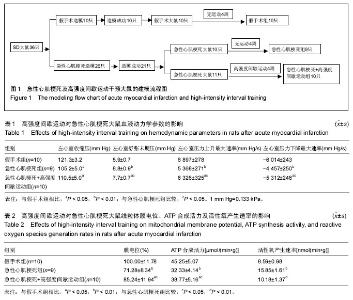
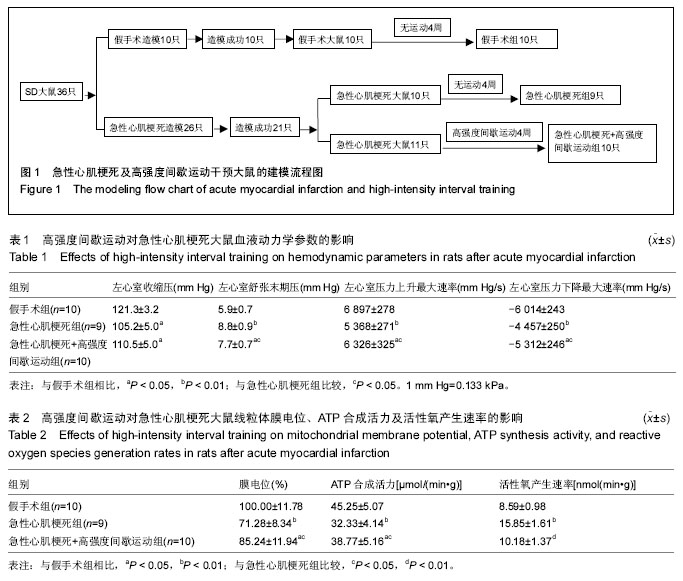
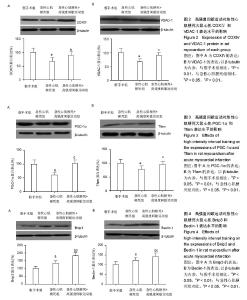
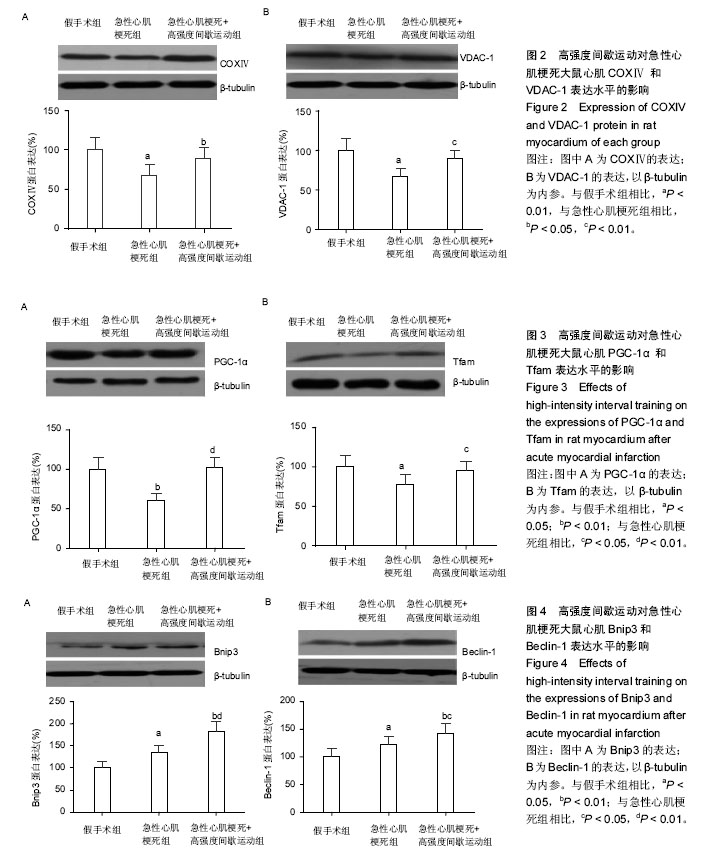
| [1] Dai W, Shi J, Gupta RC, et al. Bendavia, a mitochondria- targeting peptide, improves postinfarction cardiac function, prevents adverse left ventricular remodeling, and restores mitochondria- related gene expression in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;64(6):543-553.
[2] Alleman RJ, Stewart LM, Tsang AM, et al. Why Does Exercise “Trigger” Adaptive Protective Responses in the Heart. Dose Response. 2015;13(1). pii: dose-response.14-023.
[3] Bo H, Jiang N, Jia LL, et al. Mitochondrial redox metabolism in aging: Effect of exercise interventions. Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2013;2(2):67-74.
[4] 侯伊玲,薄海,刘子泉,等.运动训练对心肌梗死后心室重构及MMP-2,MMP-9表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2010, 25(3):200-204.
[5] Scalzo RL, Peltonen GL, Binns SE, et al. Greater muscle protein synthesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in males compared with females during sprint interval training. FASEB J. 2014;28(6):2705-2714.
[6] Seiler S, Jøranson K, Olesen BV, et al. Adaptations to aerobic interval training: interactive effects of exercise intensity and total work duration. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(1):74-83.
[7] Oliveira BR, Slama FA, Deslandes AC, et al. Continuous and high-intensity interval training: which promotes higher pleasure. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e 79965.
[8] Freyssin C, Verkindt C, Prieur F, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation in chronic heart failure: effect of an 8-week, high-intensity interval training versus continuous training. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 93(8):1359-1364.
[9] Cooper MP. Interplay of mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative stress in heart failure. Circulation. 2013; 127(19):1932-1934.
[10] Bøtker HE. Mitochondrial care in acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(2):77-79.
[11] Mandò C, De Palma C, Stampalija T, et al. Placental mitochondrial content and function in intrauterine growth restriction and preeclampsia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014;306(4):E404-413.
[12] Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N. Coordination of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis during ageing in C. elegans. Nature. 2015;521(7553):525-528.
[13] Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N. Balancing mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy to maintain energy metabolism homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(9):1399-1401.
[14] Kraljevic J, Marinovic J, Pravdic D, et al. Aerobic interval training attenuates remodelling and mitochondrial dysfunction in the post-infarction failing rat heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;99(1):55-64.
[15] 刘岩,周勇,杨水祥,等.心肌梗死模型大鼠心功能与血管活性物质释放关键蛋白NSF-siRNA[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(27):4287-4292.
[16] Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.
[17] Bo H, Jiang N, Ma G, et al. Regulation of mitochondrial uncoupling respiration during exercise in rat heart: role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and uncoupling protein 2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;44(7):1373-1381.
[18] Gac M, Bigda J, Vahlenkamp TW. Increased mitochondrial superoxide dismutase expression and lowered production of reactive oxygen species during rotavirus infection. Virology. 2010;404(2):293-303.
[19] 薄海,李玲,段富强,等.低氧复合运动抑制低氧诱导的骨骼肌线粒体DNA氧化损伤[J].生理学报,2014,66(5):597-604.
[20] 肖频,庞奕辉,彭朋,等. α-硫辛酸抑制慢性低氧大鼠骨骼肌线粒体的氧化应激[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(28): 5216-5222.
[21] Holloway TM, Bloemberg D, da Silva ML, et al. High intensity interval and endurance training have opposing effects on markers of heart failure and cardiac remodeling in hypertensive rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121138.
[22] Seneviratna A, Lim GH, Devi A, et al. Circadian Dependence of Infarct Size and Acute Heart Failure in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction. PLoS One. 2015; 10(6):e0128526.
[23] 薄海,彭朋,秦永生,等.低氧复合运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体含量的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2014,30(8):1461-1466.
[24] Laker RC, Xu P, Ryall KA, et al. A novel MitoTimer reporter gene for mitochondrial content, structure, stress, and damage in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(17):12005-12015.
[25] Gomes KM, Campos JC, Bechara LR, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 activation in heart failure restores mitochondrial function and improves ventricular function and remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;103(4):498-508.
[26] Yoboue ED, Mougeolle A, Kaiser L, et al. The role of mitochondrial biogenesis and ROS in the control of energy supply in proliferating cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1837(7):1093-1098.
[27] Karamanlidis G, Garcia-Menendez L, Kolwicz SC Jr, et al. Promoting PGC-1α-driven mitochondrial biogenesis is detrimental in pressure-overloaded mouse hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;307(9):H1307-1316.
[28] Fan W, Evans R. PPARs and ERRs: molecular mediators of mitochondrial metabolism. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;33:49-54.
[29] 薄海,何炜,刘子泉.非诺贝特在急性心肌缺血性损伤中的作用及机制探讨[J].中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2008, 3(5):264-267.
[30] Bo H, Kang W, Jiang N, et al. Exercise-induced neuroprotection of hippocampus in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via upregulation of mitochondrial 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:834502.
[31] Disatnik MH, Hwang S, Ferreira JC, et al. New therapeutics to modulate mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in cardiac diseases. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015; 93(3):279-287.
[32] Shirihai OS, Song M, Dorn GW 2nd. How mitochondrial dynamism orchestrates mitophagy. Circ Res. 2015;116 (11): 1835-1849.
[33] Oka T, Hikoso S, Yamaguchi O, et al. Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure. Nature. 2012;485(7397): 251-255.
[34] Smiles WJ, Camera DM .More than mitochondrial biogenesis: alternative roles of PGC-1α in exercise adaptation. J Physiol. 2015;593(9):2115-2117.
[35] Jiang HK, Miao Y, Wang YH, et al. Aerobic interval training protects against myocardial infarction-induced oxidative injury by enhancing antioxidase system and mitochondrial biosynthesis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;41(3):192-201.
[36] Jiang HK, Miao Y, Wang YH, et al. Aerobic interval training protects against myocardial infarction-induced oxidative injury by enhancing antioxidase system and mitochondrial biosynthesis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;41(3):192-201.
[37] Ding H, Zhang ZY, Zhang JW, et al. Role of mitochondrial quality control in exercise-induced health adaptation. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013;29(6): 543-553.
[38] Kim YA, Kim YS, Oh SL, et al. Autophagic response to exercise training in skeletal muscle with age. J Physiol Biochem. 2013;69(4):697-705.
[39] 薄海,李玲,段富强,等. 低氧联合运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自噬的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(10):908-912.
[40] Li H, Miao W, Ma J, et al. Acute Exercise-Induced Mitochondrial Stress Triggers an Inflammatory Response in the Myocardium via NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation with Mitophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016: 1987149. |