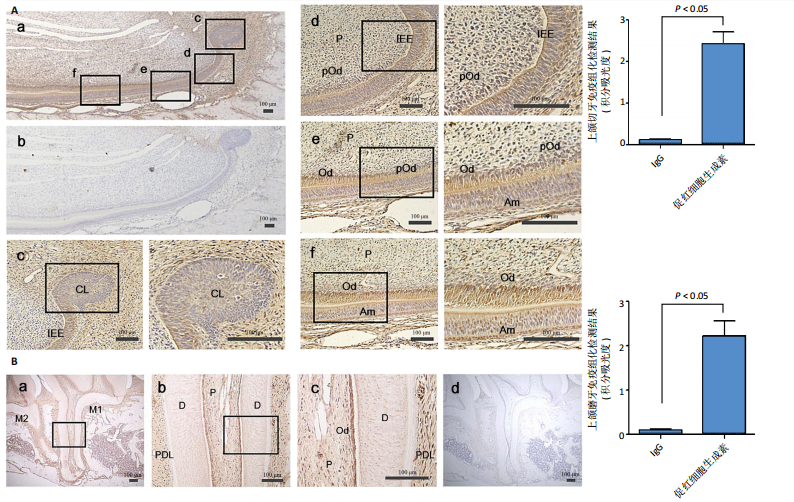
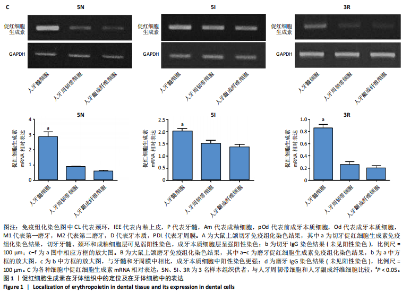
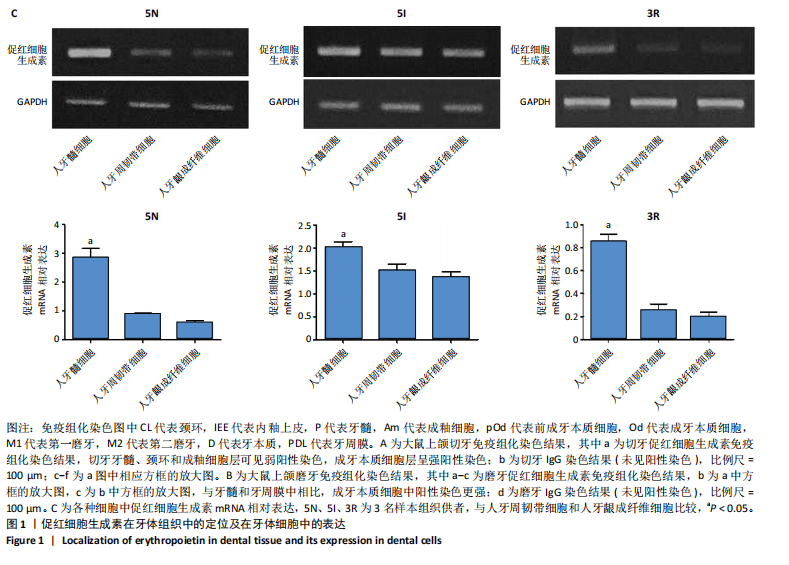
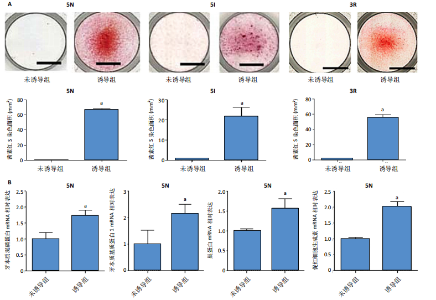
[1] CUSHLEY S, DUNCAN HF, LAPPIN MJ, et al. Efficacy of direct pulp capping for management of cariously exposed pulps in permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Endod J. 2021;54(4): 556-571.
[2] NIE E, YU J, JIANG R, et al. Effectiveness of direct pulp capping bioactive materials in dentin regeneration: A systematic review. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(22):6811-6824.
[3] PRIBADI N, ROSSELLE VR, ZUBAIDAH N, et al. The solubility and water sorption properties of a combination of Ca(OH)2and propolis when used as pulp capping material. Indian J Dent Res. 2020;31(4):557-561.
[4] SHARMA V, NAWAL RR, AUGUSTINE J, et al. Evaluation of endosequence root repair material and endocem MTA as direct pulp capping agents: An in vivo study. Aust Endod J. 2022;48(2):251-257.
[5] WIDJIASTUTI I, DEWI MK, PRASETYO EA, et al. The cytotoxicity test of calcium hydroxide, propolis, and calcium hydroxide-propolis combination in human pulp fibroblast. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2020; 11(1):20-24.
[6] HOSEINIFAR R, ESKANDARIZADEH A, PARIROKH M, et al. Histological evaluation of human pulp response to direct pulp capping with MTA, CEM cement, and biodentine. J Dent (Shiraz). 2020;21(3):177-183.
[7] Peskersoy C, Lukarcanin J, Turkun M. Efficacy of different calcium silicate materials as pulp-capping agents: Randomized clinical trial. J Dent Sci. 2021;16(2):723-731.
[8] MICHOT B, CASEY SM, GIBBS JL. Effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on dental pulp stem cell viability, proliferation, and differentiation. J Endod. 2020;46(7):950-956.
[9] FLORIMOND M, MINIC S, SHARPE P, et al. Modulators of Wnt signaling pathway implied in dentin pulp complex engineering: A literature review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10582-10592.
[10] TOMC J, DEBELJAK N. Molecular insights into the oxygen-sensing pathway and erythropoietin expression regulation in erythropoiesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):7074-7089.
[11] LV W, CHEN W, HUANG S, et al. Reduction of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization in mice with erythropoietin RNA interference. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022;11(8):1-11.
[12] 李雪洋,尹硕,谢金芳,等.促红细胞生成素对大鼠即刻再植牙牙髓血运重建的促进作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2020,46(1):56-60.
[13] IPPOSHI K, TOMOKIYO A, ONO T, et al. Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 promotes odontoblastic differentiation and reparative dentin formation in dental pulp cells. Cells. 2021;10(9):2491-2507.
[14] ANDREI M, VACARU RP, CORICOVAC A, et al. The effect of calcium-silicate cements on reparative dentinogenesis following direct pulp capping on animal models. Molecules. 2021;26(9):2725-2752.
[15] MILANI AJ, CASTILHO T, ASSAF AV, et al. Impact of traumatic dental injury treatment on the oral health-related quality of life of children, adolescents, and their family: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent Traumatol. 2021;37(6):735-748.
[16] KENJALE MA, SHAH P, DESAI S, et al. Clinical evaluation of overall efficacy and pain perception of ultrasonic oscillating tips and conventional high-speed burs for removal of dental caries in children in age-group of 6-8 years. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023;16(2):251-258.
[17] LI Z, LIU L, WANG L, et al. The effects and potential applications of concentrated growth factor in dentin-pulp complex regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):357-366.
[18] WEN B, HUANG Y, QIU T, et al. Reparative dentin formation by dentin matrix proteins and small extracellular vesicles. J Endod. 2021;47(2): 253-262.
[19] ROSAIAN AS, RAO GN, MOHAN SP, et al. Regenerative capacity of dental pulp stem cells: A systematic review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020;12(1): S27-S36.
[20] MATA M, PEYDRÓ S, DE LLANO JJM, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells differentiate into cementoid-like-secreting cells on decellularized teeth scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15588-15600.
[21] KANG W, WANG Y, LI J, et al. TAS2R supports odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in the inflammatory microenvironment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):374-384.
[22] DOU L, YAN Q, YANG D. Effect of five dental pulp capping agents on cell proliferation, viability, apoptosis and mineralization of human dental pulp cells. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(3):2377-2383.
[23] EDWARDS D, STONE S, BAILEY O, et al. Preserving pulp vitality: Part two - vital pulp therapies. Br Dent J. 2021;230(3):148-155.
[24] KAUR D, BEHL T, SEHGAL A, et al. Unravelling the potential neuroprotective facets of erythropoietin for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Metab Brain Dis. 2022;37(1):1-16.
[25] TÓTHOVÁ Z, ŠEMELÁKOVÁ M, SOLÁROVÁ Z, et al. The role of PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in erythropoietin signalization. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7682-7695.
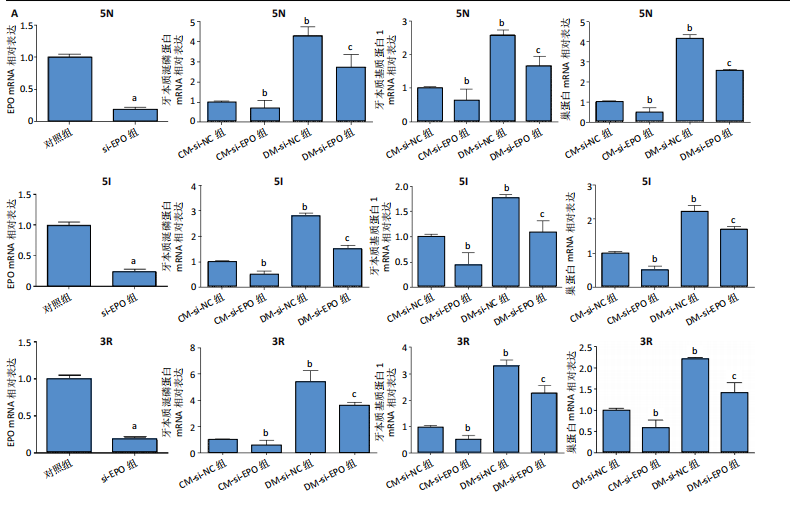
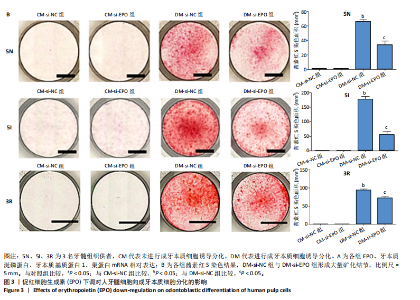
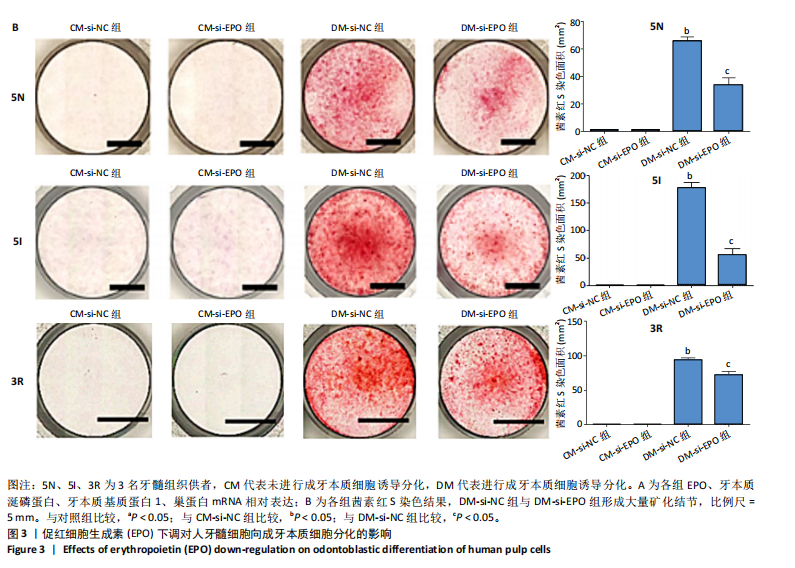
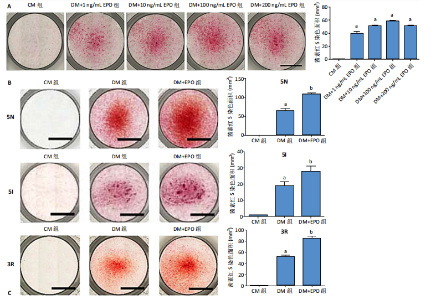
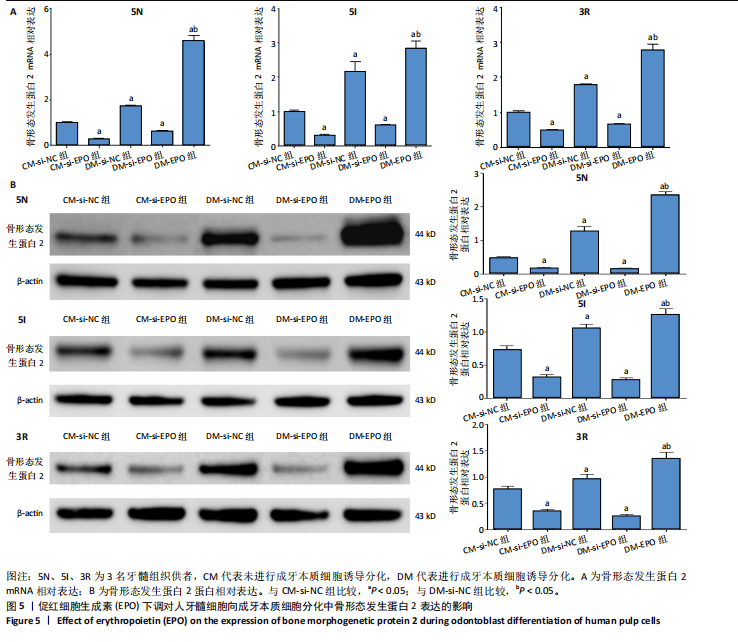
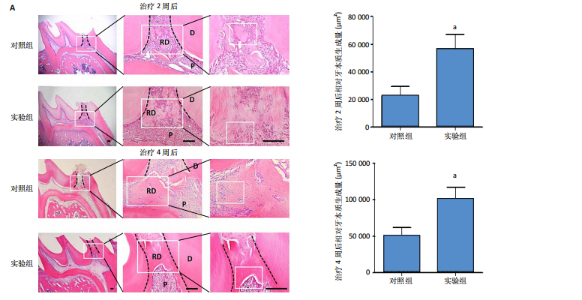
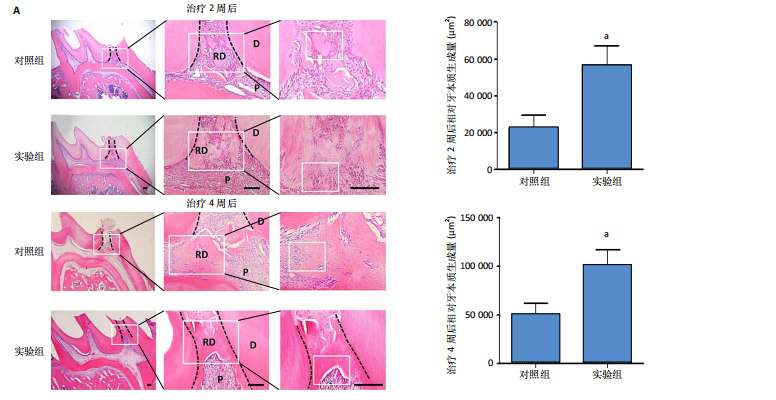
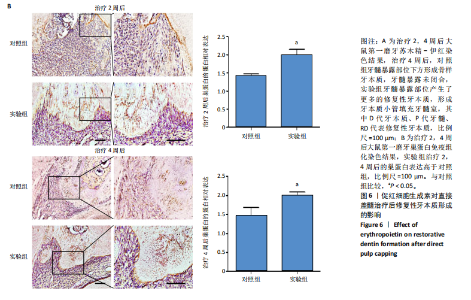
[26] GONG Q, ZENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of erythropoietin on angiogenic potential of dental pulp cells. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(4):1079-1086.
[27] HALLORAN D, DURBANO HW, NOHE A. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 in development and bone homeostasis. J Dev Biol. 2020;8(3):19-48.
[28] LI Y, LIU Y, GUO Q. Silk fibroin hydrogel scaffolds incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles repair articular cartilage defects by regulating TGF-β1 and BMP-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):50-60.
[29] PARSEGIAN K. The BMP and FGF pathways reciprocally regulate odontoblast differentiation. Connect Tissue Res. 2023;64(1):53-63.
[30] SHAMSZADEH S, ASGARY S, TORABZADEH H, et al. Cytokine co-stimulation effect on odontogenic differentiation of stem cells. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26(7):4789-4796.
[31] LEDESMA-COLUNGA MG, WEIDNER H, VUJIC SPASIC M, et al. Shaping the bone through iron and iron-related proteins. Semin Hematol. 2021; 58(3):188-200.
[32] GONZÁLEZ-DOMÍNGUEZ Á, VISIEDO-GARCÍA FM, DOMÍNGUEZ-RISCART J, et al. Iron metabolism in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5529-5555.
[33] KOWDLEY KV, GOCHANOUR EM, SUNDARAM V, et al. Hepcidin signaling in health and disease: Ironing out the details. Hepatol Commun. 2021;5(5):23-735. |