Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Posterior vertebral column resections combined with titanium screw rod fixation for the treatment of severe spinal deformity
Kahaer•Aikenmu1, Chu Ge1, Huang Jia2, Gao Qi-le2, Wu Jia-wen2, Lin Min-zhong2
- 1First Team of Department of Spine Surgery, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410000, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2013-06-24Revised:2013-07-11Online:2013-10-22Published:2013-11-02 -
Contact:Chu Ge, Attending physician, Studying for doctorate, First Team of Department of Spine Surgery, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China xiaochu138@sina.com -
About author:Kahaer?Aikenmu★, Master, Attending physician, First Team of Department of Spine Surgery, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 330659692@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Kahaer•Aikenmu, Chu Ge, Huang Jia, Gao Qi-le, Wu Jia-wen, Lin Min-zhong. Posterior vertebral column resections combined with titanium screw rod fixation for the treatment of severe spinal deformity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.43.006.
share this article
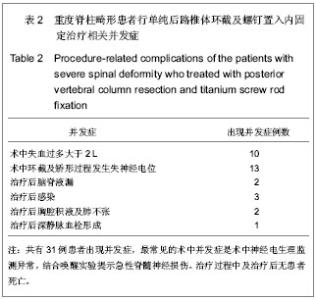
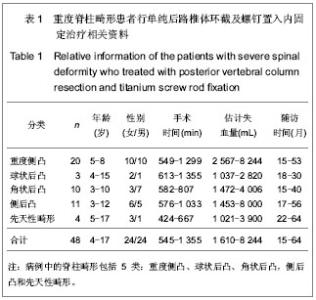
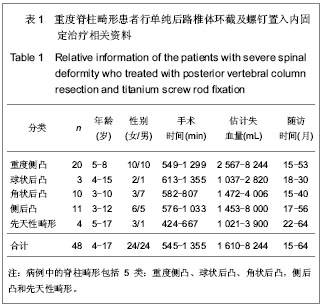
2.3 影像学分析结果 所有患者治疗前平均冠状面畸形角度由84°矫正到35°,总的矫正率达到54%。治疗前平均矢状面畸形角度由90°矫正到42°,矢状面 Cobb 平均减小了48°。 48例患者中脊柱侧后凸畸形11例,重度侧凸畸形20例,先天性脊柱畸形4例,球状后凸畸形3例,角状后凸畸形10例,收集所有患者治疗前、治疗后平均直立、屈曲位下Cobb角度数值(矫正率及平均后凸角度减小度数)。 对于重度侧弯的患者冠状面侧弯Cobb角在侧曲位片上由 104°减小为78°,治疗后首次拍片冠状面平均Cobb角为32°,最后一次随访为33°,平均矫正率为67%。 对于球面畸形的患者治疗前平均最大矢状面后凸Cobb角度101°,治疗前过伸位为79°,治疗后首次平均矢状面Cobb角46°,最后一次随访为47°,平均后凸角减小54°。 对于角状后凸畸形患者,治疗前平均最大矢状面Cobb角88°,屈伸位片几乎没改善,治疗后首次拍片矫正到39°,最后一次随访为38°,后凸角平均减小50°。 对于侧后凸患者,治疗前冠状面平均Cobb角为91°,侧曲位片减小为65°,治疗后首次平均冠状面Cobb角43°,最近一次随访平均Cobb角为44°,冠状位平均矫形率达51%;治疗前矢状面平均Cobb角104°,治疗后平均首次47°,最后一次随访无变化,后凸角度平均减小57°。 对于先天性脊柱畸形患者,治疗前冠状面平均Cobb角度47°,治疗后首次拍片显示治疗后平均矫正到22°,最后一次无变化,矫形率为46%;治疗前平均矢状面Cobb角56°,治疗后首次为30°,最后一次随访为32°,后凸角减小了24°。 2.4 并发症 见表2。"
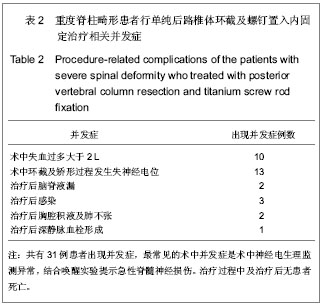
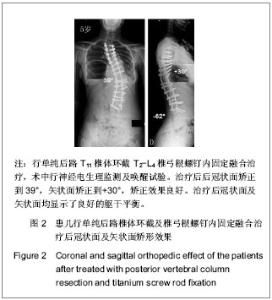
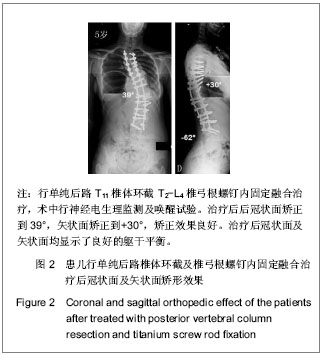
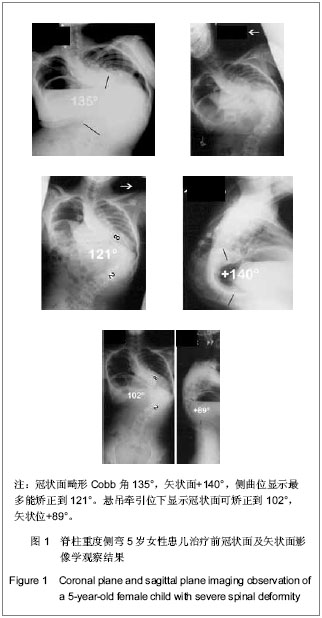
共有31例患者出现并发症,最常见的术中并发症是术中神经电生理监测异常,结合唤醒实验提示急性脊髓神经损伤,其次最常见的术中并发症为术中估计失血量多于2 L,最常见治疗后早期并发症为呼吸系统相关并发症,包括肺部感染、重度肺不张、胸腔积液和切口感染。治疗过程中及治疗后无患者死亡。 2.5 SRS-22评分结果 所有患者治疗前及治疗后1年内应用SRS-30评分量表评价疗效,治疗前平均为3.6 (2.4-4.5)分,术后平均4.2(2.5-4.7)分,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.001)。 疼痛评分改善由4.0分到4.3分(P=0.136),外观自我评价从2.8分改善到4.2分(P < 0.001),功能改善从3.8分到4.1分(P=0.023),精神心理状态从3.8分改善到4.1分(P=0.035),满意度改善从3.0分改善4.3分(P < 0.001),所有患者治疗后评分均较治疗前明显改善。 2.6 典型病例 见图1,2。"
| [1] Dick J, Boachie-Adjei O, Wilson M. One-stage versus two-stage anterior and posterior spinal reconstruction in adults. Comparison of outcomes including nutritional status, complication rates, hospital costs, and other factors . Spine. 1992; 17: 310-316 . [2] Johnson JR, Holt RT. Combined use of anterior and posterior surgery for adult scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1988;19: 361-370. [3] Leatherman KD , Dickson RA . Two-stage corrective surgery for congenital deformities of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979;61:324-328 . [4] Leatherman KD. The management of rigid spinal curves. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973;93:215-224. [5] Bradford DS. Vertebral column resection. Printed abstract from the Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons Annual Meeting. Orthop Trans. 1987;11:502. [6] Boachie-Adjei O, Bradford DS. Vertebral column resection and arthrodesis for complex spinal deformities. J Spinal Disord. 1991;4:193-202 . [7] Suk SI, Chung ER, Lee SM, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection in fi xed lumbosacral deformity. Spine. 2005; 30: E703-E710. [8] Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformity. Spine. 2002;27:2374- 2382 . [9] Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis. Spine. 2005;30:1682-1687 . [10] Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine. Is it safe? Spine. 2004; 29:333-342. [11] Bradford DS, Tribus CB. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of rigid coronal decompensation. Spine. 1997;22: 1590-1599. [12] Lenke LG, O’Leary PT, Bridwell KH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection (VCR) for severe pediatric deformity: Minimum 2-year follow-up of 35 consecutive patients. Spine . 2009; 34:2213-2221. [13] Lenke LG, Sides BA, Koester LA, et al. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:687- 699. [14] Powers A , O’Shaughnessy BA , Lenke LG . Posterior thoracic vertebral column resection. In: Wang JC, ed. Advanced Reconstruction: Spine . Instructional Course Lecture 58: North American Spine Society, Rosemont, IL: AAOS; 2011;58: 265-275. [15] Dorward I, Lenke LG. Osteotomies in the posterior-only treatment of complex adult spinal deformity: a comparative review. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28:E4. [16] Giampietro PF, Blank RD, Raggio CL, et al. Congenital and idiopathic scoliosis: clinical and genetic aspects. Clin Med Res. 2003;1(2):125-136. [17] Winter RB, Moe JH, Lonstein JE. Posterior spinal arthrodesis for congenital scoliosis. An analysis of the cases of two hundred and ninety patients, five to nineteen years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(8):1188-1197. [18] Lazar RD, Hall JE. Simultaneous anterior and posterior hemivertebra excision. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(364):76-84. [19] Mcmaster MJ, David CV. Hemivertebra as a cause of scoliosis. A study of 104 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986; 68(4):588-595. [20] Kesling KL, Lonstein JE, Denis F, et al. The crankshaft phenomenon after posterior spinal arthrodesis for congenital scoliosis: a review of 54 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003; 28(3):267-271. [21] Uzumcugil A, Cil A, Yazici M, et al. Convex growth arrest in the treatment of congenital spinal deformities, revisited. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(6):658-666. [22] Hosseinpour-Feizi H, Soleimanpour J, Sales JG, et al. Lenke and King classification systems for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: interobserver agreement and postoperative results. Int J Gen Med. 2011;4:821-825. [23] Cho KJ , Bridwell KH , Lenke LG, et al. Comparison of Smith-Petersen versus pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine. 2005; 30: 2030- 2037. [24] Mcmaster MJ, Ohtsuka K. The natural history of congenital scoliosis. A study of two hundred and fifty-one patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(8): 1128-1147. [25] Shufflebarger HL, Clark CE. Prevention of the crankshaft phenomenon. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(8 Suppl): S409-S411. [26] Perdriolle R, Vidal J. Thoracic idiopathic scoliosis curve evolution and prognosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1985;10(9): 785-791. [27] O'Leary PT, Sturm PF, Hammerberg KW, et al. Convex hemiepiphysiodesis: the limits of vertebral stapling. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(19):1579-1583. [28] Thompson AG, Marks DS, Sayampanathan SR, et al. Long-term results of combined anterior and posterior convex epiphysiodesis for congenital scoliosis due to hemivertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(12):1380-1385. [29] Thomasen E . Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis . Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;194: 142-152 . [30] Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Denis F, et al. Convex growth arrest for progressive congenital scoliosis due to hemivertebrae. J Pediatr Orthop. 1988;8(6):633-638. [31] Yaszay B, O'Brien M, Shufflebarger HL, et al. Efficacy of hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis: a multicenter retrospective comparison of three surgical techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(24):2052-2060. [32] Jalanko T, Rintala R, Puisto V, et al. Hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis in young children: comparison of clinical, radiographic, and health-related quality of life outcomes between the anteroposterior and posterolateral approaches. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(1):41-49. [33] Dimeglio A. Growth in pediatric orthopaedics. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21(4): 549-555. [34] Ruf M, Harms J. Posterior hemivertebra resection with transpedicular instrumentation: early correction in children aged 1 to 6 years. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(18):2132- 2138. [35] Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, et al. Thoracic pedicle screw fi xation in spinal deformities: are they really safe ? Spine. 2001; 26:2049-2057 . [36] Xu W, Yang S, Wu X, et al. Hemivertebra excision with short-segment spinal fusion through combined anterior and posterior approaches for congenital spinal deformities in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2010;19(6):545-550. [37] Smith JT, Gollogly S, Dunn HK. Simultaneous anterior-posterior approach through a costotransversectomy for the treatment of congenital kyphosis and acquired kyphoscoliotic deformities. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(10):2281-2289. [38] Mladenov K, Kunkel P, Stuecker R. Hemivertebra resection in children, results after single posterior approach and after combined anterior and posterior approach: a comparative study. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(3):506-513. [39] Mehlman CT, Araghi A, Roy DR. Hyphenated history: the Hueter-Volkmann law. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1997; 26(11):798-800. [40] Kioschos HC, Asher MA, Lark RG, et al. Overpowering the crankshaft mechanism. The effect of posterior spinal fusion with and without stiff transpedicular fixation on anterior spinal column growth in immature canines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(10):1168-1173. [41] Aydogan M, Ozturk C, Tezer M, et al. Posterior vertebrectomy in kyphosis, scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis due to hemivertebra. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2008;17(1): 33-37. [42] Ruf M, Jensen R, Letko L, et al. Hemivertebra resection and osteotomies in congenital spine deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(17):1791-1799. |
| [1] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [2] | Wang Shuai, Wang Liancheng, Zhang Shuhao, Li Fuli, Dong Jiaxing, Zhang Yajie. Correlation of the electromyography ratio of the paraspinal muscles on the convex and concave sides with Cobb angle, apical vertebra translation, and coronal balance distance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1402-1406. |
| [3] | Bao Xianguo, Gao Zengxin, Wu Zhanpo, Chen Youmin, Cheng Qinghua, Lu Haitao, Guo Changzheng, Xu Shuai. Correlation between lumbar posterior muscle and local kyphosis in patients with degenerative thoracolumbar kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1418-1423. |
| [4] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [5] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| [6] | Xie Jiang, Guo Huili, Li Hui, Dai Jie, Zhu Xu. Finite element analysis of reconstruction of sagittal balance in ankylosing kyphosis with vertebral column resection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5259-5264. |
| [7] | Wu Chao, Gao Mingjie, Wang Jianzhong, Zhang Yunfeng, Yu Jinghong, Cai Yongqiang, Wang Haiyan, He Yujie, Tong Ling, Li Jiawei, Gao Shang, Wang Xing, Wu Min, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element analysis of stress and displacement of Lenke 3 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis thoracolumbar spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5273-5280. |
| [8] | Zhu Feilong, Zhang Ming, Wu Yu, Wang Bin, Guo Xiaoqi, Cao Jiangang, Zhu Qian, Chen Wei. Foot posture and gait in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients: three-dimensional morphological analysis and biomechanics evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5294-5300. |
| [9] | Ma Riji, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen, Liang Kaiheng, Wang Ziao, Shi Fan. Correlation of endplate fractures with height loss of injured vertebral body, kyphosis and chronic pain after vertebral augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(30): 4857-4862. |
| [10] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Zhu Zhenqi, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of sciatic scoliosis caused by lumbar disc herniation: a 2-year follow-up of coronal and sagittal balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 409-413. |
| [11] | Yuan Wangshu, Chen Lixia, Shen Jianxiong, Yu Keyi. Correlation between axial trunk rotation angle and Cobb angle in different ages, genders, and types of idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4386-4389. |
| [12] | Wang Ziao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen . Short-segment fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: method modification and strategies to reduce failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3902-3907. |
| [13] | Zhou Chen, Xing Wenhua. Application advantages of three-dimensional printing technology and finite element analysis in scoliosis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1898-1903. |
| [14] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [15] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||