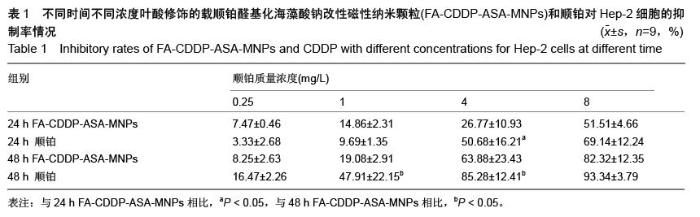
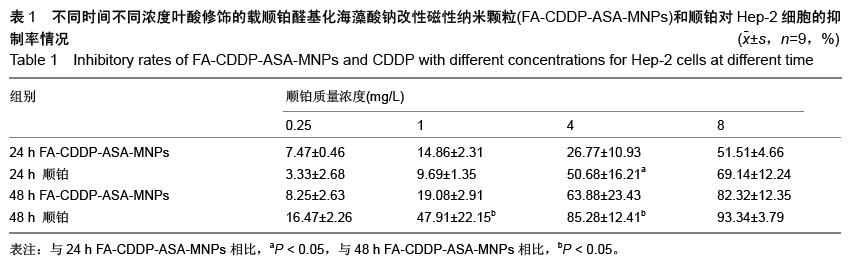
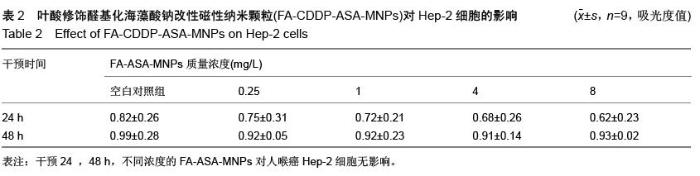
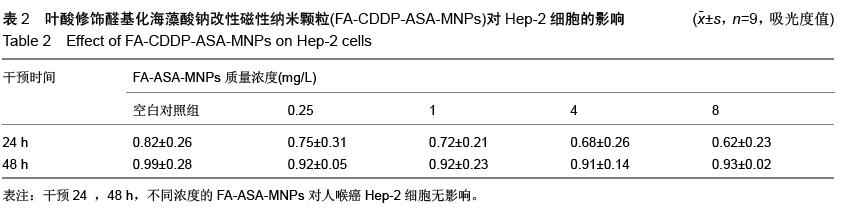
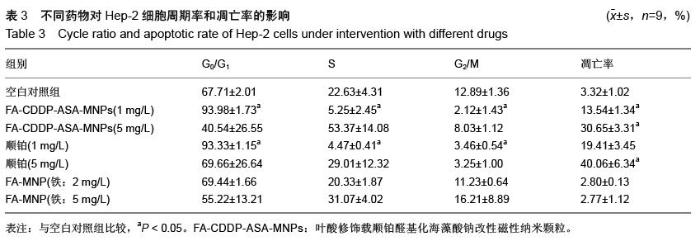
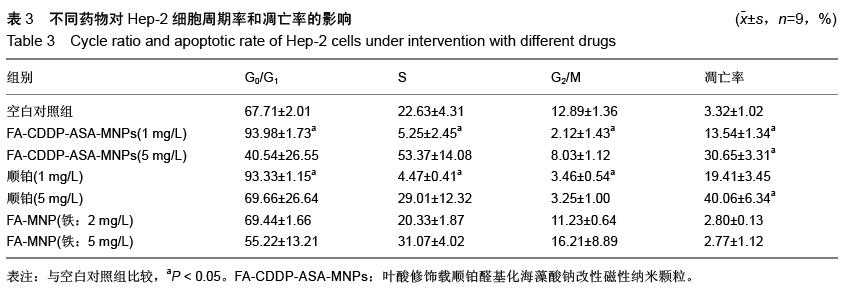
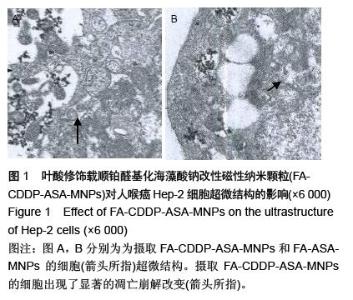
| [1] 赫捷,赵平,陈万青.中国肿瘤登记年报[M].北京:军事医学科学出版社,2012.
[2] 龚萍,杨月婷,石碧华,等.纳米探针在分子影像领域的研究进展[J].科学通报,2013,58:762-776.
[3] 杨祥良.纳米药物[M].北京:科学出版社,2010.
[4] Claudon J, Bleuse J, Malik NS, et al. A highly efficient single-photon source based on a quantum dot in a photonic nanowire. Nat Photonics. 2010;4:174-177.
[5] Maune B, Borselli M, Huang B, et al. Coherent singlet-triplet oscillations in a silicon-based double quantum dot. Nature. 2012;481:344-347.
[6] Ip A H, Thon S M, Hoogland S, et al. Hybrid passivated colloidal quantum dot solids. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7: 577-582.
[7] Fowley C, Nomikou N, McHale AP, et al. Extending the tissue penetration capability of conventional photosensitisers: a carbon quantum dot-protoporphyrin IX conjugate for use in two-photon excited photodynamic therapy. Chem Commun. 2013;49: 8934-8936.
[8] Huang HC, Barua S, Sharma G, et al. Inorganic nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy. J Control Release. 2011;155:344-357.
[9] Liu D, Wang Z, Jiang X. Gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric and fluorescent detection of ions and small organic molecules. Nanoscale. 2011;3:1421-1433.
[10] Mukherjee S, Chowdhury D, Kotcherlakota R, et al. Potential theranostics application of bio-synthesized silver nanoparticles (4-in-1 system). Theranostics. 2014;4:316.
[11] Kennedy LC, Bickford LR, Lewinski NA, et al. A new era for cancer treatment: gold-nanoparticle-mediated thermal therapies. Small. 2011;7:169-183.
[12] Zhang Q. Carbon Nanotubes and Their Applications. Boca Raton: CRC Press. 2012.
[13] Hu W, Peng C, Lv M, et al. Protein corona-mediated mitigation of cytotoxicity of graphene oxide. ACS Nano. 2011;5:3693-3700.
[14] Das M, Datir SR, Singh RP, et al. Augmented anticancer activity of a targeted, intracellularly activatable, theranostic nanomedicine based on fluorescent and radiolabeled, methotrexate-folic acid-multiwalled carbon nanotube conjugate. Mol Pharm. 2013;10:2543-2557.
[15] Sheng Z, Song L, Zheng J, et al. Protein-assisted fabrication of nano-reduced graphene oxide for combined in vivo photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials. 2013;34:5236-5243.
[16] Akhavan O, Ghaderi E. Graphene nanomesh promises extremely efficient in vivo photothermal therapy. Small. 2013;9:3593-3601.
[17] Kucheryavy P, He J, John VT, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with variable size and an iron oxidation state as prospective imaging agents. Langmuir. 2013;29:710-716.
[18] Lee N, Hyeon T. Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Cheml Soc Rev. 2012;41:2575-2589.
[19] Daldrup-Link HE, Golovko D, Ruffell B, et al. MRI of tumor-associated macrophages with clinically applicable iron oxide nanoparticles. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5695-5704.
[20] Hu F, Jia Q, Li Y, et al. Facile synthesis of ultrasmall PEGylated iron oxide nanoparticles for dual-contrast T1-and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Nanotechnology. 2011;22:245604-245611.
[21] Yang X, Hong H, Grailer JJ, et al. cRGD-functionalized, DOX-conjugated, and Cu-labeled superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted anticancer drug delivery and PET/MR imaging. Biomaterials. 2011;32: 4151-4160.
[22] Hu DH, Sheng ZH, Zhang PF, et al. Hybrid gold-gadolinium nanoclusters for tumor-targeted NIRF/CT/MRI triple-modal imaging in vivo. Nanoscale. 2013;5:1624-1628.
[23] Xu H, Cheng L, Wang C, et al. Polymer encapsulated upconversion nanoparticle/iron oxide nanocomposites for multimodal imaging and magnetic targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9364-9373.
[24] Allen TM, Cullis PR. Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2013;65:36-48.
[25] Chang HI, Yeh MK. Clinical development of liposome-based drugs: formulation, characterization, and therapeutic efficacy. Int J Nanomed. 2012;7:49.
[26] Zheng MB, Zhao PF, Luo ZY, et al. Robust ICG theranostic nanoparticles for folate targeted cancer imaging and highly effective photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2014;6:6709-6716.
[27] Ren J, Yu C, Wu S, et al. Cationic liposome mediated delivery of FUS1 and hIL-12 coexpression plasmid demonstrates enhanced activity against human lung cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Tar. 2014;14:167-180.
[28] Agarwal A, Mackey MA, El-Sayed MA, et al. Remote triggered release of doxorubicin in tumors by synergistic application of thermosensitive liposomes and gold nanorods. ACS Nano. 2011;5:4919-4926.
[29] Dicheva BM, ten Hagen TL, Li L, et al. Cationic thermosensitive liposomes: A novel dual targeted heat-triggered drug delivery approach for endothelial and tumor cells. Nano Lett. 2013;13:2324-2331.
[30] Novio F, Simmchen J, Vazquez-Mera N, et al. Coordination polymer nanoparticles in medicine. Coord Chem Rev. 2013;257:2839-2847.
[31] Ding D, Wang J, Zhu Z, et al. Tumor accumulation, penetration, and antitumor response of cisplatin-loaded gelatin/poly (acrylic acid) nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2012;4: 1838-1846.
[32] Li Z, Barnes JC, Bosoy A, et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:2590-2605.
[33] Chen NT, Cheng SH, Souris JS, et al. Theranostic applications of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their organic/inorganic hybrids. J Mater Chem. 2013; 1:3128-3135.
[34] Mai WX, Meng H. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: a multifunctional nano therapeutic system. Integ Biol. 2013;5:19-28.
[35] Zhang Z, Wang L, Wang J, et al. Mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods as a light-mediated multifunctional theranostic platform for cancer treatment. Adv Mater. 2012;24:1418-1423.
[36] Tse NMK, Kennedy DF, Kirby N, et al. Mesoporous gadolino-aluminosilicate nanoparticles as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J Mater Chem. 2013;1:1219-1222.
[37] Alexiou C, Sehmid RJ, Jurgons R, et al. Targeting caneer cells:magnetic nanoparticles as drug carriers. Eur Biophys J. 2006;35(5):446-450.
[38] Alexiou C, Jurgons R, Seliger C, et al. Delivery of superparamagnetic nanoPartieles for loeal chemotherapy after intraarterial infusion and magnetic drug targeting. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(4A):2019-2022.
[39] 张宏征,谢民强,康庄,等.顺铂磁性纳米药物体内靶向性的研究[J].南方医科人学学报,2008,28(10):1756-1759.
[40] Ross JE, Chaudhuri PK, Ratuam M. Differential regulation of folate receptor isoforms in Nonllal and malignant tissues in vivo and in established cell lines. Physiologic and elinieal implications. Cancer. 1994; 73(9):2432-2443.
[41] 许熠铭.叶酸靶向载MMPZ反义寡核营酸磁性纳米复合物治疗喉癌的研究[D].广州:中山大学,2010. |