Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4552-4559.doi: 10.12307/2025.813
Previous Articles Next Articles
Short-term effect of manipulation therapy for lumbar disc herniation quantitatively evaluated by three-dimensional scoliosis angle
Gu Jiangpeng1, 2, Chen Xujing2, Liu Yikang3, Guo Wei1, 2, Liu Xiaomin4, Wang Fei1, 2, Feng Wei1
- 1Department of Orthopedics of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Air Force Special Medical Center, Beijing 100142, China; 2Fifth Clinical Medical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; 3Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China; 4School of Electronic Information and Control Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100024, China
-
Received:2024-04-24Accepted:2024-07-05Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-06 -
Contact:Wang Fei, MD, Master’s supervisor, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Air Force Special Medical Center, Beijing 100142, China; Fifth Clinical Medical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China Feng Wei, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Air Force Special Medical Center, Beijing 100142, China -
About author:Gu Jiangpeng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Air Force Special Medical Center, Beijing 100142, China; Fifth Clinical Medical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:Project of Health Bureau of Logistics Support Department of Central Military Commission, No. 2021ZY005 (to FW); Project of Air Force Military Medical University, No. 2019ZTA03 (to FW); Science and Technology Boost Project of Air Force Medical Center, No. 2022ZTYB32 (to WF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Jiangpeng, Chen Xujing, Liu Yikang, Guo Wei, Liu Xiaomin, Wang Fei, Feng Wei. Short-term effect of manipulation therapy for lumbar disc herniation quantitatively evaluated by three-dimensional scoliosis angle[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4552-4559.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
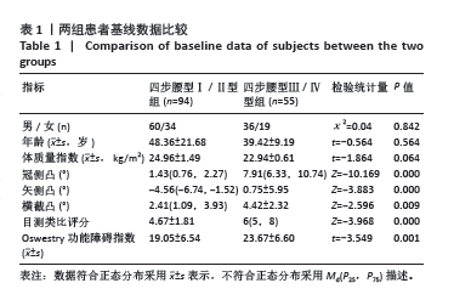
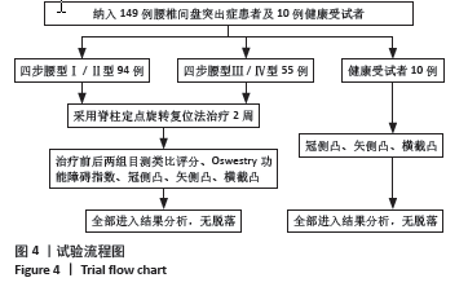
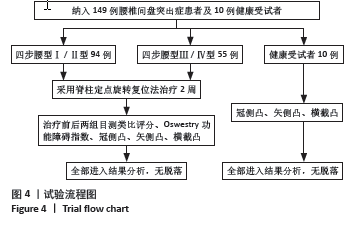
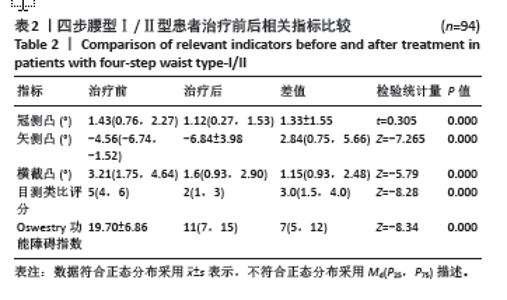
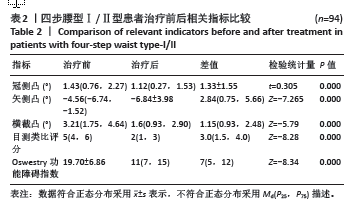
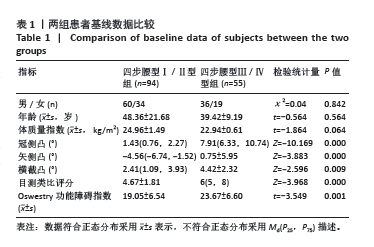
2.3 四步腰型Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者基线数据比较 共纳入149例腰椎间盘突出症患者,其中四步腰型Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者94例(男60,女34),Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者55例(男36,女性19),卡方检验两组男女构成比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组患者年龄差异也无显著性意义 (P > 0.05)。临床测量中发现冠侧凸和横截凸治疗前后角度的方向一致,此时正负号代表的方向已无意义,故选用角度的绝对值进行计算分析。但治疗前后矢侧凸有方向变化,故用正负号代表角度的变化。最终结果显示,Ⅰ/Ⅱ型和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者入院冠侧凸、矢侧凸、横截凸、目测类比评分和Oswestry功能障碍指数相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。见表1。"
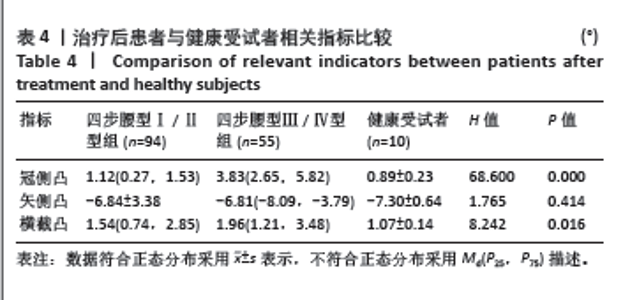
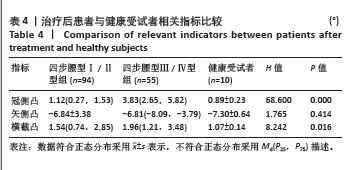
2.5 四步腰型Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者、Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后与健康受试者比较 如表4所示,Ⅰ/Ⅱ型、Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后和健康受试者冠侧凸有统计学差异,两两比较后发现Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者治疗后冠侧凸和健康受试者差异无显著性意义(P=0.431),Ⅰ/Ⅱ型治疗后冠侧凸和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),健康受试者冠侧凸和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001)。Ⅰ/Ⅱ型、Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后和健康受试者矢侧凸差异无显著性意义。Ⅰ/Ⅱ型、Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后和健康受试者横截凸相比差异有显著性意义,两两比较后发现Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者治疗后横截凸和健康受试者差异无显著性意义(P=0.086),Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者治疗后横截凸和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型差异无显著性意义(P=0.470),Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后横截凸和健康受试者相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.015)。将Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后数据根据腰型冠侧凸截断值分型,结果显示55例Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗后有17例腰型分型还为Ⅲ/Ⅳ型,其余腰型均获得改善。"
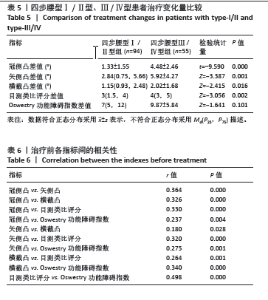
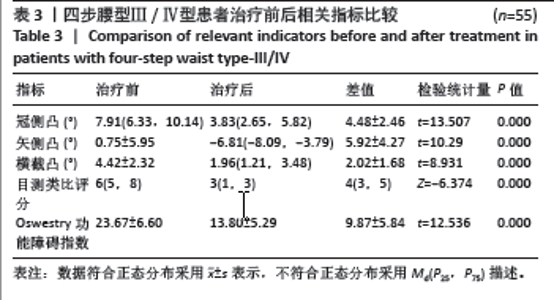
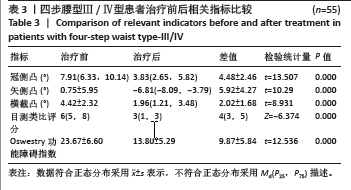
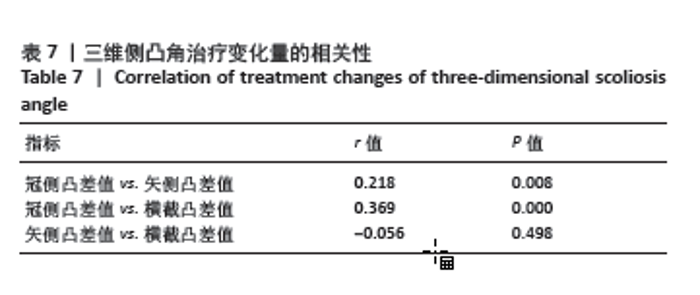
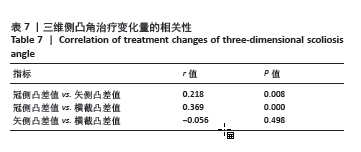
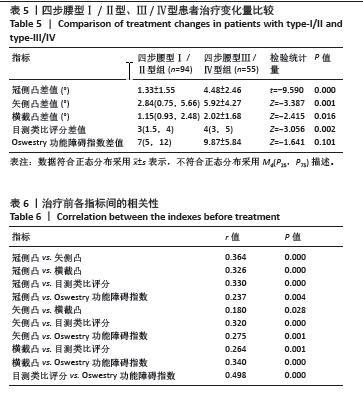
2.6 四步腰型Ⅰ/Ⅱ型、Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗变化量比较 如表5所示,将Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗前后各指标差值进行比较,Ⅰ/Ⅱ型和Ⅲ/Ⅳ型患者治疗前后冠侧凸差值、矢侧凸差值、横截凸差值、目测类比评分差值差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),Oswestry功能障碍指数差值之间差异无显著性意义 2.7 各指标间相关性 将两组患者治疗前各指标数据汇总进行相关性分析,如表6所示,冠侧凸与矢侧凸、横截凸、目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数呈正相关(r=0.364,0.326,0.330,0.237,P < 0.05);矢侧凸与横截凸、目测类比评分和Oswestry功能障碍指数呈正相关性(r=0.180,0.320,0.275,P < 0.05);横截凸与目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数呈正相关(r=0.264,0.340,P < 0.05)。"
| [1] 冯天有.中西医结合治疗软组织损伤[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社,2002. [2] 冯天有.中西医结合治疗软组织损伤的临床研究[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社,2002. [3] NAVARRO IJRL, ROSA BND, CANDOTTI CT. Anatomical reference marks, evaluation parameters and reproducibility of surface topography for evaluating the adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Gait Posture. 2019;69:112-120. [4] HANNINK E, DAWES H, SHANNON TML, et al. Validity of sagittal thoracolumbar curvature measurement using a non-radiographic surface topography method. Spine Deform. 2022;10(6):1299-1306. [5] NAVARRO IJRL, GODINHO RAT, CANDOTTI CT. Validating Surface Topography for the Measurement of the Thoracic Kyphosis Angle in Patients With Scoliosis: A Prospective Study of Accuracy. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2021;44(6):497-503. [6] BOLZINGER M, BERNARDINI I, THEVENIN LEMOINE C, et al. Monitoring adolescent idiopathic scoliosis by measuring ribs prominence using surface topography device. Spine Deformity. 2021;9(5):1349-1354. [7] 胡希鉴, 赵斌, 柴火, 等. 体表形态度量在脊柱弯曲异常中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1462-1468. [8] 龚成,谢瑛,郭伟,等.脊柱定点旋转复位手法治疗对613例腰椎间盘突出症患者腰椎活动度及活动度对称性的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(1):599-601. [9] 郭伟,赵颀,龚成,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者手法治疗前后腰椎关节活动度的力学评估研究[J].空军航空医学,2020,36(3):231-233. [10] 冯伟, 冯天有, 许奎, 等. 新医正骨疗法治疗Ⅲ、Ⅳ型腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 中医正骨,2015,27(5):62-64. [11] 冯子鹤, 冯伟, 王飞, 等. 单(多)个椎体位移致足下垂型腰椎间盘突出的临床研究[J]. 空军航空医学,2023,40(1):44-48. [12] 范宇, 张军, 郭伟, 等. 脊柱手法纠正“骨错缝”治疗腰椎间盘突出症的随机对照临床研究[J]. 北京中医药,2015,34(8):603-607. [13] 许尘鏖. 腰椎间盘突出症非手术治疗与MRI影像表现的相关性研究[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2017,26(10):1091-1093. [14] 冯宇, 毕永民, 杨文东. 应用320排螺旋CT三维重建腰椎棘突顶线的临床研究[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(4):461-463. [15] ZHANG Y, LI W, XU L, et al. Sciatic Scoliosis Evolution after Lumbar Discectomy: A Comparison Between Adolescents and Young Adults. Pain Physician. 2019;22(5):E457-E465. [16] KIM R, KIM RH, KIM CH, et al. The Incidence and Risk Factors for Lumbar or Sciatic Scoliosis in Lumbar Disc Herniation and the Outcomes after Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6): 555-564. [17] 张兴祥, 廖运生, 张成明. 针刀、拨松针配合整脊手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症伴脊柱侧弯60例临床疗效观察[J]. 按摩与康复医学, 2020,11(5):8-11. [18] 陈伟凯, 戴寿旺, 葛成孟. 经皮内镜下椎板间入路治疗合并脊柱侧弯的青少年腰椎间盘突出症的早期疗效观察[J]. 浙江医学,2018, 40(9):987-989. [19] 吴巍, 杨川, 谢波, 等. 经皮内镜椎间孔入路治疗青少年腰椎间盘突出症合并脊柱侧弯28例[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2024,24(3):208-212. [20] 李丽, 于少泓, 周霞, 等. 中医康复临床实践指南·儿童青少年特发性脊柱侧弯[J]. 康复学报,2023,33(4):295-302. [21] 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会基础研究与转化学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊治与康复管理指南[J]. 中华外科杂志,2022,60(5): 401-408. [22] 中华医学会骨科学分会脊柱外科学组, 中华医学会骨科学分会骨科康复学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊疗指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(8):477-487. [23] 马超, 王飞, 刘晓民, 等. 应用体表地形图量化腰椎间盘突出症腰型客观化指标:下腰曲线弹性固定转折点的三维成角[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):924-928. [24] MATSUI H, OHMORI K, KANAMORI M, et al. Significance of sciatic scoliotic list in operated patients with lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 1998;23(3):338-342. [25] 董津含, 于忠行. 针刺阿是穴治疗腰椎间盘突出症发生侧弯腰痛患者的临床疗效[J]. 中国药物经济学,2020,15(11):67-70. [26] TU Z, WANG B, LI L, et al. Early Experience of Full-Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy for Adolescent Lumbar Disc Herniation with Sciatic Scoliosis. Pain Physician. 2018;21(1):E63-E70. [27] YANG J, LUAN H, REN J, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for single and double segment lumbar disc herniation with sciatic scoliosis in adults: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2024;24(1): 41. [28] YANG J, ZHANG K, FAN H, et al. Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for scoliosis screening using back images. Commun Biol. 2019;2:390. [29] MADIRAJU A, MULCAHEY PJ, KNOTT PT, et al. Assessing clinical trunk change with surface topography: anterior scoliosis correction as a model to evaluate curve progression. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(12): 3533-3539. [30] MINOTTI M, NEGRINI S, CINA A, et al. Deep learning prediction of curve severity from rasterstereographic back images in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-08052-1. [31] ZHAO Y, QI L, DING C, et al. Characteristics of Sciatic Scoliotic List in Lumbar Disc Herniation. Global Spine J. 2024;14(3):894-901. [32] WU W, CHEN Y, YU L, et al. Coronal and sagittal spinal alignment in lumbar disc herniation with scoliosis and trunk shift. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1): 264. [33] 冯宇. 冯天有教授脊柱定点旋转复位法治疗腰椎间盘突出症学术思想研究[D]. 北京: 中国人民解放军军医进修学院,2012. [34] 冯伟. 新医正骨疗法治疗难治型旋盆翘臀型腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 空军航空医学,2020,36(4):307-309. [35] 陈龙, 刘伟东, 张维顺, 等. 微创与开放TLIF治疗腰椎间盘突出伴功能性侧弯[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(18):1708-1711. [36] 吕立江, 李景虎, 杨超, 等. 杠杆定位手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效及对Cobb角影响[J]. 中国骨伤,2021,34(1):86-90. [37] ENDO K, SUZUKI H, TANAKA H, et al. Sagittal spinal alignment in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(3):435-438. |
| [1] | Zhang Chunlin, Hou Zhaohua, Yan Xu, Jiang Yan, Fu Su, Ning Yongming, Li Dongzhe, Dong Chao, Liu Xiaokang, Wang Yongkui, Cao Zhengming, Yang Tengyue. Decompression mechanism of symmetrically adduction of lumbar decompression induced resorption of herniated nucleus pulpous [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1810-1819. |
| [2] | Lu Qi, Sun Maji, Wang Xuezhi, Song Ting, Ma Yiming, Yuan Feng, Chen Hongliang. Two visual arthroplasty techniques for L5-S1 disc herniation: a half-year follow-up evaluation of clinical outcomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1841-1847. |
| [3] | Feng Zhimeng, Sun Ning, Sun Zhaozhong, Li Yuefei, Liu Changzhen, Li Sa. Three-dimensional image reconstruction can safely assist one-hole split endoscope in treatment of #br# L5/S1 far lateral lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1876-1882. |
| [4] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [5] | Yang Yu, Li Yinghao, Duo Zhuangzhi, Zhou Dingrong. Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101. |
| [6] | Liu Ning, Sun Yingjin, Huang Long, Feng Shuo, Chen Xiangyang. Optimal rotational alignment of the tibial component during Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7158-7164. |
| [7] | Jiang Zehua, Du Wenjun, Ren Zhishuai, Cui Haojun, Zhu Rusen. Percutaneous vertebroplasty via Kambin's triangle for treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures: evaluation of safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7181-7188. |
| [8] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [9] | Li Tangbo, Zhang Nan, Hao Guobing, Liu Kun, Qiao Lin, Zhu Zexing, Song Diyu. Bone cement injection during percutaneous curved vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the upper 1/3 of the vertebral body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5977-5984. |
| [10] |
Wang Qianliang, Zhang Qianzhongyi, Peng Yujian, Yan Jun.
Effects of unilateral biportal endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion on paraspinal muscles
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5862-5868.
|
| [11] | Bai Liang, Fu Su, Yan Xu, Zhang Chunlin, Li Ying . Measurement of intervertebral disc height and analysis of strength after induced resorption of herniated nucleus pulpous [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5785-5794. |
| [12] | Zhu Tianrui, Shi Jipeng, Sun Jiahe, Wang Luyi, Zhang Chen, Xu Hongqi, Quan Helong. Effectiveness of different exercise regimens to reduce fall risks in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5662-5672. |
| [13] | Zhang Ruofan, Guan Huanhuan, He Zhuoqun, Zhang Yunfeng, Jin Feng, Wang Zhiqiang, Wang Jianzhong, Li Xiaohe, Zhu Yong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Kai. Effect of minimally invasive interbody fusion device height on lumbar biomechanics in patients with adolescent lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4421-4429. |
| [14] | Lin Qing, Liu Huan, Cheng Yongzhong, Jiang Junjie, Li Yongyao, Li Guangyao. Meta-analysis of external stent fixation and internal plate fixation for treatment of comminuted distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4602-4611. |
| [15] | Wang Qianliang, Chen Jianpeng, Wang Yuanbin, Yan Jun. Mechanism of circ05188 targeting miR-199a-5p involved in nociceptive hypersensitivity in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4230-4238. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||