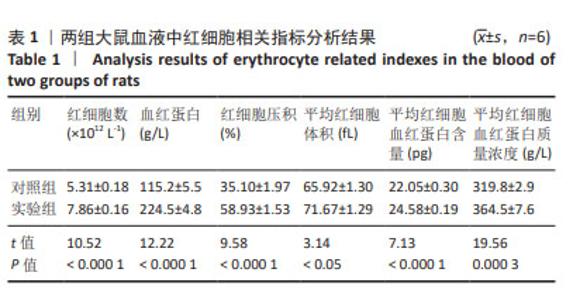
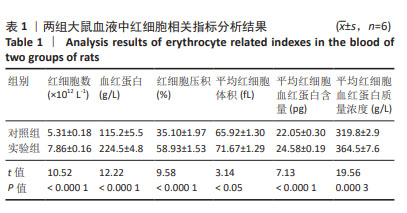
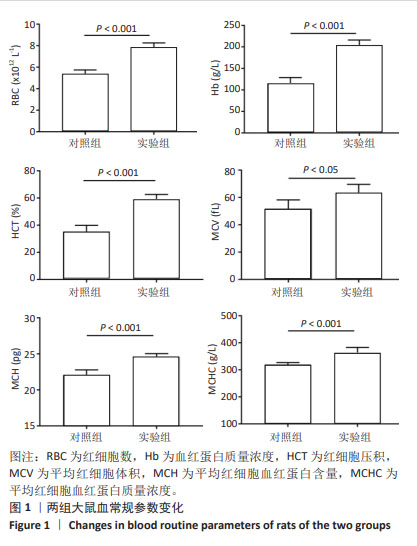
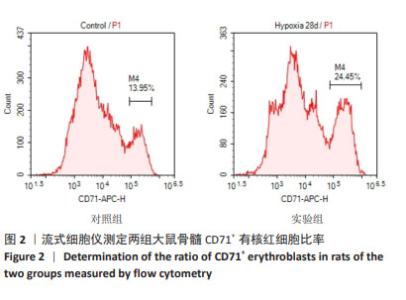
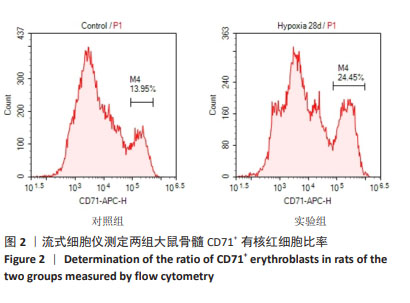
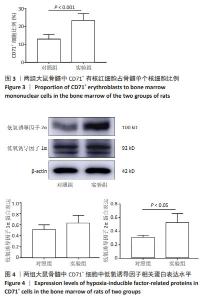
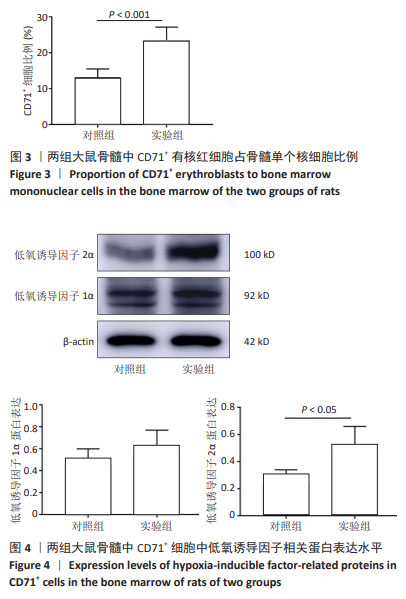
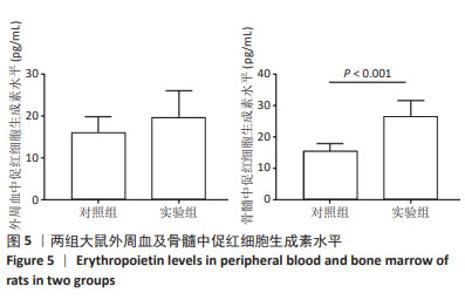
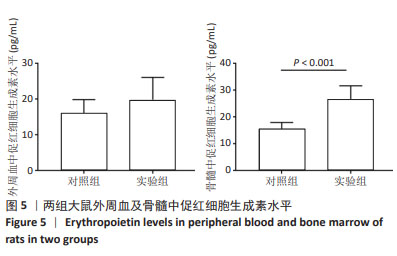
[1] 廖霞,罗凤鸣.高原人群肺动脉高压与血红蛋白浓度的相关研究进展[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2022,21(3):225-228.
[2] 罗秀勇,耿惠.慢性高原病的发病机制、诊断及治疗进展[J].临床医学进展,2022,12(4):3005-3009.
[3] 高志奇,谢慎威,高文祥.10年前后移居高原人群慢性高原病比较分析[J].军事医学,2022,46(2):90-94.
[4] 郭勇,王生艳,易静静.红景天苷对高原红细胞增多症模型大鼠骨髓CD71+有核红细胞凋亡的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2023, 49(5):1174-1181.
[5] HAN DG, KWAK J, CHOI E, et al. Physicochemical characterization and phase II metabolic profiling of echinochrome A, a bioactive constituent from sea urchin, and its physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in rats and humans. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;162:114589.
[6] LYU Q, BAI Y, CHENG J, et al. Intermittent short-duration reoxygenation protects against simulated high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. FASEB J. 2021;35(2):e21212.
[7] LIU H, TANG F, SU J, et al. EPAS1 regulates proliferation of erythroblasts in chronic mountain sickness. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020;84:102446.
[8] ZHU H, ZHONG L, LI J, et al. Differential Expression of Metabolism-Related Genes in Plateau Pika (Ochotona curzoniae) at Different Altitudes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front Genet. 2022;12: 784811.
[9] FAGO A. New insights into survival strategies to oxygen deprivation in anoxia-tolerant vertebrates. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022;235(3):e13841.
[10] LI F, QIAO Z, DUAN Q, et al. Adaptation of mammals to hypoxia. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021;4(4):311-318.
[11] LI M, PAN D, SUN H, et al. The hypoxia adaptation of small mammals to plateau and underground burrow conditions. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021;4(4):319-328.
[12] GAO CH, LI JM, XU B, et al. Responses of blood parameters and hemoglobin subtypes in plateau zokors and plateau pikas to different altitude habitats. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2023;75(1):69-81.
[13] SCHIPPEL N, SHARMA S. Dynamics of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell differentiation to the erythroid lineage. Exp Hematol. 2023;123:1-17.
[14] RIABOV V, MOSSNER M, STÖHR A, et al. High erythroferrone expression in CD71+ erythroid progenitors predicts superior survival in myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 2021;192(5):879-891.
[15] 冯婷婷,冀林华,刘芳,等.慢性高原病患者骨髓 CD71+、CD235a+有核红细胞增殖及凋亡变化[J].山东医药,2016,56(37):56-58.
[16] LEE P, CHANDEL NS, SIMON MC. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia through hypoxia inducible factors and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(5):268-283.
[17] SEMENZA GL. Heritable disorders of oxygen sensing. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185(11):3334-3339.
[18] BAI J, LI L, LI Y, et al. Genetic and immune changes in Tibetan high-altitude populations contribute to biological adaptation to hypoxia. Environ Health Prev Med. 2022;27:39.
[19] SEMENZA GL. Regulation of Erythropoiesis by the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Pathway: Effects of Genetic and Pharmacological Perturbations. Annu Rev Med. 2023;74:307-319.
[20] APANOVICH NV, APANOVICH PV, MANSORUNOV DJ, et al. Panel of Candidate Genes to Predict the Survival of Patients with Clear Cell Renal Cancer on the Basis of Gene Expression Regulated by HIF1α/HIF2α. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022;172(6):738-742.
[21] KARAGHIANNIS V, MARIC D, GARREC C, et al. Comprehensive in silico and functional studies for classification of EPAS1/HIF2A genetic variants identified in patients with erythrocytosis. Haematologica. 2023;108(6):1652-1666.
[22] JAŚKIEWICZ M, MOSZYŃSKA A, KRÓLICZEWSKI J, et al. The transition from HIF-1 to HIF-2 during prolonged hypoxia results from reactivation of PHDs and HIF1A mRNA instability. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27(1):109.
[23] HAHNE M, SCHUMANN P, MURSELL M, et al. Unraveling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α in the adaption process of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) to hypoxia: Redundant HIF-dependent regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Microvasc Res. 2018;116:34-44.
[24] SEROCKI M, BARTOSZEWSKA S, JANASZAK-JASIECKA A, et al. miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: a novel therapeutic target. Angiogenesis. 2018;21(2):183-202.
[25] YANG M, ZHU M, SONG K, et al. VHL gene methylation contributes to excessive erythrocytosis in chronic mountain sickness rat model by upregulating the HIF-2α/EPO pathway. Life Sci. 2021;266:118873.
[26] WATTS D, GAETE D, RODRIGUEZ D, et al. Hypoxia Pathway Proteins are Master Regulators of Erythropoiesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(21):8131.
[27] TOMC J, DEBELJAK N. Molecular Insights into the Oxygen-Sensing Pathway and Erythropoietin Expression Regulation in Erythropoiesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):7074.
[28] YASUOKA Y, IZUMI Y, FUKUYAMA T, et al. Effects of Roxadustat on Erythropoietin Production in the Rat Body. Molecules. 2022;27(3):1119.
[29] PORTOLÉS J, MARTÍN L, BROSETA JJ, et al. Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:642296.
[30] 易元月,刘宝,官立彬,等.模拟高原不同时间缺氧暴露对大鼠红细胞结构与功能的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(1):130-135.
[31] VILLAFUERTE FC, MACARLUPÚ JL, ANZA-RAMÍREZ C, et al. Decreased plasma soluble erythropoietin receptor in high-altitude excessive erythrocytosis and Chronic Mountain Sickness. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014;117(11):1356-1362. |