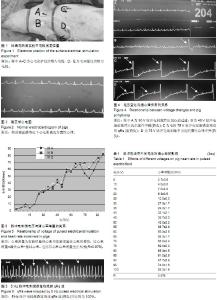
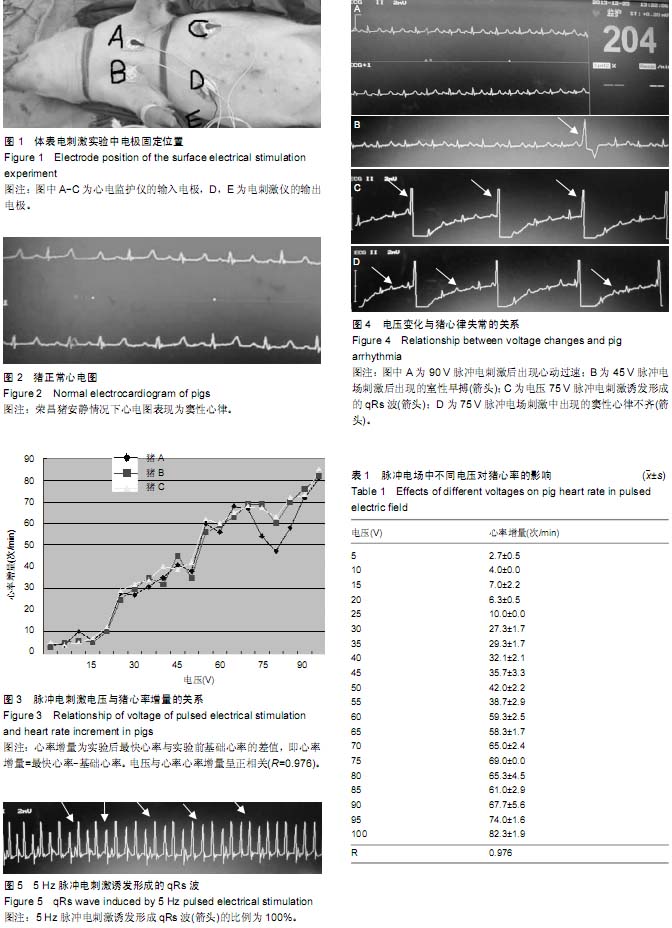
| [1] 王彤,吴海东,符岳,等.电刺激诱发猪心室颤动模型的研究和改进[J].岭南急诊医学杂,2006,32(2):132-136.
[2] 白怀,Mccaing CD,Forrester JV,等.微电场影响血管内皮细胞血管新生行为的分子机制[C].第九届西南三省一市生物化学与分子生物学学术交流会,2008:45.
[3] Li X, Kolega J. Effects of direct current electric fields on cell migration and actin filament distribution in bovine vascular endothelial cells. J Vasc Res. 2002;39(5):391-404.
[4] Small JV. Lamellipodia architecture: actin filament turnover and the lateral flow of actin filaments during motility. Semin Cell Biol. 1994;5(3):157-163.
[5] Cortese B, Palamà IE, D'Amone S, et al. Influence of electrotaxis on cell behaviour. Integr Biol (Camb). 2014; 6(9):817-830.
[6] Herman IM. Molecular mechanisms regulating the vascular endothelial cell motile response to injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 Suppl 4:S25-36.
[7] Fujino Y, Tanishima T. Actin in wound-healing of rabbit corneal endothelium. II. Study by nitrobenzoxadiazole-phallacidin method. Jpn J Ophthalmol.1987;31(3):393-404.
[8] Zhao M, Agius-Fernandez A, Forrester JV, et al. Orientation and directed migration of cultured corneal epithelial cells in small electric fields are serum dependent. J Cell Sci. 1996; 109 ( Pt 6):1405-1414.
[9] Bai H, McCaig CD, Forrester JV, et al. DC electric fields induce distinct preangiogenic responses in microvascular and macrovascular cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004; 24(7): 1234-1239.
[10] Le Clainche C, Carlier MF. Regulation of actin assembly associated with protrusion and adhesion in cell migration. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(2):489-513.
[11] Wu S, Wang Y, Guo J, et al. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields as a novel drug free therapy for breast cancer: an in vivo study. Cancer Lett. 2014;343(2):268-274.
[12] Chen X, Zhuang J, Kolb JF, et al. Long term survival of mice with hepatocellular carcinoma after pulse power ablation with nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2012;11(1):83-93.
[13] Guo F, Yao C, Li C, et al. In vivo evidences of nanosecond pulsed electric fields for melanoma malignancy treatment on tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2014;13(4):337-344.
[14] Chen R, Sain NM, Harlow KT, et al. A protective effect after clearance of orthotopic rat hepatocellular carcinoma by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(15): 2705-2713.
[15] Wu S, Guo J, Wei W, et al. Enhanced breast cancer therapy with nsPEFs and low concentrations of gemcitabine. Cancer Cell Int. 2014;14(1):98.
[16] Chen X, Kolb JF, Swanson RJ, et al. Apoptosis initiation and angiogenesis inhibition: melanoma targets for nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010; 23(4): 554-563.
[17] Chen X, Yin S, Hu C, et al. Comparative study of nanosecond electric fields in vitro and in vivo on hepatocellular carcinoma indicate macrophage infiltration contribute to tumor ablation in vivo. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86421.
[18] Zou H, Gan XL, Linghu LJ, et al. Intense nanosecond pulsed electric fields promote cancer cell apoptosis through centrosome-dependent pathway involving reduced level of PLK1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(2):152-160.
[19] Burke PA, DeNardo SJ, Miers LA, et al. Cilengitide targeting of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptor synergizes with radioimmunotherapy to increase efficacy and apoptosis in breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res. 2002;62(15): 4263-4272.
[20] Dineen SP, Sullivan LA, Beck AW, et al. The Adnectin CT-322 is a novel VEGF receptor 2 inhibitor that decreases tumor burden in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:352.
[21] Stratmann A, Acker T, Burger AM, et al. Differential inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by tie2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 dominant-negative receptor mutants. Int J Cancer. 2001;91(3):273-282.
[22] 李自立,张萍.电刺激对心血管系统影响[J].心血管病进展,2010, 17(5): 28.
[23] 甘世祥,冯济凤,董菲洛,等.贵州小型猪正常心电图研究[J].贵阳中医学院学报,1996,18(1):21-22.
[24] Oppenheimer SM. Neurogenic cardiac effects of cerebrovascular disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 1994;7(1):20-24.
[25] 王艺明,刘兴德,董为伟,等.电刺激大鼠岛叶对心电图和心率变异性的影响[J].中国医师杂志,2003,5(12):1065-1067.
[26] 吴子建,龙迪和,何璐,等.不同频率电针“内关”穴对急性心肌缺血模型家兔心交感神经电活动的影响[J].时珍国医中药,2012, 23(6):241-244.
[27] 汪克明,周美启,王月兰,等.电针“脾俞”穴对胃窦部溃疡大鼠平滑肌电活动的干预作用及机制探讨[J].安徽中医学院学报,2003, (6):222-226.
[28] Ziegelstein RC. Acute emotional stress and cardiac arrhythmias. JAMA. 2007;298(3):324-329.
[29] 周矗,刘政疆.乌鲁木齐“7•5事件”伤者临床心电图变化分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(18):4327-4327.
[30] 徐新萍,左红艳,王少霞,等,高压脉冲电流对家兔心脏功能与结构的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2011,36(6):633-635. |