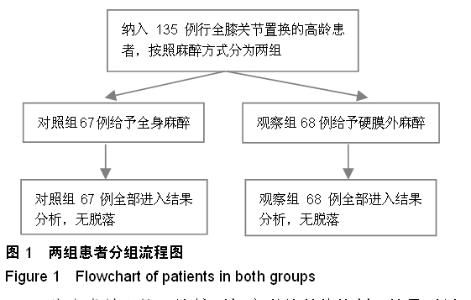
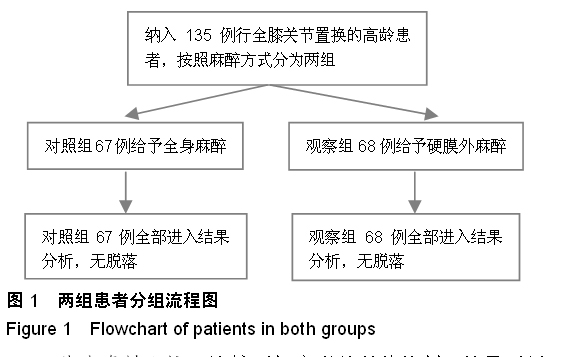
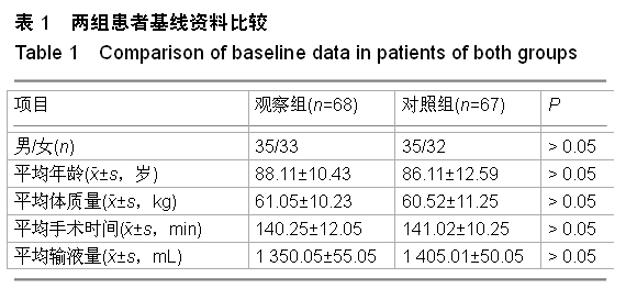
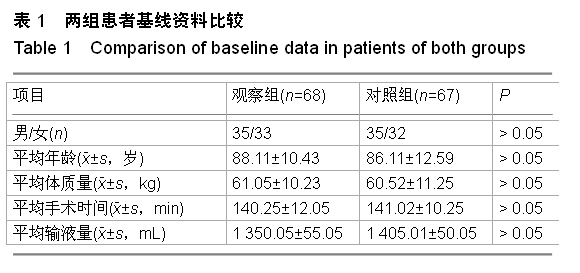
| [1] 宋万军,董江龙,李欣,等.不同麻醉方式对老年膝关节置换术患者围术期凝血功能的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(4): 549-550.
[2] 于花.麻醉方式对全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓发生率的影响[J].医学综述,2013,19(24):4587-4589.
[3] 韩东峰.喉罩全麻复合腰丛-坐骨神经阻滞应用于老年患者全膝关节置换术的临床观察[D].山东大学,2013.
[4] 杜秋.下肢骨关节手术患者围手术期采取硬膜外麻醉和全麻对凝血功能的影响[J].四川医学,2014,35(6):666-667.
[5] 盛洪广,罗振中,蔡俊赢,等.急性非等容量血液稀释对硬膜外阻滞复合全麻手术患者循环和凝血功能的影响[J].江西医学院学报, 2007,47(6):66-69.
[6] 姚菊,沈施仁,罗锡珍,等.不同麻醉方法对围手术期患者40例凝血功能的影响[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2010,30(4):288-289.
[7] 吴永健.硬膜外复合静脉麻醉与全静脉麻醉对术后炎性反应及纤溶功能的影响比较[J].中国基层医药,2012,19(3):444-445.
[8] 王向东,丑维斌,刘喻,等.麻醉浅低温对老年髋关节置换术中失血量影响的临床研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2010,9(14):1079-1080.
[9] 刘若杉,朱文忠,邓小明,等.体外循环下心瓣膜置换术患者血小板及凝血功能的变化及普鲁泊福对其的影响[J].第二军医大学学报, 2005,26(6):671-674.
[10] Hollmann MW, Kathrin S, Wieczorek MS, et al.Epidural anes-thesia prevents hypercoagulation in patients undergoing major or-thopedic surgery. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001;3(26): 215-222.
[11] Bruckner S,Reinke U,Roth-Isigkeit A,et al.Comparison of general and spinal anesthesia and their influence on hemostatic markers in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty.J Clin Anesth.2003;9(15):433-440.
[12] 林仙菊,丁进峰,杨志海,等.6%羟乙基淀粉对股骨干骨折患者凝血状态和炎性反应调控的影响[J].浙江创伤外科,2011,19(5): 605-606.
[13] 招伟贤.外科手术中稀释性凝血障碍的研究进展[J].广东医学, 2009,30(3):321-324.
[14] 欧玉清.双管喉罩联合椎管内麻醉在骨科下肢手术麻醉的临床研究[J].四川医学,2014,35(1):73-75.
[15] 姚静.双管喉罩联合椎管内麻醉在骨科下肢手术麻醉的临床研究[J].中国医药指南,2009,7(20):64-66.
[16] 周立志,肖晋,于梅芳,等.高渗氯化钠羟乙基淀粉40预扩容对蛛网膜下腔和硬膜外腔联合麻醉后血流动力学及凝血功能的影响[J].中国医师进修杂志,2008,31(33):52-55.
[17] Cho KY,Kim KI,Khurana S,et al.Is routine chemoprophylaxis necessary for prevention of venous thromboembolism following knee arthroplasty in a low incidence population? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(4): 551-559.
[18] 李云龙,王华,叶慧仪,等.不同麻醉方法对下肢骨关节手术患者围术期凝血功能的影响[J].中国现代药物应用,2013,7(8):9-11.
[19] 王华,叶慧仪,李云龙,等.腰硬联合麻醉对患者下肢骨关节手术围术期凝血功能的影响[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(24):1-4.
[20] 胡弋,葛衡江.麻醉对凝血功能的影响[C].//2004中华医学会全国麻醉学术年会知识更新讲座,2004:479-481.
[21] 陈传义,符丽,何柱良,等.术后不同镇痛方式对老年患者应激反应和凝血功能的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2009,26(6):786-788.
[22] Bonnin MP, Schmidt A, Basiglini L, et al. Mediolateral oversizing influences pain, function, and flexion after TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 2(110): 2314-2324.
[23] Macdonald DW,Higgs G,Parvizi J,et al. Oxidative properties and surface damage mechanisms of remelted highly crosslinked polyethylenes in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2013;37(4): 611-615.
[24] 贺雅琳,丁志刚,梁华,等.外周神经阻滞联合静脉快通道麻醉在高龄下肢骨科手术中的应用[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(6): 935-937.
[25] 刘唐生,王心田,高晓秋,等.连续腰麻与腰硬联合麻醉用于老年人下肢手术的比较[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2006,22(8):590-592.
[26] 郑辉利,马保新.喉罩与腰-硬联合麻醉在侧卧位下肢手术的应用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2011,27(5):489-490.
[27] Huisman MV, Quinlan DJ, Dahl OE, et al. Enoxaparin versus dabig?atran or rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis after hip or knee arthroplasty : results of separate pooled analyses of phase III multicenterrandomized trials. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3(6):652-660.
[28] 邱燕文,周泽钢,何志文,等.老年患者下肢手术椎管内麻醉不同方法的比较[J].实用医学杂志,2008,24(8):1330-1332.
[29] 李佳清,毛菇,常胜和,等.不同麻醉方法在高龄患者下肢手术中的应用效果比较[J].山东医药,2013,53(26):70-72.
[30] 井郁陌,王香梅,刘莉,等.腰-硬联合麻醉用于高龄高危患者下肢手术的临床观察[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2007,23(6):504-505.
[31] 胡小雪,李建松.SLIPA喉罩全麻复合硬膜外阻滞在膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国临床医学,2010,17(1):121-122.
[32] 曹雅军,严霞.两种麻醉方法在老年关节置换中的临床效果比较[J].海南医学院学报,2012,18(7):959-961.
[33] 刘沁爽,李淮安,梁淑娟,等.全麻及硬膜外麻醉对骨科大手术老年患者术后早期认知功能的影响[J].山东医药,2011,51(26): 68-69.
[34] 宛春甫,赵东,朱鹤,等.硬膜外阻滞复合全麻用于老年患者膝关节置换手术的可行性[J].河北医药,2008,30(8):1171-1172.
[35] 吴继敏,樊理华,章玲宾,等.硬膜外麻醉与全身麻醉在膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2013,(22):42-43.
[36] 陈虎,曹力,杨德盛,等.麻醉方式与全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓发生率分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(5):402-405.
[37] 王焕彬,陈枝.两种麻醉方法对老年髋关节置换术患者血液流变学的影响[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2014,36(3):329-331.
[38] 毛宾尧.怎样才能成功实施人工踝关节置换术——关于手术适应证和手术注意要点[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(24): 1915-1916.
[39] 曾令全,石宗莉,刘艳,等.两种麻醉方式用于髋关节置换术的临床比较[J].重庆医学,2011,40(35):3607-3609.
[40] 周子戎,汪春英.腰-硬联合麻醉在80岁以上高危老年病人骨科手术的应用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2008,24(1):40-41.
|