Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2009-2016.doi: 10.12307/2024.173
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of risk factors for short-term death after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Gao Siyu1, Yao Lihong2, Bian Zhilei1, Zhang Suping1, Li Li1, Fan Jinpeng1, Qin Jing1, Peng Yingnan1, Wan Dingming1
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; 2Yellow River Sanmenxia Hospital, Sanmenxia 472000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-10Accepted:2023-06-19Online:2024-05-08Published:2023-08-28 -
Contact:Wan Dingming, Professor, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Gao Siyu, Master candidate, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China Yao Lihong, Attending physician, Yellow River Sanmenxia Hospital, Sanmenxia 472000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82170211 (to BZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Siyu, Yao Lihong, Bian Zhilei, Zhang Suping, Li Li, Fan Jinpeng, Qin Jing, Peng Yingnan, Wan Dingming. Analysis of risk factors for short-term death after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2009-2016.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
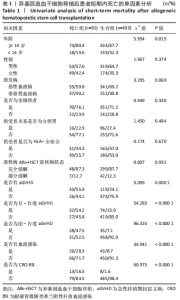
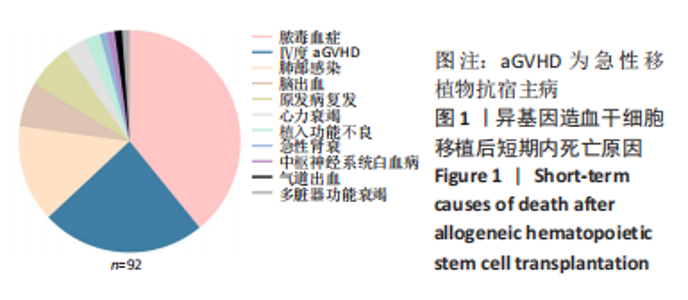
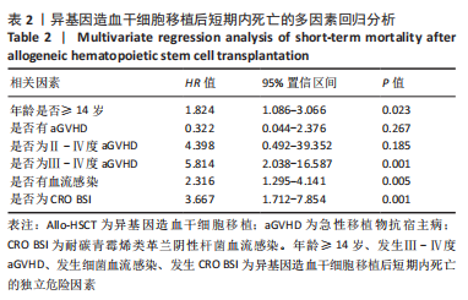
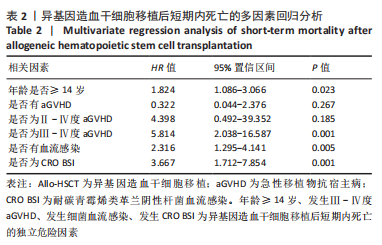
2.1 统计学资料 2018-01-01/2021-06-30郑州大学第一附属医院造血干细胞移植中心共行585例Allo-HSCT,有92例死于移植后100 d内,死亡率为15.7%(92/585),中位年龄为26.5岁(1-56岁),中位生存时间为48 d(0-97 d);其中男性患者53例,女性患者39例;再生障碍性贫血患者占33.7%(31/92),急性髓系白血病患者占25%(23/92),急性淋巴细胞白血病占20.7%(19/92),骨髓增生异常综合征占12.0%(11/92),嗜血细胞综合征占2.2%(2/92),淋巴瘤占2.2%(2/92),其他疾病占4.2%(4/92)。根据Allo-HSCT后100 d内是否死亡,将病例分为死亡组与生存组,基线特征对比见表1。"

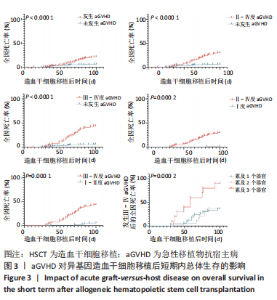
2.3.2 造血干细胞移植前疾病状态 对于恶性血液病患者(396/585),Allo-HSCT前原发病的缓解状态分为完全缓解(347/396)与部分缓解(49/396),对完全缓解患者与部分缓解患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内总体生存率进行比较,未见明显统计学差异(P=0.932)。 2.3.3 供者选择 有164例病例的供者为非血缘供者,421例为亲缘供者,是否为亲缘供者对Allo-HSCT后100 d内总体生存率无明显影响(P=0.277);在421例亲缘供者的病例中,供受者关系是否为女供男(P=0.484)及是否为HLA-全相合(P=0.67)均对Allo-HSCT后100 d内总体生存无明显影响。 2.3.4 原发病 585例Allo-HSCT患者中,恶性血液病患者占67.7%(396/585),其中包括急性髓系白血病、急性淋巴细胞白血病、骨髓增生异常综合征、淋巴瘤等,非恶性血液病病例占32.3%(189/585),包括再生障碍性贫血、阵发性睡眠性血红蛋白尿、嗜血细胞综合征等,对两组患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内总体生存率进行对比,无明显统计学差异(P=0.069)。对各病种患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内总体生存率进行两两对比,发现急性髓系白血病优于再生障碍性贫血(P=0.044),急性髓系白血病优于骨髓增生异常综合征(P=0.02)。 2.3.5 aGVHD 排除33例中性粒细胞尚未植入的患者,不参与aGVHD的评估,在剩余的552例患者中,共有152例患者出现aGVHD,发生率为27.5%(152/552)。无aGVHD组移植后100 d内全因死亡率为6.5%(26/400),aGVHD组为21.7%(33/152),两组全因死亡率之间存在显著统计学差异(P < 0.000 1),见图3。"
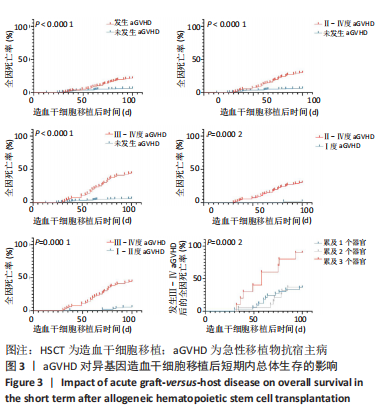
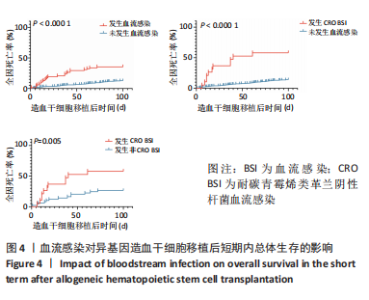
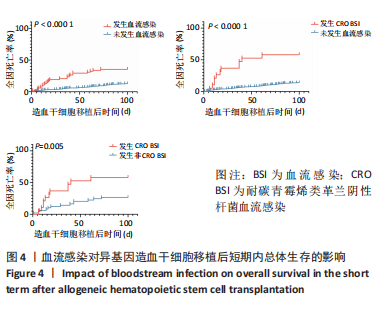
在aGVHD组中,Ⅰ度aGVHD占30.3%(46/152),Ⅱ-Ⅳ度aGVHD占69.7%(106/152),Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD占41.4%(63/152),Ⅳ度aGVHD占23.7%(36/152),且均为糖皮质激素耐药的aGVHD。Ⅰ度aGVHD、Ⅱ-Ⅳ度aGVHD、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD及Ⅳ度aGVHD患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内全因死亡率分别为2.17%(1/46),30.2%(32/106),44.4%(28/63)及63.9% (23/36)。Ⅱ-Ⅳ度aGVHD患者、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD患者分别与无aGVHD患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内全因死亡率进行对比,均有显著统计学差异,见图3。 对不同分度的aGVHD患者造血干细胞移植后100 d内全因死亡率进行对比,Ⅰ度与Ⅱ-Ⅳ度aGVHD组之间存在显著统计学差异(P=0.000 2),见图3;Ⅰ-Ⅱ度与Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD组之间也存在显著统计学差异(P=0.000 1),见图3,说明aGVHD,尤其是Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD对Allo-HSCT后100 d内患者是致命的。在Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD患者中,累及肠道病例占87.3%(55/63),所占比例最大;根据aGVHD累及器官数量对Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD组进行分类,累及1,2,3个器官的患者分别占54.0%(34/63),30.2%(19/63),15.8%(10/63),对这3类患者的总体生存率进行对比,具有显著统计学差异(P=0.000 2),见图3。 2.3.6 血流感染 共有70例患者在Allo-HSCT后100 d内发生细菌性血流感染,发生率为11.97%(70/585),发生的中位时间为7 d(0-14 d),具体感染菌株为耐碳青霉烯类肺炎克雷伯菌12例(17.1%)、耐碳青霉烯类铜绿假单胞菌5例(7.1%)、耐碳青霉烯类大肠埃希菌3例(4.3%)、耐碳青霉烯类鲍曼不动杆菌1例(1.4%)、大肠埃希菌16例(22.6%)、铜绿假单胞菌6例(8.6%)、肺炎克雷伯菌5例(7.1%)、解甘露醇罗尔斯顿菌6例(8.6%)、表皮葡萄球菌3例(4.3%)、屎肠球菌2例(2.8%),剩余11种菌株各1例(16.1%)。革兰阴性杆菌血流感染所占比例最大,为85.7%(60/70);细菌性血流感染患者中Allo-HSCT后100 d内死亡率为37.1%(26/70),且直接死因为细菌性血流感染的患者占死亡患者的61.5%(16/26),非细菌血流感染患者的死亡率为12.8%(66/515),对两组患者的死亡率进行对比,具有显著统计学差异(P < 0.000 1),见图4A。在细菌性血流感染患者中,CRO BSI患者占30.0%(21/70),其Allo-HSCT后100 d内死亡率为61.9%(13/21),与非细菌血流感染患者死亡率进行对比,具有显著统计学差异(P < 0.000 1),见图4。CRO BSI患者与非CRO BSI患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内死亡率进行对比(61.9% vs. 27.1%),具有显著统计学差异(P=0.005),见图4。根据血培养、血感染病原高通量测序技术(Next generation sequencing,NGS)、肛周拭子细菌培养等结果及药敏试验结果,在血流感染发生后尽早应用对病原菌敏感的抗生素,对于不同种类的感染菌株,敏感的抗生素也均有不同。对于CRO BSI的治疗,根据药敏试验结果,多采用以替加环素、多黏菌素、头孢他啶/阿维巴坦钠为主的治疗方案。"
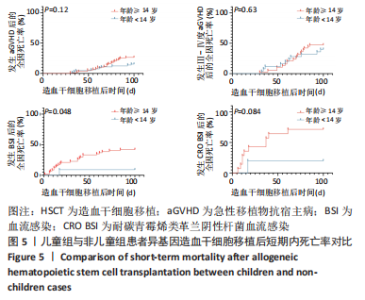
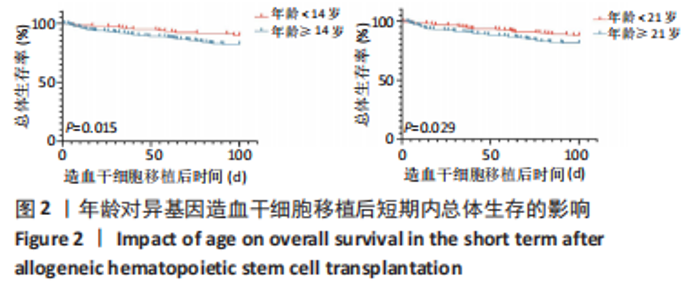
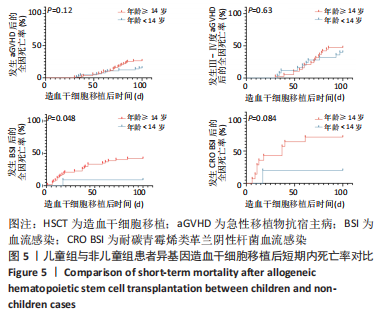
2.5 儿童组与非儿童组Allo-HSCT后短期内全因死亡率对比 前文中,将年龄< 14岁定义为儿童组,≥14岁定义为非儿童组,儿童组在移植后100 d内发生aGVHD、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD、细菌性血流感染、CRO BSI的全因死亡率分别为15.4%(10/65),40%(10/25),9.0%(1/11),20%(1/5);非儿童组在移植后100 d内发生aGVHD、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD、细菌性血流感染、CRO BSI的全因死亡率分别为26.4%(23/87),47.4%(18/38),44.1%(26/59),75%(12/16);将儿童组与非儿童组发生aGVHD、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD、细菌性血流感染、CRO BSI患者在Allo-HSCT后100 d内的全因死亡率进行对比,提示在Allo-HSCT后100 d内发生细菌性血流感染,儿童组的死亡率显著低于非儿童组(P=0.048),见图5,而发生aGVHD (P=0.09)、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD(P=0.83)、CRO BSI(P=0.084),儿童组与非儿童组的全因死亡率无显著统计学差异,见图5。"
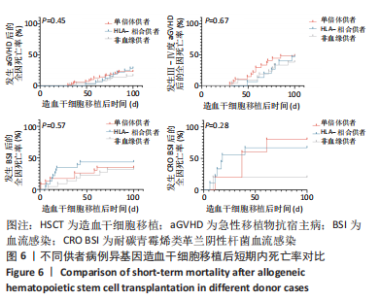
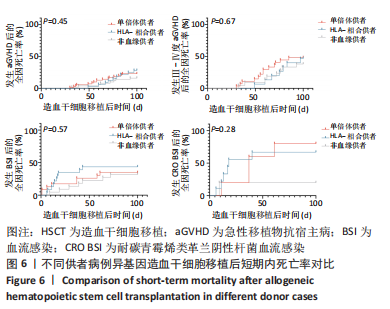
2.6 不同供者类型患者Allo-HSCT后100 d内死亡率对比 将供者类型分类为非血缘供者、单倍体供者、HLA-全相合供者,3组患者在移植后100 d内发生aGVHD的全因死亡率分别为16%(8/50),22.8%(16/70),28.1%(9/32);发生Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD的全因死亡率分别为38.1%(8/21),48.1%(13/27),46.7%(7/15);发生细菌性血流感染的全因死亡率分别为31.8%(7/22),37.5%(9/24),45.8%(11/24);发生CRO BSI的全因死亡率分别为20%(1/5),83.3%(5/6),70%(7/10);将这3组中发生aGVHD、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD、细菌性血流感染、CRO BSI患者在Allo-HSCT后100 d内的全因死亡率进行对比,发现移植后100 d内发生aGVHD(P=0.45)、Ⅲ-Ⅳ度aGVHD (P=0.67)、细菌性血流感染(P=0.57)、CRO BSI(P=0.28),3组患者全因死亡率无显著统计学差异,见图6。"
| [1] WANG Y, HUANG XJ. Advances in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological disease. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2019;40(8):704-708. [2] EHMANN MA, MEDINGER M, BODENMANN B, et al. Histologic features of hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy are best percepted in deep skin biopsies and renal biopsies, while showing a significant overlap with changes related to severe acute graft-versus-host disease in gastrointestinal biopsies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(9):1847-1850. [3] MARTINEZ MT, BUCHER CH, STUSSI G, et al. Transplant-associated microangiopathy (TAM) in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005;36(11):993-1000. [4] LUFT T, DIETRICH S, FALK C, et al. Steroid-refractory GVHD: T-cell attack within a vulnerable endothelial system. Blood. 2011;118(6):1685-1692. [5] GIRMENIA C, BERTAINA A, PICIOCCHI A, et al. Incidence, Risk Factors and Outcome of Pre-engraftment Gram-Negative Bacteremia After Allogeneic and Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Italian Prospective Multicenter Survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11): 1884-1896. [6] GATZA E, REDDY P, CHOI SW. Prevention and Treatment of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26(5):e101-e112. [7] NIVISON-SMITH I, BARDY P, DODDS AJ, et al. A Review of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Australia and New Zealand, 2005 to 2013. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(2):284-291. [8] PARK JH, LEE JH, LEE JH, et al. Incidence, Management, and Prognosis of Graft Failure and Autologous Reconstitution after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(23):e151. [9] SAHIN U, TOPRAK SK, ATILLA PA, et al. An overview of infectious complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Infect Chemother. 2016;22(8):505-514. [10] TOMBLYN M, CHILLER T, EINSELE H, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009; 15(10):1143-1238. [11] MIKULSKA M, AVERBUCH D, TISSOT F, et al. Fluoroquinolone prophylaxis in haematological cancer patients with neutropenia: ECIL critical appraisal of previous guidelines. J Infect. 2018;76(1):20-37. [12] WEISSER M, THEILACKER C, TSCHUDIN SUTTER S, et al. Secular trends of bloodstream infections during neutropenia in 15 181 haematopoietic stem cell transplants: 13-year results from a European multicentre surveillance study (ONKO-KISS). Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(11):854-859. [13] 秦菁,张素平,李丽,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后带状疱疹病毒感染的危险因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(33):5292-5297. [14] KERN WV, RIEG S. Burden of bacterial bloodstream infection-a brief update on epidemiology and significance of multidrug-resistant pathogens. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(2):151-157. [15] YANG TT, LUO XP, YANG Q, et al. Different screening frequencies of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: which one is better? Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020;9(1):49. [16] CHEN L, HAN X, LI Y, et al. Assessment of Mortality-Related Risk Factors and Effective Antimicrobial Regimens for Treatment of Bloodstream Infections Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021;65(9):e0069821. [17] LI C, LI Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Treatment options and clinical outcomes for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae bloodstream infection in a Chinese university hospital. J Infect Public Health. 2019;12(1):26-31. [18] CASTÓN JJ, LACORT-PERALTA I, MARTÍN-DÁVILA P, et al. Clinical efficacy of ceftazidime/avibactam versus other active agents for the treatment of bacteremia due to carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in hematologic patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;59:118-123. [19] TANG Y, XU C, XIAO H, et al. Gram-Negative Bacteria Bloodstream Infections in Patients with Hematological Malignancies - The Impact of Pathogen Type and Patterns of Antibiotic Resistance: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Infect Drug Resist. 2021;14:3115-3124. [20] SATLIN MJ, COHEN N, MA KC, et al. Bacteremia due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in neutropenic patients with hematologic malignancies. J Infect. 2016;73(4):336-345. [21] World Health Organization. Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bac teria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics. http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/WHO-PPL-Short_Summary_25Feb-ET_NM_WHO.pdf. [22] EL-JAWAHRI A, LI S, ANTIN JH, et al. Improved Treatment-Related Mortality and Overall Survival of Patients with Grade IV Acute GVHD in the Modern Years. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(5):910-918. [23] JAGASIA MH, GREINIX HT, ARORA M, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(3):389-401. [24] SCHOEMANS HM, LEE SJ, FERRARA JL, et al. EBMT-NIH-CIBMTR Task Force position statement on standardized terminology & guidance for graft-versus-host disease assessment. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(11):1401-1415. [25] STEM CELL APPLICATION GROUP, CHINESE SOCIETY OF HEMATOLOGY, CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION. Chinese consensus of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological disease (Ⅲ) -acute graft-versus-host disease (2020). Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(7):529-536. [26] 中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组.中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅰ)——适应证、预处理方案及供者选择(2014年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2014,35(8):775-780. [27] MIŚKIEWICZ-BUJNA J, MIŚKIEWICZ-MIGOŃ I, SZMIT Z, et al. Short- and long-term outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in infants: A single-center experience over 20 years. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:956108. [28] STYCZYŃSKI J, TRIDELLO G, KOSTER L, et al. Death after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: changes over calendar year time, infections and associated factors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(1):126-136. [29] PENACK O, MARCHETTI M, RUUTU T, et al. Prophylaxis and management of graft versus host disease after stem-cell transplantation for haematological malignancies: updated consensus recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(2):e157-e167. [30] 许慧敏,张素平,曹伟杰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性急性移植物抗宿主病的单臂临床研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(31):4921-4927. [31] 王卓,陶芳,唐威,等.儿童异基因造血干细胞移植后肠道急性移植物抗宿主病的临床研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2022,30(2): 600-606. [32] WACHSMUTH LP, PATTERSON MT, ECKHAUS MA, et al. Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide prevents graft-versus-host disease by inducing alloreactive T cell dysfunction and suppression. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(6):2357-2373. [33] CASTILLA-LLORENTE C, MARTIN PJ, MCDONALD GB, et al. Prognostic factors and outcomes of severe gastrointestinal GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014; 49(7):966-971. [34] LIN C, SHEN H, ZHOU S, et al. Assessment of infection in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients: risk factors and main characteristics. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20(1):699. [35] XU CH, SU Y, LYU YX, et al. Perianal swabs surveillance cultures of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae(CRE) can be hints for CRE bloodstream infection in patients with hematological diseases. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018;39(12):1021-1025. [36] CAO W, ZHANG J, BIAN Z, et al. Active Screening of Intestinal Colonization of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae for Subsequent Bloodstream Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Infect Drug Resist. 2022;15:5993-6006. [37] POUCH SM, SATLIN MJ. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in special populations: Solid organ transplant recipients, stem cell transplant recipients, and patients with hematologic malignancies. Virulence. 2017;8(4):391-402. [38] GORRIE CL, MIRCETA M, WICK RR, et al. Gastrointestinal Carriage Is a Major Reservoir of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Intensive Care Patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(2):208-215. [39] KUMAR A, MOHAPATRA S, BAKHSHI S, et al. Rectal Carriage of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A Menace to Highly Vulnerable Patients. J Glob Infect Dis. 2018;10(4):218-221. [40] BALLO O, TARAZZIT I, STRATMANN J, et al. Colonization with multidrug resistant organisms determines the clinical course of patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing intensive induction chemotherapy. PLoS One. 2019;14(1):e0210991. [41] 张成涛,康志杰,杨岩,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗骨髓增生异常综合征及其转化急性髓系白血病的疗效分析[J].大连医科大学学报,2023,45(1):25-31. [42] 娄典,刘利,严学倩,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗难治/复发急性髓系白血病的疗效及预后因素分析[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2022,30(5):1577-1585. [43] TODISCO E, CICERI F, BOSCHINI C, et al. Factors predicting outcome after allogeneic transplant in refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a retrospective analysis of Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(7):955-961. [44] 宋晓露,王晓刚,彭也,等.中高危骨髓增生异常综合征及其转化急性髓系白血病异基因造血干细胞移植时机与疗效的临床研究[J].中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(10):867-872. [45] CIFTCILER R, DEMIROGLU H, BUYUKASIK Y, et al. Efficacy and Feasibility of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019;19(3):177-182. [46] CRADDOCK C, LABOPIN M, PILLAI S, et al. Factors predicting outcome after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation in primary refractory acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2011;25(5):808-813. |
| [1] | Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin, Wang Yang, Wang Xiaojuan, Lyu Peng, Chen Long, Shi Zhen, Xie Wei, Zhu Yiliang, Li Xugui. Risk factors for cage retropulsion following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1394-1398. |
| [2] | Yang Cekai, Cai Zhuoyan, Chen Ming, Liu Hao, Weng Rui, Cui Jianchao, Zhang Shuncong, Yao Zhensong. Relationship between degeneration of paraspinal muscle and refractures in postmenopausal women treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| [3] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [4] | Wang Dening, Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui, Du Changling, Wang Xin. Imaging analysis of anatomical morphological risk factors for posterior cruciate ligament injury of the knee [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2887-2894. |
| [5] | Jiang Yu, Luo Yan, Lin Xisheng, Wang Yilin, Gao Zefu, Lyu Houchen, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu, Liu Yujie. Effect of dementia on postoperative complications in older patients with hip fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2895-2900. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Hu Li, Yang Zhongya, Han Peng. A cross-sectional survey on the prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in the elderly in some areas of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2197-2201. |
| [7] | Zhang Wenhui, Pei Xiaohang, Kong Dai, Liu Zhongwen. Efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells replacing donor bone marrow cells in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2042-2046. |
| [8] | Abuduwupuer•Haibier, Alimujiang•Yusufu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Maihemuti•Yakufu, Aiben•Kayierhan, Yimuran•Abudukelimu, Alimujiang•Aximu, Lin Hang, Tuerhongjiang•Abudurexiti. Influence of bone cement volume and distribution on surgical and adjacent vertebral refractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1586-1591. |
| [9] | Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Wang Yehua. Anatomic risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tears combined with anterior cruciate ligament injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 663-668. |
| [10] | Shen Lianwei, Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Risk factor analysis of metabolic syndrome and construction of a nomogram prediction model in middle-aged and elderly people [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 657-662. |
| [11] | Yu Jian, Zhou Bingqian, Wang Zhao, Li Yue, Chang Yaru, Cao Hong. Comparison of random forest model and logistic regression model in predicting the prolonged length of stay of hip fracture patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5413-5420. |
| [12] | Qin Jing, Zhang Suping, Li Li, Zhang Ran, Peng Yingnan, Gao Siyu, Fan Jinpeng, Bian Zhilei, Wan Dingming. Analysis of risk factors for varicella-zoster virus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5292-5297. |
| [13] | Meng Xiangli, Lyu Xiaohong. Effects of eccentric exercise patterns on exercise-induced muscle damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5132-5136. |
| [14] | Yuan Haibo, Li Dongya, Pan Bin, Guan Kai, Chen Feng, Yuan Feng, Wu Jibin. Sagittal related factors of upper lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4984-4989. |
| [15] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||