Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (31): 4565-4574.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.31.001
Correlation between hidden blood loss and nutritional status in elderly patients after total hip replacement
Zhu Dong-mei1, Liu Guo-yin1, Bao Lei1, Wang Meng-ru2, Ye Ming-zhu3, Leng Nan-nan1, Yang Zheng-qian3, Xu Xiao-xiao3, Chen Jian-min1
- 1the 81 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2016-05-19Online:2016-07-22Published:2016-07-22 -
Contact:Chen Jian-min, Master, Associate chief physician, the 81 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhu Dong-mei, Nurse-in-charge, the 81 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Nanjing Science and Technology Project, No. 201303039; the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Nanjing Military Region, No. MS055
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Dong-mei, Liu Guo-yin, Bao Lei, Wang Meng-ru, Ye Ming-zhu, Leng Nan-nan, Yang Zheng-qian, Xu Xiao-xiao, Chen Jian-min. Correlation between hidden blood loss and nutritional status in elderly patients after total hip replacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4565-4574.
share this article

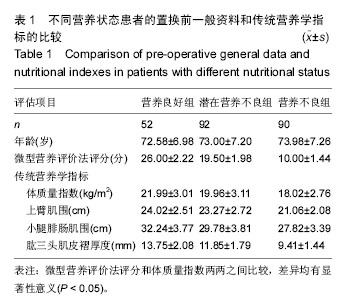
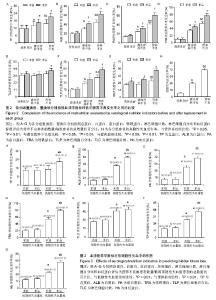
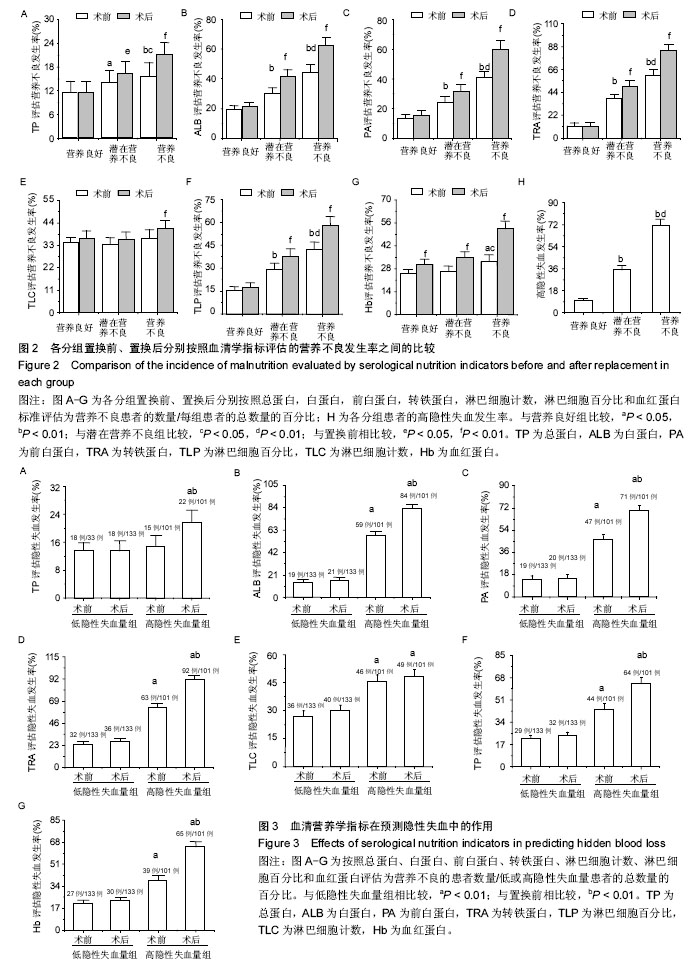
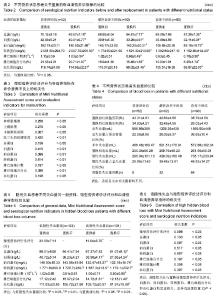
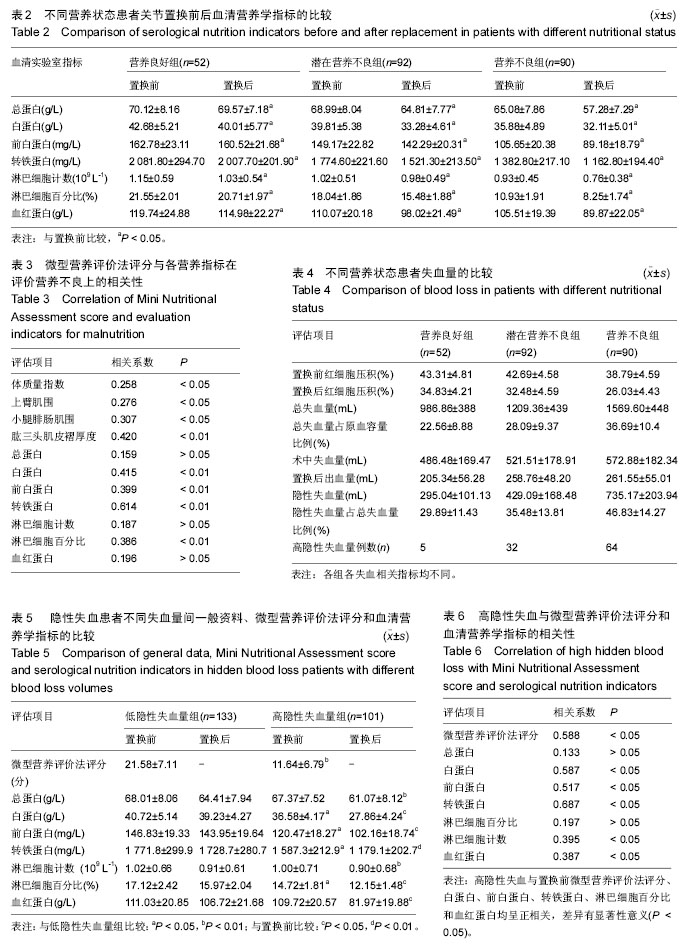
2.3 各种营养评价方法评定患者置换前营养状况 2.3.1 置换前传统营养学指标与微型营养评价法评分结果的关系 在3组患者中,置换前体质量指数、上臂肌围、小腿腓肠肌围和肱三头肌皮褶厚度平均值的变化趋势均与微型营养评价法评分相关,并随营养状态的恶化而呈现下降趋势(表1)。各组患者置换前平均微型营养评价法评分,两两间比较差异有显著性意义(图1A),营养不良组患者置换前体质量的平均值低于营养良好组和潜在营养不良组(P < 0.05;图1B)。 由于各组患者的营养学指标数值差异变化波动较大,会对试验结果造成误差。为了排除这些因素的干扰,文章进一步对比分析置换前传统营养学指标评估营养不良的发生率(置换前分别按照上臂肌围、小腿腓肠肌围和肱三头肌皮褶厚度标准评估为营养不良患者的数量/每组患者的总数量),结果表明:营养不良患者置换前上臂肌围、小腿腓肠肌围和肱三头肌皮褶厚度评估营养不良的发生率明显高于营养良好患者(图1C-E),营养不良患者置换前上臂肌围和肱三头肌皮褶厚度评估营养不良的发生率明显高于潜在营养不良患者(图1C,E),潜在营养不良患者置换前小腿腓肠肌围评估营养不良的发生率明显高于营养良好患者(图1D)。 2.3.2 置换前血清营养学指标与微型营养评价法评分的关系 对各组患者的血清营养学指标分析后发现,置换前这些指标平均值的变化趋势均与微型营养评价法评分评估的营养状态存在相关性(表2)。随着营养不良状 态的加重,血清营养学指标的平均值逐渐降低。 为排除指标差异变化波动对实验的干扰,文章分别对置换前血清营养学指标评估营养不良的发生率(置换前分别按照血清营养学指标的标准评估为营养不良患者的数量/每组患者的总数量)进行了对比分析:营养不良患者总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白评估的置换前营养不良发生率明显高于营养良好患者(图2A-D,图2F,G);潜在营养不良患者总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白和淋巴细胞百分比评估的置换前营养不良发生率明显高于营养良好患者(图2A-D,图2F);营养不良患者总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白评估的置换前营养不良发生率明显高于潜在营养不良患者 (图2A-D,图2F,G)。 2.4 不同营养状态患者关节置换前后血清营养学指标的变化 表2显示,各分组患者置换后血清营养学指标的数值均低于入院时(置换前)的总体水平(P < 0.05)。为了进一步明确置换后这些指标评估营养不良发生率的变化,并排除这些指标数值的差异变化波动对实验结果的影响,文章将关节置换前后分别按照血清营养学指标的标准评估为营养不良患者的数量/每组患者的总数量进行对比分析后发现:营养良好患者置换后按照血红蛋白标准评估的营养不良发生率高于置换前(P < 0.01;图2G),但是,营养良好患者关节置换前后分别按照总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和淋巴细胞计数评估的营养不良发生率之间差异无显著性意义(图2A-F);潜在营养不良患者置换后按照总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白 标准评估的营养不良发生率明显高于置换前(P < 0.05)(图2A-D,图2F,G);营养不良患者置换后按照总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞计数、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白标准评估的营养不良发生率显著高于置换前,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01;图2A-G)。 2.5 微型营养评价法评分与各种营养评价指标的相关性 微型营养评价法评分与传统营养学指标(体质量指数、上臂肌围、小腿腓肠肌围和肱三头肌皮褶厚度)和血清实验室指标(白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白和淋巴细胞百分比)均呈正相关,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);微型营养评价法评分与总蛋白、淋巴细胞计数和血红蛋白之间的相关系数分别为0.159、0.187和0.196,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。 2.6 隐性失血发生情况分析 试验中234例患者的总失血量平均为1 298.47 mL,占原血容量的30.1%;隐性失血总量平均为517.03 mL,占总失血量的39.8%。各分组患者置换前后红细胞压积、总失血量及其占原血容量比例、置换后失血量、置换后出血量、隐性失血量及其占总失血量比例和发生高隐性失血量的患者例数,见表4。 根据平均隐性失血量占总失血量的比例将患者分为低隐性失血量组(< 39.82%)和高隐性失血量组 (> 39.82%),其中低隐性失血量组有133例患者,高隐性失血量组有101例患者。高隐性失血发生率分析:如图2H所示,在营养良好、潜在营养不良和营养不良3组患者中,高隐性失血发生率随着营养状态的恶化而逐渐升高,高隐性失血发生率两两之间比较,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05); 2.7 隐性失血与微型营养评价法评分和血清营养学指标的关系 见表5。 高隐性失血量组置换前微型营养评价法评分、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白和淋巴细胞百分比的平均值明显低于低隐性失血量组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);高隐性失血量组置换后白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白的平均值明显低于置换前(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。为了进一步明确隐性失血患者的血清营养学指标在关节置换前后的变化规律及隐性失血量与血清营养学指标之间的关系,并排除这些指标数值的差异变化波动对实验结果的干扰,文章对经关节置换前后血清营养学指标评估的隐性失血发生率(按照血清营养学指标标准评估为营养不良患者的数量/高或低隐性失血量患者的总数量)进行比较后发现:置换前高隐性失血量组白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞计数、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白评估的隐性失血发生率明显高于低隐性失血量组(图3B-G;P < 0.01),置换后高隐性失血量组总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞计数、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白评估的隐性失血发生率明显高于低隐性失血量组(图3A-G;P < 0.01);高隐性失血量组置换后总蛋白、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白评估的隐性失血发生率明显高于置换前(图3A-D,F-G;P < 0.01)。 2.8 高隐性失血与微型营养评价法评分和血清营养学指标的相关性 高隐性失血与置换前微型营养评价法评分、白蛋白、前白蛋白、转铁蛋白、淋巴细胞百分比和血红蛋白均呈正相关,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);高隐性失血与总蛋白和淋巴细胞计数之间的相关系数分别为0.133和0.197,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表6。"
| [1] Smith T, Hameed Y, Cross J, et al. Assessment of people with cognitive impairment and hip fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57(2):117-126. [2] Chaudhry H, Devereaux PJ, Bhandari M. Cognitive dysfunction in hip fracture patients. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44:153-162. [3] Nie H, Zhao B, Zhang YQ, et al. Pain and cognitive dysfunction are the risk factors of delirium in elderly hip fracture Chinese patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012; 54:e172-e174. [4] Sierra RJ, Mabry TM, Sems SA, et al. Acetabular fractures: the role of total hip replacement. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B:11-16. [5] Smith GH, Tsang J, Molyneux SG, et al. The hidden blood loss after hip fracture. Injury. 2011;42:133-135. [6] Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Y, et al. Hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthrop. 2011;26:1100-1105. [7] Foss NB, Kehlet H. Hidden blood loss after surgery for hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:1053-1059. [8] Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009;33:1263-1268. [9] Kieffer WK, Rennie CS, Gandhe AJ. Preoperative albumin as a predictor of one-year mortality in patients with fractured neck of femur. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013;95:26-28. [10] Yamaguchi S, Kitamura J, Yamamoto K. Perioperative management of the elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgical repair under spinal anesthesia-a comparison between bipolar hip prosthesis and open reduction and internal fixation. Masui. 2013;62:916-923. [11] Koren-Hakim T, Weiss A, Hershkovitz A, et al. The relationship between nutritional status of hip fracture operated elderly patients and their functioning, comorbidity and outcome. Clin Nutr. 2012;31:917-21. [12] Carpintero P, Lopez P, Leon F, et al. Men with hip fractures have poorer nutritional status and survival than women: a prospective study of 165 patients. Acta Orthop. 2005;76:331-335. [13] Garcia-Casanova MC, Estevez-Pereda MI, Valverde-Quintairos MA, et al. Nutritional status in patients older than 65 after a hip fracture. Enferm Clin. 2011;21:75-83. [14] Hoekstra JC, Goosen JH, de Wolf GS, et al. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary nutritional care on nutritional intake, nutritional status and quality of life in patients with hip fractures: a controlled prospective cohort study. Clin Nutr. 2011;30:455-461. [15] Murphy MC, Brooks CN, New SA, et al. The use of the Mini-Nutritional Assessment (MNA) tool in elderly orthopaedic patients. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000;54:555-562. [16] Guigoz Y, Vellas B, Garry PJ. Assessing the nutritional status of the elderly: the mini nutritional assessment as part of the geriatric evaluation. Nutr Rev. 1996;54: S59-S65. [17] Dwyer JT, Gallo JJ, Reichel W. Assessing nutritional status in elderly patients. Am Fam Physician. 1993; 47:613-620. [18] Scholl R. Nutrition and aging: assessing the nutritional status of the elderly patient. J Kans Med Soc. 1982; 83:368-370. [19] Utrilla AL, Reig JS, Munoz FM, et al. Trochanteric gamma nail and compression hip screw for trochanteric fractures: a randomized, prospective, comparative study in 210 elderly patients with a new design of the gamma nail. J Orthop. 2005;19: 229-233. [20] Moroni A, Faldini C, Pegreffi F, et al. Dynamic hip screw compared with external fixation for treatment of osteoporotic pertrochanteric fractures. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87: 753-759. [21] Cram P, Lu X, Kaboli PJ, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of Medicare patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty, 1991-2008. JAMA. 2011;305: 1560-1567. [22] Nikkel LE, Fox EJ, Black KP, et al. Impact of comorbidities on hospitalization costs following hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:9-17. [23] Miyanishi K, Jingushi S, Torisu T. Mortality after hip fracture in Japan: the role of nutritional status. J Orthop Surg. 2010;18:265-270. [24] Brauer CA, Coca-Perraillon M, Cutler DM, Rosen AB. Incidence and mortality of hip fractures in the United States. JAMA. 2009;302:1573-1579. [25] Johnell O, Kanis JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence, mortality and disability associated with hip fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15:897-902. [26] Boddaert J, Raux M, Khiami F, et al. Perioperative management of elderly patients with hip fracture. Anesthesiology. 2014;121:1336-1341. [27] Boddaert J, Cohen-Bittan J, Khiami F, et al. Postoperative admission to a dedicated geriatric unit decreases mortality in elderly patients with hip fracture. PLoS One. 2014;9:e83795. [28] Benetos IS, Babis GC, Zoubos AB, et al. Factors affecting the risk of hip fractures. Injury. 2007;38: 735-744. [29] Salminen H, Saaf M, Johansson SE, et al. Nutritional status, as determined by the Mini-Nutritional Assessment, and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study of an elderly female population. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60:486-493. [30] Sargento L, Longo S, Lousada N, et al. The importance of assessing nutritional status in elderly patients with heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2014; 11:220-226. [31] Perez Durillo FT, Ruiz Lopez MD, Bouzas PR, et al. Nutritional status in elderly patients with a hip fracture. Nutr Hosp. 2010;25:676-681. [32] Sancarlo D, D'Onofrio G, Franceschi M, et al. Validation of a Modified-Multidimensional Prognostic Index (m-MPI) including the Mini Nutritional Assessment Short-Form (MNA-SF) for the prediction of one-year mortality in hospitalized elderly patients. J Nutr Health Aging. 2011;15:169-173. [33] Vandewoude M, Van Gossum A. Nutritional screening strategy in nonagenarians: the value of the MNA-SF (mini nutritional assessment short form) in NutriAction. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17:310-314. [34] Ortega-Andreu M, Perez-Chrzanowska H, Figueredo R, et al. Blood loss control with two doses of tranexamic Acid in a multimodal protocol for total knee arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2011;5:44-48. [35] McConnell J, Dillon J, Kinninmonth A, Sarungi M, Picard F. Blood loss following total knee replacement is reduced when using computer-assisted versus standard methods. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012;78:75-79. [36] Aguilera X, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Bosch A, et al. Efficacy and safety of fibrin glue and tranexamic acid to prevent postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:2001-2007. [37] Bao N, Zhou L, Cong Y, et al. Free fatty acids are responsible for the hidden blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Med Hypotheses. 2013;81:104-107. [38] Smorgick Y, Baker KC, Bachison CC, et al. Hidden blood loss during posterior spine fusion surgery. Spine J. 2013;13:877-881. [39] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:561-565. [40] Zhao J, Li J, Zheng W, et al. Low body mass index and blood loss in primary total hip arthroplasty: results from 236 consecutive ankylosing spondylitis patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:742393. [41] Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003; 90:596-599. [42] Myint MW, Wu J, Wong E, et al. Clinical benefits of oral nutritional supplementation for elderly hip fracture patients: a single blind randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing. 2013;42:39-45. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||