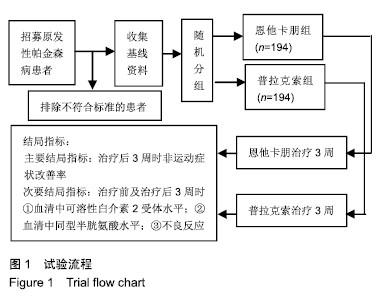
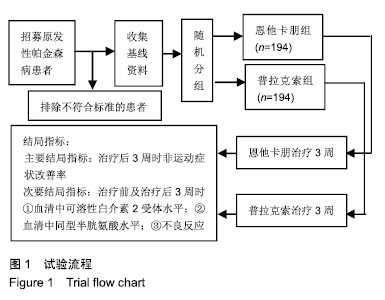
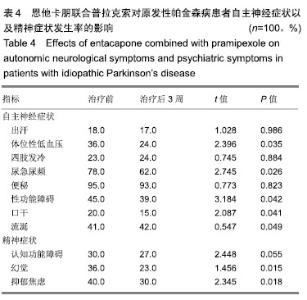
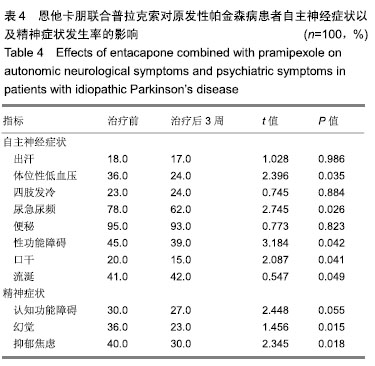
| [1]Buetow SA, Martinez-Martin P, Hirsch MA, et al. Beyond patient-centered care: person-centered care for Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2016;2:16019.[2]Ikeda A, Matsushima T, Daida K, et al. A novel mutation of CHCHD2 p.R8H in a sporadic case of Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2017;34:66-68.[3]Rodríguez-Violante M, Zerón-Martínez R, Cervantes-Arriaga A, et al. Who Can Diagnose Parkinson's Disease First? Role of Pre-motor Symptoms. Arch Med Res. 2017;48(3):221-227.[4]Campolo J, De Maria R, Cozzi L, et al. Antioxidant and inflammatory biomarkers for the identification of prodromal Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2016;370:167-172.[5]Nagayama H, Maeda T, Uchiyama T, et al. Anhedonia and its correlation with clinical aspects in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:403-407.[6]Pfeiffer RF. Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016;22 Suppl 1:S119-122.[7]Schapira AHV, Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18(7):435-450.[8]Schaeffer E, Berg D. Dopaminergic Therapies for Non-motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(7): 551-570.[9]Stocchi F, Adagio Investigators. Benefits of treatment with rasagiline for fatigue symptoms in patients with early Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(2):357-360.[10]赵国华,孙菲,冯学功,等.龟羚帕安颗粒治疗帕金森病肝肾不足证非运动症状的多中心随机双盲对照研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2013,33(4):476-479.[11]Rascol O, Fitzer-Attas CJ, Hauser R, et al. A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson's disease (the ADAGIO study): prespecified and post-hoc analyses of the need for additional therapies, changes in UPDRS scores, and non-motor outcomes. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(5):415-423.[12]Reichmann H, Jost WH. Efficacy and tolerability of rasagiline in daily clinical use--a post-marketing observational study in patients with Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9): 1164-1171.[13]陈路,韦一佛,刘明,等.补肾益髓法对帕金森病肾虚髓减证患者非运动症状的影响[J].中医杂志,2019,60(3):229-231,236.[14]范瑞娟.多巴丝肼联合普拉克索对帕金森病非运动症状的治疗效果[J].临床医学研究与实践,2018,3(08):20-21.[15]张江伟,李乾露.美金刚改善帕金森病患者运动及非运动症状临床观察[J].现代仪器与医疗,2018,24(01):111-113.[16]胡火有,韩漫夫,肖小华,周艳霞,陈李芳.添加普拉克索治疗对帕金森病患者UPDRS评分及非运动症状的影响分析[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2016,33(05):425-428.[17]杨宁,宁厚旭,过伟峰,刘卫国,乔飞.益肾除颤汤联合多巴丝肼片治疗帕金森病随机对照研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2017, 37(9):1081-1084.[18]Li J, Lou Z, Liu X, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Adjuvant Treatment with Entacapone in Advanced Parkinson's Disease with Motor Fluctuation: A Systematic Meta-Analysis. Eur Neurol. 2017;78(3-4):143-153.[19]Senek M, Nielsen EI, Nyholm D. Levodopa-entacapone- carbidopa intestinal gel in Parkinson's disease: A randomized crossover study. Mov Disord. 2017;32(2):283-286.[20]Kuoppamäki M, Leinonen M, Poewe W. Efficacy and safety of entacapone in levodopa/carbidopa versus levodopa/ benserazide treated Parkinson's disease patients with wearing-off. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015;122(12): 1709-1714.[21]Kvernmo T, Härtter S, Burger E. A review of the receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopamine agonists. Clin Ther. 2006;28(8):1065-1078.[22]Shen T, Ye R, Zhang B. Efficacy and safety of pramipexole extended-release in Parkinson's disease: a review based on meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24(6):835-843.[23]Wang Y, Sun SG, Zhu SQ, et al. Analysis of pramipexole dose-response relationships in Parkinson's disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11:83-89.[24]Olanow CW, Kieburtz K, Leinonen M, et al. A randomized trial of a low-dose Rasagiline and Pramipexole combination (P2B001) in early Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2017; 32(5):783-789.[25]Schapira AH, Mcdermott MP, Barone P, et al. Pramipexole in patients with early Parkinson's disease (PROUD): a randomised delayed-start trial. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(8): 747-755.[26]Meriç C, Pirdo?an E, Günday Toker , et al. Mania with psychotic feature induced by the use of pramipexole in Parkinson's disease: a case report. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2014;25(3):212-214.[27]Silindir M, Ozer AY. The benefits of pramipexole selection in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(10): 1505-1511.[28]中华医学会神经病学分会帕金森病及运动障碍学组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会帕金森病及运动障碍专业委员会.中国帕金森病的诊断标准(2016版)[J].中华神经科杂志, 2016,49(4): 268-271.[29]Rana AQ, Ahmed US, Chaudry ZM, et al. Parkinson's disease: a review of non-motor symptoms. Expert Rev Neurother. 2015;15(5):549-562.[30]韩霞,王丙聚,黄宇青,等.帕金森病患者促炎症因子与焦虑抑郁?睡眠及疲劳的相关性分析[J].国际精神病学杂志, 2016,43(4): 596-599.[31]Weiland G. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)--a new serodiagnostic method for the detection of parasitic infections (author's transl). MMW Munch Med Wochenschr. 1978;120(44):1457-1460.[32]刘培茹.高同型半胱胺酸血症与帕金森病认知功能的相关性研究[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2016,43(1):30-33.[33]赵睿,李琼,张平.血塞通注射液联合普拉克索改善帕金森病人非运动症状的疗效研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2018, 16(9):1286-1288.[34]Kurt EE, Büyükturan B, Büyükturan , et al. Effects of Ai Chi on balance, quality of life, functional mobility, and motor impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease<sup/>. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;40(7):791-797.[35]Sto?ek J, Rudzińska M, Pustu?ka-Piwnik U, et al. The effect of the rehabilitation program on balance, gait, physical performance and trunk rotation in Parkinson's disease. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016;28(6):1169-1177.[36]Samoudi G, Jivegård M, Mulavara AP, et al. Effects of Stochastic Vestibular Galvanic Stimulation and LDOPA on Balance and Motor Symptoms in Patients With Parkinson's Disease. Brain stimulation. 2015;8(3):474-480.[37]Lemay S, Chouinard S, Blanchet P, et al. Lack of efficacy of a nicotine transdermal treatment on motor and cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2004;28(1):31-39.[38]Zhang L, Zhang Z, Chen Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of rasagiline as an adjunct to levodopa treatment in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-controlled, multi-centre trial. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;16(7):1529-1537. |