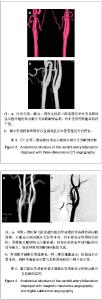
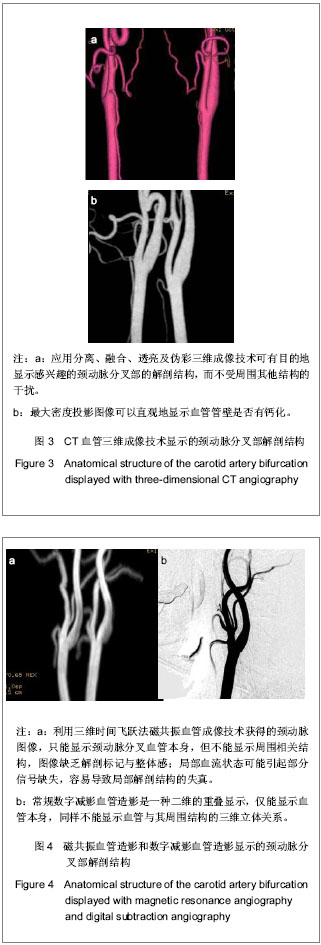
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional CT angiography for anatomic measurements of the carotid artery bifurcation
Duan Shao-yin1, 2, Lin Chang-hua1, Jing Jing1, Yang Lie1, Lin Qing-chi1, 2
- 1 School of Postgraduate Education of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China
2 Department of Radiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2012-12-03Revised:2013-02-28Online:2013-04-09Published:2013-04-09 -
About author:Duan Shao-yin☆, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, School of Postgraduate Education of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China; Department of Radiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China xmdsy@xmu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071214
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Duan Shao-yin1, 2, Lin Chang-hua1, Jing Jing1, Yang Lie1, Lin Qing-chi1, 2. Three-dimensional CT angiography for anatomic measurements of the carotid artery bifurcation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.15.011.
share this article
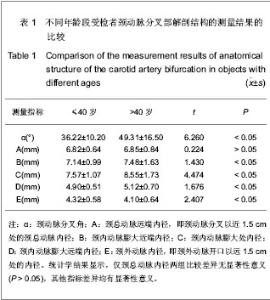
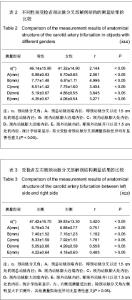
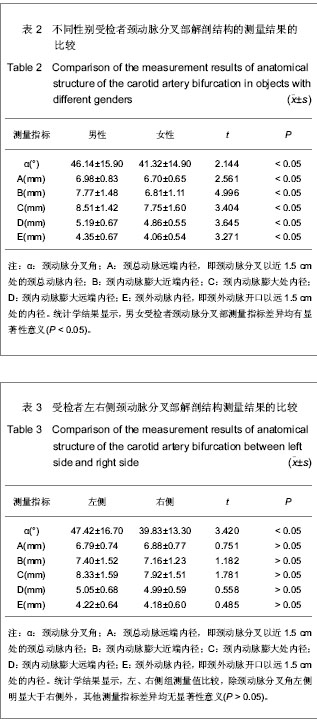
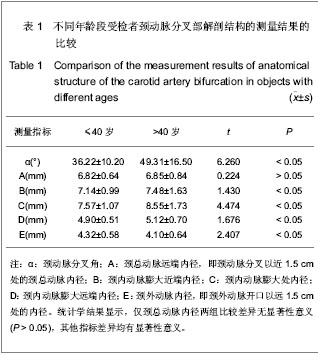
2.3 三维CT对颈动脉分叉部解剖结构的测量结果 测量结果显示受试者颈动脉分叉角为(43.5±12.3)°,颈总动脉远端内径(6.83±0.65) mm,颈内动脉膨大区近端内径(7.25±1.04) mm,颈内动脉膨大区最大内径(8.15±1.35) mm,颈内动脉膨大区远端内径(5.03± 0.55) mm,颈外动脉内径(4.22±0.60) mm。 2.4 不同年龄段受检者颈动脉分叉部解剖结构的测量结果 测量结果显示,与≤40岁组比较,>40岁组颈动脉分叉角度、颈内动脉膨大区近端内径、颈内动脉膨大区最大内径、颈内动脉膨大区远端内径均明显粗大,颈外动脉内径明显细小(P < 0.05),而颈总动脉内径差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1。"
| [1] Friedman MH, Deters OJ, Mark FF, et al. Arterial geometry affects hemodynamics: a potential risk factor for atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1983;46(2):225-231.[2] Thomas JB, Antiga L, Che SL, et al. Variation in the carotid bifurcation geometry of young versus older adult. Stroke. 2005; 36(11):2450-2456.[3] Lee SW, Antiga L, Spence JD, et al. Geometry of the Carotid Bifurcation Predicts Its Exposure to Disturbed Flow. Stroke. 2008;39(8):2341-2347.[4] Ding ZR, Wang KQ. Shanghai Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao. 2002; 36(1):87-90.丁祖荣,王克强.人颈动脉分叉的TF-AHCB模型[J].上海交通大学学报,2002,36(1):87-90.[5] He YF, Xu ZZ. Zhonghua Chaosheng Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 1997;6(5):169-172.何银凤,徐智章.正常颈动脉和椎动脉彩色多普勒超声检测[J].中华超声影像学杂志,1997,6(5):169-172. [6] Krejza J, Arkuszewski M, Kasner SE, et al. Carotid artery diameter in men and women and the relation to body and neck size. Stroke. 2006;37(4):1103-1105. [7] Yang XY, Hu YM, Wei W, et al. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 2012;20(6):472-474,480.杨晓燕,胡元明,魏玮,等.64层螺旋CT血管造影及超声造影评价颈动脉斑块[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2012,20(6):472-474,480.[8] Yang YW, Li YJ, Xie T, et al. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 2012;20(8):607-610.杨毓雯,李沿江,谢天.高频超声评价颈动脉管壁形态对冠心病的预测价值[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2012,20(8):607-610. [9] Wang XY. Qiqihaer Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2012;33(2):186-187.王心宇.颈动脉超声对糖尿病患者颈动脉测量的分析研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2012,33(2):186-187.[10] Cinthio M, Jansson T, Eriksson A, et al. Evaluation of an algorithm for arterial lumen diameter measurements by means of ultrasound. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010; 48(11): 1133-1140.[11] Sarikaya B, Lohman B, McKinney AM, et al. Correlation between carotid bifurcation calcium burden on non-enhanced CT and percentage stenosis, as confirmed by digital subtraction angiography.Br J Radiol. 2012;85(1015): e284-292. [12] Wang Y, Wang Q, Cai J, et al. Feasibility of carotid bifurcation angle measurement with oblique sagittal T(1)-weighted black-blood magnetic resonance imaging. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2013;33(1):93-98.[13] Ilea D, Duffy C, Kavanagh L, et al. Fully automated segmentation and tracking of the intima media thickness in ultrasound video sequences of thecommon carotid artery. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013;60(1):158-177.[14] Xue YJ, Gao PY, Lin Y, et al. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2008;42(8):849-853.薛蕴菁,高培毅,林燕,等.应用图像后处理技术测量和分析人体颈动脉分叉血管几何学指标[J].中华放射学杂志,2008,42(8): 849-853. [15] Bressloff NW. Parametric geometry exploration of the human carotid artery bifurcation. J Biomech. 2007;40(11):2483-2491.[16] Schulz UG, Rothwell PM. Major variation in carotid bifurcation anatomy: a possible risk factor for plaque development? Stroke. 2001;32(11):2522-2529.[17] Goubergrits L, Affeld K, Fernandez-Britto J, et al. Geometry of the human common carotid artery: A vessel cast study of 86 specimens. Pathol Res Pract. 2002;198(8):543-551.[18] Sehirli US, Yalin A, Tulay CM, et al. The diameters of common carotid artery and its branches in newborns. Surg Radiol Anat. 2005;27(4):292-296. [19] van Gils MJ, Bodde MC, Cremers LG, et al. Determinants of calcification growth in atherosclerotic carotid arteries; a serial multi-detector CT angiography study. Atherosclerosis. 2013; 227(1):95-99. [20] Wong EY, Nikolov HN, Rankin RN, et al. Evaluation of distal turbulence intensity for the detection of both plaque ulceration and stenosis grade in thecarotid bifurcation using clinical Doppler ultrasound. Eur Radiol. In press.[21] Huang TC, Chang CK, Liao CH, et al. Quantification of blood flow in internal cerebral artery by optical flow method on digital subtraction angiography in comparison with time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54678. [22] Ye F, Lv SM, Kang JH, et al. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2010;44(9):975-979.叶锋,吕绍茂,康江河,等.寰枢关节区分解、融合、透亮及伪彩三维成像技术的应用[J].中华放射学杂志,2010,44(9):975-979. [23] Pizzolato R, Hirsch JA, Romero JM. Imaging challenges of carotid artery in-stent restenosis. J Neurointerv Surg. In press. [24] Appel AA, Chou CY, Larson JC, et al. An initial evaluation of analyser-based phase-contrast X-ray imaging of carotid plaque microstructure. Br J Radiol. 2013;86(1021):20120318. [25] Wang QJ, Wang Y, Cai JM, et al. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 2011;19(5):367-372.王庆军,王勇,蔡剑鸣,等.斜矢状位高分辨三维黑血磁共振成像在粥样硬化颈动脉支架术前评估的应用价值[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2011,19(5):367-372.[26] Lu XY, Zhang WS, Wang D, et al. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 2001;9(3):186-189.鲁晓燕,张挽时,王东,等.螺旋CT血管造影及CT仿真内窥镜诊断颈动脉狭窄[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2001,9(3):186-189.[27] Chen X, He HT, Li D. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2011; 139(2):2587-2588.陈曦,何海涛,李丹.螺旋CT血管成像与彩色多普勒血流成像评价颈动脉狭窄与脑梗死[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,139(2): 2587-2588.[28] Chen YJ, Xie BZ, Chen LJ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(52):9787-9791. 陈雍君,谢柏臻,陈丽君,等.枕寰枢复合体后方静脉结构三维CT解剖[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(52): 9787-9791. [29] Yang L, Huang X, Duan S. Clinical application and technique of 64-slice spiral CT subtraction angiography in head and neck. Vasa. 2012;41(1): 27-33.[30] Jaff MR, Goldmakher GV, Lev MH, et al. Imaging of the carotid arteries: the role of duplex ultrasonography, magnetic resonance arteriography, and computerized tomographic arteriography. Vasc Med, 2008;13(4):281-292.[31] Romijn M, Gratama van Andel HA, van Walderveen MA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of CT angiography with matched mask bone elimination for detection of intracranial aneurysms: comparison with digital subtraction angiography and 3D rotational angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(1): 134-139.[32] Forsting M. CTA of the ICA bifurcation and intracranial vessels. Eur Radiol. 2005;15 Suppl 4:D25-27.[33] Chen BL, Yang Y, Yong Q, et al. Zhonghua Chaosheng Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 2010;19(2):120-123.陈百玲,杨颖,勇强,等.超声检测颈动脉内-中膜厚度的重复性评价[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2010,19(2):120-123.[34] Wang SB, Lv L, Li P. Shiyong Fangshexue Zazhi. 2011;27(11): 1648-1651.王绍波,吕梁,李鹏.颈动脉分叉特征与动脉粥样硬化相关性分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2011,27(11):1648-1651.[35] Takemoto K, Ueba T, Takano K, et al. Quantitative evaluation using the plaque/muscle ratio index panels predicts plaque type and risk of embolism in patients undergoing carotid artery stenting. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012:S0303-8467 (12)00611-7. [36] Tang H, van Onkelen RS, van Walsum T, et al. A semi-automatic method for segmentation of the carotid bifurcation and bifurcation angle quantification on black blood MRA. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2010;13(Pt 3):97-104.[37] Pons Y, Ukkola-Pons E, Clément P, et al. Relevance of 5 different imaging signs in the evaluation of carotid artery invasion by cervical lymphadenopathy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(5):775-778.[38] Zhou YF, Han P, Wang XD, et al. Linchuang Fangshexue Zazhi. 2010;29(1):39-42.周运锋,韩萍,王向东,等.多层螺旋CT血管成像对颈动脉体瘤的诊断价值[J].临床放射学杂志,2010,29(1):39-42. |
| [1] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [2] | Xie Jingshu, Zhang Xianglin, Liu Jinlei, Wen Jing. Application of High Resolution reconstruction algorithm in precision CT scans of the middle and inner ears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3614-3618. |
| [3] | Yu Yinghao, Zhao Jijun, Liu Dongcheng, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Clinical significance of preoperative planning assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with digital imaging system for fixed-bearing prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3324-3331. |
| [4] | Liu Xing, Wei Xiaohan, Deng Jie, Li Zhongming . Preparing a blunt contusion model of rabbit skeletal muscle under different blow strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 196-200. |
| [5] | Du Xueting, Yang Yang, Huang Wenhua, Chen Wubiao. Clinical application and breakthrough of three-dimensional printing based on medical imaging technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2887-2894. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Luo Guanghua, Liu Jincai . Correlation of infrapatellar fat pad edema with trochlear and patellofemoral joint morphology: MRI evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2410-2415. |
| [7] | Ma Long, Tan Xiaoxin, Sun Guoshao. A 5-year follow-up on sagittal alignment and radiological outcomes of consecutive three-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion and hybrid surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1879-1885. |
| [8] | Deng Biyong, Deng Bixiang. Differences in relative parameters of acetabulum in hip arthroplasty between CT horizontal plane and CT true pelvic plane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1405-1409. |
| [9] | Zhao Chuntao, Qing Mingsong, Yu Langbo, Peng Jiachen . Meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty guided by kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| [10] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [11] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [12] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [13] | Cao Bin, Zuo Yuqiang, Li Cunrui, Kang Weifeng, Yu Haiquan, Su Jingyang. Correlation of parameters of lordosis type cervical spine saggital plane in asymptomatic adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 898-902. |
| [14] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [15] | Yan Shu, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian. Analysis of programs on tissue engineering funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China between 2013 and 2018 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 731-735. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||