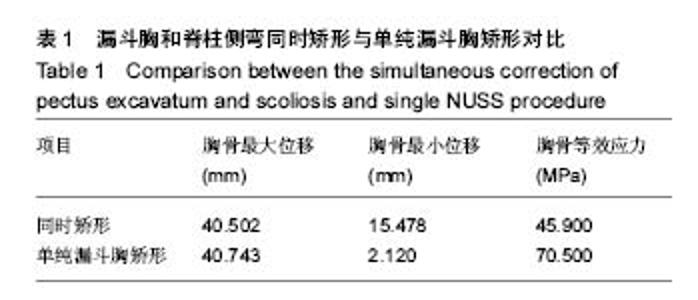
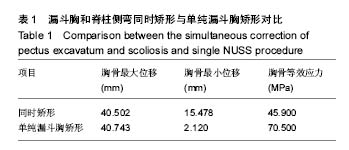
| [1] 梁林,叶金铎,王志芹,等. Nuss手术矫正漏斗胸过程的数值模拟[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2011,15(4):316-318.[2] Felts E, Jouve JL, Blondel B, et al. Child pectus excavatum: Correction by minimally invasive surgery. Orthop Traumato Surg Res. 2009;95 (3) :190-195.[3] Dean C, Etienne D, Hindson D, et al.Pectus excavatum (funnel chest): a historical and current prospective, Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34(7):573.[4] Iida H. Surgical repair of pectus excavatum. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;58(2):55-61. [5] 曹强,王启,许瑞彬. 漏斗胸的诊断与外科治疗[J]. 辽宁医学院学报,2014,35(1):98-101. [6] 韩冰,寇瑛琍. 漏斗胸患者Nuss手术前后肺功能的对比分析[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2014,45(1):177-178. [7] 赵媚娇. 漏斗胸合并脊柱侧弯微创矫形过程的数值模拟[D]. 天津理工大学, 2015.[8] 孙相华,洪志鹏.漏斗胸发病机制研究进展[J].医学综述, 2006 , 12 (20) :1261-1263.[9] 冯杰雄.漏斗胸病因学研究进展[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2002 , 23 (2) :172-173.[10] Frick SL. Scoliosis in children with anterior chest wall deformities. Chest Surg Clin North Am. 2000;10(2): 427-436.[11] 戈烽,廖泉,肖蜀梅,等. Wada手术治疗成人漏斗胸[J]. 综合临床医学,1996,12(3):27-28. [12] 苏群,张宝,韩志峰. Nuss手术与胸骨翻转术治疗漏斗胸效果比较[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2013,12:124-125. [13] 况军. 改良胸骨抬举术治疗儿童先天性漏斗胸临床分析[J]. 现代诊断与治疗,2013,24(10):2251-2252.[14] 曾骐,张娜,范茂槐,等. Nuss手术与改良Ravitch手术的对比研究[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志, 2005, 26(8): 397-398.[15] 余升华,尹得龙,杨展翔.青少年脊柱侧弯的研究进展[J].岭南现代临床外科, 2014, 14 (6) :708-711.[16] Cobb J.Outline for the study of scoliosis. Instruct Course Lect. 1947;5 :261-275.[17] 唐云德.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的脊柱后路矫形及其影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,20(48):7770-7775.[18] 杨卫周,李涛,李锋,等.运用CT三维重建测量重度先天性脊柱侧凸Cobb角的临床应用[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015,15(34): 6664-6667+6707.[19] 黄忍,王星,李志军,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯的诊治进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(4):472-475.[20] Emans JB, Kaelin A, Bance P, et al.The Boston bracing system for idiopathic scoliosis. Follow-up results in 295 patients. Spine. 1986;11(8) :792-801.[21] 赵自平,兰海峰,冯建忠.Providence夜用型支具治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的效果分析[J].中国当代医药, 2014, 21(17) :26-28.[22] 柳思羽,陈庆贺,王仑.非手术方法治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013 , 21(7) :722-725.[23] 赵吕国,蒋仁伟,陆炳全,等. 鲁克(luque)手术在脊柱矫形外科的应用[J].川北医学院学报, 1988,14(3): 62-65.[24] Cotrel Y, Dubousset J. Nouvelle technique dosteosynthese rechidienne segmentaire Par voie posterieure.Revue de Chirurgie Orthopedique. 1984;70 :489.[25] 陈丽萍,刘安琴.C-D手术矫治脊柱侧凸的护理[J].中华护理杂志, 2001, 36 (1) :29-31.[26] 叶启彬,主编.脊柱侧弯的预防与治疗[M].北京:北京医科大学/中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1994.[27] 叶启彬,主编.脊柱侧弯外科学[M].北京:中国协和医科大学联合出版社,2003.[28] 杨智君. 32例漏斗胸患者行微创矫形术(NUSS)的麻醉处理[D]. 中国医科大学, 2012.[29] 梁海龙,刘吉福,赵京,等.Nuss手术矫正成年人漏斗胸22例临床分析[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2011, 39(1): 76-78.[30] 刘士杰.6例胸腔镜下漏斗胸矫形术患儿的护理[J].中华护理杂志, 2008, 43(7): 603-604.[31] Chang PY, Hsu ZY, Chen DP, et al. Preliminary analysis of the forces on the thoracic cage of patients with pectus excavatum after the Nuss procedure. Clin Biomech. 2008;23(7):881-885.[32] 胡辉莹,何忠杰,吕丽萍,等.应用Mimics软件辅助重建人体胸廓三维有限元模型的研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2008,33(3):273-275.[33] 胡辉莹,钟世镇,聂晨阳. 人体骨骼生物力学中有限元分析的研究进展[J]. 广东医学,2007,28(9):1532-1534.[34] 胡辉莹,钟世镇,张美超,等.人体胸廓三维有限元模型的建立及应力分析研究[J]. 中国急救医学,2007,27(12):1098-1100+1164.[35] 胡辉莹,何忠杰,张美超,等. 人体胸廓胸外按压的生物力学测试[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(5):592-594.[36] Nagasao T, Noquchi M, Miyamoto J, et al. Dynamic effects of the Nuss procedure on the spine in asymmetric pectus excavatum. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg.2010;140(6): 1294-1299.[37] Ye JD, Liu BL, Liu JF, et al. Research on electrical measurement experiment of deformation of artificial thorax model. J Mech Med Biol. 2016. doi: 10.1142/ S0219519417500 579.[38] 彭春政,张胜年,陆爱云.人体躯干骨骼-肌肉-韧带结构三维有限元模型的建立和验证[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2010,29(6):702-705.[39] 田慧中.脊柱侧弯合并漏斗胸的诊断与治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(5):393-394.[40] Bafus BT, Chiravuri D, van der Velde ME, et al.Severe hypotension associated with the prone position in a child with scoliosis and pectus excavatum undergoing posterior spinal fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(6):451-454.[41] 张春月. 漏斗胸合并脊柱侧弯微创矫形数值模拟计算模型的研究[D].天津理工大学, 2016. |