| [1] 吴采荣,丁亮华,梁春红,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎退变性疾病的短期疗效观察[J].中国医师进修杂志:综合版,2010, 33(5):7-9.
[2] Kaneko K, Hashiguchi A, Kato Y, et al.Investigation of motor dominant C5 paralysis after laminoplasty from the results of evoked spinal cord responses.J Spinal Disord Tech.2006; 19(5): 358-361.
[3] Komagata M, Nishiyama M, Endo K, et al.Prophylaxis of C5 palsy after cervical expansive laminoplasty by bilateral partial foraminotomy.Spine J.2004;4(6):650-655.
[4] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-5-12. https://www.cnki.net
[5] 金毅,赵炬才,刘珂位.颈椎后路单开门加侧块内固定治疗椎管狭窄伴颈椎不稳定疗效观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗,2010,24(2): 184-185.
[6] 方军,张凤清.后路寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉固定治疗寰枢椎不稳38例疗效观察[J].医学信息(上旬刊),2011,24(9):6122-6123.
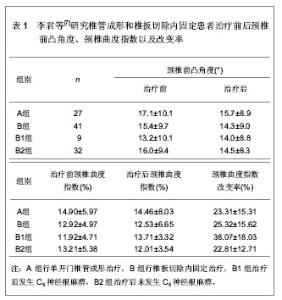
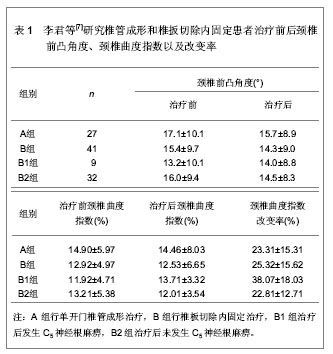
[7] 李君,王新伟,袁文,等.颈椎管成形术与椎板切除内固定术后C5神经根麻痹比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(5):415-419.
[8] 巩腾.脊髓型颈椎病减压术后神经并发症发生机理与颈髓周围性神经通路体系间关系的临床和基础研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2009:2-6.
[9] 雷仲民,孙佩宇,张翔.腰椎棘突间动态稳定系统(Wallis)在腰椎退行性疾病中的应用及近期效果观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2009,17(10):26-27.
[10] 贾连顺,袁文,陈雄生,等.脊髓型颈椎病外科干预及其影响因素[J].中国医学科学院学报,2005,27(2):165-167.
[11] Roy-Camille, Saillant G. Fractures do Rachis Cervical.Paris: Mass on & Gie,1970:157-195.
[12] Sherk HH, Dunn HJ, Eismount FJ, et al. The cervi cal spine[M]. 2nd ed. Philadelphia:JB Linppincott Inc,1989: 390-404.
[13] Shinomiya K, Kurosa Y, Fuchioka M, et al.Clinical study of dissociated motor weakness following anterior cervical decompression surgery.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1989; 14(11): 1211-1214.
[14] Yonenobu K, Hosono N, Iwasaki M, et al.Neurologic complications of surgery for cervical compression myelopathy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(11):1277-1282.
[15] Saunders RL.On the pathogenesis of the radiculopathy complicating multilevel corpectomy.Neurosurgery.1995;37(3):408-412;413.
[16] Ikenaga M, Shikata J, Tanaka C.Radiculopathy of C-5 after anterior decompression for cervical myelopathy.J Neurosurg Spine.2005;3(3):210-217.
[17] Hasegawa K, Homma T, Chiba Y.Upper extremity palsy following cervical decompression surgery results from a transient spinal cord lesion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(6): E197-202.
[18] Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y, et al.Long-term outcome of laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy due to disc herniation: a comparative study of laminoplasty and anterior spinal fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(7):756-759.
[19] Chen Y, Chen D, Wang X, et al.C5 palsy after laminectomy and posterior cervical fixation for ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament.J Spinal Disord Tech.2007;20(7): 533-535.
[20] Takemitsu M, Cheung KM, Wong YW, et al.C5 nerve root palsy after cervical laminoplasty and posterior fusion with instrumentation.J Spinal Disord Tech.2008;21(4):267-272.
[21] Seichi A, Takeshita K, Kawaguchi H, et al.Postoperative expansion of intramedullary high-intensity areas on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging after cervical laminoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(13):1478-1482.
[22] 占蓓蕾,叶舟,王巍.跳跃式颈椎椎板减压与成形并棘突重建的临床应用[J].颈腰痛杂志,2006,27(6):445-447.
[23] 王义生,翟福英,殷力,等.前或后路手术治疗颈椎退变性疾病的远期疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(2):103-106.
[24] 王开明.脊髓型颈椎病的手术治疗及进展[J].淮海医药,2007, 25(2): 188-190.
[25] 赵定麟.对颈椎病外科干预中几个问题的我见[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(2):87-88. |