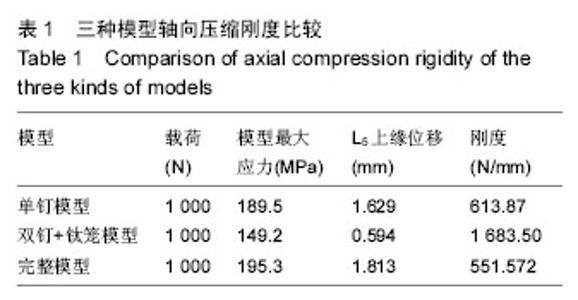
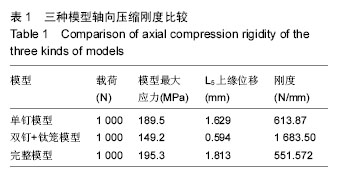
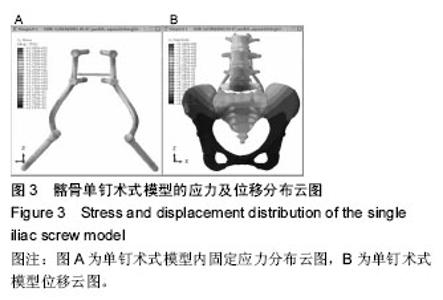
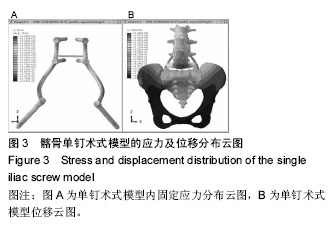
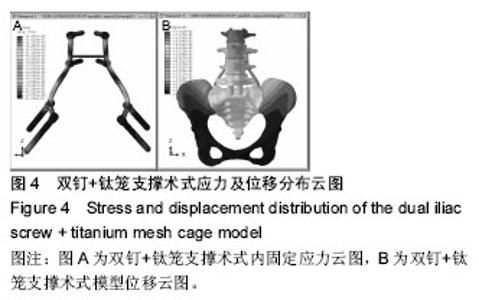
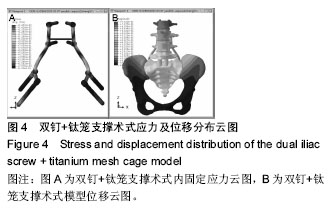
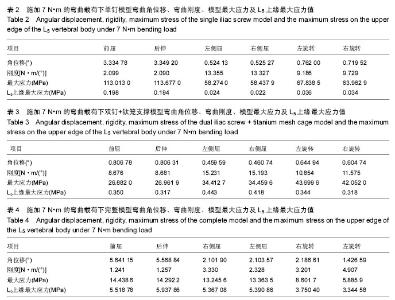
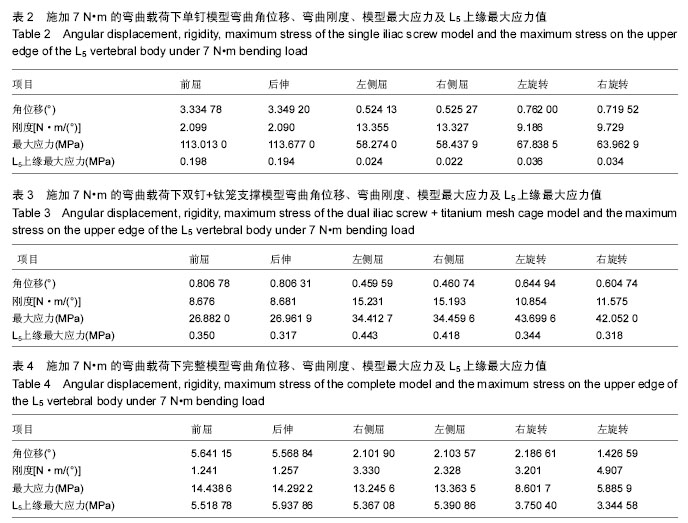
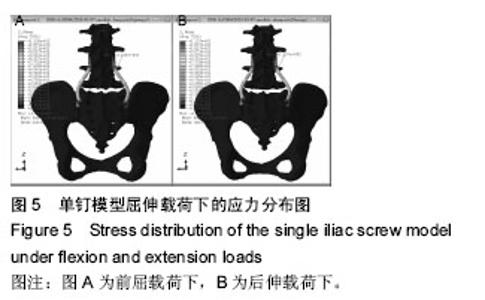
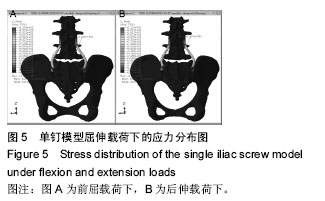
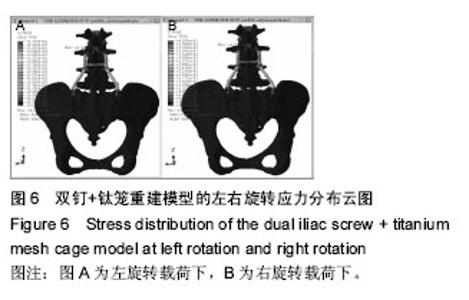
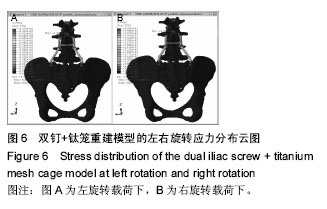
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (39): 5859-5866.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.39.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Single iliac screw and dual iliac screws and titanium mesh cage fixation in the reconstruction of lumbosacral defects with finite element analysis
Ma Liang1, Guo Wei-chun1, Xu Yong-tao2
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Renmin Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Jingzhou 434020, Hubei Province, China
-
Revised:2016-07-10Online:2016-09-23Published:2016-09-23 -
Contact:Guo Wei-chun, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Renmin Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Ma Liang, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Renmin Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Liang, Guo Wei-chun, Xu Yong-tao. Single iliac screw and dual iliac screws and titanium mesh cage fixation in the reconstruction of lumbosacral defects with finite element analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(39): 5859-5866.
share this article
| [1] Uvaraj NR, Bosco A, Gopinath NR. Global Reconstruction for Extensive Destruction in Tuberculosis of the Lumbar Spine and Lumbosacral Junction: A Case Report. Global Spine J. 2015;5(4):e17-e21. [2] Xu Z, Wang X, Shen X, et al. One-stage lumbopelvic fixation in the treatment of lumbosacral junction tuberculosis. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(8):1800-1805. [3] Varga PP, Szoverfi Z, Lazary A. Surgical resection and reconstruction after resection of tumors involving the sacropelvic region. Neurol Res. 2014;36(6):588-596. [4] Bederman SS, Shah KN, Hassan JM, et al.Surgical techniques for spinopelvic reconstruction following total sacrectomy: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(2):305-319. [5] Le VH, Heckmann N, Jain N, et al.Biomechanical evaluation of supplemental percutaneous lumbo-sacro-iliacscrewsfor spinopelvic fixation following total sacrectomy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015; 28(4):E181-185. [6] Guo LX, Wang ZW, Zhang YM, et al. Material property sensitivity analysis on resonant frequency characteristics of the human spine. J Appl Biomech. 2009;25(1):64-72. [7] Rohlmann A , Zander T, Schmidt H , et al. Analysis of the influence of disc degeneration on the mechanical behaviour of a lumbar motion segment using the finite element method. J Biomech. 2006; 39(13):2484-2490. [8] 于滨生,郑召民,庄新明,等.髂骨双钉在腰-髂重建结构中的生物力学优势[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(6):589-593. [9] 李全,张治宇,郑龙坡,等. 骶骨次全切除术后骨盆有限元模型的建立及验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(44):8649-8652. [10] Li JH, Zhang ZH, Shi T, et al. Surgical treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis by one-stage debridement and anterior instrumentation with allograft through an extraperitoneal anterior approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:62. [11] 高延征,余正红,高坤,等.腰骶结核不同手术方式的选择及疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(2):143-148. [12] Varga PP, Szövérfi Z, Lazary A. Surgical treatment of primary malignant tumors of thesacrum. Neurol Res. 2014;36(6):577-587. [13] Zang J, Guo W, Yang R, et al. Is total en bloc sacrectomy using a posterior-only approach feasible and safe for patients with malignant sacral tumors? J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(6):563-570. [14] Phukan R, Herzog T, Boland PJ,et al.How Does the Level of Sacral Resection for Primary Malignant Bone Tumors Affect Physical and Mental Health, Pain, Mobility, Incontinence, and Sexual Function? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2016; (3): 687-696. [15] Ooi A, Foo L, Tan BK, et al. Massive sacral chordoma resection and reconstruction with a combination of pedicled and free flaps. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2015; 31(1): 76-78. [16] KayaniB , Hanna SA , Sewell MD, et al.A review of the surgical management of sacral chordoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40(11): 1412-1420. [17] Dudda M, Hoffmann M, Schildhauer TA. Sacrum fractures and lumbopelvic instabilities in pelvic ring injuries: classification and biomechanical aspects. Unfallchirurg. 2013;116(11):972-978. [18] Wangtaphan W, Oo M, Paholpak P, et al.Traumatic lumbosacral spondyloptosis treated five months after injury occurrence: a case report. Spine. 2012;37(22): E1410-1414. [19] Sullivan MP, Smith HE, Schuster JM, et al. Spondylopelvic dissociation.Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(1):65-75. [20] Dalbayrak S, Yaman O, Ayten M, et al.Surgical treatment in sacral fractures and traumatic spinopelvic instabilities. Turk Neurosurg. 2014;24(4):498-505. [21] Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, Mba MD, et al. Axial interbody arthrodesis of the L5-S1 segment: a systematic review of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(3):314-319. [22] Whang PG, Sasso RC, Patel VV, et al.Comparison of axial and anterior interbody fusions of the L5-S1 segment: a retrospective cohort analysis.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(8):437-443. [23] Mobbs RJ, Loganathan A, Yeung V, et al. Indications for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Surg. 2013; 5(3):153-163. [24] Yoshihara H. Surgical options for lumbosacral fusion: biomechanical stability, advantage, disadvantage and affecting factors in selecting options. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24Suppl 1:S73-82. [25] Roetman B, Schildhauer TA. Lumbopelvic stabilization for bilateral lumbosacral instabilities: indications and techniques. Unfallchirurg. 2013; 116(11):991-999. [26] Zeng ZY, Zhang JQ, Song YX, et al. Combination of percutaneous unilateral translaminar facet screw fixation and interbody fusion for treatment of lower lumbar vertebra diseases: a follow-up study. Orthop Surg. 2014; 6(2):110-117. [27] Pola E, Rossi B, Nasto LA, et al.Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16 Suppl 2:79-85. [28] Bederman SS, Hassan JM, Shah KN, et al.Fixation techniques for complex traumatic transverse sacral fractures: a systematic review.Spine.2013;38(16): E1028-1040. [29] Kato M, Taneichi H, Suda K. Advantage of Pedicle Screw Placement Into the Sacral Promontory (Tricortical Purchase) on Lumbosacral Fixation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(6):E336-342. [30] Kim JH, Horton W, Hamasaki T, et al.Spinal instrumentation for sacral-pelvic fixation: a biomechanical comparison between constructs ending with either S2 bicortical, bitriangulated screws or iliac screws.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(8):506-512. [31] Néron JB, Gadéa F, Fournier J, et al.Lumbosacral arthrodesis for neuromuscular scoliosis using a simplified Jackson technique.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7):845-851. [32] Zwingmann J, Hauschild O, Bode G, et al. Malposition and revision rates of different imaging modalities for percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation following pelvic fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(9):1257-1266. [33] Ilyas H, Place H, Puryear A. A Comparison of Early Clinical and Radiographic Complications of Iliac Screw Fixation Versus S2Alar Iliac (S2AI) Fixation in the Adult and Pediatric Populations.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015; 28(4):E199-205. [34] Baek SW, Park YS, Ha KY, et al. The analysis of spinopelvic parameters and stability following long fusions with S1, S2 or iliacfixation. Int Orthop. 2013; 37(10):1973-1980. [35] Park SA, Kwak DS, You SL. Entry zone ofiliac screwfixation to maintain proper entry width andscrewlength. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 (11): 2573-2579. [36] Fridley J, Fahim D, Navarro J, et al. Free-hand placement of iliac screws for spinopelvic fixation based on anatomical landmarks: technical note. Int J Spine Surg. 2014;8. doi: 10.14444/1003. eCollection 2014. [37] Santos ER, Sembrano JN, Mueller B, et al. Optimizing iliac screw fixation: a biomechanical study on screw length, trajectory, and diameter. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14(2):219–225. [38] Wang T, Liu H, Zheng Z, et al.Biomechanical effect of 4-rod technique on lumbosacral fixation: an in vitro human cadaveric investigation.Spine. 2013;38(15): E925-929. [39] Amaritsakul Y, Chao CK, Lin J. Multiobjective optimization design of spinal pedicle screws using neural networks and genetic algorithm: mathematical models and mechanical validation. Comput Math Methods Med. 2013;2013:462875. [40] Zhao Y, Zhang S, Sun T, et al. Mechanical comparison between lengthened and short sacroiliac screws in sacral fracture fixation: afinite element analysis. Orthop TraumatolSurg Res. 2013;99(5):601-606. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||