Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (22): 4144-4151.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.22.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of acetabular protrusion secondary to rheumatoid arthritis
Tang Song-jun1, Liu Wei2, Li Xiao-hua3
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Youdian Hospital, Shanghai 200040, China
2 Department of Orthopedics, Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China
3 Department of Orthopedics, Changzheng Hospital, Shanghai 200003, China
-
Online:2013-05-28Published:2013-05-28 -
Contact:Liu Wei, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China liuliumsn@hotmail.com -
About author:Tang Song-jun, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Youdian Hospital, Shanghai 200040, China 346203236@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Song-jun, Liu Wei, Li Xiao-hua. Total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of acetabular protrusion secondary to rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(22): 4144-4151.
share this article
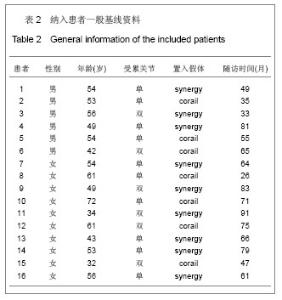
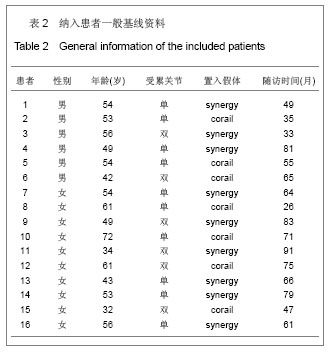
2.2 参与者数量分析 随访期间,患者无感染、脱位、假体周围骨折等并发症发生。除1例患者因其他系统疾病(脑血管意外)死亡外,其他患者均获得随访,随访28-94 (50.2±6.8)个月,均纳入结果分析。 2.3 围置换期情况 所有患者置换顺利,置换时间55-95(78±14.2) min,置换过程中显性失血量150-450 (225.0±25.6) mL,围手术期总失血量420-1 240 (550.0±44.8) mL。在院期间未发生下肢深静脉栓塞,出院患肢功能恢复良好。 2.4 影像学分析 所有患者随访X射线平片均显示所有假体均获得良好稳定,假体周围无明显透亮线,自体移植骨与髋臼底骨面出现连续性骨小梁,移植骨稳定,愈合良好。2例患者出现局部移植骨密度降低,但均小于1/3,为轻度重吸收。股骨头中心到Kohler线的距离由置换前的(18.8±3.9) mm增加到置换后的(28.5± 3.5) mm,股骨头中心点到坐骨结节连线的距离由置换前的(82.3±3.3) mm减少到(72.8±4.3) mm,置换后股骨头中心明显向外下移动,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表3。"
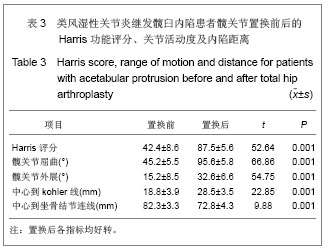
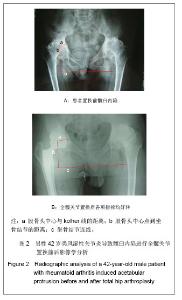
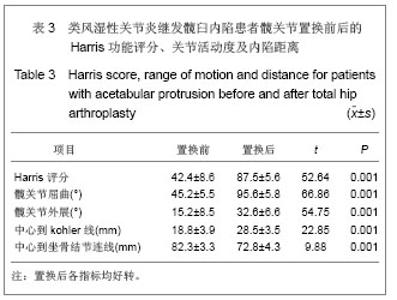
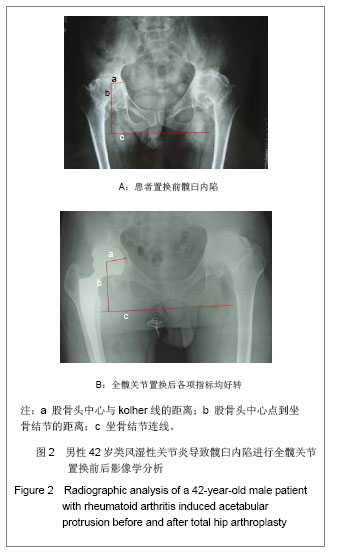
2.5 典型病例结果分析 见图2。 42岁男性患者,置换前诊断为类风湿性关节炎引起髋臼内陷,涉及双侧髋关节,置换前Harris评分为51分,髋关节活动度屈曲为50°,外展15°,股骨头中心点到kohler线为14.4 mm,到坐骨结节连线为80.2 mm,图2A;置换后随访,Harris评分为84分,款关节活动度屈曲为95°,外展30°,股骨头中心点至kohler线为26.2 mm,到坐骨结节连线为70.7 mm,见图2B。 2.6 关节功能比较分析 置换前患者Harris髋关节评分为42.4±8.6,至末次随访为87.5±5.6,较置换前平均改善47.1分,差异具有显著性意义(P < 0.001)。髋关节活动范围置换前屈曲(45.2±5.5)°,末次随访为(95.6±5.8)°,较置换前平均改善50.4°,差异具有显著性意义(P < 0.01);置换前外展(15.2±8.5)°,末次随访为(32.6±6.6)°,较置换前平均改善17.4°,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表3。 "
| [1]Zhou CP, Zhou ZK, Shen B, et al. Zhonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi(Dianziban). 2012;6(5):23-26.周程沛,周宗科,沈彬,等. 膝关节类风湿关节炎伴重度屈曲畸形患者关节置换术后的中长期随访[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012,6(5):23-26.[2]Wang TJ, Wang B, Lv HS. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2012; 35(32):21-23.王铁军,王波,吕厚山. 膝关节骨性关节炎与类风湿关节炎患者全膝人工关节置换术术前检查的区别及注意事项[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(32):21-23.[3]Zhang YD, Gao MJ, Wang RM, et al. Zhonguo laonianxue Zazhi. 2012;32(21): 4795-4796.张永东,高默杰,王瑞珉,等.人工全膝关节置换在中老年类风湿关节炎中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(21): 4795-4796.[4]Yao J, Zhao Y, Zhong CL. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(13):2389-2398.姚进,赵允,仲丛丽. 髋关节置换研究:Scopus数据库5年文献检索与分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(13):2389-2398.[5]Mullaji AB, Marawar SV. Primary total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli using impacted morsellized bone grafting and cementless cups: a medium-term radiographic review. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(8):1143-1149.[6]Mochida Y, Saito I, Akamatsu Y, et al. Clinical and radiological results of non-cement impaction bone-graft method of total hip arthroplasty for rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2007; 17(3):235-238.[7]Gerber SD, Harris WH. Femoral head autografting to augment acetabular deficiency in patients requiring total hip replacement. A minimum five-year and an average seven-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(8): 1241-1248.[8]Guo TY, Zhou JS. Zhongguo Guy u Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2013,28(2):196-198.郭通亚,周建生.人工全髋关节翻修术中髋臼缺损重建的研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(2):196-198.[9]Yuan MW, Pan J, Zhang XD. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(39):7227-7231.袁明武,潘江,张晓冬.全髋关节置换并结构性植骨治疗CroweⅢ型髋臼发育不良性骨关节炎[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(39): 7227-7231.[10]Chen ZW, Yuan J, Cao SJ, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2012;26(3):292-294.陈志伟,袁杰,曹盛俊,等.人工全髋关节置换治疗髋臼内陷症的早期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(3):292-294.[11]Gusis SE, Maldonado Cocco JA, et al. Protrusio acetabuli in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1993;12(1): 36-40.[12]Ries MD. Total hip arthroplasty in acetabular protrusio. Orthopedics. 2009;32(9):708-712.[13]Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Diaz-Martin A, Madero R, et al. Loosening of the cup after low-friction arthroplasty in patients with acetabular protrusion. The importance of the position of the cup. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(1):108-115.[14]Blumenfeld TJ, Bargar WL. Surgical technique: a cup-in-cup technique to restore offset in severe protrusio acetabular defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(2):435-441.[15]Sochart DH, Porter ML. Long-term results of total hip replacement in young patients who had ankylosing spondylitis. Eighteen to thirty-year results with survivorship analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(8):1181-1189. [16]Bayley JC, Christie MJ, Ewald FC, et al. Long-term results of total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli. J Arthroplasty. 1987;2(4):275-279. [17]Krushell RJ, Fingeroth RJ, Gelling B. Primary total hip arthroplasty using a dual-geometry cup to treat protrusio acetabuli. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(8):1128-1131.[18]Gaiani L, Bertelli R, Palmonari M,et al. Total hip arthroplasty revision in elderly people with cement and Burch-Schneider anti-protrusio cage. Chir Organi Mov. 2009;93(1):15-19[19]Borland WS, Bhattacharya R, Holland JP,et al. Use of porous trabecular metal augments with impaction bone grafting in management of acetabular bone loss. Acta Orthop. 2012; 83(4):347-352.[20]Figueras Coll G, Salazar Fernandez de Erenchu J, Roca Burniol J. Results of acetabular wiremesh and autograft in protrusio acetabuli. Hip Int. 2008;18(1):23-28.[21]Mibe J, Imakiire A, Watanabe T, et al. Results of total hip arthroplasty with bone graft and support ring for protrusio acetabuli in rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10(1):8-14.[22]Rosenberg WW, Schreurs BW, de Waal Malefijt MC, et al. Impacted morsellized bone grafting and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular protrusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an 8- to 18-year follow-up study of 36 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(2):143-146.[23]Patil N, Hwang K, Goodman SB. Cancellous impaction bone grafting of acetabular defects in complex primary and revision total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2012;35(3): e306-312.[24]Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Cruz-Pardos A, Garcia-Rey E ,et al. The survival and fate of acetabular reconstruction with impaction grafting for large defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(12):3304-3313.[25]Dutka J, Sosin P, Skowronek P,et al. Total hip arthroplasty with bone grafts for protrusio acetabuli. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2011;13(5):469-477. [26]Cichý Z. Treatment of dysplastic acetabulum using total hip arthroplasty: our intermediate-term results. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006;73(5):340-344.[27]Heywood AW. Arthroplasty with a solid bone graft for protrusio acetabuli. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980;62(3):332-336.[28]Slooff TJ, Huiskes R, Van Hom J, et al. Bone grafting in total hip replacement for acetabular protrusion. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55(6):593-596.[29]Rosenberg WW, Schreurs BW, de Waal Malefijt MC,et al. Impacted morsellized bone grafting and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular protrusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an 8- to 18-year follow-up study of 36 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(2):143-146. [30]Busch VJ, Gardeniers JW, Verdonschot N, et al. Acetabular reconstruction with impaction bone-grafting and a cemented cup in patients younger than fifty years old: a concise follow-up, at twenty to twenty-eight years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(4):367-371.[31]Welten ML, Schreurs BW, Buma P, et al. Acetabular reconstruction with impacted morcellized cancellous bone autograft and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty: a 10- to 17-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(7):819-824. [32]Rosenberg AWJ, Schreurs WB, et al. Impaceted morsellized bone grafting and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular protrusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Orthop Scand,2000;71:143[33]Schulte KR, Callaghan JJ, Kelley SS, et al. The outcome of Charnley total hip arthroplasty with cement after a minimum twenty-year follow-up. The results of one surgeon. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(7):961-975.[34]Ballard WT, Callaghan JJ, Sullivan PM, et al. The results of improved cementing techniques for total hip arthroplasty in patients less than fifty years old. A ten-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(7):959-964.[35]Barrack RL, Mulroy RD Jr, Harris WH. Improved cementing techniques and femoral component loosening in young patients with hip arthroplasty. A 12-year radiographic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(3):385-389.[36]Busch VJ, Gardeniers JW, Verdonschot N,et al. Acetabular reconstruction with impaction bone-grafting and a cemented cup in patients younger than fifty years old: a concise follow-up, at twenty to twenty-eight years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(4):367-371.[37]Clohisy JC, Harris WH. Matched pair analysis of cemented and cementless acetabular reconstruction in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;16(6):697-705.[38]Berend ME. Acetabular protrusio: a problem in depth. Orthopedics. 2008;31(9):895-896.[39]Berger RA, Jacobs JJ, Quigley LR, et al. Primary cementless acetabular reconstruction in patients younger than 50 years old. 7- to 11-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (344): 216-226.[40]Matsuno H, Yasuda T, Yudoh K,et al. Cementless cup supporter for protrusio acetabuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Orthop. 2000;24(1):15-18.[41]Wang YG, Tang BS. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2011;6(32): 30-32.王永贵,唐本森. 全髋关节置换术治疗类风湿性髋关节炎的临床观察[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(32):30-32.[42]Chen LJ, Zhang Y. Zhonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi (Dianziban). 2011;5(1):55-58.陈林建,张毅.人工全髋关节置换术髋臼杯准确安放的影响因素[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2011,5(1):55-58.[43]Lundby R, Kirkhus E, Hald J, et al. CT of the hi ps in the investigation of protrusio acetabuli in Marfan syndrome. A case control study. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(7):1485-1491.[44]Sun JW, Yin WP, Zhang C, et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(22):4006-4009.孙剑伟,尹望平,张春,等.髋臼区域皮质骨厚度分布特征的三维图像测量[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(22):4006-4009.[45]Li DS, Li SQ, Cai B, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(48): 9104-9108.李冬松,李叔强,蔡波,等.成人髋臼发育不良髋臼内壁内移截骨的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(48): 9104-9108.[46]Xiang SS, Chen Y, Fu M, et al. ZHonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi(Dianziban). 2012;6(3):68-71.向珊珊,陈艺,傅明,等.髋臼旋转截骨术时髋臼后上方植骨前后髋关节生物力学的改变及其对比[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012,6(3):68-71. |
| [1] | Chen Zehua, Ye Xiangling, Chen Weijian, Du Jianping, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng. Effect of pronated foot posture on proprioception and postural stability based on foot posture index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1324-1328. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [4] | Wang Jiangna, Zheng Huifen, Sun Wei. Changes in dynamic stability, motor coordination and joint mechanics of the lower extremity during stair descent and performing phone task [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 837-843. |
| [5] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [6] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [7] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Xu Xirui, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Effectiveness of Tuina in the treatment of pain after total knee arthroplasty in patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2840-2845. |
| [8] | Xue Jingbo, Zhu Bin, Li Zepeng, Wang Cheng, Ouyang Zhihua, Yan Yiguo. Biomechanical characteristics of a sleeve-type guided growth rod in a six-degree-of-freedom joint robot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2297-2302. |
| [9] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [10] | Liu Kun, Xu Hao, Wang Yingzhen, Zhang Haining, Fang Yuan, Xiang Shuai, Lü Chengyu. Direct repair of medial collateral ligament injury combined with brace in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2352-2357. |
| [11] | Li Yonghe, Wang Xiankang, Meng Yu, Liu Lu, Zhang Chunqiu, Ye Jinduo . Mechanical analysis on the position difference of short-stemmed prosthesis in hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2394-2399. |
| [12] | Shen Fu, Kuang Gaoyan, Yang Zhuo, Wen Meng, Zhu Kaimin, Yu Guizhi, Xu Wuji, Deng Bo . Immune infiltration mechanism of differential expression genes in rheumatoid arthritis and potential therapeutic prediction of Chinese herbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2183-2191. |
| [13] | Qiu Feng, Xu Xilin, Ma Xiangyang, Fang Zhouqun, Jiang Weicheng, Tian Shuzhao, Zheng Zelong. Biomechanical comparison of atlantoaxial crossed rod and parallel rod fixation technique for C2 unilateral lamina screws [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1805-1809. |
| [14] | Milalimmu•Multiza, Zhao Wei, Varesjiang•Nyyaz, Yuan Hong, Wang Li. Direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: comparison of early postoperative patient’s perception [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1318-1323. |
| [15] | Liu Yu, Zhang Nanxin, Dai Liqun, Ying Wei. Meta-analysis of the effectiveness of cold therapy after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1443-1448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||