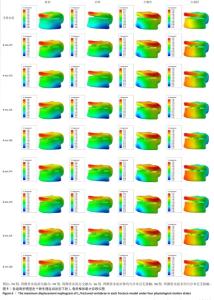
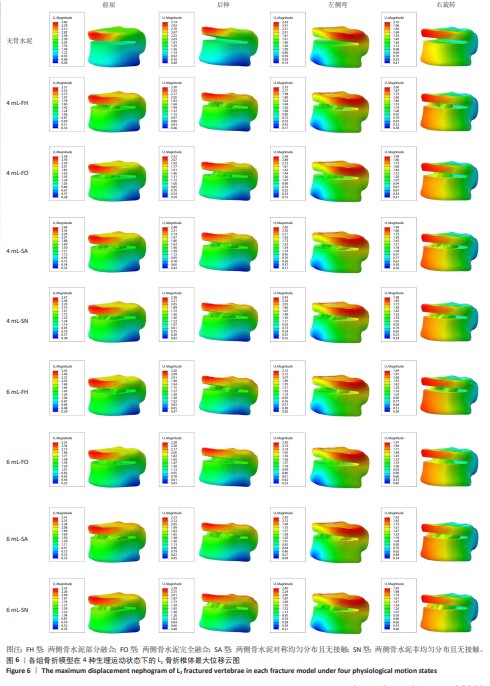
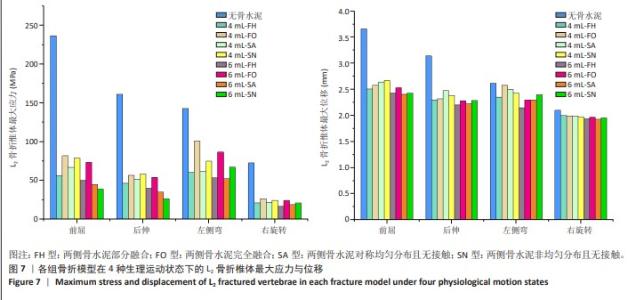
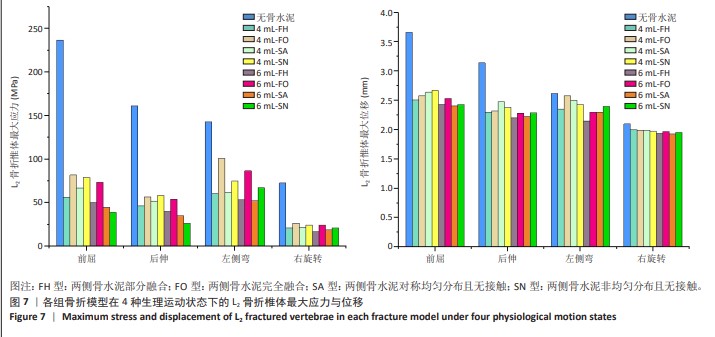
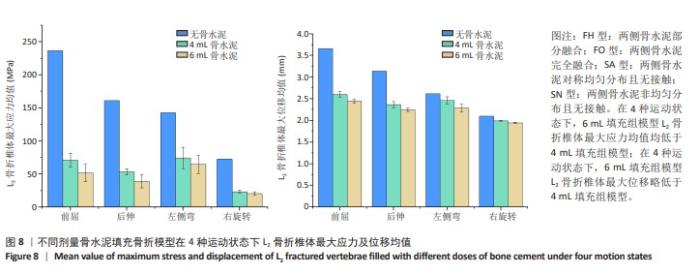
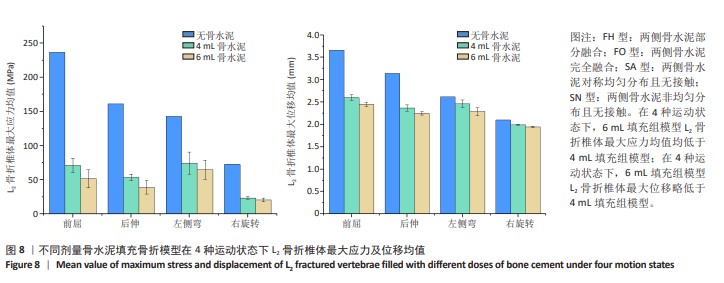
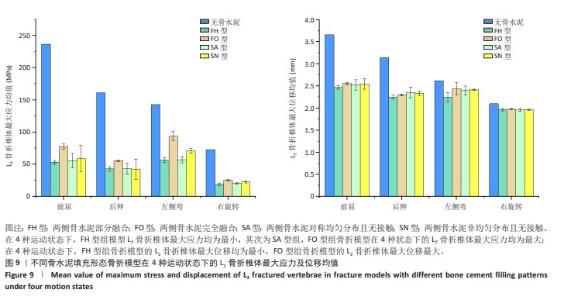
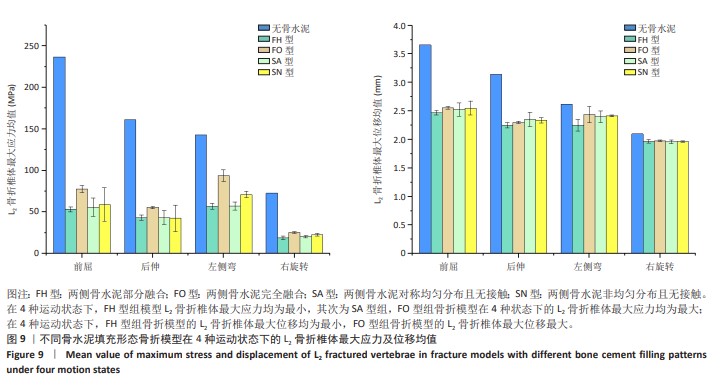
[1] YE LQ, LIANG D, JIANG XB, et al. Risk Factors for the Occurrence of Insufficient Cement Distribution in the Fractured Area after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Physician. 2018;21(1):E33-E42.
[2] 唐本强,王彦辉,许崧杰,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体强化术后椎体内骨水泥分布类型的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2022,42(5):320-330.
[3] LOU S, SHI X, ZHANG X, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus non-operative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int. 2019; 30(12):2369-2380.
[4] YAO G, SHEN YX, LI M, et al. [Biomechanical effects of different bone cement diffusion patterns after vertebroplasty: finite element analysis]. Zhong guo Gu Shang. 2021;34(8):732-737.
[5] CHEN Z, SONG C, CHEN M, et al. What are risk factors for subsequent fracture after vertebral augmentation in patients with thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021; 22(1):1040.
[6] DAI H, LIU Y, HAN Q, et al. Biomechanical comparison between unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:978917.
[7] ZHANG X, CHEN T, MENG F, et al. A finite element analysis on different bone cement forms and injection volumes injected into lumbar vertebral body in percutaneous kyphoplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):621.
[8] HE S, ZHANG Y, LV N, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on clinical efficacy after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(50): e18217.
[9] SONG SY, KANG SW, CHO SH, et al. Effects of Location and Volume of Intraosseous Cement on Adjacent Level of Osteoporotic Spine Undergoing Kyphoplasty: Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg, 2022;162:e73-e85.
[10] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):142.
[11] 李文银,尹红灵,蒋钰钢.PVP术中腰椎不同骨水泥注入量的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(18):1695-1700.
[12] GUO H, ZHANG S, GUO D, et al. Influence of cement-augmented pedicle screws with different volumes of polymethylmethacrylate in osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae over the adjacent segments: a 3D finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):460.
[13] 李嘉睿,燕杨,武晓刚,等.单边双通道内镜下腰椎椎间融合的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(34):5523-5529.
[14] JIA H, XU B, QI X. Biomechanical evaluation of percutaneous cement discoplasty by finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):594.
[15] 叶林强,卢国樑,江晓兵,等.骨水泥填充位置对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的生物力学特性影响:一项三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4435-4440.
[16] LIAO J. Impact of Osteoporosis on Different Type of Short-Segment Posterior Instrumentation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture—A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020;139:e643-e651.
[17] 张勋,孟凡超,庞倩文,等.腰椎经皮穿刺球囊扩张椎体成形手术理想骨水泥形态分布及注射量的有限元分析[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报,2022,56(1):36-41.
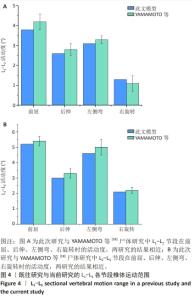
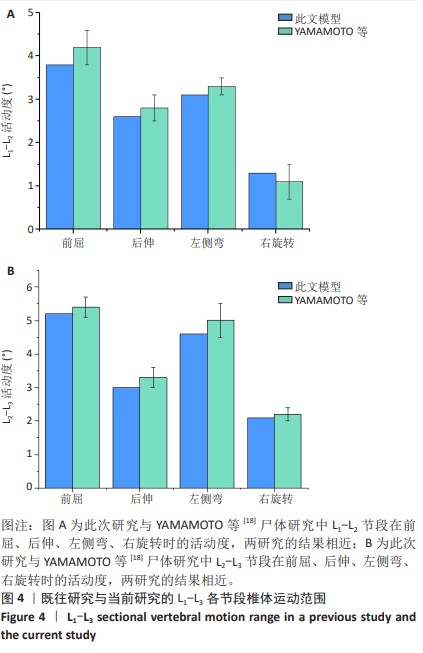
[18] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[19] LIU Z, ZHANG X, LIU H, et al. A nomogram for short-term recurrent pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2021;33(4):851-860.
[20] YUAN L, BAI J, GENG C, et al. Comparison of targeted percutaneous vertebroplasty and traditional percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the elderly. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):359.
[21] LIN WC, LEE YC, LEE CH, et al. Refractures in cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective analysis EUR Spine J. 2008;17(4): 592-599.
[22] RODER C, BOSZCZYK B, PERLER G, et al. Cement volume is the most important modifiable predictor for pain relief in BKP: results from SWISS spine, a nationwide registry. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(10): 2241-2248.
[23] WANG D, LI Y, YIN H, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(3):1062-1072.
[24] KWON HM, LEE SP, BAEK JW, et al. Appropriate Cement Volume in Vertebroplasty: A Multivariate Analysis with Short-Term Follow-Up. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(2):128-134.
[25] GRAHAM J, AHN C, HAI N, et al. Effect of bone density on vertebral strength and stiffness after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(18):E505-E511. |