Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (44): 6590-6598.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.44.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bridging external fixation combined with Kirschner-wire fixation versus volar locked plate fixation for unstable fractures of the distal radius
Lian Zhi-ming1, Yang Jing2, Zhang Tai-liang1, Ma Chuang1, Liu Qiang3, Yang Guang-zhong1
- 1Department of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, 3Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2016-09-07Online:2016-10-28Published:2016-10-28 -
Contact:Yang Guang-zhong, Master, Chief physician, Department of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Lian Zhi-ming, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81560350
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lian Zhi-ming, Yang Jing, Zhang Tai-liang, Ma Chuang, Liu Qiang, Yang Guang-zhong. Bridging external fixation combined with Kirschner-wire fixation versus volar locked plate fixation for unstable fractures of the distal radius[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6590-6598.
share this article
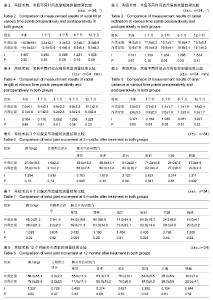
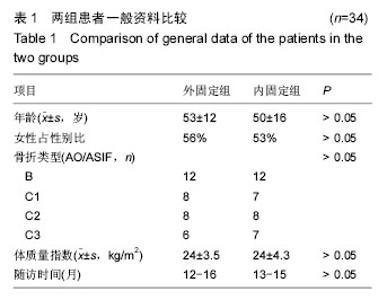
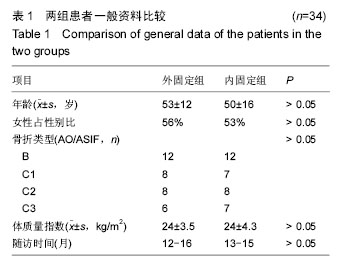
2.4 两组影像学结果比较 见表2-5。 所有随访期内,患者的掌倾角、尺偏角、桡骨高度、尺骨变异组间差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.5 两组腕关节功能活动度及Cooney评分比较 见表6-9。 每组在每一个连续的评估中,手腕的活动范围均被改善(表6-8),测量结果显示内固定组的活动范围较好。在3个月随访时,腕关节的旋前(P=0.011)、旋后(P= 0.05)、掌屈(P=0.045)和桡偏(P= 0.002)2组差异均有显著性意义。到6个月时这些差异有所减小,然而腕关节掌屈、旋前活动度仍较好(P分别为0.001和0.001)。这些差异在1年时仍存在。尽管内固定组的腕关节活动度较好,但是2组间的握力在1年随访期的任何时间点差异无显著性意义。在每个随访时间获得的平均目测类比评分显示2组间相似,差异无显著性意义。由表9可见,术后3,6,12个月对2组患者进行腕关节Cooney评分,行对照配对t 检验,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。同时对2组患者术后12个月进行优良率评定,其中外固定组优13例,良16例,可5例,优良率85%(29/34);内固定优14例,良16例,可4例,优良率88%(30/34)。"
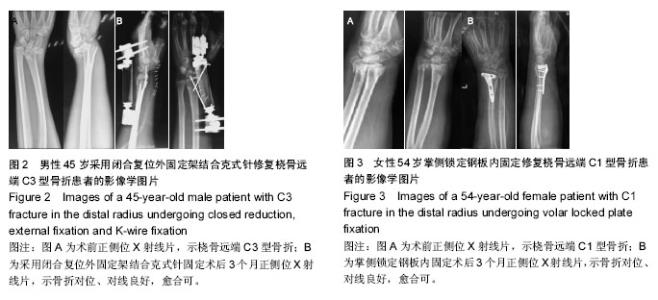
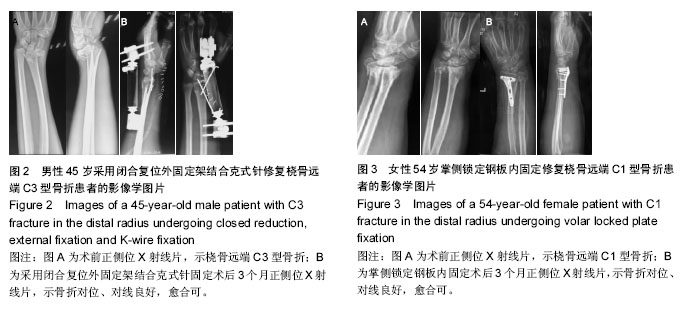
2.6 典型病例 典型病例1:患者,男,45岁,车祸致左侧桡骨远端骨折,入院后行左侧桡骨远端骨折闭合复位外固定, 术后给予防治感染、消肿对症治疗,复查X射线片示:骨折对位对线良好,并于医生指导下行患肢各关节功能锻炼。术后1,3,6,12个月随访,腕关节功能恢复良好,术后3个月时其旋前、旋后、掌屈及桡偏恢复较内固定组差,随着时间推移,差别逐渐减小,到12个月时,与内固定组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图2。 典型病例2:患者,女,54岁,摔伤致左侧桡骨远端骨折,完善相关检查后行左侧桡骨远端骨折切开复位内固定,术后复查X射线片见骨折对位对线良好,术后1,3,6,12个月对患者进行临床及影像学随访,结果显示术后早期腕关节活动度较外固定好,但远期效果趋于一致,见图3。 2.7 两组间并发症比较 2组间的并发症发生率是相似的,外固定组有5例(15%)患者出现并发症,钢板组有4例(12%)患者出现并发症,差异无显著性意义(P= 0.45)。在外固定组中,2例患者出现神经炎症状,给予营养神经药物配合物理治疗后症状改善;2例发生钉道轻度感染,经换药及抗生素治疗后3周感染控制;1例患者由于术后关节僵硬行关节囊切除术+肌腱松解术。在内固定组中3例患者因术后伤口感染行抗生素治疗后伤口愈合;1例拇长伸肌腱断裂行肌腱移植术后拇指背伸功能恢复良好。"
| [1] Chung KC, Watt AJ, Kotsis SV et al. Treatment of unstable distal radial fractures with the volar locking plating system. J Bone Jt Surg. 2006;88-A: 2687-2694. [2] Ruch DS, McQueen MM. Distal radius and ulna fractures.In: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P (eds) Rockwood and green’s fractures in adults, 7th edn. Wolters Kluver, Philadelphia, 2010: 829-880. [3] Fernandez DL, Wolfe SW. Distal radius fractures. In:Green DP, Hotchkiss RN, Pederson WC, Wolfe SW (eds) Green’s operative hand surgery, 5th edn. Churchill Livingstone,Philadelphia, 2005: 645-710. [4] Geissler WB, Fernandez DL. Percutaneous and limited open reduction of the articular surface of the distal radius. J Orthop Trauma. 1991;5:255-264. [5] Hove LM, Furnes O, Nilsen PT et al. Closed reduction and external fixation of unstable fractures of distal radius. Scand JPlast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 1997; 31:159-164. [6] Cooney WP. Fratures of the distal radius:a modem treatment based classification. Orthop Clin North(Am). 1993;24:21l-216. [7] Knirk JL,Jupiter JB. Intraarticular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg. 1986;68:659-674. [8] Wright TW, Horodyski M,Smith DW,et al. Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures:ORIF with a volar fixed-angle tine plate versus external fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30(2):289-299. [9] Margaliot Z,Haase SC,Kotsis SV,et al.A meta-analysis of out-comes of external fixation versus plate osteosynthesis for unstable distal radius fractures.J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30(6):1185-1199. [10] 王岩,周永刚,毕文志,等主译. 坎贝尔骨科手术学[M]. 11版. 北京:人民军医出版社,2009. [11] Riis J, Fruensgaard S. Treatment of unstable distal Colles’fractures with external fixation. J Hand Surg. 1989; 4:145-148. [12] Rikli DA, Kupfer K, Bodoky A . Long term results of external fixation distal radius fractures. J Trauma. 1998;44:970-976. [13] Sanders RA, Keppel FL, Waldrop JI. External fixation ofdistal radius fractures: results and complications. J Hand Surg. 1991; 16:385-391. [14] Liporace FA,Gupta S,Jeong GK,et al.A biomechanical comparison of a dorsal 3.5ram T-plate and a volar fixed-angle plate in a modal of dorsally unstable distal radius fractures.J Orthp Trauma. 2005;19:187-191. [15] Fernandez DL, Wolfe SW. Distal radius fractures. In:Green DP, Hotchkiss RN, Pederson WC, Wolfe SW (eds) Green’s operative hand surgery, 5th edn. Churchill Livingstone,Philadelphia, 2005:645-710. [16] Kandemir U,Matityahu A,Desai R. Does a volar locking plate provide equivalent stability as a dorsal nonlocking plate in a dorsally comminuted distal radius fracture:a biomechanical study. J Orthop Tauma. 2008;22(9):605. [17] Figl M, Weninger P, Liska M. Volar fixed-angle plate osteosynthes is of unstable distal radius fractures:12 months results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129(5):661-669. [18] Gehrmann SV, Windolf J, Kaufmann RA. Distal radius fracture management in elderly patients:a literature review. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(3):421-429. [19] Kim JK,Cho SW.The effects of a displaced dorsal rim fracture on outcomes after volar plate fixation of a distal radius fracture. Injury. 2012;43(2):143-146. [20] Frattini M, Soncini G, Corradi M,et al. Complex fractures of the distal radius treated with angular stability plates. Musculoskelet Surg. 2009; 93:155-162. [21] Dobretz H, Kutscha-Lissberg E. Osteosynthesis of distal radial fractures with volar locking plate system. Int Orthop. 2003; 27:1-6. [22] Ruch DS, McQueen MM. Distal radius and ulna fractures.In: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P (eds). Rockwood and green’s fractures in adults, 7th edn. Wolters Kluver, Philadelphia, 2010: 829-880. [23] Margaliot Z, Haase SC, Kotsis SV, et al. A meta-analysis of outcomes of external fixation versus plate osteosynthesis for unstable distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg [Am].2005;30:1185-1199. [24] Paksima N, Panchal A, Posner MA, et al. A meta-analysis of the literature on distal radius fractures: review of 615 articles. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2004;62:40-46. [25] Handoll HH, Madhok R. Surgical interventions for treating distal radial fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;4:CD003209. [26] Kapoor H, Agarwal A, Dhaon BK. Displaced intra-articular fractures of distal radius: a comparative evaluation of results following closed reduction, external fixation and open reduction with internal fixation. Injury. 2000;31:75-79. [27] Khanduja V, Ng L, Dannawi Z, et al. Complications and functional outcome following fixation of complex, intra-articular fractures of the distal radius with the AO Pi-Plate.Acta Orthop Belg. 2005;71:672-677. [28] Hahnloser D, Platz A, Amgwerd M, et al. Internal fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal dislocation: pi-plate or two 1/4 tube plates?: a prospective randomized study. J Trauma. 1999;47:760-765. [29] Keller M, Steiger R. Open reduction and internal fixation of distal radius extension fractures in women over 60 years of age with the dorsal radius plate (pi-plate). Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2006;38: 82-89. [30] Ruch DS, Papadonikolakis A. Volar versus dorsal plating in the management of intra-articular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2006;31:9-16. [31] Simic PM, Robinson J, Gardner MJ, et al. Treatment of distal radius fractures with a low-profile dorsal plating system: an outcomes assessment. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2006;31:382-386. [32] Knirk JL,Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68:647-659. [33] Wright TW, Horodyski M, Smith DW. Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures: ORIF with a volar fixed angle time plate versus external fixation. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2005;30:289-299. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||