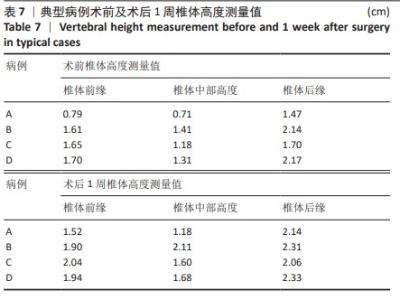
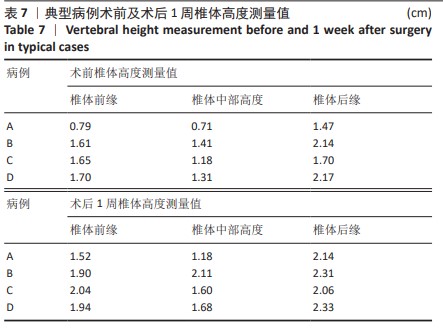
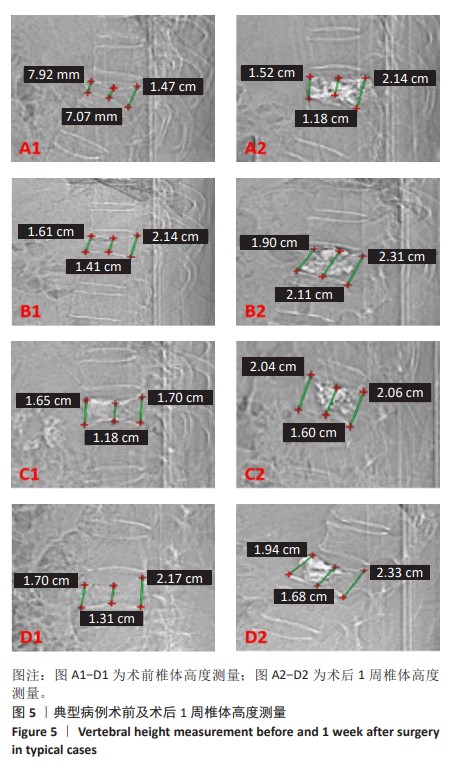
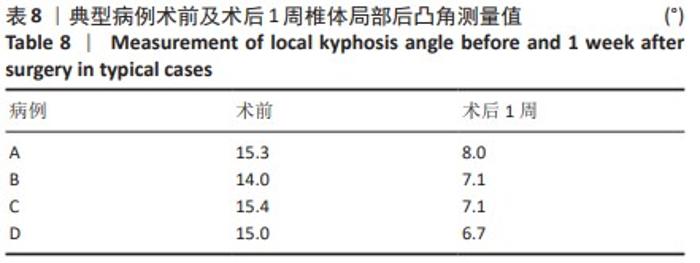
[1] LIANG L, CHEN X, JIANG W, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty or percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture? An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Saudi Med. 2016; 36(3):165-174.
[2] PARREIRA PCS, MAHER CG, MEGALE RZ, et al. An overview of clinical guidelines for the management of vertebral compression fracture: a systematic review. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1932-1938.
[3] LIN J, QIAN L, JIANG C, et al. Bone cement distribution is a potential predictor to the reconstructive effects of unilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty in OVCFs: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13(1):140.
[4] ZHOU C, HUANG S, LIAO Y, et al. Correlation analysis of larger side bone cement volume/vertebral body volume ratio with adjacent vertebral compression fractures during vertebroplasty. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1072087.
[5] SANLI I, VAN KUIJK SMJ, DE BIE RA, et al. Percutaneous cement augmentation in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVFs) in the elderly: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7): 1553-1572.
[6] ODéN A, MCCLOSKEY EV, KANIS JA, et al. Burden of high fracture probability worldwide: secular increases 2010-2040. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(9):2243-2248.
[7] 孙育良,熊小明,何本祥,等.椎体成形骨填充材料的研究与现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(14):2285-2290.
[8] LI X, LU Y, LIN X. Refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body after treatment by balloon kyphoplasty: Three cases report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(49):e8961.
[9] 沈松,徐彬.经皮椎体成形骨水泥呈弥散型分布可减少邻近椎体再骨折的发生率[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):499-503.
[10] 许伟阳.单双侧经皮穿刺椎体成形术对骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的疗效及对骨钙素的影响[J].吉林医学,2023,44(2): 414-416.
[11] SONG Q, ZHAO Y, LI D, et al. Effect of different bone cement distributions in percutaneous kyphoplasty on clinical outcomes for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(12):e33309.
[12] CLARK W, BIRD P, GONSKI P, et al. Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fractures (VAPOUR): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 388(10052):1408-1416.
[13] WANG Y, LIU B, SUN Z, et al. Comparative Efficacy of Three Minimally Invasive Procedures for Kümmell’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front Surg. 2022;9:893404.
[14] LV B, JI P, FAN X, et al. Clinical Efficacy of Different Bone Cement Distribution Patterns in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty: A Retrospective Study. Pain physician. 2020;23(4):E409-E416.
[15] LI Q, LONG X, WANG Y, et al. Clinical observation of two bone cement distribution modes after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021; 22(1):577.
[16] HUAWEI M. Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty in the treatment of senile osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Med Equip. 2022;35:82-83.
[17] LI K, JI C, LUO D, et al. Role of percutaneous vertebroplasty with high-viscosity cement in the treatment of severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4602.
[18] XIAO JT, LING LL, XIAO MC, et al. Percutaneous spinal endoscopic treatment of PVP/PKP bone cement leakage with neurological symptoms. Chin J Orthop. 2020;28:182-185.
[29] FAN X, LI S, ZENG X, et al. Risk factors for thoracolumbar pain following percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(1):300060521989468.
[20] LIN Z. Risk factors of adjacent vertebral re-fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Med Equip. 2021;34:74-75.
[21] MA X, XING D, MA J, et al. Risk factors for new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: qualitative evidence synthesized from a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(12):E713-E722.
[22] 阿卜杜吾普尔·海比尔,阿里木江·玉素甫,麦麦提敏·阿卜力米提,等.经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥量和分布对手术椎体及邻近椎体再发骨折的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(10):1586-1591.
[23] CLARENÇON F, FAHED R, GABRIELI J, et al. Safety and Clinical Effectiveness of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in the Elderly (≥80 years). Eur Radiol. 2016;26(7):2352-2358.
[24] ROUSING R, HANSEN KL, ANDERSEN MO, et al. Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty: a clinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(5):478-482.
[25] BOUSSON V, GUINEBERT S, ODRI G, et al. Curved Discography Needle for Percutaneous Cervical Spine Vertebroplasty: A Technical Note. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;31(4):686-689.
[26] ZHOU C, HUANG S, LIAO Y, et al. Correlation analysis of larger side bone cement volume/vertebral body volume ratio with adjacent vertebral compression fractures during vertebroplasty. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1072087.
[27] 祁振良,李为勇,于永刚,等.单侧和双侧经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩性骨折的疗效比较[J].颈腰痛杂志,2016,37(6): 501-503.
[28] 张惠林,殷世武,项廷淼,等.单侧及双侧经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折临床疗效比较[J].临床外科杂志,2023, 31(1):89-92.
[29] ZHANG L, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. Bone cement distribution in the vertebral body affects chances of recompression after percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:431-436.
[30] LIANG X, ZHONG W, LUO X, et al. Risk factors of adjacent segmental fractures when percutaneous vertebroplasty is performed for the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):399.
[31] ZHONG W, LIANG X, LUO X, et al. Vertebroplasty and vertebroplasty in combination with intermediate bilateral pedicle screw fixation for OF4 in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a retrospective single-Centre cohort study. BMC Surg. 2019;19(1):178.
[32] ZHANG L, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. Bone cement distribution in the vertebral body affects chances of recompression after percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:431-436.
[33] CHEVALIER Y, PAHR D, CHARLEBOIS M, et al. Cement distribution, volume, and compliance in vertebroplasty: some answers from an anatomy-based nonlinear finite element study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(16):1722-1730.
[34] ZHONG W, LIANG X, LUO X, et al. Vertebroplasty and vertebroplasty in combination with intermediate bilateral pedicle screw fixation for OF4 in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a retrospective single-Centre cohort study. BMC Surg. 2019;19(1):178.
[35] 陈柏龄,林焘,谢登辉,等.定量骨水泥在椎体中的不同分布对改善骨质疏松椎体整体刚度的影响:有限元分析[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2015,7(3):162-168.
[36] HAIBIER A, YUSUFU A, LIN H, et al. Effect of different cement distribution in bilateral and unilateral Percutaneous vertebro plasty on the clinical efficacy of vertebral compression fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):908.
[37] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1547-1554.
[38] JENSEN ME, EVANS AJ, MATHIS JM, et al. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(10):1897-1904. |