Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (35): 5244-5249.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.35.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of personalized locking clavicle plate model and finite element analysis
Yin Feng, Wang Xiao-dong, Liang Wei, Ren Long-tao
- Department of Orthopedics, Taiyuan City Central Hospital, Taiyuan 030009, Shanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2016-06-27Online:2016-08-26Published:2016-08-26 -
Contact:Wang Xiao-dong, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Taiyuan City Central Hospital, Taiyuan 030009, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Yin Feng, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Taiyuan City Central Hospital, Taiyuan 030009, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Feng, Wang Xiao-dong, Liang Wei, Ren Long-tao . Establishment of personalized locking clavicle plate model and finite element analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5244-5249.
share this article
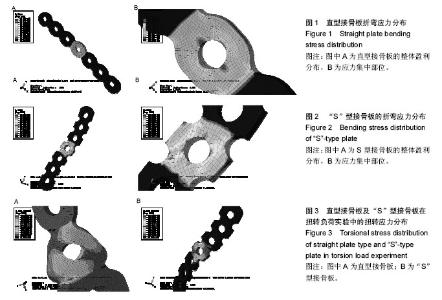
2.1 正常锁骨的有限元模型 实验建立了正常锁骨的有限元模型,以及与之相匹配的7孔直型接骨板和“S”型接骨板的有限元模型。所得接骨板模型可通过3D打印机直接打印出适合单个个体的个性化接骨板。 2.2 直型接骨板和“S”型接骨板有限元模型的受力分析结果 2.2.1 直型接骨板及“S”型接骨板折弯实验 直型接骨板的有限元模型,模拟远近端各3孔拧入螺钉固定,中间孔旷置,在近端固定,远端向下垂直钛板长轴方向施加大小为200 N的力,结果显示应力集中于钛板正中,即中间孔及周围(第4孔),该孔在手术实际操作中,旷置于锁骨骨折断端,故应力、应变集中处与骨折应力最大处相重叠,在外力作用下,易导致断板发生(图1)。 “S”型接骨板的有限元模型,依据以上方式施加同样大小的力,应力、应变的最大部位同样位于中间孔及周围,但较直型钛板应力分散(图2)。 2.3 直型接骨板及“S”型接骨板的扭转负荷实验 直型接骨板及“S”型接骨板的有限元模型,同样模拟远近端各3孔拧入螺钉固定,中间孔旷置,在近端固定,远端轴向分别施加200 N•mm的扭转力,其应力集中部位位于钛板中段正中,该部位易发生断裂(图3)。"
| [1] Brunner A, Wedi E, Babst R, et al. Bilateral fracture of the medial clavicles treated by open reduction and internal fixation using angle stable locking T-plates. Injury Extra. 2008;39(2):276-278. [2] Goswami T, Markert RJ, Anderson CG, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a pre-contoured clavicle plate. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):815-818. [3] Postacchini F, Gumina S, De Santis P, et al. Epidemiology of clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):452-456. [4] Hughes PJ, Maggs B. Fractures of the clavicle in adults. Curr Orthop. 2002;16(2):133-138. [5] Harnroongroj T, Tantikul C, Keatkor S. The clavicular fracture: a biomechanical study of the mechanism of clavicular fracture and modes of the fracture. J Med Assoc Thai. 2000;83(6):663-667. [6] Iannotti MR, Crosby LA, Stafford P, et al. Effects of plate location and selection on the stability of midshaft clavicle osteotomies: a biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002t;11(5):457-462. [7] Lampasi M, Bochicchio V, Bettuzzi C, et al. Sternoclavicular physeal fracture associated with adjacent clavicle fracture in a 14-year-old boy: a case report and literature review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(7):699-702. [8] Al-Yassari G, Hetzenauer M, Tauber M, et al. Novel method to treat sterno-clavicular joint instability and medial clavicle fracture symptomatic nonunion. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(4):553-555. [9] Harnroongroj T, Vanadurongwan V. Biomechanical aspects of plating osteosynthesis of transverse clavicular fracture with and without inferior cortical defect. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1996;11(5): 290-294. [10] Demirhan M, Bilsel K, Atalar AC, et al. Biomechanical comparison of fixation techniques in midshaft clavicular fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(5): 272-278. [11] Kayanja MM, Togawa D, Lieberman IH. Biomechanical changes after the augmentation of experimental osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the cadaveric thoracic spine. Spine J. 2005;5(1):55-63. [12] Harnroongroj T, Jeerathanyasakun Y. Intramedullary pin fixation in clavicular fractures: A study comparing the use of small and large pins. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2000;8(2):7-11. [13] Gaitanis IN, Carandang G, Phillips FM, et al. Restoring geometric and loading alignment of the thoracic spine with a vertebral compression fracture: effects of balloon (bone tamp) inflation and spinal extension. Spine J. 2005;5(1):45-54. [14] Asavamongkolkul A, Harnroongroj T, Suteeraporn W, et al. The second fracture of the same clavicle: prevalence and fracture configurations. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012;95(12):1524-1527. [15] Wu JH, Liao QD, Chen G, et al. Clavicular hook plate in the treatment of dislocation of acromioclavicular joint and fracture of distal clavicle. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006;31(4):595-598. [16] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317. [17] Rybicki EF, Simonen FA, Weis EB Jr. On the mathematical analysis of stress in the human femur. J Biomech. 1972;5(2):203-215. [18] 钱齐荣.骶髂关节与骨盆三维有限元模型的建立与应力分布的理论研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,1997. [19] Huang CH, Liau JJ, Huang CH, et al. Stress analysis of the anterior tibial post in posterior stabilized knee prostheses. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(4):442-449. [20] Liau JJ, Cheng CK, Huang CH, et al. The effect of malalignment on stresses in polyethylene component of total knee prostheses--a finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2002;17(2):140-146. [21] Huang CH, Liau JJ, Huang CH, et al. Influence of post-cam design on stresses on posterior-stabilized tibial posts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;450:150-156. [22] Lin KJ, Huang CH, Liu YL, et al. Influence of post-cam design of posterior stabilized knee prosthesis on tibiofemoral motion during high knee flexion. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(8):847-852. [23] Assor M, Aubaniac JM. Influence of rotatory malposition of femoral implant in failure of unicompartimental medial knee prosthesis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2006;92(5):473-484. [24] Hanson GR, Suggs JF, Kwon YM, et al. In vivo anterior tibial post contact after posterior stabilizing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(11):1447-1453. [25] Cheng CK, Huang CH, Liau JJ, et al. The influence of surgical malalignment on the contact pressures of fixed and mobile bearing knee prostheses--a biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(3):231-236. [26] Yang RS, Lin HJ. Contact stress on polyethylene components of a new rotating hinge with a spherical contact surface. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001; 16(6):540-546. [27] Chandran N, Amirouche F, Gonzalez MH, et al. Optimisation of the posterior stabilised tibial post for greater femoral rollback after total knee arthroplasty--a finite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3): 687-693. [28] Perillo-Marcone A, Taylor M. Effect of varus/valgus malalignment on bone strains in the proximal tibia after TKR: an explicit finite element study. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(1):1-11. [29] Akasaki Y, Matsuda S, Shimoto T, et al. Contact stress analysis of the conforming post-cam mechanism in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2008;23(5):736-743. [30] Hamai S, Miura H, Matsuda S, et al. Contact stress at the anterior aspect of the tibial post in posterior-stabilized total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(8):1765-1773. [31] Giffin JR, Stabile KJ, Zantop T, et al. Importance of tibial slope for stability of the posterior cruciate ligament deficient knee. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35(9):1443-1449. [32] Li G, Papannagari R, Most E, et al. Anterior tibial post impingement in a posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(3):536-541. [33] Argenson JN, Scuderi GR, Komistek RD, et al. In vivo kinematic evaluation and design considerations related to high flexion in total knee arthroplasty. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):277-284. [34] 贺锦阳.个性化解剖型接骨板的有限元分析研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2012. [35] 张云鹏.计算机辅助设计制作股骨远端个性化解剖型接骨板的基础理论研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2010. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||