Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (48): 8361-8367.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.48.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta analysis of intramedullary nail versus plate fixation in treatment of extra-articular distal tibial fractures
Li Jian-gang1, Wang Lei2, Dong Zhe2, Wang Feng-feng2, Ma Gai-ping3, Liu Mei-mei2, Hu Fang2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Zichang County, Zichang 717300, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Fourth Ward, Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Blood Immunology, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2013-11-26Published:2013-11-26 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Wang Lei, Master, Fourth Ward, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China wangleizhuimeng@163.com -
About author:Li Jian-gang, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Zichang County, Zichang 717300, Shaanxi Province, China 977255498@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jian-gang, Wang Lei, Dong Zhe, Wang Feng-feng, Ma Gai-ping, Liu Mei-mei, Hu Fang . Meta analysis of intramedullary nail versus plate fixation in treatment of extra-articular distal tibial fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(48): 8361-8367.
share this article
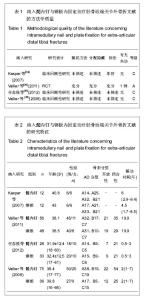
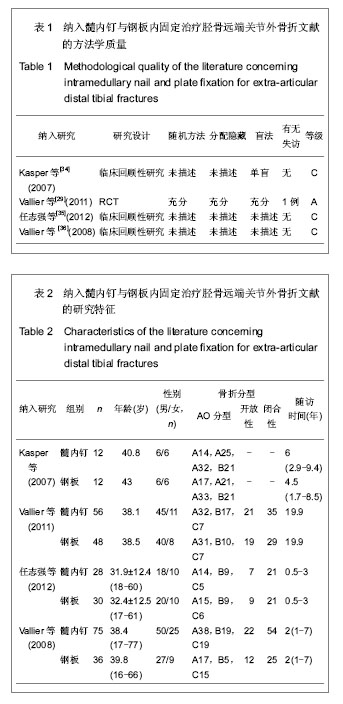
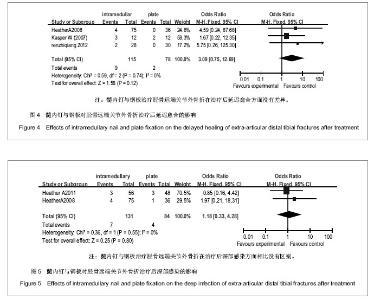
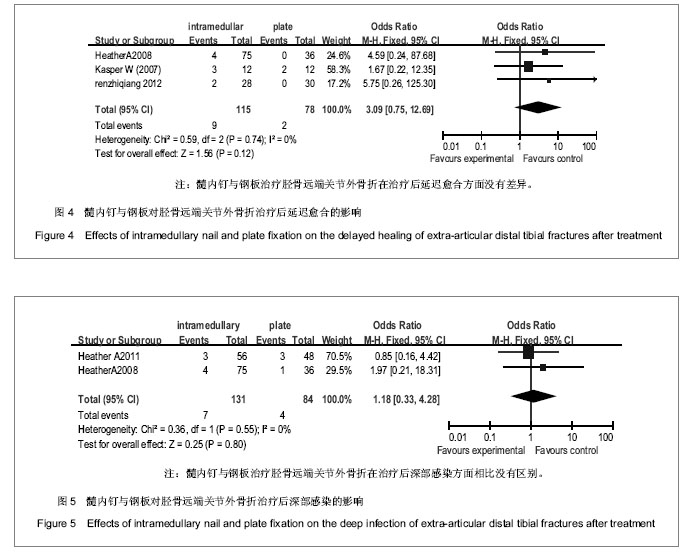
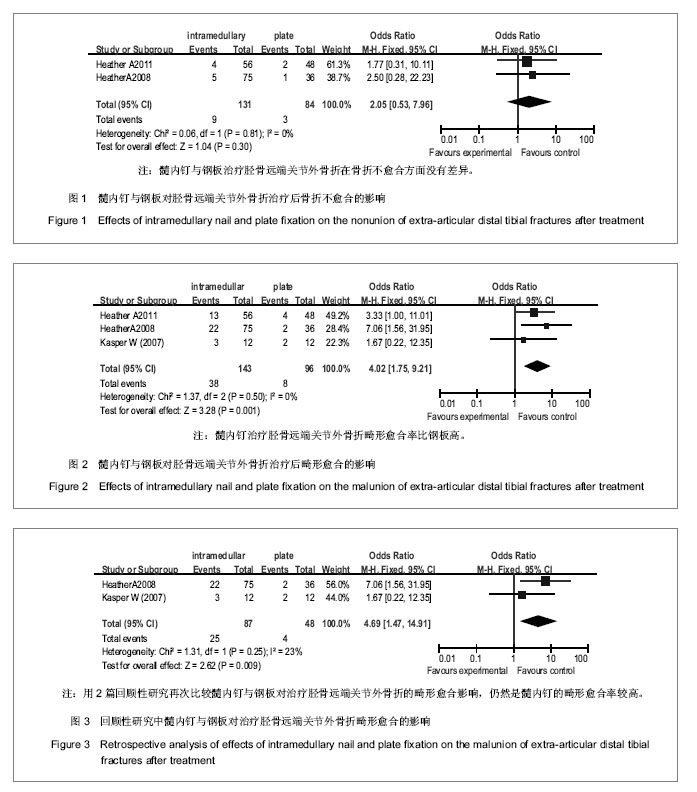
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折后不愈合的差异 4个纳入的文献研究中有2个对胫骨远端骨折治疗后骨折的不愈合进行了研究,共有215例患者,其中接受髓内钉治疗131例,钢板治疗84例,各研究间具有同质性(P=0.81,I2=0%),根据以上统计学方法采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析,结果显示差异没有显著性意义[RR 2.05,95%CI(0.53,7.96)],即钢板与髓内钉治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折在骨折不愈合方面无差异,见图1。 2.2.2 髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折后畸形愈合的差异 4个纳入的文献研究中有3篇文献对胫骨远端关节外骨折治疗后畸形愈合进行了研究,共计有239例患者,其中接受髓内钉治疗143例,钢板治疗96例,Meta分析结果见图2。各研究具有同质性(P=0.50,I2=0%),采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析,结果显示差异有显著性意义[RR 4.02,95%CI(1.75,9.21)]。这表明与钢板治疗了胫骨远端骨折相比,髓内钉治疗有较高的畸形愈合率。 但3篇文献中有2篇是回顾性研究,而且只有Vallier等的文章为随机对照研究,分成亚组进行进一步分析,用2篇回顾性研究再做比较,共计135例,其中接受髓内钉治疗87例,钢板治疗48例,Meta分析结果见图3。各研究间没有异质性(P=0.25,I2=23%),根据以上统计学方法采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析,结果这2种疗法差异有显著性意义[RR 4.69,95%CI(1. 47,14.91)]。表明与钢板治疗相比,髓内钉治疗的胫骨远端关节外骨折后畸形愈合率较高。 2.2.3 髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折后延迟愈合的差异 4个纳入的文献研究中有3篇文献研究对胫骨远端(关节外)骨折治疗后骨折的延迟愈合进行了研究,共计有193例患者,其中髓内钉组有115例,钢板组78例,Meta分析结果见图4。各研究间具有同质性(P=0.74,I2=0%),采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析,结果显示差异没有显著性意义[RR 3.09,95%CI(0.75,12.69)]。这表明与钢板治疗胫骨远端骨折相比,髓内钉治疗没有区别。 2.2.4 髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折后深部感染的差异 4个研究有2个报道了胫骨远端骨折治疗后的深部感染,共计215例患者,其中接受髓内钉治疗131例,钢板治疗84例,Meta分析结果见图5。各研究间具有同质性(P=0.55,I2=0%),根据固定效应模式进行Meta分析,结果显示差异没有显著性意义[RR 1.81,95%CI(0.33,4.28)]。这说明髓内钉与钢板在治疗了胫骨远端关节外骨折术后深部感染方面相比没有区别。 2.2.5 髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折的住院时间、手术时间、负重时间和关节功能的差异 4个纳入文献中只有Kasper等报道了住院时间、手术时间和负重时间,其余3篇都没有报道,分别为髓内钉组住院时间为9.8(4-20) d,手术时间为123(75-195) min;钢板组住院时间为9.5(4-15) d,手术时间为107(60-195) min。髓内钉组胫骨远端关节外骨折患者住院及手术时间均比钢板组长(P < 0.01)。而2组胫骨远端关节外骨折患者的负重时间的差异无显著性意义(髓内钉组3.3个月,钢板组3.8个月,P=0.14)。但因只有1篇文献对住院时间、手术时间和负重时间进行了研究,故不能对统计量进行Meta分析。 对于骨折愈合时间,Vallier等(2011)没有报道,其余3篇文献分别为髓内钉组19(14-32)周、13.6±2.8(10-16)周、3.3个月,钢板组21(13-28)周、9-16(13.2±2.6)周、3.5个月。两组在骨折愈合时间上差异没有显著性意义(P > 0.05)。由于Kasper等和Vallier等(2008)只提供了骨折愈合时间的均数,未提供2组骨折愈合时间的标准差,故不合并统计量进行Meta分析。对于治疗后关节功能,4个研究中只有Kasper等进行了报道,髓内钉组和钢板组患者治疗后的美国膝关节学会膝关节功能评分中跪地痛评分分别为43(0-100)和7(0-50),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);蹲坐疼痛评分分别为29(0-95)和9(0-50),差异也有显著性意义(P < 0.05),即髓内钉在治疗胫骨远端骨折有较高的术后膝关节疼痛率,但因其只有1篇文献,故不能对统计量进行Meta分析。"
| [1] Rommens PM, El Attal R, Hansen M, et al. Intramedullary nailing of proximal tibia fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2011;23(5):411-422. [2] Stewart CM, Kiner D, Nowotarski P. Intramedullary nail fixation of fibular fractures associated with tibial shaft and pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(5):e114-117. [3] Zhu HB, Wu LG, Fang ZS, et al. Clinical application of blocking screws and rooting technique in the treatment of distal tibial fracture with interlocking intramedullary nail. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7):569-571. [4] Pob?ocki K, Domaradzki M, Gawdzik J, et al. Complications after intramedullary nailing of the tibia. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2011;76(5):274-277. [5] Ronga M, Shanmugam C, Longo UG, et al. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures using locking plates. Orthop Clin North Am. 2009;40(4):499-504, ix. [6] Leonard M, Magill P, Khayyat G. Minimally-invasive treatment of high velocity intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. Int Orthop. 2009;33(4):1149-1153. [7] Morin PM, Reindl R, Harvey EJ, et al. Fibular fixation as an adjuvant to tibial intramedullary nailing in the treatment of combined distal third tibia and fibula fractures: a biomechanical investigation. Can J Surg. 2008;51(1):45-50. [8] Ryf C, Götsch U, Perren T, et al. New surgical treatment procedures in fractures of the distal tibia (LCP, MIPO). Ther Umsch. 2003;60(12):768-775. [9] Kumar A, Charlebois SJ, Cain EL, et al. Effect of fibular plate fixation on rotational stability of simulated distal tibial fractures treated with intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A(4):604-608. [10] Strømsøe K, Eikvar K, Løken S, et al. Miniinvasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures.Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen.1999;119(29):4316-4318. [11] Mosheiff R, Safran O, Liebergall N. Biological fixation of distal tibial fractures. Harefuah.1997;132(10):727-730. [12] Hansen M, El Attal R, Blum J, et al. Intramedullary nailing of the tibia with the expert tibia nail. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2009;21(6):620-635. [13] 李国胜,胡永成.经皮微创锁定加压钢板置入内固定治疗新鲜胫骨远端骨折32例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2011,15(13): 2454-2457. [14] 吴兴旺.不同固定方法固定胫骨远端骨折生物力学研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2012.. [15] Feng YZ, Hong JJ, Peng L, et al. Comparison of two minimally invasive internal fixed methods for the treatment of distal tibio-fibula fractures. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011; 49(2):113-118. [16] Kubiak EN, Widmer BJ, Horwitz DS. Extra-articular technique for semiextended tibial nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(11): 704-708. [17] Müller TS, Sommer C. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of the distal tibia. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24(4-5):354-367. [18] Aksekili MA, Celik I, Arslan AK, et al. The results of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) in distal and diaphyseal tibial fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46(3):161-167. [19] 冯传汉,张铁良.临床骨科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 1172. [20] Xue D, Zheng Q, Li H, et al. Reamed and unreamed intramedullary nailing for the treatment of open and closed tibial fractures: a subgroup analysis of randomised trials. Int Orthop. 2010;34(8):1307-1313. [21] Devitt AT, Coughlan KA, Ward T, et al. Patellofemoral contact forces and pressures during intramedullary tibial nailing. Int Orthop. 1998;22(2):92-96. [22] Casstevens C, Le T, Archdeacon MT, et al. Management of extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012; 20(11):675-683. [23] Richter D, Ostermann PA, Ekkernkamp A, et al. Distal tibial fracture--an indication for osteosynthesis with the unreamed intramedullary nail? Langenbecks Arch Chir Suppl Kongressbd.1997;114:1259-1261. [24] Kuhn S, Hansen M, Rommens PM. Extending the indications of intramedullary nailing with the Expert Tibial Nail. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2008;75(2):77-87. [25] 黄鹏,唐佩福,姚琦,等.胫骨干骨折带锁髓内钉固定和钢板螺钉固定的对比研究[J].中国骨伤,2008,21(4):261-263. [26] Casstevens C, Le T, Archdeacon MT, et al. Management of extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012; 20(11):675-683. [27] Duan X, Al-Qwbani M, Zeng Y, et al. Intramedullary nailing for tibial shaft fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;1:CD008241. [28] Mauffrey C, McGuinness K, Parsons N, et al. A randomised pilot trial of "locking plate" fixation versus intramedullary nailing for extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):704-708. [29] Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25(12):736-741. [30] 罗杰.60例带锁髓内钉与普通钢板螺钉内固定治疗胫骨骨折效果比较[J].现代医药卫生,2006,22(8):1136. [31] 李海波,刘文全,伍星.胫骨开放骨折加压钢板与带锁髓内钉治疗比较[J].四川医学,2001,22(12):1145-1146. [32] 方国华,曾青东,孙新,等.带锁髓内钉与加压钢板治疗开放性胫腓骨骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(2):143-144. [33] 王磊,陈根元,王凤凤,等.扩髓与非扩髓髓内钉置入固定治疗成人闭合性胫骨干骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(17):3130-3133. [34] Janssen KW, Biert J, van Kampen A. Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail: a retrospective outcome analysis of matched pairs of patients. Int Orthop. 2007;31(5):709-714. [35] 任志强,焦文学,王振昊.锁定髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2012,5(30):90-91. [36] Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5):307-311. [37] Li Y, Liu L, Tang X, et al. Comparison of low, multidirectional locked nailing and plating in the treatment of distal tibial metadiaphyseal fractures. Int Orthop. 2012;36(7):1457-1462. [38] 李乾明,周家钤,赵宏谋,等.髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端关节外骨折的比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012, 27(4): 317-320. [39] Stegemann P, Lorio M, Soriano R, et al. Management protocol for unreamed interlocking tibial nails for open tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(2):117-1120. [40] Whorton AM, Henley MB. The role of fixation of the fibula in open fractures of the tibial shaft with fractures of the ipsilateral fibula: indications and outcomes. Orthopedics. 1998;21(10): 1101-1105. [41] Bhandari M, Guyatt GH, Swiontkowski MF, et al. Treatment of open fractures of the shaft of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(1):62-68. [42] DeLee JC, Heckman JD, Lewis AG. Partial fibulectomy for ununited fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63(9):1390-1395. [43] Nadkarni B, Srivastav S, Mittal V, et al. Use of locking compression plates for long bone nonunions without removing existing intramedullary nail: review of literature and our experience. J Trauma. 2008;65(2):482-486. [44] Braly HL, O'Connor DP, Brinker MR. Percutaneous Autologous Bone Marrow Injection in the Treatment of Distal Meta-diaphyseal Tibial Nonunions and Delayed Unions. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(9):527-533. [45] Krishan A, Peshin C, Singh D. Intramedullary nailing and plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal metaphyseal tibia and fibula. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2009;17(3): 317-320. [46] Shen WJ, Shen YS. Fibular nonunion after fixation of the tibia in lower leg fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;(287): 231-232. [47] Richmond J, Colleran K, Borens O, et al. Nonunions of the distal tibia treated by reamed intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(9):603-610. [48] Mauffrey C, McGuinness K, Parsons N, et al. A randomised pilot trial of "locking plate" fixation versus intramedullary nailing for extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):704-708. [49] Sheng-Hua L. Thoughts of treatment of distal tibial fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(3):179-183. [50] Morin PM, Reindl R, Harvey EJ, et al. Fibular fixation as an adjuvant to tibial intramedullary nailing in the treatment of combined distal third tibia and fibula fractures: a biomechanical investigation. Can J Surg. 2008;51(1):45-50. [51] Schneidmueller D, Marzi I. Surgical treatment of fractures of the distal tibia in adolescents. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2008; 20(4-5):354-363. [52] Newman SD, Mauffrey CP, Krikler S. Distal metadiaphyseal tibial fractures. Injury. 2011;42(10):975-984. [53] Beardi J, Hessmann M, Hansen M, et al. Operative treatment of tibial shaft fractures: a comparison of different methods of primary stabilisation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(7): 709-715. [54] Bombaci H, Güneri B, Görgeç M, et al. A comparison between locked intramedullary nailing and plate-screw fixation in the treatment of tibial diaphysis fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2004;38(2):104-109. [55] Rzesacz EH, Könneker W, Reilmann H, et al. Combination of intramedullary nail and covered screw osteosynthesis for managing distal tibial fracture with ankle joint involvement. Unfallchirurg. 1998;101(12):907-913. [56] Asche G. Results of the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures following interlocking nailing and plate osteosynthesis. A comparative retrospective study. Zentralbl Chir. 1989;114(17):1146-1154. [57] Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Factors influencing functional outcomes after distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(3):178-183. [58] Schmidt AH, Finkemeier CG, Tornetta P 3rd. Treatment of closed tibial fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2003;52:607-622. |
| [1] | Wang Liang, Huang Zhaozhao, Yu Jiaona, Gu Weidong, Wang Ren, Qian Zhiyi. Biomechanical characteristics of bridge-link type combined internal fixation system with mixed-rod versus double-rod in the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 888-892. |
| [2] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [3] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [4] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [5] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [6] | Wang Liang, Li Lijun, Zhu Fuliang, Jiang Zhuyan, Wang Shuai, Ni Dongkui . Cortical bone trajectory screw versus pedicle screw fixation after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1291-1298. |
| [7] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [8] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [9] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [10] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [11] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [12] | Hao Liang, Zhang Zhonglin, Wang Baodong, Bi Zhenggang. Intertrochanteric fracture of the femur: improvement of internal fixation device, surgical changes and related disputes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2927-2935. |
| [13] | Yao Liquan, Ling Qinjie, Li Jiaying, Zhong Letian, Zhou Xingping, Liu Jintao, He Erxing, Yin Zhixun. Antibiotic artificial bone implantation for treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2133-2139. |
| [14] | Gong Zhibing, Wu Zhaoke, Zhang Huantang, Xu Zhiqing, Zhuang Zhikun, Zhang Qianjin. Allogeneic cortical bone plate combined with locking plate for Vancouver type B1 and C osteoporotic periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1812-1817. |
| [15] | Li Xiaofeng, Xie Furong, Zhan Long, Yang Yuan. Design of locking compression plate through transoral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1824-1828. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||