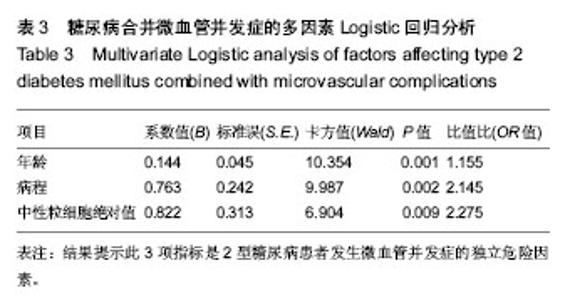
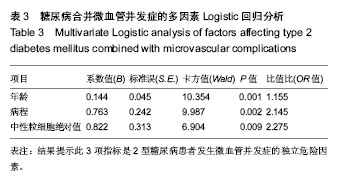
| [1] Gregg EW, Cadwell BL, Cheng YJ, et al. Trends in the prevalence and ratio of diagnosed to undiagnosed diabetes according to obesity levels in the U.S. Diabetes Care.2004; 27(12):2806-2812.
[2] Stefanska B. Curcumin ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus - insights into its mechanisms of action. Br J Pharmacol.2012;166(8):2209-2211.
[3] 张丽侠,郑丽丽,阎西艴,等.强化降糖对2型糖尿病血管并发症的影响[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2010,45(2):296-298.
[4] 杜俊文,吴韬,张俊芳,等.2型糖尿病患者腹部脂肪分布与全身炎症反应标记物间的关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(21): 4102-4103.
[5] Festa A, D'Agostino RJ, Howard G, et al. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation. 2000;102(1):42-47.
[6] Vozarova B, Weyer C, Lindsay RS, et al. High white blood cell count is associated with a worsening of insulin sensitivity and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.2002;51(2):455-461.
[7] Wang D, Zhang X, Lu L, et al. Assessment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with magnetic resonance imaging.Eur Radiol.2015; 25(2): 463-471.
[8] 张志军,马红,杨香玖.2型糖尿病微血管并发症相关因素的有序Logistic回归分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(15):3167-3170.
[9] Wang DD, Bakhotmah BA, Hu FB, et al. Prevalence and correlates of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a saudi arabic population: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One.2014;9(9): e106935.
[10] Leehey DJ, Kramer HJ, Daoud TM, et al. Progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes - beyond blood pressure control: an observational study.BMC Nephrol.2005;6:8.
[11] Gkrania-Klotsas E, Ye Z, Cooper AJ, et al. Differential white blood cell count and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional and prospective studies. PLoS One.2010;5(10):e13405.
[12] Du X, Zhu B, Hu G, et al. U-shape association between white blood cell count and the risk of diabetes in young Chinese adults. Diabet Med.2009;26(10):955-960.
[13] Pattanathaiyanon P, Phaloprakarn C, Tangjitgamol S. Comparison of gestational diabetes mellitus rates in women with increased and normal white blood cell counts in early pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res.2014;40(4):976-982.
[14] Tong PC, Lee KF, So WY, et al. White blood cell count is associated with macro- and microvascular complications in chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care.2004; 27(1):216-222.
[15] 张莹,李霆,张代民.糖尿病肾病患者血液白细胞的变化[J].临床军医杂志,2006,34(2):143-145.
[16] Ohshita K, Yamane K, Hanafusa M, et al. Elevated white blood cell count in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care.2004;27(2):491-496.
[17] Wanten G, van Emst-De V S, Naber T, et al. Nutritional lipid emulsions modulate cellular signaling and activation of human neutrophils.J Lipid Res.2001;42(3):428-436.
[18] Foy CG, Bell RA, Farmer DF, et al. Smoking and incidence of diabetes among U.S. adults: findings from the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes Care,2005; 28(10): 2501-2507.
[19] Haire-Joshu D, Glasgow R E, Tibbs T L. Smoking and diabetes. Diabetes Care,2004;27 Suppl 1:S74-S75.
[20] Lonardo A, Loria P, Leonardi F, et al. Fasting insulin and uric acid levels but not indices of iron metabolism are independent predictors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A case-control study.Dig Liver Dis,2002;34(3):204-211.
[21] Assy N, Kaita K, Mymin D, et al. Fatty infiltration of liver in hyperlipidemic patients. Dig Dis Sci,2000;45(10):1929-1934.
[22] Sattar N,Scherbakova O,Ford I,et al.Elevated alanine aminotransferase predicts new-onset type 2 diabetes independently of classical risk factors, metabolic syndrome, and C-reactive protein in the west of Scotland coronary prevention study. Diabetes,2004;53(11):2855-2860.
[23] Doi Y, Kubo M, Yonemoto K, et al. Liver enzymes as a predictor for incident diabetes in a Japanese population: the Hisayama study. Obesity (Silver Spring),2007;15(7):1841-1850.
[24] Sattar N.Biomarkers for diabetes prediction, pathogenesis or pharmacotherapy guidance? Past, present and future possibilities. Diabet Med,2012;29(1):5-13. |