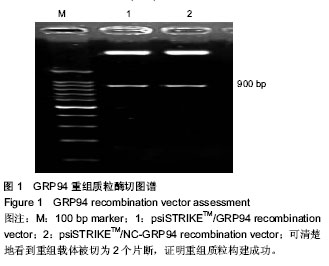
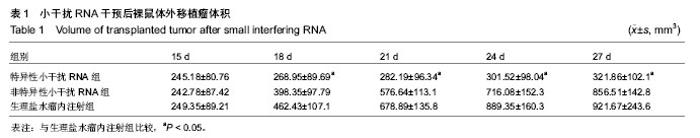
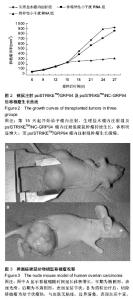
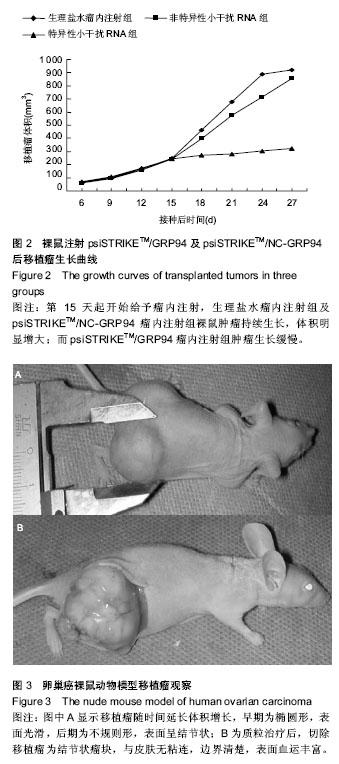
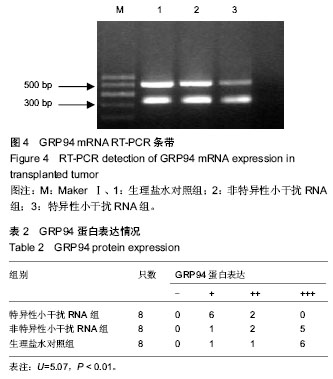
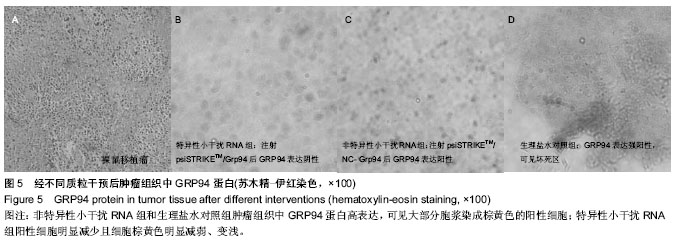
| [1] 张新晨,杨维良.葡萄糖调节蛋白在肿瘤细胞中的表达及意义[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2003,18(8):501-502.
[2] Lee AS. The glucose-regulated proteins: stress induction and clinical applications.Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26(8):504-511.
[3] Fu Y, Lee AS. Glucose regulated proteins in cancer progression, drug resistance and immunotherapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5(7):741-744.
[4] 崔照琼,张彦,李艳琼. RNA干扰技术应用新进展[J].安徽医药, 2012,16(3):283-285.
[5] 孙平,赵微,赵毅玲. RNA干扰技术的原理与应用[J].医学综述, 2011,17(2):164-167.
[6] Chiou JF, Tai CJ, Huang MT, et al. Glucose-regulated protein 78 is a novel contributor to acquisition of resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17(2):603-612.
[7] Cabanes D, Sousa S, Cebriá A, et al. Gp96 is a receptor for a novel Listeria monocytogenes virulence factor, Vip, a surface protein. EMBO J. 2005;24(15):2827-2838.
[8] Parmiani G, Testori A, Maio M, et al. Heat shock proteins and their use as anticancer vaccines. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10(24): 8142-8146.
[9] Wang XH, Qin Y, Hu MH, et al. Dendritic cells pulsed with gp96-peptide complexes derived from human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) induce specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005;54(10):971-980.
[10] Binder RJ, Srivastava PK. Peptides chaperoned by heat-shock proteins are a necessary and sufficient source of antigen in the cross-priming of CD8+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(6):593-599.
[11] Nicchitta CV, Carrick DM, Baker-Lepain JC. The messenger and the message: gp96 (GRP94)-peptide interactions in cellular immunity. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004;9(4):325- 331.
[12] Demine R, Walden P. Testing the role of gp96 as peptide chaperone in antigen processing. J Biol Chem. 2005;280 (18):17573-17578.
[13] Liu S, Wang H, Yang Z, et al. Enhancement of cancer radiation therapy by use of adenovirus-mediated secretable glucose-regulated protein 94/gp96 expression. Cancer Res. 2005;65(20):9126-9131.
[14] Di Paolo NC, Tuve S, Ni S, Hellström KE, et al. Effect of adenovirus-mediated heat shock protein expression and oncolysis in combination with low-dose cyclophosphamide treatment on antitumor immune responses. Cancer Res. 2006;66(2):960-969.
[15] Chen WT, Tseng CC, Pfaffenbach K, et al. Liver-specific knockout of GRP94 in mice disrupts cell adhesion, activates liver progenitor cells, and accelerates liver tumorigenesis. Hepatology. 2014;59(3):947-957.
[16] Langer R, Feith M, Siewert JR, et al. Expression and clinical significance of glucose regulated proteins GRP78 (BiP) and GRP94 (GP96) in human adenocarcinomas of the esophagus. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:70.
[17] Suriano R, Ghosh SK, Ashok BT, et al. Differences in glycosylation patterns of heat shock protein, gp96: implications for prostate cancer prevention. Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6466-6475.
[18] Pan Z, Erkan M, Streit S, et al. Silencing of GRP94 expression promotes apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol.2009;35(4):823-828.
[19] Chavany C, Mimnaugh E, Miller P, et al. p185erbB2 binds to GRP94 in vivo. Dissociation of the p185erbB2/GRP94 heterocomplex by benzoquinone ansamycins precedes depletion of p185erbB2. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(9): 4974-4977.
[20] Chen X, Ding Y, Liu CG, et al. Overexpression of glucose-regulated protein 94 (Grp94) in esophageal adenocarcinomas of a rat surgical model and humans. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23(1):123-130.
[21] 张超,庞全海. siRNA 与miRNA 在生物体基因调控中沉默机制的比较[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2012,28(5):393-398.
[22] Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296 (5567):550-553. PMID: 11910072
[23] Semizarov D, Frost L, Sarthy A, et al. Specificity of short interfering RNA determined through gene expression signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100 (11):6347-6352.
[24] Jackson AL, Bartz SR, Schelter J, et al. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(6):635-637.
[25] Chi JT, Chang HY, Wang NN, et al. Genomewide view of gene silencing by small interfering RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100 (11): 6343-6346.
[26] Uhlirova M, Foy BD, Beaty BJ, et al. Use of Sindbis virus-mediated RNA interference to demonstrate a conserved role of Broad-Complex in insect metamorphosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(26):15607-15612.
[27] Van der Giessen K, Di-Marco S, Clair E, et al. RNAi-mediated HuR depletion leads to the inhibition of muscle cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278 (47):47119-47128.
[28] Ashrafi K, Chang FY, Watts JL, et al. Genome-wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulatory genes. Nature. 2003;421(6920):268-272.
[29] Pothof J, van Haaften G, Thijssen K, et al. Identification of genes that protect the C. elegans genome against mutations by genome-wide RNAi. Genes Dev.2003;1517 (4):443-448.
[30] Kubota K, Tsuda S, Tamai A, et al. Tomato mosaic virus replication protein suppresses virus targeted posttranscriptional gene silencing. J Virol. 2003;77(20): 11016-11026.
[31] Vanitharani R, Chellappan P, Fauquet CM. Short interfering RNA-mediated interference of gene expression and viral DNA accumulation in cultured plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(6):9632-9636.
[32] McCaffrey AP, Nakai H, Pandey K, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol. 2003; 21(6): 639-644.
[33] Kao SC, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS, et al. BACE1 suppression by RNA interference in primary cortical neurons. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(3):1942-1949. |