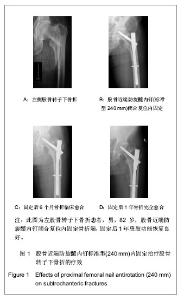
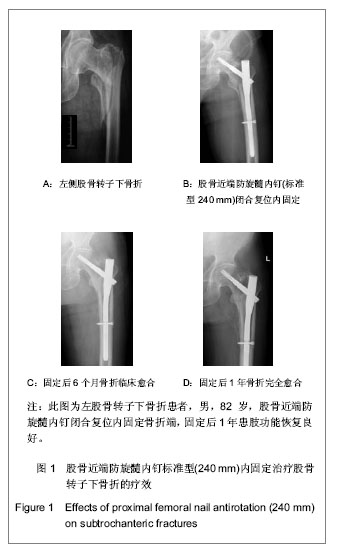
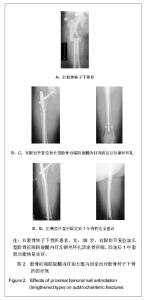
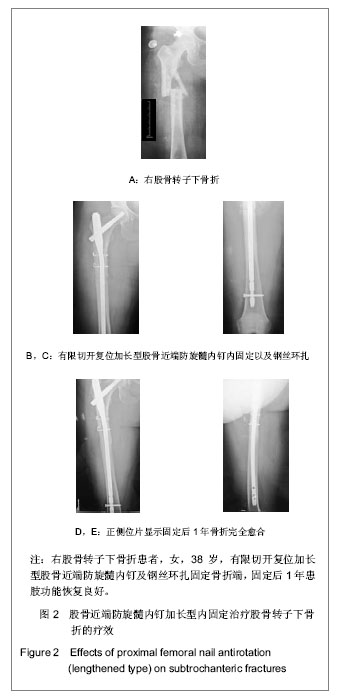
| [1] Mittal R. Proximal femoral fractures: Principles of management and review of literature. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2012;3(1):15-23.
[2] Parker MJ, Dutta BK, Sivaji C, et al. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Injury 1997;28(2):91-95.
[3] Edwards SA, Pandit HG, Clarke HJ. The long gamma nail: a DGH experience. Injury. 2000;31(9):701-709.
[4] 蒋建新,陆男吉,唐明杰,等.加长型股骨近端髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折合并同侧髋部骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(12): 1182- 1183.
[5] 孙林,王满宜,刘德全,等.股骨重建髓内针治疗股骨干骨折合并同侧髋部骨折36例[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(4):216-218.
[6] Kim KC, Lee JK, Hwang DS, et al. Stabilizing subtrochanteric femoral fractures with an interlocked intramedullary nail using the 'Joystick' technique. Orthopedics. 2007;30(9):705-708.
[7] Jiang LS, Shen L, Dai LY. Intramedullary fixation of subtrochanteric fractures with long proximal femoral nail or long gamma nail: technical notes and preliminary results. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2007;36(10):821-826.
[8] Seyhan M, Unay K, Sener N. Comparison of reduction methods in intramedullary nailing of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46(2):113-119.
[9] Vucetic CS, Dulic BV, Vukasinovic ZS, et al. The treatment of subtrochanteric fractures. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2011;139 (7-8): 540-547.
[10] Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation(PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study. Injury. 2008;39(8): 932-939.
[11] Mereddy P, Kamath S, Ramakrishnan M, et al. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2009;40(4):428-432.
[12] Loizou CL, McNamara I, Ahmed K, et al. Classification of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury. 2010;41(7):739-745.
[13] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.
[14] Takigami I, Matsumoto K, Ohara A, et al. Treatment of trochanteric fractures with the PFNA (proximal femoral nail antirotation) nail system-report of early results. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66(4):276-279.
[15] De Landevoisin ES, Bertani A, Candoni P, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFN-ATM) fixation of extra-capsular proximal femoral fractures in the elderly: retrospective study in 102 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(3): 288-295.
[16] Beingessner DM, Scolaro JA, Orec RJ, et al. Open reduction and intramedullary stabilisation of subtrochanteric femur fractures: a retrospective study of 56 cases. Injury. 2013.
[17] Tomas J, Teixidor J, Batalla L, et al. Subtrochanteric fractures: treatment with cerclage wire and long intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(7):e157-160.
[18] Brunner A, Jockel JA, Babst R. The PFNA proximal femur nail in treatment of unstable proximal femur fractures-3 cases of postoperative perforation of the helical blade into the hip joint. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(10):731-736.
[19] 李亚非,时述山,刘智,等.多次手术失败的股骨骨不连的治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(2):131-133.
[20] Forward DP, Doro CJ, O'Toole RV, et al. A biomechanical comparison of a locking plate, a nail, and a 95 degrees angled blade plate for fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(6):334-340.
[21] Baumgaertner MR, solberg BD. Awareness of tip-apex distance reduce failure of fixation of trochanteric fracture of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(6):969-971.
[22] Sehat K, Baker RP, Pattison G, et al. The use of the long gamma nail in proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2005; 36 (11):1350-1354.
[23] Yaozeng X, Dechun G, Huilin Y, et al. Comparative study of trochanteric fracture treated with the proximal femoral nail. Injury. 2010;41(12):1234-1238.
[24] Kuzyk PR, Bhandari M, McKee MD, et al. Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for subtrochanteric femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):465-470.
[25] Müller T, Topp T, Kühne CA, et al. The benefit of wire cerclage stabilisation of the medial hinge in intramedullary nailing for the treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fractures: a biomechanical study. Int Orthop. 2011;35(8):1237-1243.
[26] Steinberg EL, Shavit R. Braided cerclage wires: a biomechanical study. Injury. 2011;42(4):347-351.
[27] Kennedy MT, Mitra A, Hierlihy TG, et al. Subtrochanteric hip fractures treated with cerclage cables and long cephalomedullary nails: a review of 17 consecutive cases over 2 years. Injury. 2011;42(11):1317-1321.
[28] Ito K, Hungerbuhler R, Wahl D, et al. Improved intramedullary nail interlocking in osteoporotic bone. J Orthop Trauma. 2001; 15(3):192-196.
[29] Hwang JH, Oh JK, Han SH, et al. Mismatch between PFNa and medullary canal causing difficulty in nailing of the pertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128(12):1443-1446. |