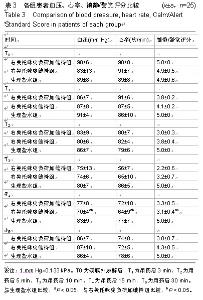
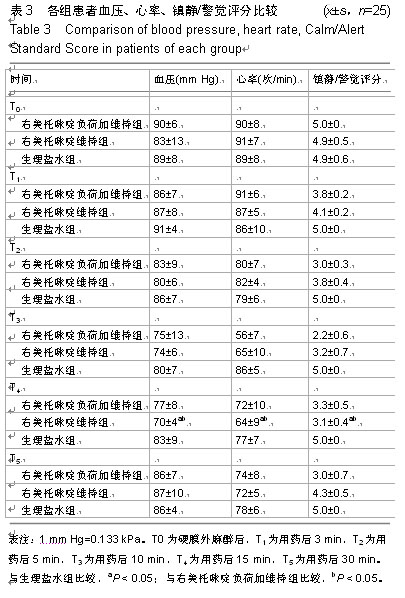
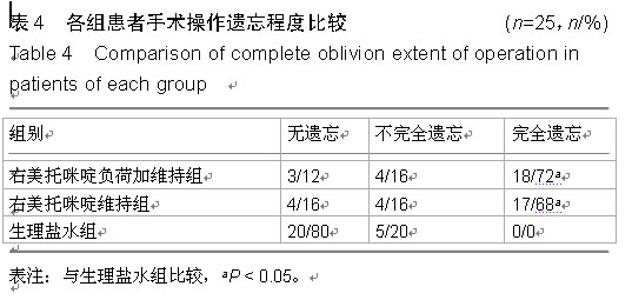
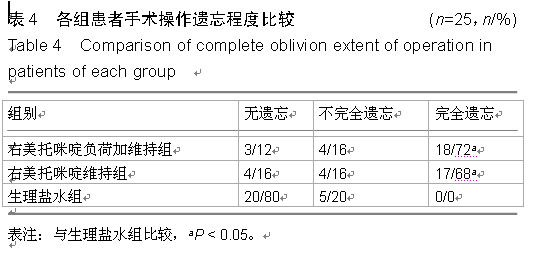
| [1] 沈卫华,陈樱,李云胜,等.复合异丙酚麻醉诱导时右美托咪定的适宜剂量[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(4):398-401.
[2] 杨云.小剂量右美托咪啶在老年高血压患者围麻醉期控制血压的疗效及安全性[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(18):5144-5145.
[3] Ahern TP, Pedersen L, Svae C, et al. The Association Between Vitamin K Antagonist Therapy and Site-specific Cancer Incidence Estimated by Using Heart Valve Replacement as an Instrumental Variable. Am J Epidemiol. 2011;174(12):1382-1390.
[4] 徐颖怡,宋兴荣,张国强,等.右美托咪啶滴鼻诱导CT检查患儿睡眠的半数有效剂量[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(24):1886-1888.
[5] 沈卫华,陈樱,李云胜,等.复合异丙酚麻醉诱导时右美托咪定的适宜剂量[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(4):398-401.
[6] 陈正,杭黎华,吴进,等.右美托咪啶对瑞芬太尼抑制切皮体动反应量效关系的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2013,29(2):121-123.
[7] Kim BG, Kang H. The Effect of Preemptive Perianal Ropivacaine and Ropivacaine with Dexmedetomidine on Pain after Hemorrhoidectomy: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind,Placebo-Controlled Study. Indian J Surg. 2014; 76 (1):49-55.
[8] 徐枫,杨承祥,刘洪珍,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶对腹腔镜卵巢囊肿剥除术患者七氟醚用量的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2011, 31(10): 1203-1205.
[9] 贾佳,王班,李艳辉,等.右美托咪啶预先给药对罗哌卡因诱发大鼠心肌毒性阈值的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2011,31(12): 1434-1436.
[10] 黄其健,翁险峰.右美托咪啶对苏醒期应激反应及寒颤发生率的影响研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2014,35(7):158-160.
[11] 王宜衡,蔡珺,余小芳,等.右美托咪啶预处理对大鼠自体原位肝移植术后肠道损伤的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2013, 34(6):845-850.
[12] 林森,杨承祥,王汉兵,等.复合异丙酚麻醉时右美托咪定用于老年患者ERCP术的适宜剂量[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(2): 186-189.
[13] 周婷,王思桦,武庆平,等.不同剂量的右美托咪啶抑制芬太尼诱发呛咳反应的临床研究[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2013, 42(4): 469-472.
[14] 李坤河,李毅,舒海华,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶复合异丙酚和瑞芬太尼用于腹部手术病人麻醉的效果[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2012, 32(7):799-801.
[15] 李远强,王志刚,宫本晶,等.不同剂量右美托咪定对体外循环下心内直视手术患儿肺损伤的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(5): 529-532.
[16] 王常永,商敏,程林,等.右美托咪啶和咪达唑仑用于危重症患者镇静效应的比较[J].海南医学院学报,2011,17(5):695-697.
[17] 孙申,黄绍强.不同剂量右美托咪啶预防舒芬太尼诱发患者全麻诱导期间呛咳反应的可行性[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2011,31(5): 539-541.
[18] 罗亮,曾勉,关开泮,等.不同维持剂量右美托咪啶对机械通气患者心率和血压的影响[J].中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志,2014,(1): 47-48.
[19] 徐尚军,洪方晓,周国庆,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶在清醒气管插管中最适剂量的比较[J].北京医学,2013,35(1):26-29.
[20] 于健,李睿,郭庆夺,等.混合罗哌卡因用于腰丛-坐骨神经阻滞时右美托咪定的适宜剂量[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(11): 1369-1371.
[21] 马盼盼,朴美花,王艳姝,等.右美托咪啶和亚麻醉剂量氯胺酮对老年骨科全麻患者术后谵妄发生率的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2013,39(1):128-132.
[22] 庞国勋,高冬艳,张煜东,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶对七氟醚抑制切皮诱发患者体动反应肺泡气最低有效浓度的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2012,32(7):808-810.
[23] 崔明珠,张加强,孟凡民,等.右美托咪定复合丙泊酚-瑞芬太尼用于轻度肝功能异常患者开腹术麻醉的适宜剂量[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2013,33(8):959-962.
[24] Hu R, Liu JX, Jiang H. Dexmedetomidine versus remifentanil sedation during awake fiberoptic nasotracheal intubation: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. J Anesth. 2013;27 (2):211-217.
[25] 胡宪文,张野,孔令锁,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶抑制气管插管诱发患者心血管反应效应的比较[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2010,30(11): 1304-1306.
[26] Ozdemir L, Elonu OH, Gocmen AY. Heart type fatty acid binding protein is more sensitive than troponin I and creatine kinase myocardial band at early stage in determining myocar dial injury caused by percutaneous coronary intervention. Int Heart J. 2011;52(3):143-145.
[27] KuniFaHwa T, Ueno M, Kurosawa A, et al. DexmedetomidiBe Cgtl stabilize hemodynamics and spare anesthetics before cardiopulmonary bypass. J Anesth. 2011;25(6):818-822.
[28] 庞国勋,高冬艳,张煜东,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶对七氟醚抑制切皮诱发患者体动反应肺泡气最低有效浓度的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2012,32(7):808-810.
[29] 于学超.地佐辛复合不同剂量右美托咪啶在术后静脉镇痛中的应用[J].天津医药,2013,54(9):917-918.
[30] 任柏林,杨清存,冯艳平,等.老年患者不同剂量右美托咪啶对丙泊酚靶控效应的影响[J].山东医药,2011,51(48):77-78.
[31] 方宁宁,侯跃东,于金贵,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶对甲状腺手术患者全身麻醉拔管期心血管反应的影响[J].山东医药,2012,52(38): 58-60.
[32] 姜燕,王世端,黄辉,等.不同剂量右美托咪啶对异丙酚抑制老年患者Supreme喉罩置入反应EC50的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2012,32(7):805-807.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|