Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (22): 3532-3536.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.22.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wedging index of thoracolumbar vertebrae in healthy persons measured by magnetic resonance imaging
Zhang Bin, Wu Guang-zhong, Wu Peng
- Imaging Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2014-03-31Online:2014-05-28Published:2014-05-28 -
Contact:Wu Guang-zhong, Technician-in-charge, Imaging Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Bin, Master, Physician, Imaging Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Bin, Wu Guang-zhong, Wu Peng. Wedging index of thoracolumbar vertebrae in healthy persons measured by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3532-3536.
share this article
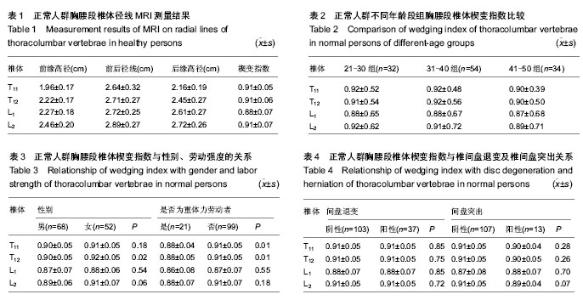
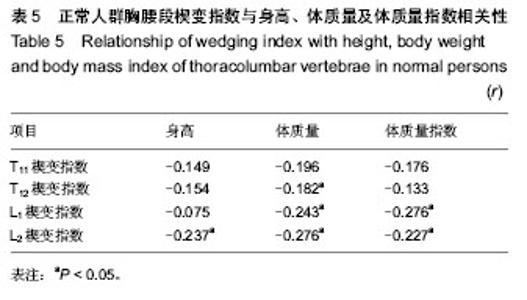
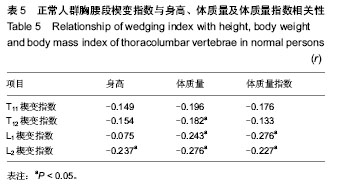
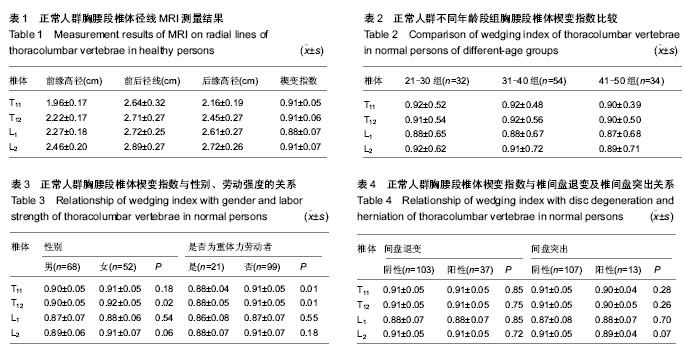
2.1 正常人群胸腰段椎体的MRI表现 所有被测量者MRI图像上均未发现椎体出现异常信号改变及压缩骨折,符合入选标准,共测量1 920次。实验共测量480个椎体,楔形变椎体452个(94.2%),其中骨髓脂肪化349个(72.7%)。测量T11-L2椎体存在楔形变的椎体个数分别为103个(23.5%)、112个(25.5%)、115个(26.3%)、108个(24.7%)。经测量T11-L2椎体楔变指数在0.71-1.0之间变化,其中L1椎体楔变指数平均值最小(表1)。37名测量者中T11-L2节段间盘存在退变,共111个椎间盘;13名存在椎间盘突出,共计26个椎间盘(图1);7名存在Schmorl’s结节;6名存在终板不规则。 2.2 年龄、性别、劳动强度及体质量指数对楔变指数的影响 经测量各年龄组间楔变指数之间差异无显著性意义,但年龄较大者楔变指数较小,男性志愿者T12、L2楔变指数(0.90,0.89)小于女性志愿者(0.92,0.91)(表2)。其中重体力劳动者(建筑工人、农民)T11、T12楔变指数(0.88,0.88)小于非重体力劳动者(其他职业志愿者)(0.91,0.91)(表3)。 楔变指数在椎间盘退变或/和突出志愿者中与椎间盘正常者中无明显差异(表4)。研究显示,终板异常及Schmorl’s结节志愿者相关节段椎体楔变指数平均值小于无终板异常、无Schmorl’s结节者,并且显示体质量指数与楔变指数存在负相关性(表5)。"
| [1] 桂柯科.胸腰段骨折的治疗进展[J].复旦学报:医学版,2010, 37(5): 612-616. [2] Verlaan JJ, Diekerhof CH, Buskens E, et al.Surgical treatment of traumatic fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a systematic review of the literature on techniques, complications, and outcome.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(7):803-814. [3] Masharawi Y, Salame K, Mirovsky Y,et al.Vertebral body shape variation in the thoracic and lumbar spine: characterization of its asymmetry and wedging.Clin Anat. 2008;21(1):46-54. [4] Masharawi Y, Kjaer P, Bendix T,et al.The reproducibility of quantitative measurements in lumbar magnetic resonance imaging of children from the general population.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(19):2094-100. [5] 刘学光,邱勇.休门氏病矫形术后交界性后凸的危险因素及预防进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(4):338-341. [6] 马新发,葛颖,关春爽.常规MRI鉴别诊断椎体转移瘤与良性压缩骨折[J].中国医学影像技术,2009,25(5):866-869. [7] 梁大利,叶道斌.常见椎体楔形变的 X 线诊断[J].西藏医药杂志,2002,23(S1):43. [8] Davies KM, Recker RR, Heaney RP.Normal vertebral dimensions and normal variation in serial measurements of vertebrae.J Bone Miner Res. 1989;4(3):341-349. [9] Abdel-Hamid Osman A, Bassiouni H, Koutri R,et al.Aging of the thoracic spine: distinction between wedging in osteoarthritis and fracture in osteoporosis--a cross-sectional and longitudinal study.Bone. 1994;15(4):437-442. [10] 曾晓华,李国雄,刘忠,等.胸腰椎体应力变形与轻度压缩骨折的X线、CT、MRI鉴别诊断[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2008,16(1): 12-14. [11] Lauridsen KN, De Carvalho A, Andersen AH.Degree of vertebral wedging of the dorso-lumbar spine.Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1984;25(1):29-32. [12] 魏本和,王军帅,厉启臣,等.正常成人T11~L1椎体DR形态学研究[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2012,10(4):335-338. [13] 王永刚,孙丰刚,高歌.正常人胸12、腰1椎体前后高度比的X线测量[J].泰山医学院学报,2005,26(6):582. [14] 程若勤,金红花,王化敏,等.成人第12胸椎及第1腰椎椎体前缘和后缘高度比率正常值的应用价值[J].重庆医学,2013,42(9): 1014-1016. [15] 童飞飞.胸腰椎压缩性骨折影像学诊断与分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2005. [16] 常林,王宁敏.脊柱脊髓伤与病鉴定的法医学研究[J].法律与医学杂志,1999, 6(2):52-55. [17] 刘振江,洪仕君,李利华,等.脊柱损伤的法医临床学鉴定研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(11):2197-2000. [18] 李生彦,黄思兴,单兴尧,等.交通事故致胸、腰椎损伤致残等级评定447例分析[J].法医学杂志,2006,22(1):61-64. [19] 叶永刚,黄载星,文德福.腰椎椎体楔形改变的X线影像诊断[J].吉林医学,2011,32(16):3191-3193. [20] Shigematsu H, Koizumi M, Yoneda M,et al.Magnification error in digital radiographs of the cervical spine against magnetic resonance imaging measurements.Asian Spine J. 2013;7(4): 267-272. [21] 潘玉萍,庄奇新,李文彬,等.MRI水样信号在椎体压缩骨折中的诊断价值[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2008,28(1):29-31. [22] 刘振生,李澄,滕皋军.MRI液体征象在良恶性椎体压缩骨折鉴别诊断中的价值[J].临床放射学杂志,2007,26(12):1243-1246. [23] 江晓兵,莫凌,姚珍松,等.SPECT、SPECT-CT与MRI对新鲜骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的诊断价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013, 23(10):891-897. [24] 庄伟雄,龙小武,文海忠,等.低场强MRI对胸腰椎新旧压缩性骨折的鉴别诊断价值[J].中国医药导报,2009,6(13):106-108. [25] 何涌,曾阳东,邱维加,等.脊柱外伤的CT和MRI诊断价值对比研究[J].广西医学,2009,31(8):1074-1076. [26] 程克斌,王晨,蒋雯,等.急性或亚急性骨质疏松性椎体骨折椎体内真空裂隙的MRI表现[J]. 中医正骨,2013,25(12):45-48. [27] 王晨,程克斌,蒋雯,等.多发骨质疏松性椎体的急性或亚急性骨折的MRI表现[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(11):975-979. [28] 魏君臣,李保朋,翟宁,等. ADC值与外伤性椎体压缩骨折时间的相关性研究[J].医学影像学杂志,2013,23(8):1285-1288. [29] 易自生,刘一平,陈志斌,等.不同序列磁共振成像诊断脊柱损伤的价值研究[J].人民军医,2011,54(12):1082-1083. [30] 陈文静,燕桂新,孙亮,等. 128排螺旋CT及MRI对诊断骨质疏松性椎体压缩的诊断价值比较[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2012,10(6): 97-99. [31] Gargas J,Yaszay B,Kruk P,et al.An analysis of cervical spine magnetic resonance imaging findings after normal computed tomographic imaging findings in pediatric trauma patients: ten-year experience of a level I pediatric trauma center.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2013;74(4):1102-1107. [32] Henry M,Scarlata K,Riesenburger RI,et al.Utility of STIR MRI in pediatric cervical spine clearance after trauma.J Neurosurg Pediatr.2013;12(1):30-36. [33] Fisher BM,Cowles S,Matulich JR,et al.Is magnetic resonance imaging in addition to a computed tomographic scan necessary to identify clinically significant cervical spine injuries in obtunded blunt trauma patients?Am J Surg.2013; 206(6):987-993. [34] Park SY,Lee SH,Suh SW,et al.Usefulness of MRI in determining the appropriate level of cement augmentation for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Spinal Disord Tech.2013;26(3):E80-85. [35] Henry M,Riesenburger RI,Kryzanski J,et al.A retrospective comparison of CT and MRI in detecting pediatric cervical spine injury.Childs Nerv Syst.2013;29(8):1333-1338. [36] Utz M,Khan S,O'Connor D,et al.MDCT and MRI evaluation of cervical spine trauma.Insights Imaging.2014;5(1):67-75. [37] Khanna P,Chau C,Dublin A,et al.The value of cervical magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of the obtunded or comatose patient with cervical trauma,no other abnormal neurological findings, and a normal cervical computed tomography.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2012; 72(3): 699-702. [38] Mahajan P,Jaffe DM,Olsen CS,et al.Spinal cord injury without radiologic abnormality in children imaged with magnetic resonance imaging.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2013;75(5): 843-847. [39] Ackland HM, Cameron PA, Wolfe R, et al.Outcomes at 12 months after early magnetic resonance imaging in acute trauma patients with persistent midline cervical tenderness and negative computed tomography.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(13):1068-1081. [40] Kaiser ML, Whealon MD, Barrios C, et al.The current role of magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing cervical spine injury in blunt trauma patients with negative computed tomography scan.Am Surg.2012;78(10):1156-1160. [41] Dundamadappa SK,Cauley KA.MR imaging of acute cervical spinal ligamentous and soft tissue trauma.Emerg Radiol.2012; 19(4):277-286. [42] Crosby CG,Even JL,Song Y,et al.Diagnostic abilities of magnetic resonance imaging in traumatic injury to the posterior ligamentous complex: the effect of years in training. Spine J.2011;11(8):747-753. [43] Furlan JC,Kailaya-Vasan A,Aarabi B,et al.A novel approach to quantitatively assess posttraumatic cervical spinal canal compromise and spinal cord compression: a multicenter responsiveness study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(10): 784-793. [44] Rumpel H,Chong Y,Porter DA,et al.Benign versus metastatic vertebral compression fractures: combined diffusion-weighted MRI and MR spectroscopy aids differentiation.Eur Radiol. 2013; 23(2):541-550. [45] 周山.颈椎弓根周围神经组织MRI的指标测量及临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(30):5564-5567. [46] Chatha DS, Schweitzer ME.MRI criteria of developmental lumbar spinal stenosis revisited.Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2011; 69(4):303-307. [47] Street J, Lenehan B, Albietz J,et al.Intraobserver and interobserver reliabilty of measures of kyphosis in thoracolumbar fractures.Spine J. 2009;9(6):464-469. [48] 刘金瑞,杨庆国,段文,等.腰骶椎矢状位形态学改变与椎间盘退变的MRI评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3139-3142. [49] Matsumoto M, Okada E, Kaneko Y,et al.Wedging of vertebral bodies at the thoracolumbar junction in asymptomatic healthy subjects on magnetic resonance imaging.Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(3):223-228. [50] 张智海,沈建雄,刘忠厚.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准回顾性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2004,10(3):255-262,287. [51] 任东风,侯树勋,彭宝淦,等.腰椎间盘损伤后MRI表现及组织学改变的实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(2):142-146. [52] 李春林,李放,张志成.腰椎间盘退变性疾患下腰椎终板形态的MRI观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(5):393-397. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [4] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [5] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [6] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [7] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [8] | Zhang Wei, Hu Jiang, Tang Liuyi, Wan Lun, Yu Yang, Lin Shu, Tang Zhi, Wang Fei. Advantages of robot assisted percutaneous biopsy in the diagnosis of spinal lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 844-848. |
| [9] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [10] | Xie Zhifeng, Liu Qing, Liu Bing, Zhang Tao, Li Kun, Zhang Chunqiu, Sun Yanfang. Biomechanical characteristics of the lumbar disc after fatigue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 339-343. |
| [11] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Zhu Zhenqi, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of sciatic scoliosis caused by lumbar disc herniation: a 2-year follow-up of coronal and sagittal balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 409-413. |
| [12] | Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen. Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [13] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [14] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [15] | Yi Meizhi, Luo Guanghua, Xiao Yawen, Hu Rong, Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng. MRI findings of anatomical variations of the talus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3888-3893. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||