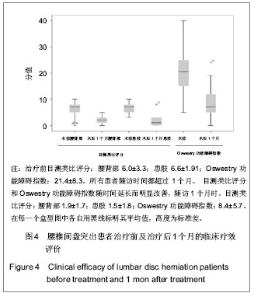
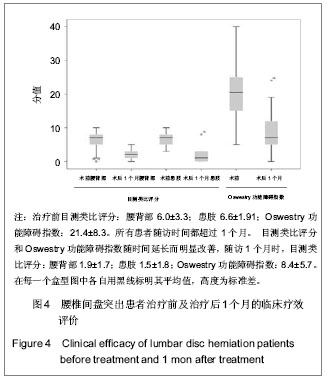
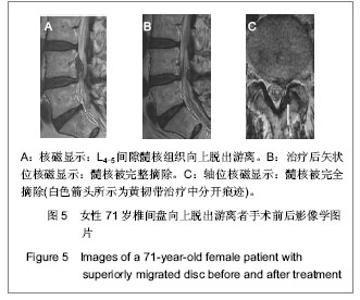
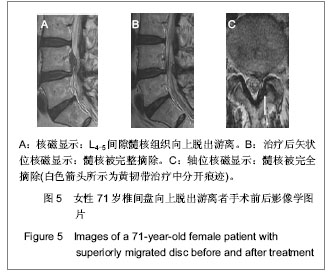
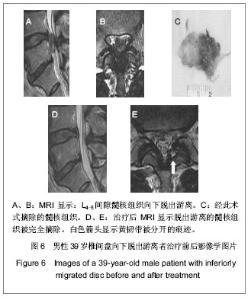
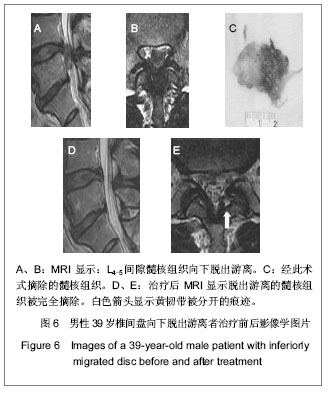
| [1] Yeung AT, Yeung CA. Minimally invasive techniques for the management of lumbar disc herniation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2007;38(3):363-372。[2] Ruetten S, Komp M, Merk H,et al. Full-endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal lumbar discectomy versus conventional microsurgical technique: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(9):931-939.[3] Yeung AT. The evolution of percutaneous spinal endoscopy and discectomy: state of the art. Mt Sinai J Med. 2000; 67(4):327-332.[4] Lee SH, Chung SE, Ahn Y,et al. Comparative radiologic evaluation of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open microdiscectomy: a matched cohort analysis. Mt Sinai J Med. 2006;73(5):795-801.[5] Kambin P, Savitz MH. Arthroscopic microdiscectomy: an alternative to open disc surgery. Mt Sinai J Med. 2000; 67(4):283-287.[6] Ruetten S, Komp M, Merk H,et al. Use of newly developed instruments and endoscopes: full-endoscopic resection of lumbar disc herniations via the interlaminar and lateral transforaminal approach. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(6): 521-530.[7] Choi G, Lee SH, Lokhande P,et al. Percutaneous endoscopic approach for highly migrated intracanal disc herniations by foraminoplastic technique using rigid working channel endoscope. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(15):E508-515.[8] Kim CH, Chung CK, Kim HJ,et al. Early outcome of posterior cervical endoscopic discectomy: an alternative treatment choice for physically/socially active patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(2):302-306.[9] Aydin Y, Ziyal IM, Duman H,et al. Clinical and radiological results of lumbar microdiskectomy technique with preserving of ligamentum flavum comparing to the standard microdiskectomy technique. Surg Neurol. 2002;57(1):5-13.[10] Ozer AF, Oktenoglu T, Sasani M, et al. Preserving the ligamentum flavum in lumbar discectomy: a new technique that prevents scar tissue formation in the first 6 months postsurgery. Neurosurgery. 2006;59(1 Suppl 1):ONS126-133.[11] Boult M, Fraser RD, Jones N, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic laser discectomy. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000;70(7):475-479.[12] Choi G, Kim JS, Lokhande P,et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy by transiliac approach: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(12):E443-446.[13] Choi G, Lee SH, Raiturker PP,et al. Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working channel endoscope. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(1 Suppl):ONS59-68.[14] Kim DY, Lee SH, Lee HY,et al.Validation of the Korean version of the oswestry disability index.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(5):E123-E127.[15] Castaldo JE, Ochoa JL. Mechanical injury of peripheral nerves. Fine structure and dysfunction. Clin Plast Surg. 1984;11(1):9-16.[16] Ahn Y, Lee SH, Lee JH,et al. Transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for upper lumbar disc herniation: clinical outcome, prognostic factors, and technical consideration. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009;151(3):199-206.[17] Lee S, Kim SK, Lee SH,et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for migrated disc herniation: classification of disc migration and surgical approaches. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(3):431-437.[18] Shin DA, Kim KN, Shin HC,et al. The efficacy of microendoscopic discectomy in reducing iatrogenic muscle injury. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(1):39-43.[19] Choi G, Lee SH, Bhanot A,et al. Percutaneous endoscopic discectomy for extraforaminal lumbar disc herniations: extraforaminal targeted fragmentectomy technique using working channel endoscope.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32(2):E93-99.[20] Kim MJ, Lee SH, Jung ES,et al. Targeted percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic diskectomy in 295 patients: comparison with results of microscopic diskectomy.Surg Neurol. 2007;68(6):623-631. [21] Deen HG. Posterolateral endoscopic excision for lumbar disc herniation: surgical technique, outcome, and complications in 307 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(18): 2081-2082.[22] de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P. Lumbar diskectomy with preservation of the ligamentum flavum. Surg Neurol. 2002; 58(1):68.[23] de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P. Preserving the ligamentum flavum in lumbar discectomy: a new technique that prevents scar tissue formation in the first 6 months postsurgery. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(6):E1340.[24] Cooper RG, Mitchell WS, Illingworth KJ,et al. The role of epidural fibrosis and defective fibrinolysis in the persistence of postlaminectomy back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991; 16(9): 1044-1048.[25] Ross JS, Robertson JT, Frederickson RC,et al. Association between peridural scar and recurrent radicular pain after lumbar discectomy: magnetic resonance evaluation. ADCON-L European Study Group. Neurosurgery. 1996; 38(4):855-861.[26] Cook SD, Prewett AB, Dalton JE,et al. Reduction in perineural scar formation after laminectomy with Polyactive membrane sheets. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(16):1815-1825.[27] Fritsch EW, Heisel J, Rupp S. The failed back surgery syndrome: reasons, intraoperative findings, and long-term results: a report of 182 operative treatments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(5):626-633.[28] Nakai O, Ookawa A, Yamaura I. Long-term roentgenographic and functional changes in patients who were treated with wide fenestration for central lumbar stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(8):1184-1191.[29] 李明,陈强,何大为,等.显微内镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国微创外科杂志,2002,2(4): 203-204.[30] Abdullah AF, Ditto EW 3rd, Byrd EB,et al. Extreme-lateral lumbar disc herniations. Clinical syndrome and special problems of diagnosis. J Neurosurg. 1974;41(2):229-234.[31] Wang QP, Lee NS, Zhang Y,et al. Intertransverse approach for extraforaminal herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22(6):701-705.[32] Kunogi J, Hasue M. Diagnosis and operative treatment of intraforaminal and extraforaminal nerve root compression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(11):1312-1320.[33] Gioia G, Mandelli D, Capaccioni B,et al. Surgical treatment of far lateral lumbar disc herniation. Identification of compressed root and discectomy by lateral approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(18):1952-1957.[34] O'Hara LJ, Marshall RW. Far lateral lumbar disc herniation. The key to the intertransverse approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(6):943-947.[35] 陈开林,谢大志,郑彬,等.经后路椎管内椎间盘镜与微创小切口手术的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2000,10(6):368.[36] 杨维权,刘大雄,孙荣华,等.后中路椎间盘镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2001,16(3):163-165.[37] 左伟,张希彦,蔺攀,等.后中路椎间盘镜治疗椎间盘突出症术后常见并发症[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2002,17(1):50-51.[38] Weinnstein JN,Wiesel SW. The International Society for t he Study of t he Lumbar Spine. Philadephia: ParwisSaunders Co. ,1990:394-399.[39] Brayda-Bruno M, Cinnella P. Posterior endoscopic discectomy (and other procedures). Eur Spine J. 2000;9 Suppl 1:S24-29.[40] 孟宪国,孟宪中,申勇,等.椎间盘镜下椎间盘摘除术并发症的处理和预防[J].中国微创外科杂志,2004,4(5):405-406.[41] 刘兆生,纪忠义,徐明雄,等.后中路椎间盘镜治疗腰椎间盘突出适应证的选择与并发症的预防[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2004, 13(11):1494-1495.[42] 赵延勋,吴小涛,齐新生,等.椎板间隙腰椎间盘镜下髓核切除术的并发症[J].铁道医学,2001, 29(3):198-199.[43] Dei-Anang K, Kessel HA, Meinig G. Clinical follow-up after surgery of lumbar disc prolapses. A critical analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 1990;13(3):201-203.[44] 镇万新,王育才,马乐群,等.脊柱后路显微内窥镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19(8):460-462. |