Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (22): 3328-3336.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.22.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
One-stage total hip arthroplasty versus femoral head arthroplasty for elderly femoral neck fractures: a meta-analysis of hip function and complications
Ye Xiang-yang, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo, Wang Hai-yu, Cheng Sheng
- Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-03-22Online:2016-05-27Published:2016-05-27 -
Contact:Ye Xiang-yang, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Ye Xiang-yang, Master, Attending physician, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ye Xiang-yang, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo, Wang Hai-yu, Cheng Sheng . One-stage total hip arthroplasty versus femoral head arthroplasty for elderly femoral neck fractures: a meta-analysis of hip function and complications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3328-3336.
share this article
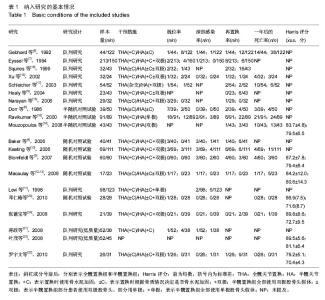
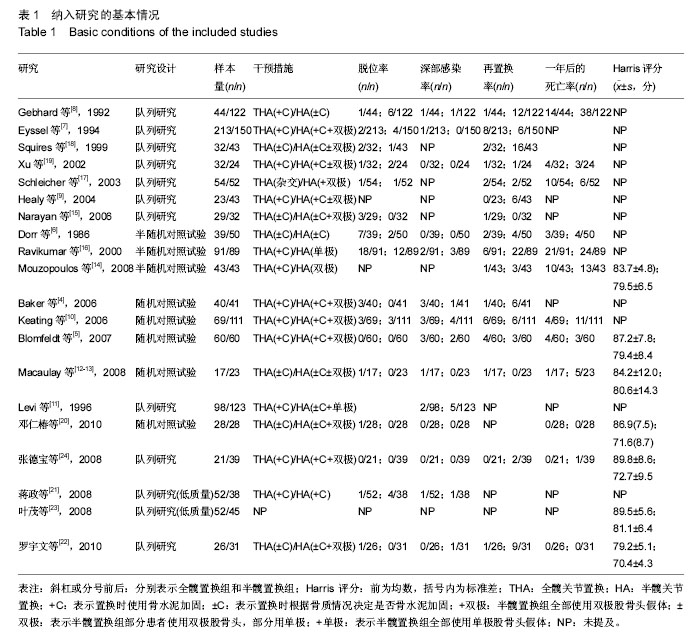
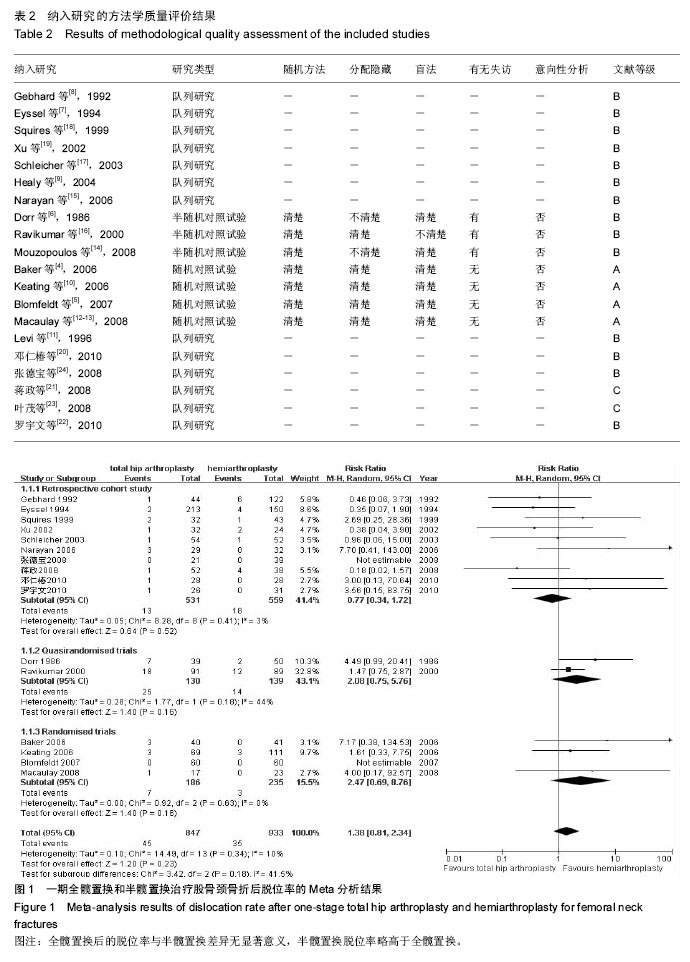
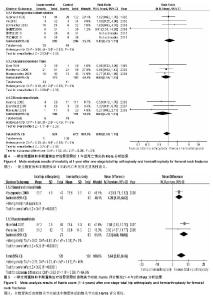
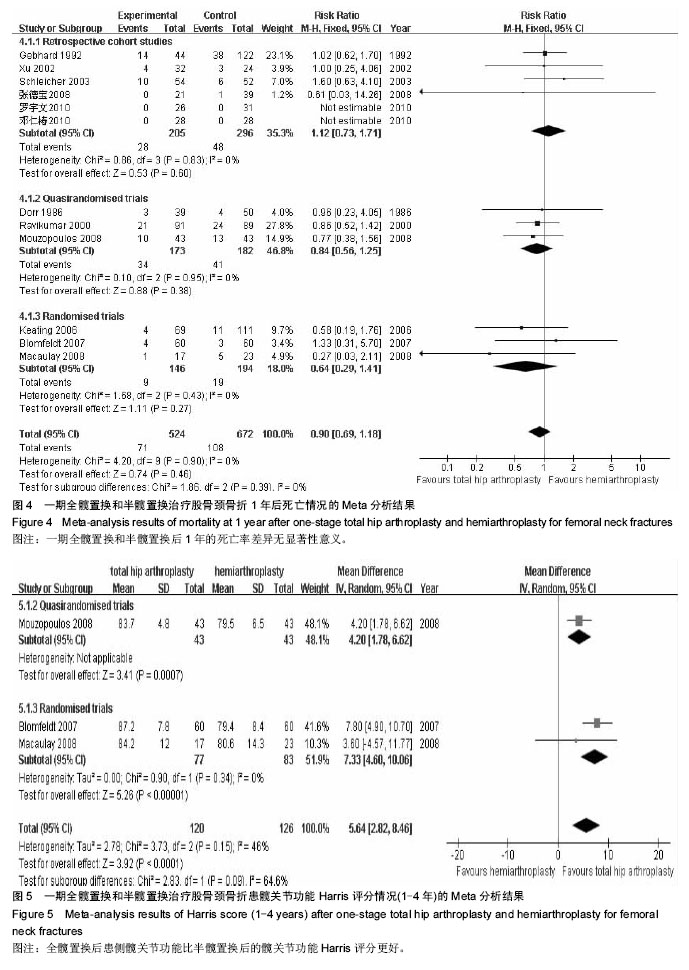
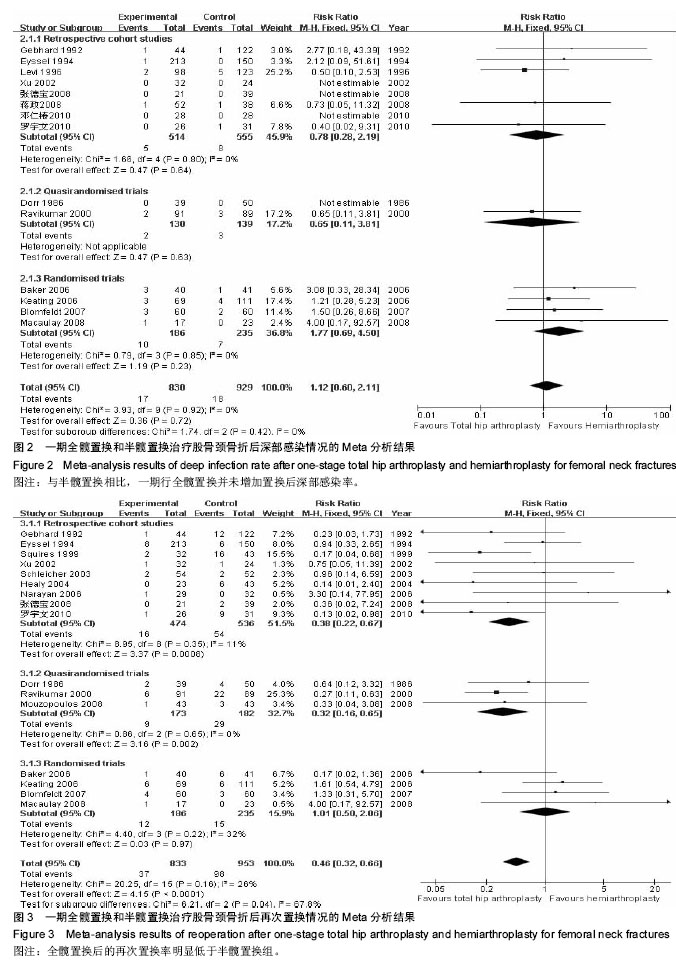
一期全髋置换和半髋置换治疗股骨颈骨折后深部感染情况的Meta分析结果:共14个研究[4-8,10-12,16, 19-22,24],显示置换后深部感染情况差异无显著性意义(RR=1.12,95%CI:0.60-2.11),见图2,表明与半髋置换相比,一期行全髋置换并未增加置换后深部感染率。 一期全髋置换和半髋置换治疗股骨颈骨折后再次置换情况的Meta分析结果:共16个研究[4-10,12,14-19, 22,24],显示置换后再次置换率差异有显著性意义(RR=0.46, 95%CI:0.32-0.66),见图3,表明全髋置换后的再次置换率明显低于半髋置换组。 一期全髋置换和半髋置换治疗股骨颈骨折1年后死亡情况的Meta分析结果:共12个研究显示置换后1年死亡率[5-6,8,10,12,14,16,17,19-20,22,24],差异无显著性意义(RR=0.90,95%CI:0.69-1.18),见图4,表明一期全髋置换和半髋置换后1年的死亡率差异无显著性意义。 一期全髋置换和半髋置换治疗股骨颈骨折患髋关节功能Harris评分情况的Meta分析结果:共3个研究[5,13,14],显示一期全髋置换和半髋置换治疗股骨颈骨折患髋关节功能Harris评分差异有显著性意义(MD=5.64,95%CI:2.82-8.46),见图5,表明全髋置换后患侧髋关节功能比半髋置换后的关节功能更好。 "
| [1] 黄梦全,余斌,胡岩君,等.非扩髓髓内钉与外固定器治疗Ⅱ/Ⅲ型开放性胫骨骨折的系统评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(22):1695-1699. [2] 陈耀龙,李幼平,杜亮,等.医学研究中证据分级和推荐强度的演进[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008,8(2):127-133. [3] 王丹,翟俊霞,牟振云,等.Meta分析中的异质性及其处理方法[J].中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(10):1115-1118. [4] Baker RP, Squires B, Gargan MF, et al. Total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty in mobile, independent patients with a displaced intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck: a randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:2583-2589. [5] Blomfeldt R, Tornkvist H, Eriksson K, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:160-165. [6] Dorr LD, Glousman R, Hoy AL, et al. Treatment of femoral neck fractures with total hip replacement versus cemented and noncemented hemiarthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1986;1:21-28. [7] Eyssel M, Schwenk W, Badke A, et al. Total endoprosthesis or dual head prosthesis in endoprosthetic management of femoral neck fractures? Unfallchirurg. 1994;97:347-352. [8] Gebhard JS, Amstutz HC, Zinar DM, et al. A comparison of total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty for treatment of acute fracture of the femoral neck. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;(282): 123-131. [9] Healy WL, Iorio R. Total hip arthroplasty: optimal treatment for displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(429): 43-48. [10] Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, et al. Randomized comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. Treatment of displaced intracapsular hip fractures in healthy older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:249-260. [11] Levi N. Early mortality after cervical hip fractures. Injury. 1996;27:565-567. [12] Macaulay W, Nellans KW, Garvin KL, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing hemiarthroplasty to total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: winner of the Dorrawa. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:2-8. [13] Macaulay W, Nellans KW, Iorio R, et al. Total hip arthroplasty is less painful at 12 months compared with hemiarthroplasty in treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture. HSS J. 2008;4:48-54. [14] Mouzopoulos G, Stamatakos M, Arabatzi H, et al. The four-year functional result after a displaced subcapital hip fracture treated with three different surgical options. Int Orthop. 2008;32:367-373. [15] Narayan KK, George T. Functional outcome of fracture neck of femur treated with total hip replacement versus bipolar arthroplasty in a South Asian population. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126:545-548. [16] Ravikumar KJ, Marsh G. Internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for displaced subcapital fractures of femur-13 year results of a prospective randomised study. Injury. 2000;31: 793-797. [17] Schleicher I, Kordelle J, Jurgensen I, et al. Femoral neck fractures in the elderly-bipolar hemiarthroplasty in total hip replacement. Unfallchirurg. 2003;106: 467-471. [18] Squires B, Bannister G. Displaced intracapsular neck of femur fractures in mobile independent patients: total hip replacement or hemiarthroplasty? Injury. 1999;30: 345-348. [19] Xu X, Liu Y, Liu J, et al. Prosthetic replacement in treatment of subcapital femoral neck fractures in the elderly. Chin J Traumatol. 2002;5:28-31. [20] 邓仁椿,洪澜,崔华明,等.全髋关节和人工股骨头置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010, 25(6): 532-533. [21] 蒋政,李静,吕玉江,等.老年移位性股骨颈骨折的术式选择与疗效比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2008,28:1720-1721. [22] 罗宇文.人工股骨头置换术与人工全髋置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的临床疗效比较[D].南宁:广西医科大学, 2010. [23] 叶茂,房振春,梅海强.人工股骨头及全髋关节置换术治疗老年人股骨颈骨折的比较研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2008,7(5):52-55. [24] 张德宝,王铁军,谷贵山.高龄股骨颈骨折患者行全髋关节置换与人工双极股骨头置换的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(9):1651-1654. [25] Hopley C, Stengel D, Ekkernkamp A, et al. Primary total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in older patients: systematic review. BMJ. 2010;340:1-14. [26] Kester BS, Minhas SV, Vigdorchik JM, et al. Total knee arthroplasty for posttraumatic osteoarthritis: is it time for a new classification? J Arthroplasty. 2016. [27] Bern MM, Hazel D, Deeran E, et al. Low dose compared to variable dose Warfarin and to Fondaparinux as prophylaxis for thromboembolism after elective hip or knee replacement surgery; a randomized, prospective study. Thromb J. 2015;13:32. [28] Lim SJ, Yeo I, Park CW, et al. Outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:278. [29] Li J, Jing JH, Shi ZJ, et al. Case-control study on effect of rivaroxaban on the risk of hidden bleeding after total hip arthroplasty. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(1): 34-37. [30] Mallen-Trejo A, Torres-Gómez A. Perioperative epidemiology of total hip arthroplasty. Acta Ortop Mex. 2013;27(6):358-362. [31] Levitan B, Yuan Z, Turpie AG, et al. Benefit-risk assessment of rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip or knee arthroplasty. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014;10: 157-167. [32] Chang CH, Chang Y, Chen DW, et al. Topical tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates associated with primary total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1552-1557. [33] Turpie AG, Haas S, Kreutz R, et al. A non-interventional comparison of rivaroxaban with standard of care for thromboprophylaxis after major orthopaedic surgery in 17,701 patients with propensity score adjustment. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(1): 94-102. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||