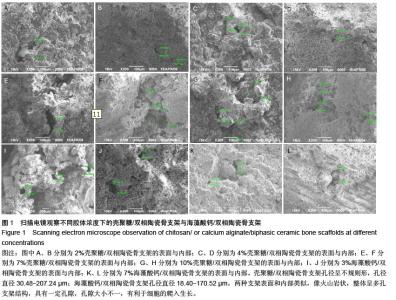
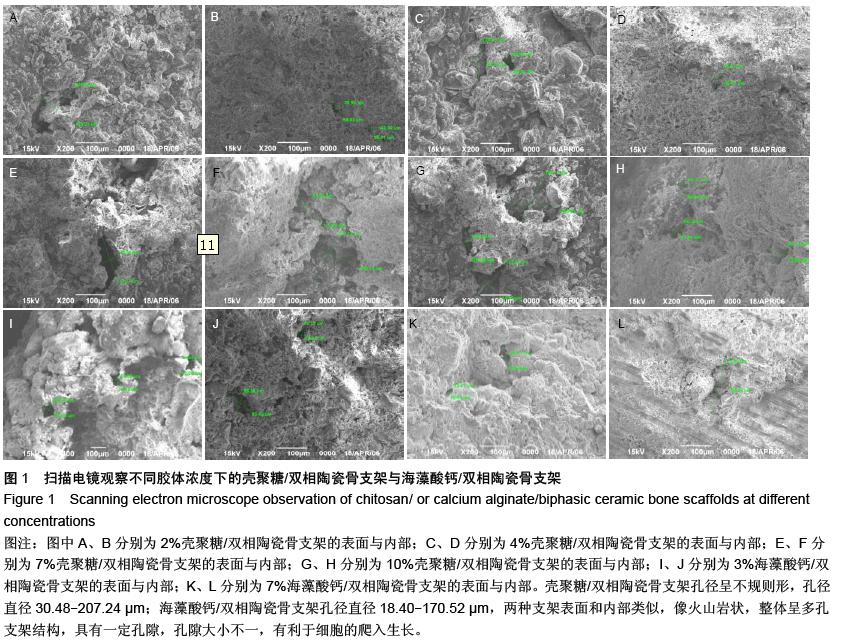
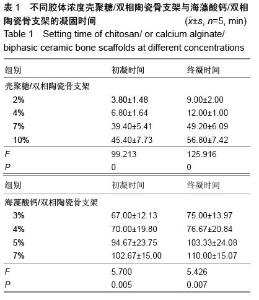
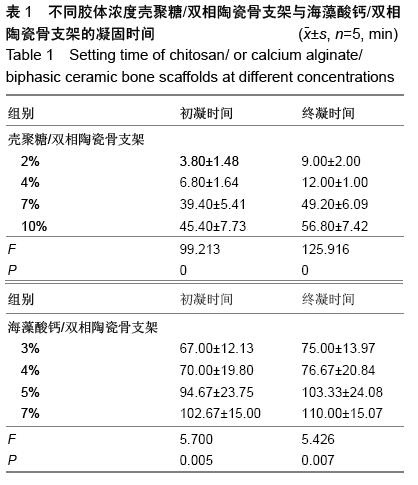
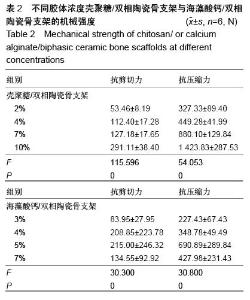
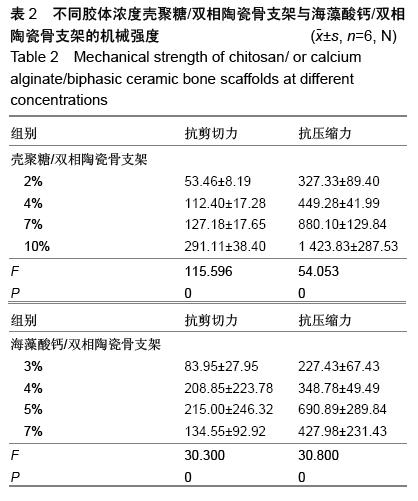
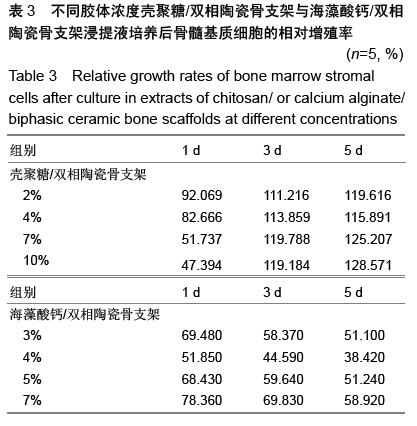
| [1] Burg KJ,Porter S,Kellam IF.Biomaterial developments for bone tissue gineering. Biomaterials. 2000;21(23): 2347-2359.
[2] Villacampa AI,Garcia-Ruiz JM.Synthesis of a newhydroxyapatite Silicacomposite material.J Crystal Growth. 2000;211:111-115.
[3] 崔杰,李征,何惠宇,等.去抗原羊椎松质骨支架微观空间结构的分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,14(10): 7425-7429.
[4] 许慧芬,何惠宇.不同方法制备异种骨材料的生物相容性研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(47): 8749-8752.
[5] 许慧芬,何惠宇.物理联合化学或化学方法处理去抗原异种松质骨支架与骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞相容性研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2012,16(6):958-962
[6] Qiao Y,Zhai Z,Chen I,et al.Cytocompatible 3D chitosan/ hydroxyapatite composites endowed with antibacterial properties: towards a self-sterilized bone tissue engineering scaffold.Sci Bull. 2015;60:1193-1202.
[7] 7Hutmacher DW.Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and age.Biomaterials.2000;21(24):2529-2543.
[8] Billstrom GH,Blom AW,Larsson S,et al.Application of scaffolds for bone regeneration: current trends and future direcyions. Injury.2013;44(2):S28-S33.
[9] 邬薇薇,胡杨,何惠宇,等.BMP-2,bFGF基因转染的大鼠骨髓干细胞与牙胚细胞在体外混合培养对成牙基因的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(1):18-22.
[10] Calis M,Demirtas TT,Atilla P,et al.Estrogen as a novel agent forinduction of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for osteogen?ic differentiation.Plastic Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(4):499-510.
[11] Park S,Kim JH,Kim IH,et al.Evaluation of Poly (lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Plate and Screw System for BoneFixation.J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(3): 1021-1025.
[12] Park SH,Park DS,Shin JW,et al.Scaffolds for bone tissueengineering fabricated from two different materials by therapid prototyping technique: PCL versus PLGA.J Mater SciMater Med. 2012;23(11): 2671-2678.
[13] 袁景,甄平.骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2015,6(12):2123-2130.
[14] Mouriño V,Cattalini JP,Roether JA,et al. Compositepolymer-bioceramic scaffolds with drug delivery capability for bone tissue engineering.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013;10(10):1353-1365.
[15] Thein-Han WW,Misra RD.Biomimetic chitosan— nanohydroxyapatite conlpte scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater.2009;5:1182-1197.
[16] 马文渊,何惠宇,杨楠,等.海藻酸钠凝胶粘合羊椎骨支架粉末力学性能实验[J].口腔医学研究, 2013,29(6): 501-504.
[17] 胡杨,胡建江,王峰,等.海藻酸钙或聚乙烯醇双相陶瓷骨支架与牙胚细胞相容性的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志, 2015, 9(7):1168-1173.
[18] 刘杨,任力,季培红,等.海藻酸钠的提纯及海藻酸钙多孔支架的制备[J].华南理工大学学报, 2012,40(7):143-147.
[19] Zuo PP,Feng HF,Xu ZZ.Fabrication of biocompatibleand mechanically reinforced graphene oxide-chitosan nano—composite films.Chem Cent J. 2013;7(1):39.
[20] SuwanPrateeb J,Sanngam R,SuwanPreuk W.Fabrieation of bioactive hydroxyapatite/bis- GMA based composite via three dimensional Printing.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(7):2637-2645.
[21] 刘璐,李瑞欣,张莉,等.透明质酸改性壳聚糖-胶原-羟基磷灰石复合支架力学特性及成骨细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(38):7127-7131.
[22] van Susante JV,Buuma P,van Osch GJ,et al. Culture of chondrocytes in alginate and collagen carrier gels.Acta Orthop Scand.1995;66:549-556.
[23] Pan Z,Ding J.Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) porous scaffolds fortissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Interface Focus.2012;2(3):366-377.
[24] Drury JL,Mooney DJ.Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4337-4351.
[25] Sanzana ES,Navarro M,Ginebra MP,et al.Role of porosity and pore architecture in the in vivo bone regeneration capacity of biodegradable glass scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(6): 1767-1773.
[26] Marsich E,Bellomo F,Turco G,et al.Nano-composite scaffoldsfor bone tissue engineering containing silver nanoparticles:preparation, characterization and biological properties.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2013; 24(7):1799-1807.
[27] 巴娇娇,何惠宇,胡杨,等.牙胚细胞体外培养过程中成牙基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(2):193-198.
[28] McCullen SD,Gittard SD,Miller PR,et al.Laser ablation impartscontrolled micro-scale pores in electrospun scaffolds for tissue engi?neering applications. Ann Biomed Eng. 2011;39(12):3021-3030.
[29] 孔丽君,敖强,奚静,等.MC3T3-E1细胞在纳米羟基磷灰 石/壳聚糖复合支架上的增殖和分化[J].生物工程学报, 2007,23(2):262-267.
[30] Sagar N,Pandey AK,Gurbani D.In-Vivo Eficacy of Compliant 3D Nano-Composite in Critical-Size Bone DefectRepair:a SixMonth Preclinical Study in Rabbit. PLoS One. 2013;(10):e77578.
[31] Nayak D,Minz AP,Ashe S,et al.Synergistic combination of antioxidants, silver nanoparticles and chitosan in a nanoparticle based formulation: Characterization and cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;470:142-152.
[32] Zhong X,Song Y,Yang P,et al.Titanium Surface Priming with Phase-Transited Lysozyme to Establish a Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Antibacterial Multilayer via Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly. PLoS One.2016;11(1):e0146957.
[33] Yang X,Zhang C,Qiao C,et al.A simple and convenient method to synthesize N-[(2-hydroxyl)-propyl-3- trimethylammonium] chitosan chloride in an ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym.2015;130:325-332.
[34] Li K,Wang Y,Huang M,et al.Preparation of chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide magnetic composite microspheres for enhanced selective removal of mercury ions from water.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;455:261-270.
[35] Li X,Zhou H,Wu W,et al.Studies of heavy metal ion adsorption on chitosan/sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide composites.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;448:389-397.
[36] Francis R,Baby DK,Gnanou Y.Synthesis and self-assembly of chitosan-g-polystyrene copolymer: a new route for the preparation of heavy metal nanoparticles.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;438: 110-115. |