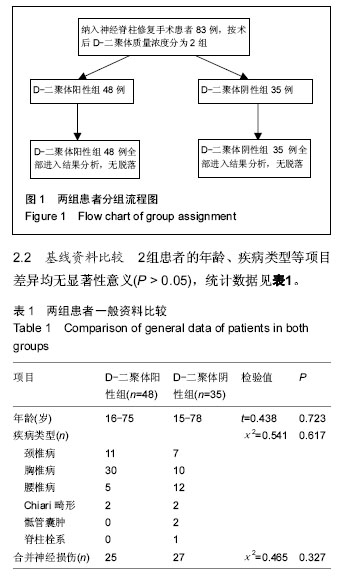
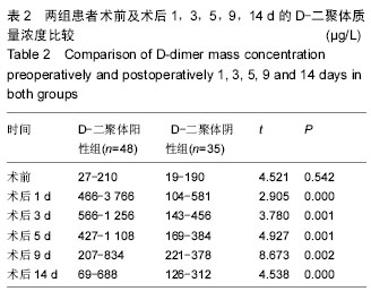
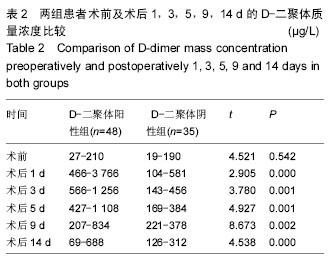
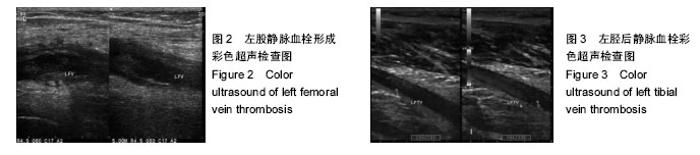
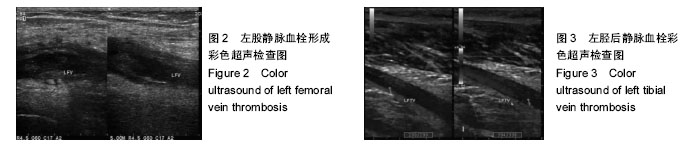
| [1] 倪伟.骨科手术后深静脉血栓形成的预防研究及护理[J]. 中国社区医师,2015,31(19):127-128.
[2] 姜延海.脊柱术后应用抗凝药物预防深静脉血栓安全性的相关研究[D].青岛大学,2014.
[3] 中华医学会放射学分会介入学组.下肢深静脉血栓形成介入治疗规范的专家共识[J].中华放射学杂志,2011, 45(3): 293-296.
[4] 潘颐聪.D-二聚体的监侧对评估急性期下下肢静脉血栓的疗效及预后的作用[D].广西医科大学,2013.
[5] 司文腾,张华果,孙宜保,等.脊柱术后血浆D-二聚体浓度变化与深静脉血栓的关系研究[J].中国骨伤, 2014,27(5): 405-408.
[6] Schouten HJ, Geersing GJ, Koek HL,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of conventional or age adjusted D-dimer cut-off values in older patients with suspected venous thromboembolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;346:f2492.
[7] 赵玉芬,段小凯.D-二聚体定量检测在外科患者手术后病情监测中的应用[J].河南外科学杂志,2013,19(6): 50-54.
[8] 山慈明,尹慧珍,杜书明,等. 围手术期深静脉血栓形成的物理预防研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志,2014,49(3): 349-354.
[9] 刘华磊,王淑霞.下肢动静脉血栓30例超声诊断分析[J]. 河南外科学杂志,2015,21(3):130-131.
[10] 陶方,季红莉,李中侠,等. 高龄住院患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床分析及护理[J].河北医药,2015,37(15): 2385-2387.
[11] 欧永强.D-二聚体、同型半胱氨酸、超敏C反应蛋白对深静脉血栓性疾病早期诊断及预后的价值[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,11(32):2290-2293.
[12] 沈毓,王龙,陈彬.深静脉血栓形成的实验室检查现状与进展[J].诊断学理论与实践,2011,10(2):172-174.
[13] 李仁科,李学婷,王少华.麻醉对全髋关节置换术患者D-二聚体及深静脉血栓发生率的影响[J].医药论坛杂志, 2012, 33(11):115-118.
[14] 王占鳌.静脉血栓栓塞症的临床预测模型构建研究[D].宁夏医科大学,2012
[15] 邓长华.血浆D-二聚体对脊柱结核患者术后早期深静脉血栓形成的诊断价值[J].中国实验诊断学,2015,19(3): 471-473.
[16] Kearon C,Ginsberg JS,Douketis J.Management of suspected deep vein thrombosis in outpatients by using clinical assessment and D-dimer testing.Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(2):296-304.
[17] Anderson DR,Kovacs MJ,Kovacs G. Combined use of clinical assessment and D-dimer to improve the management of patients presenting to emergency department with suspected deep vein thrombosis(the EDITED Study). J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1(4): 645-651.
[18] Elf JL,Strandberg K,Nilsson C.Clinical probability assessment and D-dimer determination inpatients with suspected deep vein thrombosis,a prospective multicenter management study.Thromb Res. 2009; 123(4):612-616.
[19] 葛闽霞,周兰芳,李爱强.血浆C反应蛋白及 D-二聚体检测在脊柱手术中的应用[J].中医正骨,2012,24(6):66-68.
[20] 张立涛,张静梅,梁俊生,等.老年人骨折后早期下肢深静脉血栓形成情况分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(1): 43-45,82.
[21] 宫瑜,于红.周期性充气加压预防髋部骨折老年患者术后下肢深静脉血栓的效果[J].中华现代护理杂志,2013, 19(22):2715-2718.
[22] Luxembourg B,Schwonberg J,Hecking C,et al.Performance of five D-dimer assays for the exclusion of symptomatic distal legvein thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107:369-378.
[23] 王国杰,张灼锦.血浆D-二聚体检测对下肢深静脉血栓的早期诊断价值[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(14): 2368-2370.
[24] 腾飞,何新华,杨杰,等.Wells评分联合D-dimer在急性肺栓塞诊断的临床预测价值[J].中华急诊医学杂志, 2015, 24(40):422-425.
[25] Penaloza A,Roy PM,Kline J,et al.Performance of age-adjusted D-dimer cut-off to rule out pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(7):1291-1296.
[26] Righini M,Van Es J,Den Exter PL,et al. Age-adjusted D-dimer cutoff levels to rule out pulmonary embolism: the ADJUST-PE study.JAMA.2014;311(11):1117-1124.
[27] Schouten HJ,Geersing GJ,Koek HL,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of conventional or age adjusted D-dimer cut-off values in older patients with suspected venous thromboembolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;346:f2492.
[28] Lippi G, Favaloro EJ, Cervellin G. A review of the value of D-dimer testing for prediction of recurrent venous thromboembolism with increasingage. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2014;40(6):634-639.
[29] Woller SC,Stevens SM,Adams DM,et al.Assessment of the safety and efficiency of using an age-adjusted D-dimer threshold to exclude suspected pulmonary embolism. Chest.2014;146(6):1444-1451.
[30] Mullier F,Vanpee D,Jamart J,et al.Comparison of five D-dimer reagents and application of an age-adjusted cut-off for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism in emergency department. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2014;25(4):309-315.
[31] 余美琴,李俊来,曹晓林,等.老年下肢深静脉血栓患者D-二聚体的临界值研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2013, 15(1):32-34.
[32] 陈霞,张晟.血浆D-二聚体浓度筛查辅助超声联合检测髋部骨折患者下肢深静脉血栓的价值[J].广东医学, 2011, 32(23):3080-3082.
[33] 亓明,白云清.D-二聚体监测对老年长期卧床患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的早期诊断价值[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013, 33(17):4244-4245.
[34] 欧永强.D-二聚体、同型半胱氨酸、超敏C反应蛋白对深静脉血栓性疾病早期诊断及预后的价值[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(11):2290-2291.
[35] 张辉良,梁俊生,张洪斌,等.利伐沙班与华法林治疗老年髋部骨折术前并存下肢深静脉血栓比较研究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2013,29(2):323-324.
[36] 侯伟,熊小明,万趸. 骨盆骨折内固定术中应用普通肝素对术后下肢深静脉血栓发生率的影响[J]. 四川医学, 2015, 36(7):996-999.
[37] 沈明荃,谢增如.复合骨折后下肢深静脉血栓形成Wells评分与D-二聚体及纤维蛋白降解产物的预测[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(38):6136-6140.
[38] 张纪媛,郭丹青,何惠.下肢深静脉血栓患者外周血血小板p-选择素、D二聚体及超敏C反应蛋白的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国医药导报,2014,11(20):34-36.
[39] 殷明春.D-二聚体在老年下肢深静脉血栓预测中的临界值探讨[J]. 中国医药导刊,2014,11(2):313-314.
[40] 陆燕,蔡攀,汤明荣,等.高龄髋部骨折患者围术期D-二聚体的测定及临床意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2015,36(1): 25-26. |