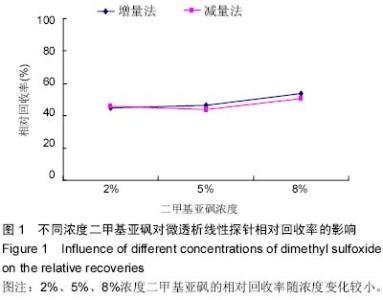
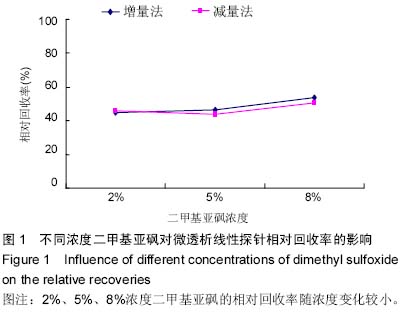
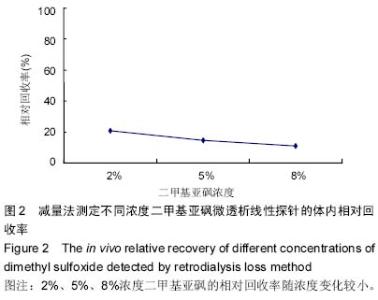
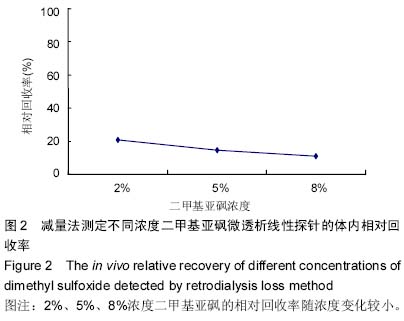
| [1] 马丽,李青旺,吴民耀.二甲基亚砜对猪精液冷冻保存效果研究[J].动物医学进展,2014,35(5):56-61.
[2] 方志聪,戚智.二甲基亚砜对生物膜的作用机理[J].生物物理学报, 2012,28(8):638-643.
[3] Holmgaard R,Nielsen JB,Benfeldt E.Microdialysis sampling for investigations of bioavailability and bioequivalence of topically administered drugs: current state and future perspectives.Skin Pharmacol Physiol.2010;23(5):225-243.
[4] 吴兆恩,王丹巧.多位点微透析技术在药代动力学研究中的应用[J].中国中药杂志,2010,35(13):1765-1768.
[5] 徐铭,李范珠.微透析取样技术及其在体内药物分析中的应用[J].药物分析杂志,2006,26(7):1030-1034.
[6] 方志聪,戚智.二甲基亚砜对生物膜的作用机理[J].生物物理学报, 2012,28(8):638-643.
[7] KLIGMAN AM.TOPICAL PHARMACOLOGY AND TOXICOLOGY OF DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. 1.JAMA. 1965; 193:796-804.
[8] 王丹,石力夫,胡晋红,等.微透析联用反相高效液相色谱对大鼠皮肤葛根素的药代动力学研究[J].分析化学,2008,36(10):1391- 1395.
[9] Kligman AM. Dimethylsulfoxide-part 2.JAMA.1965; 193(11): 923-928.
[10] Ashwood-Smith MJ,Warby C.Protective effect of low and high molecular weight com pounds on the stability of catalase subjected to freezing and thawing.Cryobiology.1972; 9(2):137-140.
[11] Arakawa T,Carpenter JF,Kita YA,et al.The basis for toxicity of certain cryoprotectants: An hypothesis.Cryobiology. 1990; 27(4):401-415.
[12] Anchordoguy TJ,Rudolph AS,Carpenter JF,et al.Modes of interaction of cryoprotectants with membrane phospholipids during freezing. Cryobiology.1987;24(4):324-331.
[13] Jin B,Higashiyama R,Nakata Y.Rapid movement of water and cryoprotectants in pig expanded blastocysts via channel processes: its relevance to their higher tolerance tocryopreservation.Biol Reprod.2013;89(4):87.
[14] Yildiz C,Mullen B,Jarvi K,et al.Effect of different cryoprotectant agents on spermatogenesis efficiency in cryopreserved and grafted neonatal mouse testicular tissue. Cryobiology.2013;67(1):70-75.
[15] 刘新峰,丁向彬,郝志明.昆明小白鼠卵巢玻璃化冷冻的研究[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2014,57(1):167-169.
[16] Wu JY,Sun YX,Wang AB,et al.Effect of newborn bovine serum on cryopreservation of adult bovine testicular tissue. Andrologia. 2014;46(3):308-312.
[17] Johnson AE,Freeman EW,Wildt DE,et al.Spermatozoa from the maned wolf (Chrysocyon brachyurus) display typical canid hyper-sensitivity to osmotic and freezing-induced injury, but respond favorably to dimethyl sulfoxide. Cryobiology.2014; 68(3):361-370.
[18] Lee YA,Kim YH,Ha SJ,et al.Effect of sugar molecules on the cryopreservation of mouse spermatogonial stem cells.Fertil Steril.2014;101(4):1165-1175.
[19] Miliorini AB.A morphological classification proposal for curimba(Prochilodus lineatus)sperm damages after cryopreservation.Aqu Res.2011;42(2):17-187.
[20] Varela Junior AS,Goularte KL,Alves JP,et al.Methods of cryopreservation of Tambaqui semen, Colossoma macropomum.Anim Reprod Sci.2015;157:71-77.
[21] Sanches EG,Oliveira IR,Serralheiro PC,et al. Cryopreservation of mutton snapper ( Lutjanus analis) sperm.An Acad Bras Cienc.2013;85(3):1083-1091.
[22] Bai C,Wang X, Lu G,et al.Cooling rate optimization for zebrafish sperm cryopreservation using a cryomicroscope coupled with SYBR14/PI dual staining. Cryobiology. 2013; 67(2):117-123.
[23] Robles V,Martínez-Pastor F,Petroni G,et al.Cryobiology of cephalopod (Illex coindetii) spermatophores. Cryobiology. 2013;66(3):288-294.
[24] Liu Y,Xu T,Robinson N,et al.Cryopreservation of sperm in farmed Australian greenlip abalone Haliotis laevigata. Cryobiology.2014;68(2):185-93.
[25] 杨春玲,赵永贞,陈秀荔,等.南美白对虾精子超低温冷冻保存技术研究[J].南方农业学报,2013,44(8):1382-1389.
[26] Tsai S,Kuit V,Lin ZG,et al.Application of a functional marker for the effect of cryoprotectant agents on gorgonian coral (Junceella juncea and J. fragilis) sperm sacs.Cryo Letters. 2014;35(1):1-7.
[27] Kozlowska-Skrzypczak M,Kubiak A,Bembnista E,et al.Analysis of the effect of cryoprotectant medium composition to viability of autologous hematopoietic cells collected by leukapheresis.Transplant Proc. 2014;46(8): 2535-2538.
[28] de Wreede L,Scholten M.Should the standard dimethyl sulfoxide concentration be reduced Results of a European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation prospective noninterventional study on usage and side effects of dimethyl sulfoxide.Transfusion.2014;54(10):2514-2522.
[29] Fry LJ,Querol S,Gomez SG,et al.Assessing the toxic effects of DMSO on cord blood to determine exposure time limits and the optimum concentration for cryopreservation.Vox Sang. 2015. [Epub ahead of print]
[30] 吴洁莹,陆琰,陈劲松,等.脐血血浆替代胎牛血清培养脐带间充质干细胞及冷冻保存[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(37): 5947- 5954.
[31] 杨强,李建民,夏群.深低温保存的节段性部分脱钙异体骨关节移植修复兔骨关节缺损[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2013,10(3): 11-16.
[32] Jia X,Yu Y,Li D.Investigation on the effect of trehalose on alpha-actinin in cryopreserved human skin.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2008;22(4):446-469.
[33] Roy S,Arora S,Kumari P,et al.A simple and serum-free protocol for cryopreservation of human umbilical cord as source of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells. Cryobiology. 2014;68(3):467-472.
[34] Rajagopal K,Chilbule SK,Madhuri V.Viability, proliferation and phenotype maintenance in cryopreserved human iliac apophyseal chondrocytes.Cell Tissue Bank.2014;15(1): 153-163.
[35] Forriol F,Longo UG,Alvarez E,et al.Scanty integration of osteochondral allografts cryopreserved at low temperatures with dimethyl sulfoxide.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2011;19(7):1184-1191.
[36] Wu J,Lu Z,Nie M,et al.Optimization of cryopreservation procedures for porcine endothelial progenitor cells.J Biosci Bioeng.2012;113(1):117-123.
[37] Kawase T,Kogami H,Nagata M,et al.Manual cryopreservation of human alveolar periosteal tissue segments: Effects of pre-culture on recovery rate.Cryobiology.2011;62(3):202-209.
[38] Liu G,Li Y,Sun J,et al.Effect of cryopreservation on growth and osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2010;24(10):1224-267.
[39] Xia Z,Duan X,Murray D,et al.A method of isolating viable chondrocytes with proliferative capacity from cryopreserved human articular cartilage.Cell Tissue Bank. 2013;14(2): 267-1222.
[40] Kim BY,Nam BM,Lee KM.Effect of preservation conditions on cartilage tissue for cell transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2014; 46(4):1139-1144.
[41] Atkins P. Physical Chemistry 8ed, New York: W. H. Freeman and Company,2006:136-173.
[42] 王丹,石立夫,胡晋红.微透析技术探针回收率的影响因素研究进展[J].国际药学研究杂志,2008,3(4):261-266. |