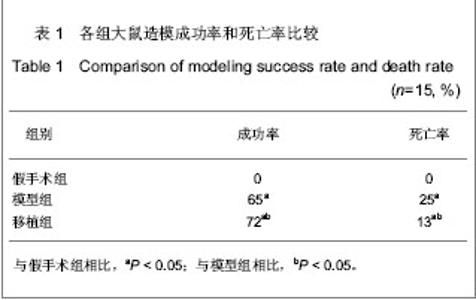
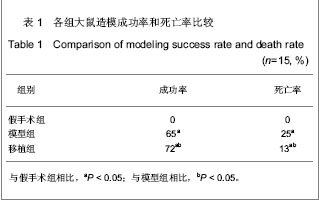
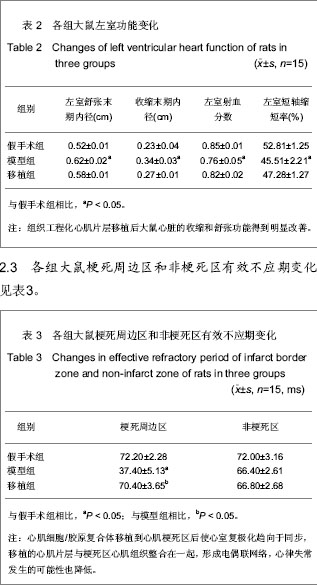
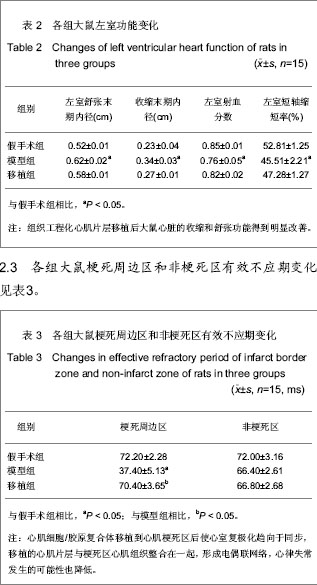
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (24): 4401-4408.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.24.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cardiac function and electrophysiological characteristics in myocardial infarction rats after tissue engineered cardiac patch transplantation
Adila·Azhati, Zhao Long, Wang Qian, Ma Yi-tong
- Cardiovascular Research Institute, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2012-10-17Revised:2012-11-27Online:2013-06-11Published:2013-06-11 -
Contact:Ma Yi-tong, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Cardiovascular Research Institute, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China mayitong@126.com -
About author:Adila?Azhati☆, M.D., Associate chief physician, Cardiovascular Research Institute, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 1057038365@qq.com Zhao Long★, Master, Attending physician, Cardiovascular Research Institute, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 294733342@qq.com Adila?Azhati and Zhao Long contributed equally to this work -
Supported by:Scientific Research Funds of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, No. 2012ZZGC06*; the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2009211B20*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Adila•Azhati, Zhao Long, Wang Qian, Ma Yi-tong. Cardiac function and electrophysiological characteristics in myocardial infarction rats after tissue engineered cardiac patch transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(24): 4401-4408.
share this article
| [1] Zimmermann WH, Melnychenko I, Wasmeier G,et al. Engineered heart tissue grafts improve systolic and diastolic function in infarcted rat hearts. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):452-458.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Engineered%20heart%20tissue%20grafts%20improve%20systolic%20and%20diastolic%20function%20in%20infarcted%20rat%20hearts[2] Leor J, Patterson M, Quinones MJ, et al. Transplantation of fetal myocardial tissue into the infarcted myocardium of rat. A potential method for repair of infarcted myocardium. Circulation. 1996;94(9 Suppl):II332-336. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Transplantation%20of%20fetal%20myocardial%20tissue%20into%20the%20infarcted%20myocardium%20of%20rat.%20A%20potential%20method%20for%20repair%20of%20infarcted%20myocardium[3] Leor J, Aboulafia-Etzion S, Dar A, et al. Bioengineered cardiac grafts: A new approach to repair the infarcted myocardium. Circulation. 2000;102(19 Suppl 3):III56-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11082363[4] E Z. Beijing:Beijing Publishing House. 1995:56.鄂征. 组织培养和分子细胞学技术.北京:北京出版社,1995:56. [5] Wang T,Yu ZB,Xie MJ,et al. Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2003;24(2):Feng2.王涛,余志斌,谢满江,等.新生大鼠心肌细胞培养技巧[J].第四军医大学学报,2003,24(2):封2. http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=4&CurRec=2&recid=&filename=DSJY200302000&dbname=CJFD2003&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[6] Le Coz F, Funck-Brentano C, Morell T, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of the effects of oral and intravenous administrations of dofetilide on ventricular repolarization.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1995;57(5):533-542.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Pharmacokinetic%20and%20Pharmacodynamic%20modeling%20of%20the%20effects%20of%20oral%20and%20intravenous%20administrations%20of%20dofetilide%20on%20ventricular%20repolarization[7] Ren CL,Gao CQ,Li LB. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2007;45(22):1578-1580.任崇雷,高长青,李力兵.细胞心肌成形术对梗死后心室重构的影响[J]. 中华外科杂志,2007,45(22):1578-1580.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_zhwk200722024[8] Yu HC. Yinanbing Zazhi. 2009;8(4):251-253.于慧春.骨髓干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死后心室重构的研究进展[J].疑难病杂志,2009,8(4):251-253.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_ynbzz200904035[9] Fink C, Ergün S, Kralisch D, et al. Chronic stretch of engineered heart tissue induces hypertrophy and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2000;14(5):669-679.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Chronic%20stretch%20of%20engineered%20heart%20tissue%20induces%20hypertrophy%20and%20functional%20improvement[10] Zimmermann WH, Schneiderbanger K, Schubert P, et al. Tissue engineering of a differentiated cardiac muscle construct.Circ Res. 2002;90(2):223-230.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Tissue%20Engineering%20of%20a%20Differentiated%20Cardiac%20Muscle%20Construct[11] Eschenhagen T, Didié M, Münzel F, et al. 3D engineered heart tissue for replacement therapy. Basic Res Cardiol. 2002;97 Suppl 1:I146- I152.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12479248[12] Freed LE, Vunjak-Novakovic G. Microgravity tissue engineering. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1997;33(5):381-385.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Microgravity%20tissue%20engineering%5BJ%5D.%20In%20Vitro%20Cell%20Dev%20Biol%20Anim[13] Hu XR,Jiang H. Xinxueguanbingxue Jinzhan. 2007;28(3):460-463.胡笑容,江洪.缝隙连接重构和室性心律失常[J].心血管病学进展,2007,28(3):460-463.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_xxgbxjz200703039[14] Wen HZ,Jiang H,Hu XR,et al. Wuhan Daxue Xuebao. 2010;32(2):170-173.温华知,江洪,胡笑容,等.美托洛尔对大鼠心肌梗死周边区缝隙连接蛋白43的影响[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2010,32(2):170-173.[15] Severs NJ, Bruce AF, Dupont E, et al. Remodelling of gap junctions and connexin expression in diseased myocardium. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;80(1):9-19.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Remodelling%20of%20gap%20junctions%20and%20connexin%20expression%20in%20diseased%20myocardium[16] Severs NJ.Gap junction remodeling and cardiac arrhythmogenesis: cause or coincidence. J Cell Mol Med. 2001;5(4):355-366.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12067469[17] Bernus O, Zemlin CW, Zaritsky RM, et al. Alternating conduction in the ischaemic border zone as precursor of reentrant arrhythmias: a simulation study. Europace. 2005;7 Suppl 2:93-104.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Alternating%20conduction%20in%20the%20ischaemic%20border%20zone%20as%20precursor%20of%20reentrant%20arrhymias%3Aa%20simulation%20study[18] Peters NS, Coromilas J, Severs NJ, et al. Disturbed connexin43 gap junction distribution correlates with the location of reentrant circuits in the epicardial border zone of healing canine infarcts that cause ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 1997;95(4):988-996.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Disturbed%20connexin43%20gap%20junction%20distribution%20correlates%20with%20the%20location%20of%20reentrant%20circuits%20in%20the%20epicardial%20border%20zone%20of%20healing%20canine%20infarcts%20that%20cause%20ventricular%20tachycardia[19] Qin D, Zhang ZH, Caref EB, et al. Cellular and ionic basis of arrhythmias in postinfarction remodeled ventricular myocardium.Circ Res. 1996;79(3):461-473.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Cellular%20and%20ionic%20basis%20of%20arrhythlnias%20in%20post-infaretion%20remodeled%20ventrieular%20myoeardium[20] Peters NS, Green CR, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. Reduced content of connexin43 gap junctions in ventricular myocardium from hypertrophied and ischemic human hearts. Circulation. 1993;88(3):864-875.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8394786[21] Wu AM,Wang SR,Zhang DM,et al. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xinnao Xueguanbing Zazhi. 2007;5(11):1078-1080.吴爱明,王硕仁,张冬梅,等.扶正化瘀胶囊对心肌梗死大鼠心肌缝隙连接蛋白43表达的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2007,5(11):1078-1080.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=0&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=ZYYY200711024&dbname=CJFD2007&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[22] Menasché P, Hagège AA, Scorsin M,et al. Myoblast transplantation for heart failure. Lancet. 2001;357(9252):279-280.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Lancet%2C+2001%2C+357(9252)%3A+279[23] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature. 2001;410(6829):701-705.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Nature%2C+2001%2C+410+(6829)%3A+701[24] Akins RE, Schroedl NA, Gonda SR, et al. Neonatal rat heart cells cultured in simulated microgravity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1997;33(5):337-343.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9196891 |
| [1] | Tan Wei, Lv Hai, Zhou Chu-song. Acellular matrix scaffold for tissue-engineered intervertebral disc which is closest to the normal three-dimensional structure of the nucleus pulposus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1289-1294. |
| [2] | Zhang Zeng-guang, Qin Ming-fang. Optimized effect of connexin 43 gene silencing on the proliferation of fetal liver stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2133-2137. |
| [3] | Fan Yan, Wang Jian-jun, Wei Feng, Fan Xiao-hai, Ma Ai-qun. Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on inflammatory response and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 900-905. |
| [4] | Li Bing-ting, Jia Ying-zhen, Liu Zhi-fang, Song Yuan, Hou Xiao-wei. Effect of freeze-dried bone xenograft and platelet-rich fibrin compound on osteogenesis and osseointegration of alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8376-8381. |
| [5] | Kang Ting, Wang Gang, Liu Yi, Liu Gang-qiang. In vitro construction of tissue engineered adipose using vascular endothelial growth factor 165 gene-modified human adipose derived stem cells with chitosan-surface modified silk fibroin scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8450-8455. |
| [6] | Wang Teng-bin, Zhu Hui, Li Tian-shi . Development of chitosan and its derivative scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8498-8503. |
| [7] | Wu Guang-wen, Ye Jin-xia, Zheng Chun-song, Chen Wen-lie, Liu Xian-xiang, Ye Hong-zhi . Effect of Tougu Xiaotong capsule on articular cartilage changes in rat models of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7924-7929. |
| [8] | Yang Shao-ling, Tang Ke-qiang, Tao Jun-jia, Gu Fang-fang, Guo Qing-kui. Establishing myocardial infarction animal models by the median sternotomy versus the left intercostal thoracotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7930-7937. |
| [9] | Zhu Wei-hong, Chen You, Wang Wan-chun, Huang Guo-liang, Chou Ke, Chen Xian-li. Autogenous tendon transplantation for repair of grade III medial collateral ligament injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7463-7467. |
| [10] | Lin Chu-wei, Zhou Sheng-hua, Dai Hai-ying, Deng Ping, Huang Hong-guang, Yin Zhi-lan, Guan Xian-song. Survival of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after transplantation into the rat infarcted myocardium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6628-6632. |
| [11] | Ruan Zheng, Yin Qing-shui, Zhang Yu. Development of articular cartilage repair technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4724-4729. |
| [12] | Sun Hao, Yan Yu-sheng, Chen Qun-qing, Li Shao-bin. Fibroin in small-caliber vascular prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2576-2581. |
| [13] | Bai Shu-meng, Liu Xi. A three-dimensional nanofiber scaffold provides an appropriate microenvironment for stem cell regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2594-2600. |
| [14] | Chen Yue-ping, Gao Hui, Chen Liang, Dong Pan-feng, Yin Qing-shui. Alcohol affects the femoral head intramedullary adipocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(35): 6221-6227. |
| [15] | Bai Wen-yuan, Gu Hong-sheng, Liao Zhen-hua, Liu Wei-qiang. Clinical application of artificial lumbar disc replacement: Present and future [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(35): 6321-6326. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||