Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (15): 3101-3109.doi: 10.12307/2025.165
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of mechanical differences between different internal fixation modalities for proximal humerus fractures
Wang Lei1, Wang Qing2, Zhang Shenshen1
- 1Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China; 2Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-15Accepted:2024-04-03Online:2025-05-28Published:2024-11-02 -
Contact:Zhang Shenshen, Master, Chief physician, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Wang Lei, Master, Associate chief physician, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China Wang Qing, Master candidate, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China Wang Lei and Wang Qing contributed equally to this article.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Lei, Wang Qing, Zhang Shenshen. Finite element analysis of mechanical differences between different internal fixation modalities for proximal humerus fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3101-3109.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 内收条件下的主要观察指标 在100 N内收载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.32 MPa) > B组(116.61 MPa) > C组(103.92 MPa);内固定物应力分布:A组(223.72 MPa) > B组(218.37 MPa) > C组(206.42 MPa), 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移:A组(0.462 mm) > C组(0.395 mm) > B组(0.280 mm),内固定物的位移分布云图未见明显差异;3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,其最大位移均出现在内固定物的远端,见图4。各组模型骨折端的相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.599 mm) > C组(0.506 mm) > B组(0.315 mm),其中A组约是B组的1.90倍,差异显著,见表3。"

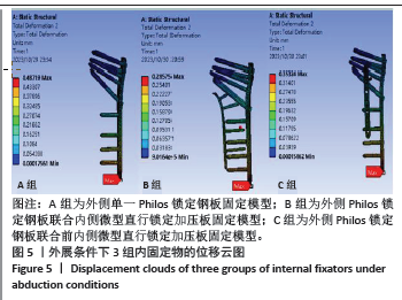
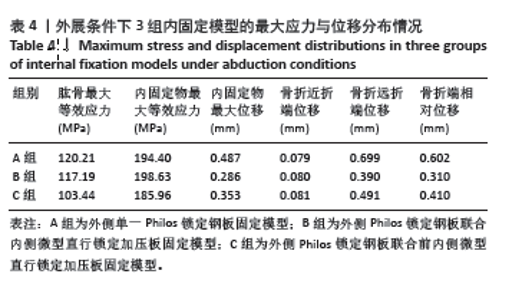
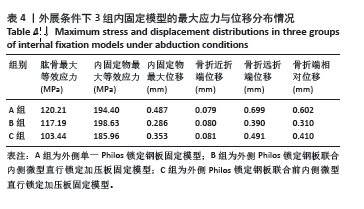
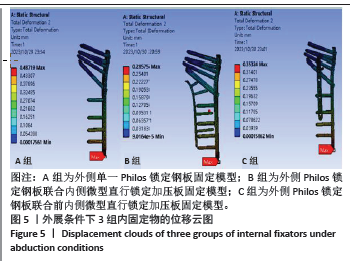
2.2 外展条件下的主要观察指标 在100 N外展载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.21 MPa) > B组(117.19 MPa) > C组(103.44 MPa);内固定物应力分布:B组(198.63 MPa) > A组(194.40 MPa) > C组(185.96 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.487 mm) > C组(0.353 mm) > B组(0.286 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,其最大位移均出现在内固定物的远端,见图5。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.602 mm) > C组(0.410 mm) > B组(0.310 mm);其中A组约是B组的1.94倍,差异显著,见表4。"
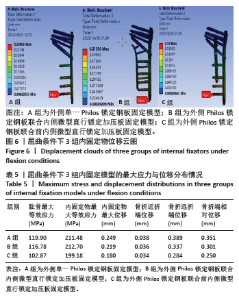
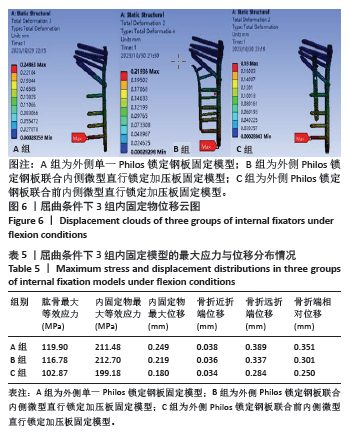
2.3 屈曲条件下的主要观察指标 在100 N屈曲载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(119.90 MPa) > B组(116.78 MPa) > C组(102.87 MPa);内固定物应力分布:B组(212.70 MPa) > A组(211.48 MPa) > C组(199.18 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.249 mm) > B组(0.219 mm) > C组(0.180 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,B组最大位移出现在内固定物的远端,而A、C组最大位移出现在最远端锁定螺钉的尖端,见图6。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.351 mm) > B组(0.301 mm) > C组(0.250 mm);其中A组(0.351 mm)约是C组(0.250 mm)的1.40倍,见表5。"
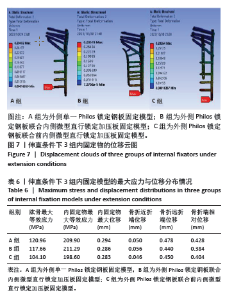
2.4 伸直条件下的主要观察指标 在100 N伸直载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.96 MPa)> B组(117.66 MPa) > C组(104.10 MPa);内固定物应力分布:B组(211.29 MPa) > A组(209.90 MPa) > C组(198.60 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.294 mm) > B组(0.286 mm) > C组(0.283 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,B、C两组的最大位移均出现在内固定物的远端,而A组最大位移出现在最远端锁定螺钉的尖端,见图7。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.428 mm) > C组(0.404 mm) > B组(0.384 mm);其中A组(0.428 mm)约是B组(0.384 mm)的1.11倍,见表6。"
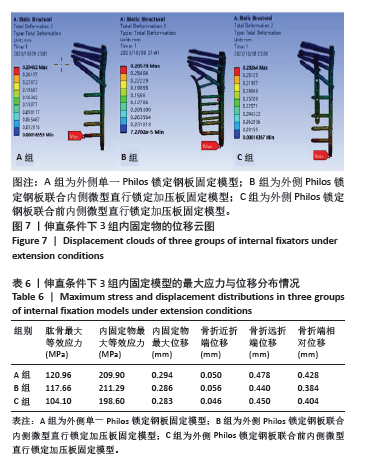

2.4 伸直条件下的主要观察指标 在100 N伸直载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.96 MPa)> B组(117.66 MPa) > C组(104.10 MPa);内固定物应力分布:B组(211.29 MPa) > A组(209.90 MPa) > C组(198.60 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.294 mm) > B组(0.286 mm) > C组(0.283 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,B、C两组的最大位移均出现在内固定物的远端,而A组最大位移出现在最远端锁定螺钉的尖端,见图7。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.428 mm) > C组(0.404 mm) > B组(0.384 mm);其中A组(0.428 mm)约是B组(0.384 mm)的1.11倍,见表6。"

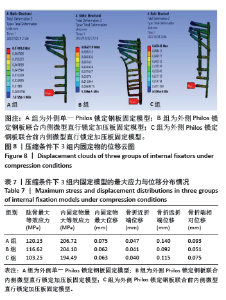
2.5 压缩条件下的主要观察指标 在200 N压缩载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.13 MPa) > B组(116.62 MPa) > C组(103.25 MPa);内固定物应力分布:A组(206.72 MPa) > B组(204.10 MPa) > C组(194.49 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.075 mm) > C组(0.063 mm)> B组(0.062 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,B组最大位移出现在内固定物的远端,而A、C组最大位移出现在最远端锁定螺钉的尖端,见图8。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.093 mm) > C组(0.075 mm) > B组(0.051 mm);其中A组(0.093 mm)约是B组(0.051 mm)的1.82倍,差异显著,见表7。"
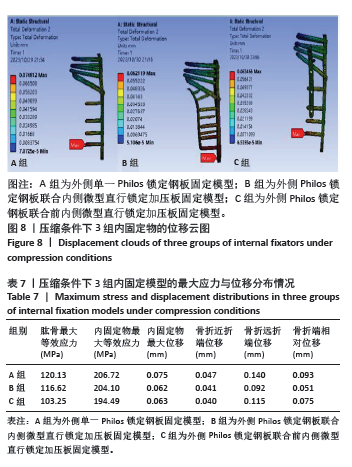

2.5 压缩条件下的主要观察指标 在200 N压缩载荷条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.13 MPa) > B组(116.62 MPa) > C组(103.25 MPa);内固定物应力分布:A组(206.72 MPa) > B组(204.10 MPa) > C组(194.49 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.075 mm) > C组(0.063 mm)> B组(0.062 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,B组最大位移出现在内固定物的远端,而A、C组最大位移出现在最远端锁定螺钉的尖端,见图8。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.093 mm) > C组(0.075 mm) > B组(0.051 mm);其中A组(0.093 mm)约是B组(0.051 mm)的1.82倍,差异显著,见表7。"


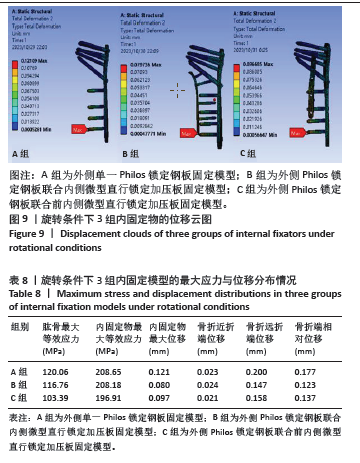
2.6 旋转条件下的主要观察指标 在7.5 Nm旋转扭矩条件下,3组固定方式的肱骨模型应力分布:A组(120.06 MPa) > B组(116.76 MPa) > C组(103.39 MPa);内固定物应力分布:A组(208.65 MPa) > B组(208.18 MPa) > C组(196.91 MPa); 3组内固定模型的内固定物应力均小于250 MPa,未超过450 MPa。观察3组内固定物位移分布云图未见明显差异,内固定物位移:A组(0.121 mm) > C组(0.097 mm) > B组(0.080 mm);3组内固定物的位移均呈现出一个清晰的趋势,即由近端向远端逐渐递增,其最大位移均出现在最远端锁定螺钉的尖端,见图9。肱骨模型相对位移通过计算及比较:A组(0.177 mm) > C组(0.137 mm) > B组 (0.123 mm);其中A组(0.177 mm)约是B组(0.123 mm)的1.44倍,见表8。"
| [1] 张玉富,蒋协远.肱骨近端骨折手术治疗的进展与思考[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(2):99-102. [2] ZHU Z, CHANG Z, ZHANG W, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of novel intra- and extramedullary assembly fixation for proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1182422. [3] MICHEL P, RASCHKE M, KATTHAGEN J, et al. Double Plating for Complex Proximal Humeral Fractures: Clinical and Radiological Outcomes. J Clin Med. 2023;12(2):696. [4] BAKER HP, GUTBROD J, CAHILL M, et al. Optimal Treatment of Proximal Humeral Fractures in the Elderly: Risks and Management Challenges.Orthop Res Rev. 2023;15:129-137. [5] WANG Y, LI J, MEN Y, et al. Intrinsic Cortical Property Analysis of the Medial Column of Proximal Humerus. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(3): 793-800. [6] DANG KH, ORNELL SS, REYES G, et al. A new risk to the axillary nerve during percutaneous proximal humeral plate fixation using the Synthes PHILOS aiming system. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(9): 1795-1800. [7] BAKER HP, GUTBROD J, STRELZOW JA, et al. Management of Proximal Humerus Fractures in Adults—A Scoping Review. J Clin Med. 2022; 11(20):6140. [8] DOSHI C. Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures using PHILOS Plate. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(7):10-13. [9] MCLEAN AS, PRICE N, GRAVES S, et al. Nationwide trends in management of proximal humeral fractures: an analysis of 77,966 cases from 2008 to 2017. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(11):2072-2078. [10] 李波,张世民,胡孙君,等.肱骨头下皮质外距螺钉重建内侧柱稳定性的三维有限元分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(8): 995-1002. [11] 常祖豪,张伟,唐佩福,等.内侧支撑重建增强固定技术在肱骨近端骨折治疗中的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3): 375-380. [12] JHAMNANI R, DHANDA MS, SURANA A. Study of Functional Outcome and Postoperative Complications Among Proximal Humerus Fracture Patients Treated With Proximal Humerus Internal Locking System (PHILOS) Plating. Cureus. 2023;15(7):42411. [13] JUNG WB, MOON ES, KIM SK, et al. Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:102. [14] RAITHATHA H, PATIL VS, PAI M, et al. Clinical and Radiological Outcome of Dual Plating for Proximal Humerus Fractures. Cureus. 2023;15(1): e33570. [15] 姚灿,杨光永,娄菊红,等.双钢板与单钢板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折的临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(6):24-28. [16] 瞿杭波,杨自荣,闫应朝,等.双钢板固定治疗老年复杂肱骨近端骨折[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(2):103-109. [17] YE Y, YOU W, ZHU W, et al. The Applications of Finite Element Analysis in Proximal Humeral Fractures. Comput Math Methods Med. 2017; 2017:1-9. [18] SANDERS BS, BULLINGTON AB, MCGILLIVARY GR, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of locked plating in proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(2):229-234. [19] 刘炎,葛鸿庆,陈文治,等.肱骨近端骨折中不同腓骨支撑方式重建内侧柱的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18): 2804-2808. [20] LI D, LV W, CHEN W, et al. Application of a lateral intertubercular sulcus plate in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures: a finite element analysis. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):98. [21] HE Y, HE J, WANG F, et al. Application of Additional Medial Plate in Treatment of Proximal Humeral Fractures With Unstable Medial Column. Medicine. 2015;94(41):e1775. [22] VAJGEL A, CAMARGO IB, WILLMERSDORF RB, et al. Comparative Finite Element Analysis of the Biomechanical Stability of 2.0 Fixation Plates in Atrophic Mandibular Fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(2): 335-342. [23] LAUX CJ, GRUBHOFER F, WERNER CML, et al. Current concepts in locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):137. [24] ADIYEKE L. Comparison of effective factors in loss of reduction after locking plate-screw treatment in humerus proximal fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022;28(7):1008-1015. [25] SEETHARAM CT, JAYARAM M, BACHHAPPA SH, et al. Study of surgical management of fracture of proximal humerus by PHILOS plate and screws. Int J Res Orthop. 2020;6(3):462-466. [26] LEE J, KIM J, KIM K, et al. Effect of Calcar Screw in Locking Compression Plate System for Osteoporotic Proximal Humerus Fracture: A Finite Element Analysis Study. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:1268774. [27] ZENG LQ, ZENG LL, JIANG YW, et al. Influence of Medial Support Screws on the Maintenance of Fracture Reduction after Locked Plating of Proximal Humerus Fractures. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(15): 1827-1833. [28] XU J, ZHAN S, LING M, et al. How can medial support for proximal humeral fractures be achieved when positioning of regular calcar screws is challenging? Slotting and off-axis fixation strategies. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31(4):782-791. [29] HE Y, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel dualplate fixation method for proximal humeral fractures without medial support. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):72. [30] YANG P. Biomechanical effect of medial cortical support and medial screw support on the locking plate fixation of the proximal humeral fractures with a medial gap: a finite element analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(2):203-209. [31] DI TULLIO P, GIORDANO V, SOUTO E, et al. Biomechanical behavior of three types of fixation in the two-part proximal humerus fracture without medial cortical support. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0220523. [32] 贾进,陆晓涛,蒙顺,等.双钢板与锁定钢板在复杂肱骨近端骨折治疗中的疗效比较[J].昆明医科大学学报,2022,43(2):82-88. [33] XIANG H, WANG Y, YANG Y, et al. Anatomical study for the treatment of proximal humeral fracture through the medial approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):17-35. [34] WANG F, WANG Y, DONG J, et al. A novel surgical approach and technique and short-term clinical efficacy for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures with the combined use of medial anatomical locking plate fixation and minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):16-29. [35] WARNHOFF M, JENSEN G, DEY HAZRA RO, et al. Double plating - surgical technique and good clinical results in complex and highly unstable proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2021;52(8):2285-2291. [36] 欧阳敏.改良肱骨近端锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折的三维有限元分析[D].南昌: 南昌大学,2023. [37] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317. [38] LEWIS GS, MISCHLER D, WEE H, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Fracture Fixation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(4):403-416. |
| [1] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [3] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [4] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [5] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [6] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [7] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [8] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [9] | Song Xubin, Wu Dou, Zhao Enzhe, Zhang Xingyu, Zhang Xiaolun, Wang Chuheng. Finite element analysis of a new femoral neck spiral blade system to treat femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7041-7047. |
| [10] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [11] | Xu Xin, Wurikaixi·Aiyiti, Lyu Gang, Maimaiaili·Yushan, Ma Zhiqiang, Ma Chao. Finite element analysis of four different internal fixation methods for complex acetabular double-column fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7063-7071. |
| [12] | Ma Shuangshuang, Gao Dedong, Shan Zhongshu, Xu Wenxu, Lu Zhirui. Finite element analysis and biomechanical validation of revision pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7087-7095. |
| [13] | Zhang Ziyi, Qin Qi, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Liu Yuzhe, Yusufu·Reheman, Ran Jian. Biomechanical analysis of three internal fixation schemes for Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7102-7108. |
| [14] | Ma Tao, Li Xing, Wei Yajun, Deng Juncai. Effects of lateral screw-rod placement positions on segmental range of motion, internal fixation and cage stress during oblique lumber interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7165-7172. |
| [15] | Xu Tianyu, Chen Modi, Xie Mingru, Ye Xinghua, Pan Zhaohui. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effect of medial or lateral malleolar ligament defects on its neighboring core tendons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7223-7230. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||