在于葡萄、花生、桑葚等植物中的天然植物抗毒素,具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗凋亡和抗癌的作用。使用白藜芦醇激活SIRT1或基因过表达SIRT1可显著抑制镉诱导的IRE-1α/XBP-1s通路和NRLP3炎性体的激活以及细胞焦亡[19-20]。葛燕红[20]在研究中发现白藜芦醇预处理后SIRT1蛋白表达升高,从而使焦亡相关蛋白NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1 p20、GSDMD-N表达下降,炎症因子细胞白细胞介素18、白细胞介素1β表达下降,抑制小鼠海马神经细胞元焦亡。 研究显示,过量表达SIRT1不仅可通过改善白细胞介素1β诱导的线粒体功能障碍和活性氧积累,还能影响PINK1/Parkin通路介导的有丝分裂来抑制NLRP3炎性体的激活以抑制细胞焦亡[21],从而缓解细胞焦亡对低氧诱导肺动脉内皮细胞的损伤[22]。此外,在大鼠模型体内,使用SIRT1激动剂SRT1720可延缓炎症应激相关椎间盘退变的进程。进一步的研究发现,SIRT1通过髓核细胞的有丝分裂缓解了白细胞介素1β诱导的NLRP3炎性体激活。此项研究表明,SIRT1可能是缓解椎间盘退变中NLRP3激活细胞焦亡的潜在治疗靶点[23]。 核因子κB是一种核转录因子,由p50、p52、RelA/p65、cRel和RelB 5个亚基组成,通过与DNA特异序列结合来调节相关基因转录[24],因此在调控氧化应激、炎症反应、细胞周期、凋亡中发挥重要作用。核因子κB活化激活炎症因子后,在人体造成损伤的同时促进活性氧生成,从而损伤组织器官并且进一步促进炎症因子的表达。有研究发现,在人主动脉内皮细胞中SIRT1和核因子κB直接结合,以影响核因子κB在赖氨酸310位点的乙酰化,进而影响核因子κB的核转位来调控NLRP3、白细胞介素1β等焦亡相关蛋白的表达[25],在细胞焦亡中发挥了一定的作用。还有研究指出,SIRT1可影响核因子κB以减轻脑出血后星形胶质细胞焦亡[26]。 综上可知,除了通过细胞焦亡经典通路和非经典通路,过表达SIRT1还可通过AMPK信号通路、IRE-1α/XBP-1s通路、PINK1/Parkin通路介导的有丝分裂以及影响核因子κB的乙酰化等不同途径参与细胞焦亡的调控,使得NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD等焦亡相关因子的表达降低。这表明SIRT1是调节细胞焦亡的重要因子之一,其可能成为治疗细胞焦亡相关疾病的新靶点,为之后更加深入的研究以及相关疾病的治疗提供了新的思路。 SIRT1在细胞焦亡中的研究进展见表1。 "
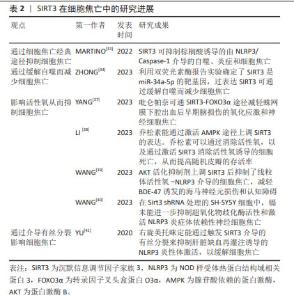
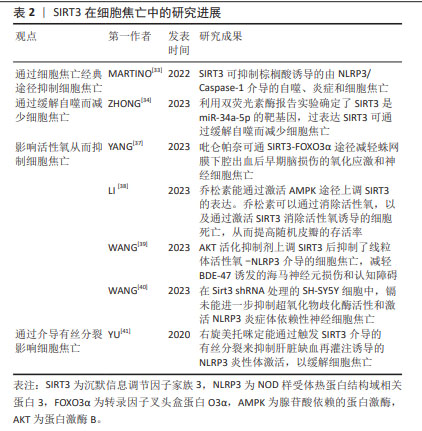
2.3 SIRT2与细胞焦亡 SIRT2在人体中广泛分布,表达于包括大脑、肾脏、胰腺、睾丸、肝脏和脂肪组织在内的多种组织器官中,它在基因组稳定性维持、细胞分化、细胞稳态、衰老、感染、炎症、氧化应激和自噬等生理过程中扮演着重要的角色[27]。 WANG等[28]研究发现,在创伤性脑损伤小鼠模型中敲除SIRT2可减轻脑水肿、血脑屏障的破坏,并且NLRP3炎性体的表达下降,从而降低Caspase-1的活性,以减少神经炎症和神经细胞焦亡,改善神经功能。此外,在体外机械拉伸损伤细胞模型中敲除SIRT2也减少了NLRP3炎症体的表达从而抑制了神经元细胞焦亡。 上述结果表明,与Sirtuin家族的其他成员不同,敲除SIRT2可抑制NLRP3炎症体介导的细胞焦亡,这提示SIRT2对细胞焦亡具有一定的影响,但SIRT2与细胞焦亡的研究较少,关于二者之间的具体机制还未完全阐明。因此,SIRT2与细胞焦亡之间的关系需要更加深入与全面的研究。 2.4 SIRT3与细胞焦亡 SIRT3是一种去乙酰化酶,位于线粒体中,其依赖于NAD+从而调节细胞能量代谢和应激反应,帮助受损细胞度过“艰难时期”。SIRT3的功能包括维持线粒体平衡、抵抗氧化应激和调节自噬[29-30]。研究表明,SIRT3与NLRP3介导的细胞焦亡密切相关[31-32]。MARTINO等[33]发现,SIRT3可抑制棕榈酸诱导的由NLRP3/Caspase-1介导的自噬、炎症和细胞焦亡。ZHONG等[34]利用双荧光素酶报告实验确定了SIRT3是miR-34a-5p的靶基因,过表达SIRT3可通过缓解自噬而减少细胞焦亡。 细胞质中的转录因子叉头盒蛋白O3(the transcription factor Forkhead box protein O3,FOXO3α)是SIRT3的靶标分子之一,它被去乙酰化后处于活化状态。活化的FOXO3α可从细胞质进入细胞核,调节锰超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶等基因的表达,影响线粒体呼吸和活性氧清除[35-36]。SIRT3的表达促进了活性氧的清除,进而缓解NLRP3诱导的细胞焦亡和炎症[37-38]。 SIRT3的过表达可恢复超氧化物歧化酶2的活性和表达,从而增强线粒体活性氧的清除能力,抑制NLRP3炎性体的激活[39-40],以改善小胶质细胞焦亡。WANG等[39]的研究也证明了这一结论,SIRT3的药理激动剂Honokiol(HKL)上调SIRT3表达后抑制了线粒体活性氧-NLRP3介导的细胞焦亡,减轻BDE-47诱发的海马神经元损伤和认知障碍。 此外,研究发现右旋美托咪定能通过触发SIRT3介导的有丝分裂来抑制肝脏缺血再灌注诱导的NLRP3炎性体激活,以缓解细胞焦亡[41]。 综上所述,SIRT3能够影响细胞焦亡。由于SIRT3存在于线粒体中,除了通过细胞焦亡经典通路影响焦亡的发生外,SIRT3还可通过恢复超氧化物歧化酶2的活性、增强线粒体活性氧的清除能力抑制细胞焦亡,但其与细胞焦亡之间的关系还需要深入研究。 SIRT3在细胞焦亡中的研究进展见表2。 "
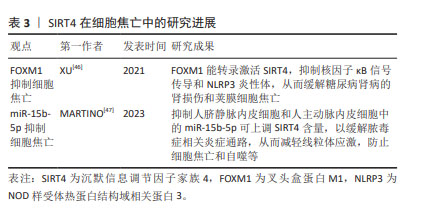
2.5 SIRT4与细胞焦亡 SIRT4是一种线粒体沉默信息调节因子,特别富集于心脏、肾脏、大脑和肝脏。与Sirtuins家族其他成员不同,SIRT4是组蛋白和牛血清白蛋白上高效的ADP核糖基转移酶,但不具有依赖NAD+的去乙酰化酶活性。 SIRT4与调节肝脏和肌肉细胞中的脂肪酸氧化和线粒体基因表达有关[42]。叉头盒蛋白M1(Forkhead box protein M1,FOXM1)可调控细胞周期、细胞凋亡和氧化应激,作为一种转录因子,FOXM1可与靶基因的启动子结合以调控转录[43-45]。XU等[46]研究表明,FOXM1能转录激活SIRT4,抑制核因子κB信号传导和NLRP3炎性体,从而缓解糖尿病肾病的肾损伤和荚膜细胞焦亡。 此外,抑制人脐静脉内皮细胞和人主动脉内皮细胞中的miR-15b-5p可上调SIRT4含量,以缓解脓毒症相关炎症通路,从而防止细胞焦亡和自噬等。研究人员利用PCSK9抑制剂(i-PCSK9)处理人脐静脉内皮细胞和人主动脉内皮细胞,提高二者中的SIRT4蛋白水平从而抑制细胞焦亡[47]。 综上所述,SIRT4可对荚膜细胞、人脐静脉内皮细胞和人主动脉内皮中存在的细胞焦亡产生影响。但SIRT4在其他细胞中的抗细胞焦亡作用仍不清楚,尚需要更多的研究。 SIRT4在细胞焦亡中的研究进展见表3。 "
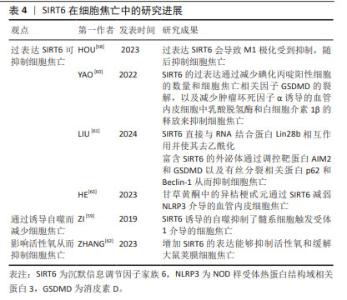
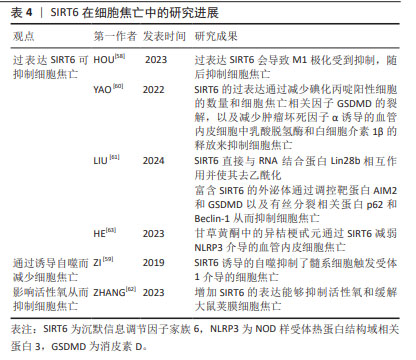
2.6 SIRT5与细胞焦亡 SIRT5主要定位在线粒体中,在大脑、心脏、肝脏和淋巴细胞中高度表达,具有包括去乙酰化、去丙氨酸化和去琥珀酸化等在内的多重酶活性[48]。 SIRT5参与细胞内代谢和能量平衡的调节,包括能量的摄入、储存和消耗,这些过程与心脏病的发生密切相关。研究发现,SIRT5缺乏加重了糖尿病心肌病小鼠的心肌损伤[49],加剧了高糖诱导的心肌细胞氧化应激和线粒体功能障碍,从而导致心肌细胞焦亡、细胞衰老和DNA损伤。相反,在SIRT5过表达后糖尿病心肌病相关心肌损伤减轻。研究人员将谷胱甘肽S-转移酶P(GSTP)敲除后再次逆转了这种损伤。这些结果表明,糖尿病心肌病中SIRT5的转录减少是SPI1下调的结果。SPI1促进SIRT5的转录,从而改善了糖尿病心肌病相关的心肌损伤。因此,SIRT5能介导GSTP1 Mal-Lys修饰和蛋白稳定性,减少细胞焦亡、衰老和DNA损伤,从而改善糖尿病心肌病相关心肌损伤。 由于SIRT5参与了更多的机体活动,尤其是在心脏疾病方面,因此,其可能为治疗相关疾病提供了新的思路。但关于SIRT5与细胞焦亡之间的关系目前研究较少,需要更加深入和全面的研究。 2.7 SIRT6与细胞焦亡 SIRT6是一种具有多种催化活性的核蛋白,可通过调节多种下游信号通路稳定基因组[50-52]。SIRT6在细胞衰老、能量代谢、氧化应激、炎症和自噬等多个生理过程中发挥着关键作用[53]。不仅如此,SIRT6能够通过水解长链乙酸乙酯发挥抗炎作用[54]。 多项研究表明,M1极化巨噬细胞与细胞焦亡之间具有一定的关联[55-57]。HOU等[58]在实验中发现过表达SIRT6使M1极化受到抑制从而抑制细胞焦亡。 ZI等[59]研究表明,SIRT6的下调与急性心肌梗死患者预后不良和严重的内皮损伤有关,阻断SIRT6诱导的自噬会导致髓系细胞触发受体1介导的细胞焦亡增加。与此相反,未阻断SIRT6诱导的自噬限制了髓系细胞触发受体1介导的细胞焦亡,并且SIRT6的过表达会减轻氧化修饰低密度脂蛋白干预后心肌细胞的炎症和细胞焦亡。由此可推断,SIRT6参与了调控细胞焦亡的过程。 此外,SIRT6可直接与RNA结合蛋白Lin28b相互作用并使其去乙酰化从而减少碘化丙啶阳性细胞的数量和细胞焦亡相关因子GSDMD的裂解,以及减少肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的血管内皮细胞中乳酸脱氢酶和白细胞介素1β的释放来抑制细胞焦亡[60]。研究发现,富含SIRT6的外泌体通过调控与细胞焦亡相关的靶蛋白AIM2和GSDMD以及与有丝分裂相关的结合系统基本蛋白p62和Beclin-1影响了心肌缺血再灌注损伤的进展[61]。来源于脂肪干细胞的SIRT6高表达外泌体抑制了AIM2,同时增强了有丝分裂,导致内皮细胞中GSDMD 裂解和细胞焦亡的显著减少。ZHANG等[62]研究表明,增加SIRT6的表达能够抑制活性氧和缓解大鼠荚膜细胞焦亡,并且甘草黄酮中的异桔梗甙元通过SIRT6减弱了NLRP3介导的血管内皮细胞焦亡[63]。 综上所述,过表达SIRT6后,可通过诱导自噬、调控细胞有丝分裂和直接作用于细胞焦亡相关因子以影响细胞焦亡,但其中的具体机制尚不清楚。因此,需进一步对SIRT6与细胞焦亡之间的关系做进一步研究。 SIRT6在细胞焦亡中的研究进展见表4。 "
| [1] BRENNAN MA, COOKSON BT. Salmonella induces macrophage death by caspase-1-dependent necrosis. Mol Microbiol. 2000;38(1):31-40. [2] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, ABRAMS JM, et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(1):107-120. [3] BERGSBAKEN T, FINK SL, COOKSON BT. Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7(2):99-109. [4] BERTHELOOT D, LATZ E, FRANKLIN BS. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(5):1106-1121. [5] RAO Z, ZHU Y, YANG P, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics. 2022;12(9):4310-4329. [6] PAN Z, DONG H, HUANG N, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation regulation of sirtuins: New insights into common oral diseases. Front Physiol. 2022;13:953078. [7] WANG Y, HE J, LIAO M, et al. An overview of Sirtuins as potential therapeutic target: Structure, function and modulators. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;161:48-77. [8] GROOTAERT MOJ, BENNETT MR. Sirtuins in atherosclerosis: guardians of healthspan and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(10):668-683. [9] PALOMER X, AGUILAR-RECARTE D, GARCÍA R, et al. Sirtuins: To Be or Not To Be in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Trends Mol Med. 2021;27(6):554-571. [10] WANG M, LIN H. Understanding the Function of Mammalian Sirtuins and Protein Lysine Acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2021;90:245-285. [11] CHEN B, ZANG W, WANG J, et al. The chemical biology of sirtuins. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(15):5246-5264. [12] HAN Y, SUN W, REN D, et al. SIRT1 agonism modulates cardiac NLRP3 inflammasome through pyruvate dehydrogenase during ischemia and reperfusion. Redox Biol. 2020;34:101538. [13] SUTTERWALA FS, OGURA Y, SZCZEPANIK M, et al. Critical role for NALP3/CIAS1/Cryopyrin in innate and adaptive immunity through its regulation of caspase-1. Immunity. 2006;24(3):317-327. [14] MA MW, WANG J, DHANDAPANI KM, et al. NADPH Oxidase 2 Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Brain after Traumatic Brain Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:6057609. [15] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3328. [16] KADONO K, KAGEYAMA S, NAKAMURA K, et al. Myeloid Ikaros-SIRT1 signaling axis regulates hepatic inflammation and pyroptosis in ischemia-stressed mouse and human liver. J Hepatol. 2022;76(4):896-909. [17] 钟泽,罗秀英,相鹏,等.组蛋白去乙酰化酶SIRT1对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤介导的细胞焦亡调控作用[J].中华心血管病杂志(网络版), 2020,3(1):13. [18] WANG Z, WEIZHONG G, ZHOU J, et al. Role and significance of SIRT1 in regulating the LPS-activated pyroptosis pathway in children with congenital hydronephrosis. World J Pediatr Surg. 2023;6(4):e000602. [19] CHOU X, DING F, ZHANG X, et al. Sirtuin-1 ameliorates cadmium-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis through XBP-1s deacetylation in human renal tubular epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93(4):965-986. [20] 葛燕红.SIRT1调控的线粒体稳态在NaAsO_2致神经细胞焦亡中的作用[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2023. [21] LIAN L, LE Z, WANG Z, et al. SIRT1 Inhibits High Glucose-Induced TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Cataract Formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023;64(3):16. [22] 龚琦,陈婷,周芝文,等. SIRT1对低氧诱导肺动脉内皮细胞损伤的保护作用及机制[J].山东医药,2023,63(10):44-48. [23] MA Z, TANG P, DONG W, et al. SIRT1 alleviates IL-1β induced nucleus pulposus cells pyroptosis via mitophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;107:108671. [24] MULERO MC, HUANG DB, NGUYEN HT, et al. DNA-binding affinity and transcriptional activity of the RelA homodimer of nuclear factor κB are not correlated. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(46):18821-18830. [25] 刘佳. SIRT1通过去乙酰化NF-κB(p65)调控H2O2诱导的人主动脉内皮细胞焦亡的机制研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022. [26] 车益军,韩冲,于欣宇,等.五味子甲素通过SIRT1/NF-κB通路减轻脑出血后星形胶质细胞焦亡的机制[J].遵义医科大学学报,2023,46(11):1041-1049. [27] ZHOU YL, YAN YM, LI SY, et al. 6-O-angeloylplenolin exerts neuroprotection against lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(1):10-21. [28] WANG W, GONG QY, CAI L, et al. Knockout of Sirt2 alleviates traumatic brain injury in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(2):350-356. [29] WANG S, ZHANG J, DENG X, et al. Advances in characterization of SIRT3 deacetylation targets in mitochondrial function. Biochimie. 2020;179:1-13. [30] YANG H, ZHOU Z, LIU Z, et al. Sirtuin-3: A potential target for treating several types of brain injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1154831. [31] GU J, HUANG H, LIU C, et al. Pinocembrin inhibited cardiomyocyte pyroptosis against doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction via regulating Nrf2/Sirt3 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;95:107533. [32] SUN Z, FANG C, XU S, et al. SIRT3 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome via autophagy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;207:115354. [33] MARTINO E, BALESTRIERI A, ANASTASIO C, et al. SIRT3 Modulates Endothelial Mitochondrial Redox State during Insulin Resistance. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(8):1611. [34] ZHONG Z, GAO Y, ZHOU J, et al. Inhibiting mir-34a-5p regulates doxorubicin-induced autophagy disorder and alleviates myocardial pyroptosis by targeting Sirt3-AMPK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115654. [35] FASANO C, DISCIGLIO V, BERTORA S, et al. FOXO3a from the Nucleus to the Mitochondria: A Round Trip in Cellular Stress Response. Cells. 2019; 8(9):1110. [36] RANGARAJAN P, KARTHIKEYAN A, LU J, et al. Sirtuin 3 regulates Foxo3a-mediated antioxidant pathway in microglia. Neuroscience. 2015;311:398-414. [37] YANG H, DING C, CHENG M, et al. Perampanel attenuates oxidative stress and pyroptosis following subarachnoid hemorrhage via the SIRT3/FOXO3α pathway. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):21320. [38] LI J, LI Y, WANG X, et al. Pinocembrin alleviates pyroptosis and apoptosis through ROS elimination in random skin flaps via activation of SIRT3. Phytother Res. 2023;37(9):4059-4075. [39] WANG D, YUAN Q, LIU S, et al. BDE-47 flame retardant exposure induces microglial pyroptosis and cognitive deficits by activating the mtROS-NLRP3 axis via Sirt3 downregulation and is salvaged by honokiol. Environ Pollut. 2023;334:122158. [40] WANG D, WU Y, SUN S, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis involvement in cadmium exposure-induced cognitive deficits via the Sirt3-mtROS axis. Sci Total Environ. 2023;903:166478. [41] YU W, LYU J, JIA L, et al. Dexmedetomidine Ameliorates Hippocampus Injury and Cognitive Dysfunction Induced by Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion by Activating SIRT3-Mediated Mitophagy and Inhibiting Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Young Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:7385458. [42] NASRIN N, WU X, FORTIER E, et al. SIRT4 regulates fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial gene expression in liver and muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(42):31995-32002. [43] HALASI M, GARTEL AL. Targeting FOXM1 in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85(5):644-652. [44] LIAO GB, LI XZ, ZENG S, et al. Regulation of the master regulator FOXM1 in cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):57. [45] WANG RT, MIAO RC, ZHANG X, et al. Fork head box M1 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression to promote the angiogenesis and tumor cell growth of gallbladder cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27(8):692-707. [46] XU X, ZHANG L, HUA F, et al. FOXM1-activated SIRT4 inhibits NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome to alleviate kidney injury and podocyte pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Exp Cell Res. 2021;408(2):112863. [47] MARTINO E, D’ONOFRIO N, BALESTRIERI A, et al. MiR-15b-5p and PCSK9 inhibition reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial dysfunction by targeting SIRT4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):66. [48] SCHLICKER C, GERTZ M, PAPATHEODOROU P, et al. Substrates and regulation mechanisms for the human mitochondrial sirtuins Sirt3 and Sirt5. J Mol Biol. 2008;382(3):790-801. [49] WEI C, SHI M, DONG S, et al. SIRT5-related lysine demalonylation of GSTP1 contributes to cardiomyocyte pyroptosis suppression in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Int J Biol Sci. 2024;20(2):585-605. [50] MOSTOSLAVSKY R, CHUA KF, LOMBARD DB, et al. Genomic instability and aging-like phenotype in the absence of mammalian SIRT6. Cell. 2006; 124(2):315-329. [51] CHEN Y, CHEN J, SUN X, et al. The SIRT6 activator MDL-800 improves genomic stability and pluripotency of old murine-derived iPS cells. Aging Cell. 2020;19(8):e13185. [52] KOROTKOV A, SELUANOV A, GORBUNOVA V. Sirtuin 6: linking longevity with genome and epigenome stability. Trends Cell Biol. 2021;31(12):994-1006. [53] LI X, LIU L, LI T, et al. SIRT6 in Senescence and Aging-Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:641315. [54] LI J, YU D, CHEN S, et al. Sirt6 opposes glycochenodeoxycholate-induced apoptosis of biliary epithelial cells through the AMPK/PGC-1α pathway. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:43. [55] JIAO Y, ZHANG T, ZHANG C, et al. Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):356. [56] XIAO T, WAN J, QU H, et al. Tripartite-motif protein 21 knockdown extenuates LPS-triggered neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglial M1 polarization via suppressing NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021;706:108918. [57] GE G, BAI J, WANG Q, et al. Punicalagin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by downregulating M1 macrophage and pyroptosis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(3):588-603. [58] HOU Y, SHI J, GUO Y, et al. DNMT1 regulates polarization of macrophage-induced intervertebral disc degeneration by modulating SIRT6 expression and promoting pyroptosis in vivo. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(10): 4288-4303. [59] ZI Y, YI-AN Y, BING J, et al. Sirt6-induced autophagy restricted TREM-1-mediated pyroptosis in ox-LDL-treated endothelial cells: relevance to prognostication of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Cell Death Discov. 2019;5:88. [60] YAO F, LV X, JIN Z, et al. Sirt6 inhibits vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis by regulation of the Lin28b/let-7 pathway in atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:109056. [61] LIU K, WANG H, WANG Y, et al. Exploring the therapeutic potential of Sirt6-enriched adipose stem cell-derived exosomes in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: unfolding new epigenetic frontiers. Clin Epigenetics. 2024;16(1):7. [62] ZHANG M, LIU W, LIU Y, et al. Astragaloside IV Inhibited Podocyte Pyroptosis in Diabetic Kidney Disease by Regulating SIRT6/HIF-1α Axis. DNA Cell Biol. 2023;42(10):594-607. [63] HE J, DENG Y, REN L, et al. Isoliquiritigenin from licorice flavonoids attenuates NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis by SIRT6 in vascular endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;303:115952. [64] VOELTER-MAHLKNECHT S, LETZEL S, MAHLKNECHT U. Fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosomal organization of the human Sirtuin 7 gene. Int J Oncol. 2006;28(4):899-908. [65] MICHISHITA E, PARK JY, BURNESKIS JM, et al. Evolutionarily conserved and nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(10):4623-4635. [66] FORD E, VOIT R, LISZT G, et al. Mammalian Sir2 homolog SIRT7 is an activator of RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 2006;20(9):1075-1080. [67] RAZA U, TANG X, LIU Z, et al. SIRT7: the seventh key to unlocking the mystery of aging. Physiol Rev. 2024;104(1):253-280. [68] TANG M, TANG H, TU B, et al. SIRT7: a sentinel of genome stability. Open Biol. 2021;11(6):210047. [69] KUMARI P, TARIGHI S, BRAUN T, et al. SIRT7 Acts as a Guardian of Cellular Integrity by Controlling Nucleolar and Extra-Nucleolar Functions. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(9):1361. [70] WU D, LI Y, ZHU KS, et al. Advances in Cellular Characterization of the Sirtuin Isoform, SIRT7. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:652. [71] MOHRIN M, SHIN J, LIU Y, et al. Stem cell aging. A mitochondrial UPR-mediated metabolic checkpoint regulates hematopoietic stem cell aging. Science. 2015;347(6228):1374-1377. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [3] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [4] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [5] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [6] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [7] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [8] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [9] | Ran Yaqin, Chen Xi, Xie Yanne, Yuan Jun. Mechanism and potential application strategies of pyroptosis in breast cancer treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7880-7888. |
| [10] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [11] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [12] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [13] | He Changliang, Wang Yan, Luo Ling, Liu Jian. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells thwart pyroptosis of lung tissue cells in septic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6642-6648. |
| [14] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [15] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||