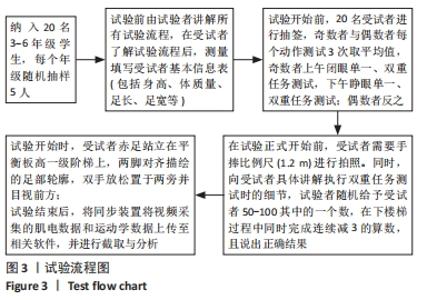
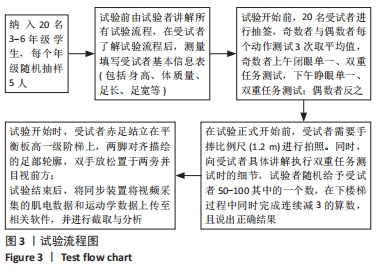
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1834-1842.doi: 10.12307/2022.504
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes in biomechanical characteristics of children’s lower limbs during visual deprivation and dual tasks
Ouyang Yiyi1, Peng Jie2, Wang Kun3, Zhang Tingran3, Luo Jiong3
- 1Institute of Physical Education, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China; 2Institute of Physical Education, Liupanshui Normal University, Liupanshui 553000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Institute of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
-
Received:2019-12-24Revised:2020-03-03Accepted:2021-09-29Online:2022-04-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Luo Jiong, Professor, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Institute of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Ouyang Yiyi, Master, Assistant, Institute of Physical Education, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China -
Supported by:Central University Fund Project, No. SWU1809386 (to OYY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ouyang Yiyi, Peng Jie, Wang Kun, Zhang Tingran, Luo Jiong. Changes in biomechanical characteristics of children’s lower limbs during visual deprivation and dual tasks[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1834-1842.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

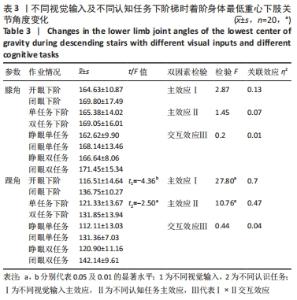
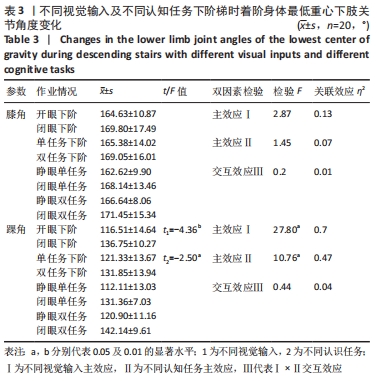
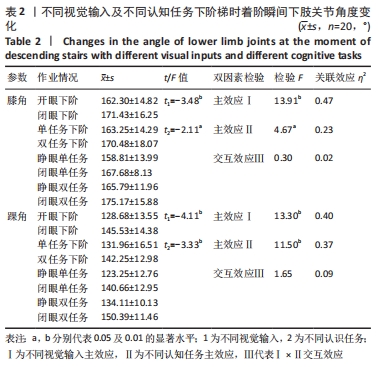
2.3 不同视觉输入及执行不同认知任务时下阶梯动作的运动学特征比较 2.3.1 触板瞬刻着板腿膝、踝角度特征比较 不同视觉输入及不同认知任务下阶梯显著影响着阶瞬间膝角、踝角大小(均P < 0.05)。关联效应η2值表明,视觉的影响力大于认知任务的影响力(0.47 > 0.23,0.40 > 0.37)。进一步经独立样本t检验发现,睁眼状况下的膝角、踝角显著小于闭眼状况下的膝角、踝角(t=-3.48,-4.11,均P < 0.01),单一任务下的膝角、踝角显著小于双重任务下的膝角、踝角(t=-2.11,-3.33,均P < 0.05)。不同视觉输入及不同认知任务对着阶瞬间膝角、踝角不存在交互影响作用(P > 0.05),详见表2。"
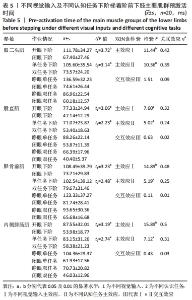
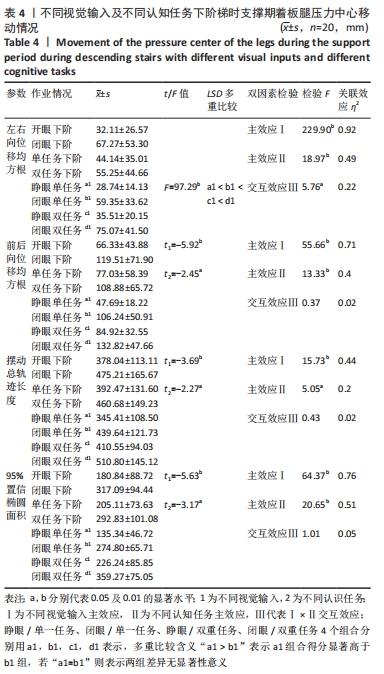
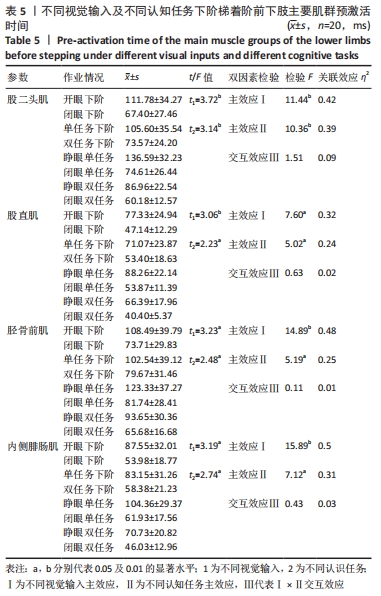
不同视觉输入及不同认知任务下阶梯显著影响支撑期压力中心前后向位移均方根、摆动总轨迹长度、95%置信椭圆面积(均P < 0.05)。关联效应η2值表明,视觉的影响力大于认知任务的影响力(0.71 > 0.40,0.44 > 0.20,0.76 > 0.51)。进一步经独立样本t检验发现,睁眼状况下的压力中心前后向位移均方根、摆动总轨迹长度、95%置信椭圆面积显著小于闭眼状况下的压力中心前后向位移均方根、摆动总轨迹长度、95%置信椭圆面积(t=-5.92, -3.69, -5.63,均P < 0.01),单一任务下的压力中心前后向位移均方根、摆动总轨迹长度、95%置信椭圆面积显著小于双重任务下的压力中心前后向位移均方根、摆动总轨迹长度、95%置信椭圆面积(t=-2.45, -2.27,-3.17,均P < 0.05)。不同视觉及不同认知任务对支撑期压力中心前后向位移均方根、摆动总轨迹长度、95%置信椭圆面积不存在交互影响作用(P > 0.05),详见表4。 2.5 不同视觉输入及不同认知任务下阶梯着板腿肌电特征比较 2.5.1 前脚掌触板前下肢主要肌群预激活时间特征比较 不同视觉输入及不同认知任务下阶梯显著影响股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌预激活时间长短(均P < 0.05)。关联效应η2值表明,视觉的影响力大于认知任务的影响力(0.42 > 0.39,0.32 > 0.24,0.48 > 0.25,0.50 > 0.31)。进一步经独立样本t检验发现,睁眼状况下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌预激活时间显著大于闭眼状况下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌预激活时间(t=3.72,3.06,3.23,3.19,均P < 0.05),单一任务下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌预激活时间显著大于双重任务下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌预激活时间(t=3.14,2.23,2.48,2.74,均P < 0.05)。不同视觉及不同认知任务对股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌预激活时间不存在交互影响作用(P > 0.05),详见表5。"
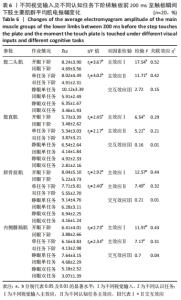
2.5.2 触板前200 ms至前脚掌触板瞬间着板腿主要肌群肌电特征比较 不同视觉输入及不同认知任务下阶梯显著影响触板前200 ms至前脚掌触板瞬间股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅大小(均P < 0.05)。关联效应η2值表明,视觉的影响力大于认知任务的影响力(0.52 > 0.42,0.29 > 0.21,0.44 > 0.32,0.43 > 0.31)。进一步经独立样本t检验发现,睁眼状况下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅显著大于闭眼状况下的股二头肌平均、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌肌电振幅(t=3.67,2.45,2.92,2.73,均P < 0.05),单一任务下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅显著大于双重任务下的股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅(t=3.02,2.17,2.40,2.34,均P < 0.05)。不同视觉及不同认知任务对触板前200 ms至前脚掌触板瞬间股二头肌、股直肌、胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅不存在交互影响作用(P > 0.05),详见表6。"
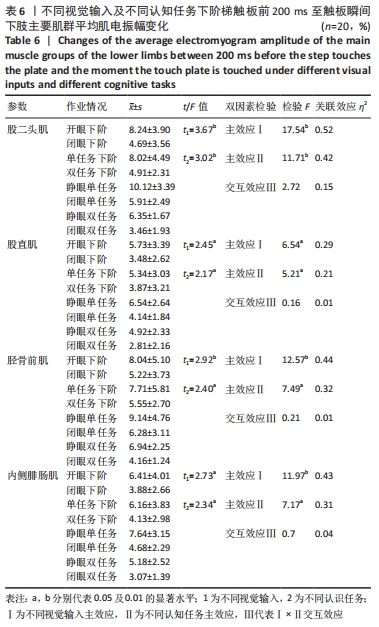
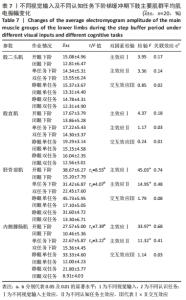
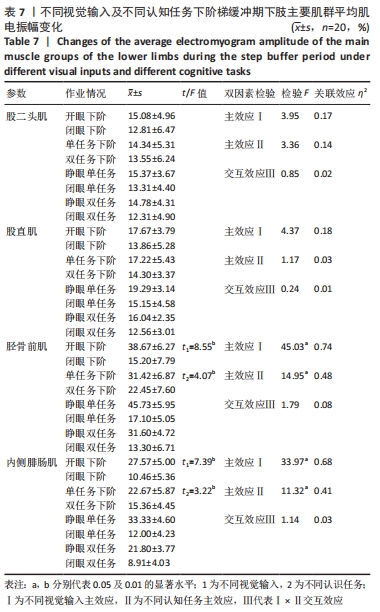
2.5.3 着板腿从前脚掌触板瞬刻至全脚掌触板过程中主要肌群肌电特征比较 不同视觉输入及不同认知任务下阶梯不会影响缓冲期股二头肌、股直肌平均肌电振幅大小(P > 0.05),但会对缓冲期胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅大小产生显著影响(均P < 0.05)。关联效应η2值表明,视觉的影响力大于认知任务的影响力(0.74 > 0.48,0.68 > 0.41)。进一步经独立样本t检验发现,睁眼状况下胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅显著大于闭眼状况下胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅(t=8.55,t=7.39,均P < 0.05),单一任务下的胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅显著大于双重任务下的胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅(t=4.07,3.22,均P < 0.05)。不同视觉及不同认知任务对缓冲期胫骨前肌、内侧腓肠肌平均肌电振幅不存在交互影响作用(P > 0.05),详见表7。"
| [1] 闫蓓,黄丽妹,彭娟娟,等.上海市儿童跌倒伤害干预项目效果评价[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2017,21(8):775-779. [2] 王卓,王德征,张颖,等.天津市2014年0-14岁儿童院内报告伤害流行特征分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2018,22(8):813-816+821. [3] KARPINSKY M , KIZILOVA N. Computerized posturography for data analysis and mathematical modelling of postural sway during different two-legged and one-legged human stance. J Vibroeng. 2007;9(3):118-124. [4] OLDHAM JR, MASTER CL, WALKER GA, et al. Impaired eye tracking is associated with symptom severity but not dynamic postural control in adolescents following concussion. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(2):138-144+253. [5] KABBALIGERE R, LEE BC, LAYNE CS. Balancing sensory inputs: sensory reweighting of ankle proprioception and vision during a bipedal posture task. Gait Posture. 2017;52:244-250. [6] BRODOEHL S, KLINGNER C, STIEGLITZ K, et al. The impact of eye closure on somatosensory perception in the elderly. Behav Brain Res. 2015;293:89-95. [7] BRODOEHL S, KLINGNER CM, WITTE OW. Eye closure enhances dark night perceptions. Sci Rep. 2015;5:1-10. [8] Lesinski M, Hortobágyi T, Muehlbauer T, et al. Dose-Response Relationships of Balance Training in Healthy Young Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2015;45:557. [9] D’HONDT E , DEFORCHE B , BOURDEAUDHUIJ ID , et al. Postural balance under normal and altered sensory conditions in normal-weight and overweight children. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(1):84-89. [10] YOUNG WR, WILLIAMS AM. How fear of falling can increase fall-risk in older adults: Applying psychological theory to practical observations. Gait Posture. 2015;41(1):7-12. [11] HUXHAM FE , GOLDIE PA , PATLA AE. Theoretical considerations in balance assessment. Aust J Physiother. 2001;47(2):89-100. [12] 金成敏,曲峰,赵享楠,等.双任务下楼梯行走时对下肢肌肉活动表现及加速度近似熵指数的影响[J].天津体育学院学报,2018,33(4):362-368. [13] 段林茹,郑洁皎,徐国会,等.感觉的平衡维持优先策略研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(11):1241-1244. [14] 杨婷,钱兴皋,张会慧,等.平衡反馈训练仪与Berg平衡量表在评定脑卒中偏瘫患者平衡功能中的相关性[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(11): 1011-1014. [15] 蔡庆,谢丽君,赵绿玉,等.基于反重力跑台训练系统的双重运动任务训练对脑卒中患者平衡功能的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018, 24(11):1315-1319. [16] 董若,倪少波,林清洋,等.双重任务起立步行测试评估脑卒中患者肢体功能的相关性分析[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2019,21(2):168-171. [17] DINGENEN B , JANSSENS L , LUYCKX T , et al. Lower extremity muscle activation onset times during the transition from double-leg stance to single-leg stance in anterior cruciate ligament injured subjects. Br J Sports Med. 2015;44(7):234-245. [18] DINGENEN B , JANSSENS L , LUYCKX T , et al. Postural stability during the transition from double-leg stance to single-leg stance in anterior cruciate ligament injured subjects. Clin Biomech. 2015;30(3): 283-289 [19] BOURLON C, LEHENAFF L, BATIFOULIER C, et al. Dual-tasking postural control in patients with right brain damage . Gait Posture. 2014;39(1):188-193. [20] 朱婷,郑洁皎,丁建伟,等.注意力分配对双重任务模型平衡和计算能力的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(4):439-443. [21] 林建志,陈重佑.着阶反弹跳的肌肉控制特征[J].体育学报,2017,50(2): 207-218. [22] 张燊,傅维杰,刘宇.不同着阶冲击模式的下肢生物力学研究[J].体育科学,2016,36(1):59-66. [23] 傅维杰,刘宇,黄灵燕,等.不同着阶方式下鞋缓冲特性对下肢肌肉活化及共激活的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014,33(9):860-868. [24] KWON EH, BLOCK ME. Implementing the adapted physical education E-learning program into physical education teacher education program. Res Dev Dis. 2017;69:18-29. [25] 彭远秋.视觉剥夺状态阶梯动作下肢肌肉组织刚度调节及肌电变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(15):2338-2344. [26] HORAK FB. Postural orientation and equilibrium: what do we need to know about neurol control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing. 2006;35(2):7-11. [27] 孙威.太极拳运动对老年女性双任务模式楼梯行走姿势控制能力的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院,2019. [28] 孟凡童.太极拳运动对老年人在双重任务下楼梯时预防跌倒的效果研究[D].济南:山东体育学院,2017. [29] HAN KS , SHIN SH , YU CH , et al. Postural responses during the various frequencies of anteroposterior perturbation. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014; 24(6):2537-2545. [30] HWANG S, TAE K, SOHN R, et al. The Balance Recovery Mechanisms Against Unexpected Forward Perturbation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009;37(8):1629-1637. [31] SCHUT IM , PASMA JH , MESTDAGH J , et al. Effect of Amplitude and Number of Repetitions of the Perturbation on System Identification of Human Balance Control During Stance. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng . 2019;27(12):2336-2343. [32] REMAUD A, BOYAS S, CARON GA, et al. Attentional Demands Associated With Postural Control Depend on Task Difficulty and Visual Condition. J Motor Behav. 2012;44(5):329-340. [33] DETTMER M, POURMOGHADDAM A, LEE BC, et al. Associations between Tactile Sensory Threshold and Postural Performance and Effects of Healthy Aging and Subthreshold Vibrotactile Stimulation on Postural Outcomes in a Simple Dual Task. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2016;2016:9797369. [34] 李宗涛.预测老年女性跌倒风险的静立平衡COP活动参数研究[J].山东体育学院学报,2013,29(1):66-69. [35] CARPENTER MG, MURNAGHAN CD, INGLIS JT. Shifting the balance: evidence of an exploratory role for postural sway. Neuroscience. 2010;171(1):196-204. [36] SINGH NB , TAYLOR WR , MADIGAN ML , et al. The spectral content of postural sway during quiet stance: Influences of age, vision and somatosensory inputs. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2012;22(1):131-136. [37] JEON SN , CHOI JH. The effects of ankle joint strategy exercises with and without visual feedback on the dynamic balance of stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(8):2515-2518. [38] LI K, BHERER L, MIRELMAN A, et al. Cognitive involvement in balance, gait and dual-tasking in aging: a focused review from a neuroscience of aging perspective. Front Neurol. 2018;9:913. [39] FUJITA H, KASUBUCHI K, WAKATA S, et al. Role of the frontal cortex in standing postural sway tasks while dual-tasking: afunctional near-infrared spectroscopy study examining working memory capacity. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7053867. [40] 陈秀恩,郑洁皎,施海涛,等.认知注意力、平衡功能双重任务训练对预防老年人跌倒的临床研究[J].中国康复,2016,31(3):215-217. [41] 裴子文,朱元霄,李贝,等.外在注意力焦点策略在脑卒中患者康复中的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(3):315-318. [42] 朱琪,羊健中,乔蕾,等.视觉代偿对系统性红斑狼疮患者平衡功能的影响[J].中国康复,2010,25(6):439-440. [43] NYLAND J, MAUSER N, CABORN DN. Sports involvement following ACL reconstruction is related to lower extremity neuromuscular adaptations, subjective knee function and health locus of control. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(9):2019-2028. [44] RODRIGUEZ KM, PALMIERI-SMITH RM, KRISHNAN C. How does anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction affect the functioning of the brain and spinal cord?A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(02):172-181. [45] 张帆,王竹影,吴志建,等.踝关节稳定程度差异对侧跳落地缓冲模式影响的研究[J].中国体育科技,2020,56(2):46-63. [46] KIPP K, PFEIFFER R, SABICK M, et al. Muscle Synergies During a Single-Leg Drop-Landing in Boys and Girls. J Appl Biomech. 2014;30(2):262-268. [47] SANTOS MJ, KANEKAR N, ARUIN AS. The role of anticipatory postural adjustments in compensatory control of posture: 1. Electromyographic analysis. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2010;20(3):388-397. [48] 温子星, 徐欣, 潘景文,等. 预测性姿势调节对人体站立受扰后姿势响应影响的研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(10):1104-1110. [49] 黄韵静,洪彰岑,黄文杰,等.视障生下阶梯动作肌肉劲度调节能力与肌电现象之研究[J].体育学报2006,39(4):47-61. [50] 张芷,王健.神经肌肉下意识前馈与反馈控制的知觉线索效应[J].心理学报,2014,46(1):50-57. [51] CHMIELEWSKI TL, TATMAN J, SUZUKI S, et al. Impaired motor control after sport-related concussion could increase risk for musculoskeletal injury: implications for clinical management and rehabilitation. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(2):154-161+253. [52] YIOU E, CADERBY T, DELAFONTAINE A, et al. Balance control during gait initiation: State-of-the-art and research perspectives. World J Orthop. 2017;8(11):815-828. [53] UEMURA K, YAMADA M, NAGAI K, et al. Fear of falling is prolonged anticipatory postural adjustment during gait initiation associated withunder dual-task conditions in older adults. Gait Posture. 2012;35(2):282-286. [54] PLATE A, KLEIN K, PELYKH O, et al. Anticipatory postural adjustments are unaffected by age and are not absent in patients with the freezing of gait phenomenon. Exp Brain Res. 2016;234(9):1-10. [55] 陈意,谢运娟,高强.预期性姿势调节的神经调控网络研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(5):568-571. [56] 冯祺,任杰.平衡与动作控制中的预期性姿势调节[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(11):1017-1025. [57] PANOUTSAKOPOULOS V, PAPACHATZIS N, KOLLIAS IA. Sport specificity background affects the principal component structure of vertical squat jump performance of young adult female athletes. Sport Health Sci. 2014; 3(3):239-247. [58] 张帆,王长生,祝捷,等. 上、下楼梯时认知任务介入对下肢协调性影响的研究[J]. 体育科学,2015,35(1):44-53. [59] BENCKE J, ZEBIS MK. The influence of gender on neuromuscular pre-activity during side-cutting. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2011;21(2):371-375. [60] KLYNE DM, KEAYS SL, BULLOCK-SAXTON JE, et al. The effect of anterior cruciate ligament rupture on the timing and amplitude of gastrocnemius muscle activation: A study of alterations in EMG measures and their relationship to knee joint stability. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2012;22(3):446-455. [61] 孙晨光,王纯.两种平衡测试中功能性踝关节不稳患者的肌肉活化特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(15):2320-2326. |
| [1] | Wang Shuai, Wang Liancheng, Zhang Shuhao, Li Fuli, Dong Jiaxing, Zhang Yajie. Correlation of the electromyography ratio of the paraspinal muscles on the convex and concave sides with Cobb angle, apical vertebra translation, and coronal balance distance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1402-1406. |
| [2] | Shang Wandi, Wang Xingze, Wei Xiaoyan. Effects of different types of abdominal support on lumbar-back muscle surface electromyography signals in people with abdominal obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1656-1661. |
| [3] | Zhang Peng, Zhang Junxia. Surface electromyography characteristics of lower limbs in heterogeneous gait environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5814-5820. |
| [4] | Ji Zhongqiu, Li Jiahui, Zhao Panchao, Jiang Guiping. Biomechanical characteristics of children with different body weights during vertical jump [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5281-5287. |
| [5] | Zhou Wenxing, Wang Lin . Effect of side cutting foot strike pattern and angle on the biomechanics of lower extremities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5184-5190. |
| [6] | Li Shanghua, Wang Haiyan. Biomechanics of lower extremities from straight forward to side-step cutting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1260-1266. |
| [7] | Xu Ping, Liang Leichao, Liang Zhenwen, Cai Ming, Chen Bo, Huang Ping, Zhang Linlin. Surface electromyogram features of the lower limb muscles in cerebral palsy children standing and walking on tiptoes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3673-3677. |
| [8] | Xia Ling, Wang Pan, Wu Chunfang, Zhang Zhaobo. Application value of surface electromyography in the repair of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1142-1148. |
| [9] | Chen Lingling, Yang Zekun, Sun Jianjun, Zhang Cun. Motion compatibility recognition of walk-aid robot based on multi-scale permutation entropy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5473-5478. |
| [10] | Lan Qingshi. Participation degree and control ability of human latissimus dorsi, trapezius, triceps, musculus and deltoid during cross support of hand ring: analysis on contribution rate of major muscle group [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 361-366. |
| [11] |
Yuan Wangshu, Chen Lixia, Shen Jianxiong, Wang Hai, Yu Keyi, Liu Ying, Zhou Jingya, Lin Youxi.
Correlation of surface electromyogram signals of the apex vertebral paraspinal muscle with Cobb angle and axial trunk rotation angle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3824-3828.
|
| [12] | Wang Meng, Li Xing, Cheng Bo, Wang Junyuan, Du Wenhua, Liu Feng. Effect of geometric design of tibial liner of knee prosthesis on its contact mechanics and kinematics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2794-2799. |
| [13] | Sun Chenguang1, Wang Chun2. Muscle activation characteristics during two balance tests in patients with functional ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2320-2326. |
| [14] | Chai Hao, Wu Ting, Shu Li, Zhang Lei. Proprioception recovery after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with and without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2332-2337. |
| [15] | Peng Yuanqiu. Muscle stiffness regulation and electromyographic changes of the lower limbs during descending stairs after visual deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2338-2344. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||