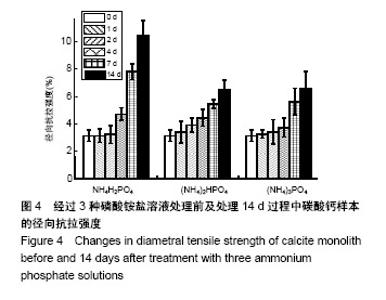
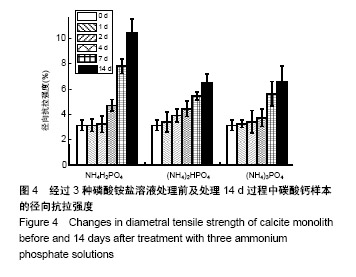
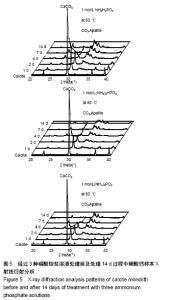
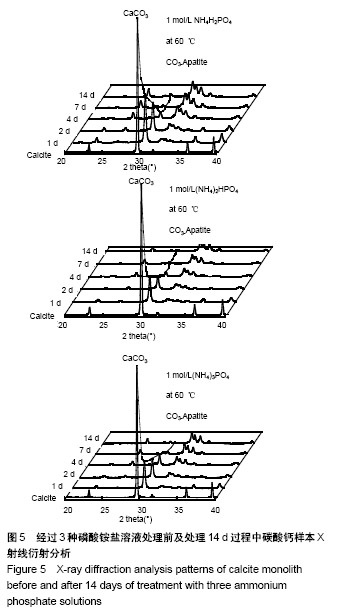
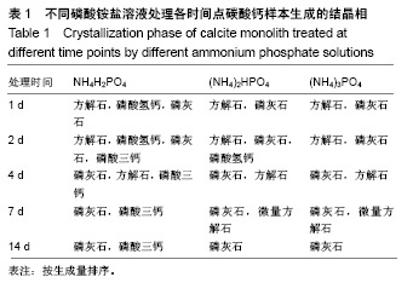
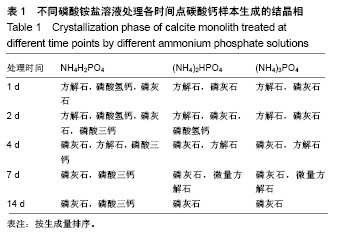
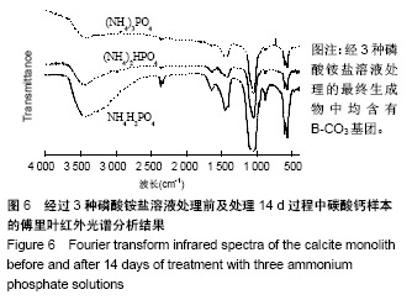
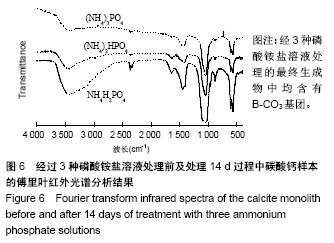
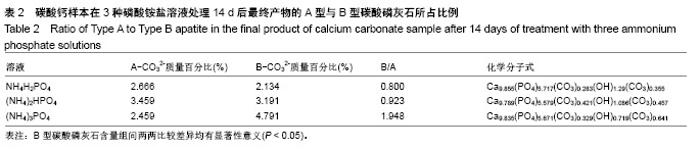
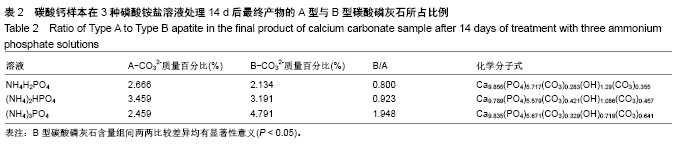
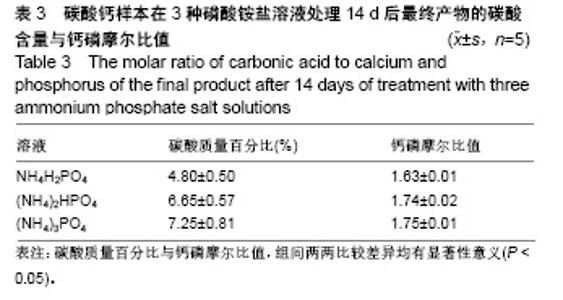
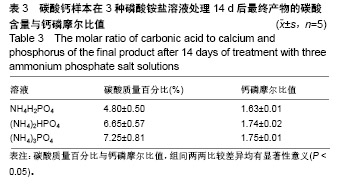
| [1]LeGeros RZ.Calcium phosphate-based osteoinductive materials.Chem Rev.2008;108(11):4742-4753.[2]Toru T, Toshiyuki,Tomohiko Y, et al.Crystal structure refinement of A-type carbonate apatite by X-ray powder diffraction.J Mater Sci Mater M.2010;45:2419-2426.[3]Nagai H, Kobayashi-Fujioka M, Fujisawa K,et al. Effects of low crystalline carbonate apatite on proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow cells.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;26(2):99.[4]Yuki S,Kanji T,Kunio I.Fabrication of arbitrarily shaped carbonate apatite foam based on the interlocking process of dicalcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate.J Mater Sci Mater M. 2017; 28:122.[5]Zakaria MN,Cahyanto A,El-Ghannam A.Calcium release and physical properties of modified carbonate apatite cement as pulp capping agent in dental application.Biomater Res. 2018; 22:35.[6]Rakhmatia YD,Ayukawa Y,Furuhashi A,et al.Carbonate Apatite Containing Statin Enhances Bone Formation in Healing Incisal Extraction Sockets in Rats.Materials (Basel).2018;11(7). pii: E1201. doi: 10.3390/ma11071201.[7]Barralet J,Akao M,Aoki H,et al.Dissolution of dense carbonate apatite subcutaneously implanted in Wistar rats.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;49(2):176-182.[8]朱庆霞,吴建青.碳酸羟基磷灰石粉体的热处理研究[J].功能材料, 2007,38(12):2055-2058.[9]张群,朱虹,刘晓红,等.气体扩散法合成花状碳酸化羟基磷灰石微球[J].硅酸盐通报,2011,30(5):1177-1181.[10]朱万华,张群,汪小红,等.碳酸钙为模板微波水热合成碳酸羟基磷灰石微球[J].安庆师范学院学报(自然科学版),2014,(3):92-97.[11]]陈继伟,沈娟,胡文远,等.以碳酸钙为模板制备空心羟基磷灰石微球及其表征[J].功能材料,2016,47(4):4169-4173.[12]钟奇伟,蔡玉荣.球形碳酸钙/羟基磷灰石的制备及药物控释[J].浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,35(5):685-690.[13]唐佩福,王继芳,卢世璧,等.可注射性多孔碳酸化羟基磷灰石骨水泥的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(12):952-955.[14]Gibson IR,Bonfield W.Novel synthesis and characterization of an AB-type carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;59(4):697-708.[15]Del Fabbro M,Bortolin M,Taschieri S,et al. Effect of autologous growth factors in maxillary sinus augmentation: a sustematic reviews.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2013;15(2):205-216.[16]Wallance SS,Tarnow DP,Froum SJ,et al. Maxillary sinus elevation by lateral window approach:evolution of technology and technique.J Evid Based Dent Pract.2012;12(3 suppl): 161-171.[17]Palmer I,Nelson J,Schatton W,et al. Biocompatibility of calcium phosphate bone cement with optimized mechanical properties.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;104(2): 308-315.[18]Liu W,Zhang J,Weiss P,et al.The influence of different cellulose ethers on both the handling and mechanical properties of calcium phosphate cements for bone substitutionActa Biomater. 2013; 9(3):5740-5750.[19]Krtiger R,Seitz JM,Ewald A,et al.Strong and tough magnesium wire reinforced phosphate cemment composites for load-bearing bone replacement.Mechan Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;20:36-44.[20]Matsuya S,Lin X,Udoh K,et al.Fabrication of porous low crystalline calcite block by carbonation of calcium hydroxide compact.J Mater Sci Mater M.2007;18:1361-1367.[21]Lin X,Matsuya S,Udoh K,et al.Effect of molding pressure on fabrication of low-crystalline calcite block.J Mater Sci Mater M. 2008;19:479-484. [22]林欣.方解石制备碳酸磷灰石骨替代材料的研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2013,29(6):555-558.[23]Mayer I,Schlam R,Featherstone JD.Magnesium-containing carbonate apatites.Inorg Biochem.1997;66(1):1-6.[24]LeGeros RZ.Apatites in biological systems.Crystal Growth Charact.1981;4:1-45. |