Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (2): 363-370.doi: 10.12307/2025.201
Previous Articles Next Articles
Compound 3k for osteoarthritis: mechanism of modulating oxidative stress pathway to improve chondrocyte glycolysis
Guo Surong1, Cao Shisheng2, Mu Xingtong2, Yang Qing2, Zhang Juan2
- 1School of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300041, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University Stomatological Hospital, Tianjin 300041, China
-
Received:2023-12-19Accepted:2024-01-27Online:2025-01-18Published:2024-05-25 -
Contact:Zhang Juan, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University Stomatological Hospital, Tianjin 300041, China -
About author:Guo Surong, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300041, China -
Supported by:Tianjin Health Science and Technology Health Project, No. TJWJ2022MS015 (to ZJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Surong, Cao Shisheng, Mu Xingtong, Yang Qing, Zhang Juan. Compound 3k for osteoarthritis: mechanism of modulating oxidative stress pathway to improve chondrocyte glycolysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 363-370.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
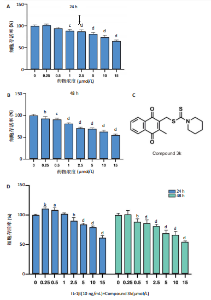
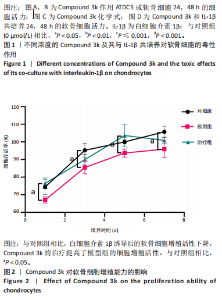
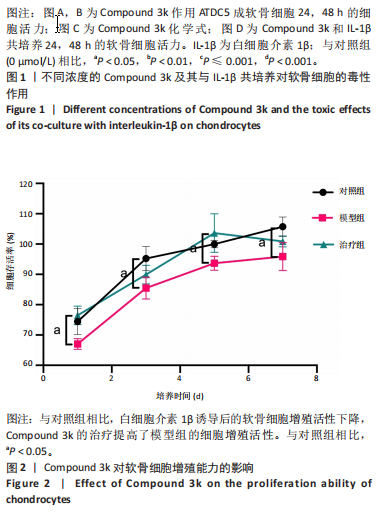
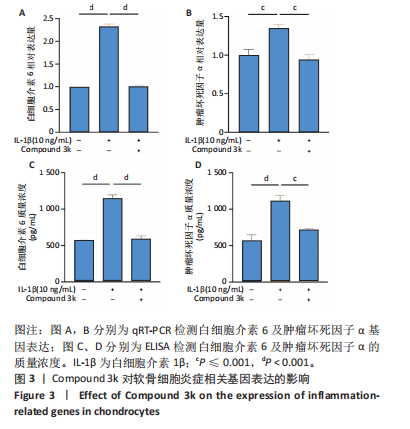
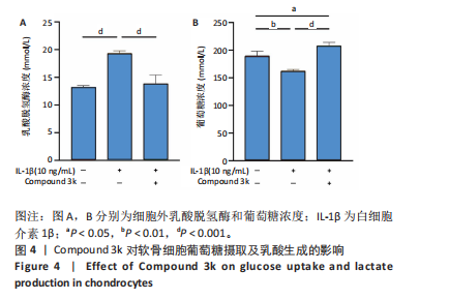
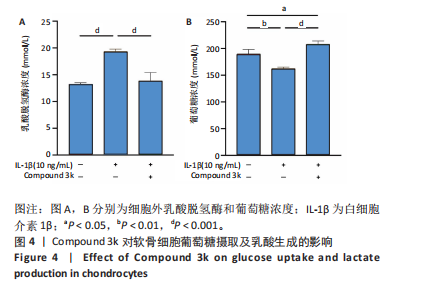
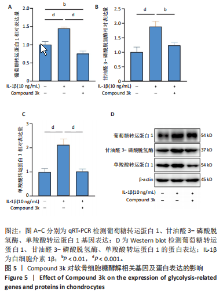
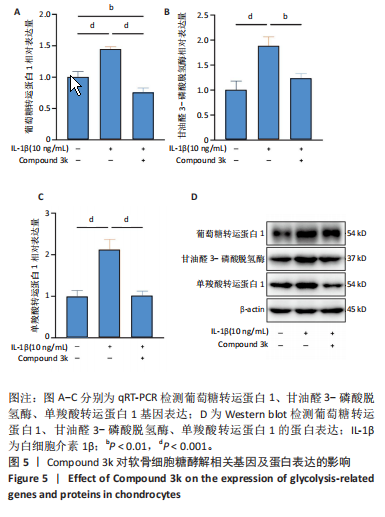
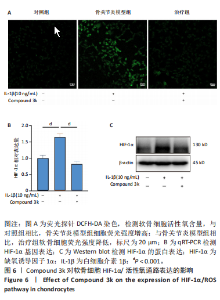
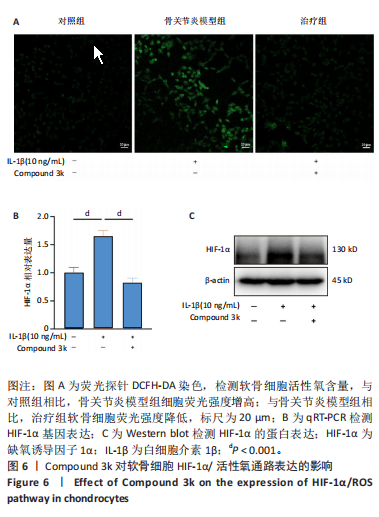
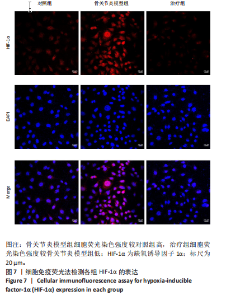
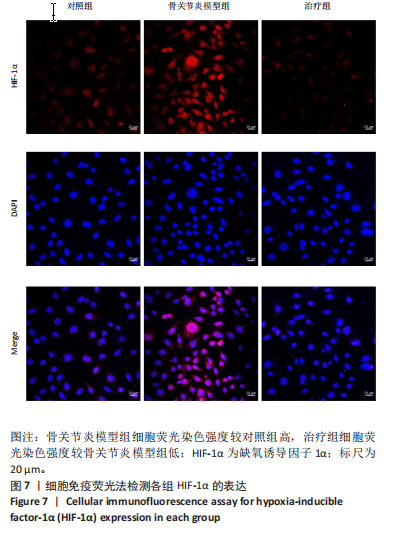
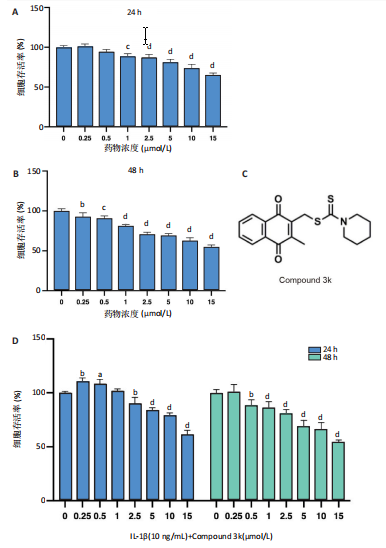
2.1 Compound 3k对软骨细胞的毒性作用 通过CCK-8实验测定Compound 3k对软骨细胞的毒性作用,用不同浓度的Compound 3k(0,0.25,0.5,1,2.5,5,10,15 μmol/L) 处理软骨细胞24 h和48 h。结果显示,Compound 3k的浓度≤1 μmol/L对软骨细胞没有明显的毒性作用,见图1A,B。Compound 3k的化学式,见图1C。将Compound 3k与白细胞介素1β共同孵育24 h和48 h,结果显示,当Compound 3k浓度为0.25 μmol/L时,软骨细胞活力反而上升,见图1D。因此,选择0.25 μmol/L的Compound 3k进行后续实验。 2.2 Compound 3k对软骨细胞增殖的影响 使用CCK-8法评估各组软骨细胞1,3,5,7 d的细胞增殖活力,结果显示,白细胞介素1β诱导的骨关节炎模型组软骨细胞增殖活力下降,而Compound 3k的治疗可提高骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖活力,见图2。 2.3 Compound 3k对软骨细胞炎症相关靶标的影响 qRT-PCR结果显示,与对照组相比,白细胞介素1β诱导后的软骨细胞中白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达升高(P < 0.05),而Compound 3k治疗后,显著降低了骨关节炎软骨细胞中白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达水平(P < 0.05),见图3A,B。ELISA实验结果与qRT-PCR实验结果趋势相同,见图3C,D。 2.4 糖酵解抑制剂Compound 3k显著降低骨关节炎软骨细胞糖酵解水平 白细胞介素1β诱导后的软骨细胞,细胞外乳酸脱氢酶含量均显著升高,而细胞外葡萄糖浓度则显著降低,这表明骨关节炎软骨细胞糖酵解水平上调,见图4A,B。同时,qRT-PCR及Western blot结果见图5A-D,模型组糖酵解关键基因葡萄糖转运蛋白1、甘油醛3-磷酸脱氢酶、单羧酸转运蛋白1的表达均上调。而与骨关节炎模型组相比,Compound 3k的治疗使骨关节炎软骨细胞过度活跃的糖酵解水平降低,具体表现为,细胞外乳酸脱氢酶含量降低,软骨细胞摄取葡萄糖减少,糖酵解关键基因葡萄糖转运蛋白1、甘油醛3-磷酸脱氢酶及单羧酸转运蛋白1的表达均稳定下调。 2.5 Compound 3k抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的缺氧诱导因子1α表达及活性氧生成 qRT-PCR及Western blot结果见图6A-C,与对照组相比,白细胞介素1β诱导的骨关节炎模型组缺氧诱导因子1α的表达水平升高(P < 0.001),而Compound 3k治疗组,缺氧诱导因子1α的表达水平稳定下调(P < 0.001)。同样地,缺氧诱导因子1α的细胞免疫荧光实验结果见图7,Compound 3k的治疗显著降低了骨关节炎软骨细胞缺氧诱导因子1α的表达。接下来,又通过荧光探针DCFH-DA检测细胞活性氧水平,见图6A,与对照组相比,骨关节炎模型组活性氧水平显著升高,而Compound 3k治疗后,软骨细胞活性氧水平较骨关节炎模型组降低。"
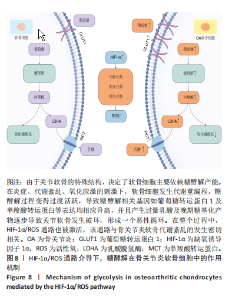
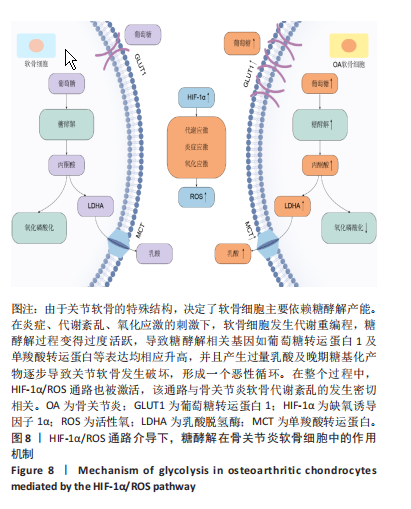
| [1] GOLDRING MB, GOLDRING SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(3):626-634. [2] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):3-6. [3] MOBASHERI A, RAYMAN MP, GUALILLO O, et al. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(5):302-311. [4] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195. [5] BARBOUR KE, HELMICK CG, BORING M, et al. Vital signs: prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation-United States, 2013-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66(9):246-253. [6] KRASNOKUTSKY S, SAMUELS J, ABRAMSON SB. Osteoarthritis in 2007. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65(3):222-228. [7] 魏洁雅,张德茂,谢静,等.软骨细胞葡萄糖代谢研究的新进展[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2021,52(6):923-928. [8] MARCONI A, HANCOCkK-RONEMUS A, GILLIS JA. Adult chondrogenesis and spontaneous cartilage repair in the skate, Leucoraja erinacea. Elife. 2020;9:e53414. [9] 刘耀升,刘蜀彬.软骨组织工程研究中细胞源-软骨细胞和成纤维细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(11):2123-2126. [10] TAN C, LI L, HAN J, et al. A new strategy for osteoarthritis therapy: Inhibition of glycolysis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1057229. [11] KONG P, CHEN R, ZOU FQ, et al. HIF-1α repairs degenerative chondrocyte glycolytic metabolism by the transcriptional regulation of Runx2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1206-1214. [12] 邵婉珍,张风娥,王森,等.糖代谢紊乱对大骨节病软骨细胞功能的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2018,49(2):221-225,270. [13] ARRA M, SWARNKAR G, KE K, et al. LDHA-mediated ROS generation in chondrocytes is a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3427. [14] SONG K, LI B, CHEN YY, et al. LRPPRC regulates metastasis and glycolysis by modulating autophagy and the ROS/HIF1-α pathway in retinoblastoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021;22:582-591. [15] LOHBERGER B, KALTENEGGER H, ECK N, et al. Shikonin derivatives inhibit inflammation processes and modulate MAPK signaling in human healthy and osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3396. [16] WANG A, FANG S, ZHONG L, et al. Shikonin, a promising therapeutic drug for osteoarthritis that acts via autophagy activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;106:108563. [17] NING X, QI H, LI R, et al. Discovery of novel naphthoquinone derivatives as inhibitors of the tumor cell specific M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;138:343-352. [18] 乔祺惠,周青.颞下颌关节骨关节病物理及药物治疗研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2018,11(9):557-563. [19] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. Is osteoarthritis a metabolic disease? Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(6):568-573. [20] Chen J, Gu YT, Xie JJ, et al. Gastrodin reduces IL-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and matrix catabolism in osteoarthritis chondrocytes and attenuates rat cartilage degeneration in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:642-651. [21] Sun FF, Hu PF, Xiong Y, et al. Tricetin protects rat chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4695381. [22] 戴金凤. 多不饱和脂肪酸影响胃癌细胞生长的机理[D].杭州:浙江大学,2013:87. [23] CHANDEL NS. Glycolysis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021;13(5): a040535. [24] JUDGE A, DODD MS. Metabolism. Essays Biochem. 2020;64(4):607-647. [25] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101249. [26] RASHEED Z, AKHTAR N, HAQQI TM. Advanced glycation end products induce the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 by receptor for advanced glycation end product-mediated activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50(5):838-851. [27] BUSTAMANTE MF, OLIVEIRA PG, GARCIA-CARBONELLl R, et al. Hexokinase 2 as a novel selective metabolic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(11):1636-1643. [28] YANG X, CHEN W, ZHAO X, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 modulates the glycolysis of chondrocyte and extracellular matrix in osteoarthritis. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37(3):271-277. [29] BEDARD PL, HYMAN DM, DAVIDS MS, et al. Small molecules, big impact: 20 years of targeted therapy in oncology. Lancet. 2020; 395(10229):1078-1088. [30] XU F, GUO M, HUANG W, et al. Annexin A5 regulates hepatic macrophage polarization via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates NASH. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101634. [31] PARK JH, KUNDU A, LEE SH, et al. Specific pyruvate kinase M2 inhibitor, compound 3K, induces autophagic cell death through disruption of the glycolysis pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(8): 1895-1908. [32] ZENG CY, WANG XF, HUA FZ. HIF-1α in Osteoarthritis: from pathogenesis to therapeutic implications. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:927126. [33] WANG P, XIONG X, ZHANG J, et al. Icariin increases chondrocyte vitality by promoting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression and anaerobic glycolysis. Knee. 2020;27(1):18-25. [34] PARK WH. Effects of antioxidants and MAPK inhibitors on cell death and reactive oxygen species levels in H2O2-treated human pulmonary fibroblasts. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(5):1633-1638. [35] TAPEINOS C, LARRANAGA A, SARASUA JR, et al. Functionalised collagen spheres reduce H2O2 mediated apoptosis by scavenging overexpressed ROS. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(7):2397-2405. [36] CHENG J, YANG HL, GU CJ, et al. Melatonin restricts the viability and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells by suppressing HIF-1α/ROS/VEGF. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):945-955. [37] WANG D, ZHAO W, LIU J, et al. Effects of HIF-1α on spermatogenesis of varicocele rats by regulating VEGF/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Reprod Sci. 2021;28(4):1161-1174. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [4] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [5] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [6] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [7] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [8] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [9] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [10] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [12] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [13] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [14] | Chen Chao, Hu Yaoquan, Lyu Zhengpin, He Qicong, Yangyang Zijiu, Luo Haoyan, Wu Guishuai, Zuo Qianlin, Wang Xuenan, Zhang Fan. tert-Butyl hydroperoxide can induce ferroptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6858-6865. |
| [15] | Nigeayi · Aihemaiti, Yilidanna · Dilixiati, An Wei, Maimaitituxun · Tuerdi. Expression of mitochondrial creatine kinase 2 in a rat model of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and its role in inflammation progression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6877-6884. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||