Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5097-5102.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1343
Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk factors for postoperative delirium in elderly patients after total hip arthroplasty
Gao Zhixiang, Jiang Yishan, Long Nengji, Xiao Cong
- Second Department of Orthopedics, the Third Hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Online:2019-11-18Published:2019-11-18 -
Contact:Xiao Cong, MD, Second Department of Orthopedics, the Third Hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Gao Zhixiang, Master, Second Department of Orthopedics, the Third Hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China Jiang Yishan, Associate chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, the Third Hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China Gao Zhixiang and Jiang Yishan contributed equally to this paper.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Zhixiang, Jiang Yishan, Long Nengji, Xiao Cong. Risk factors for postoperative delirium in elderly patients after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5097-5102.
share this article
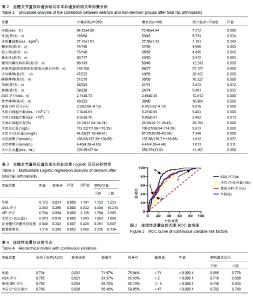
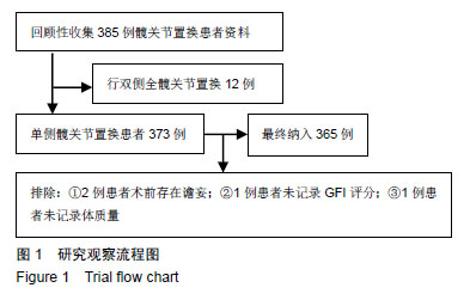
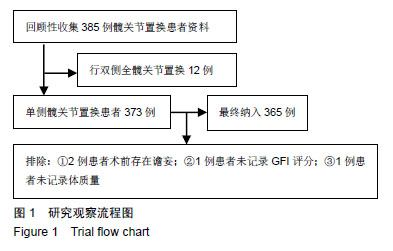
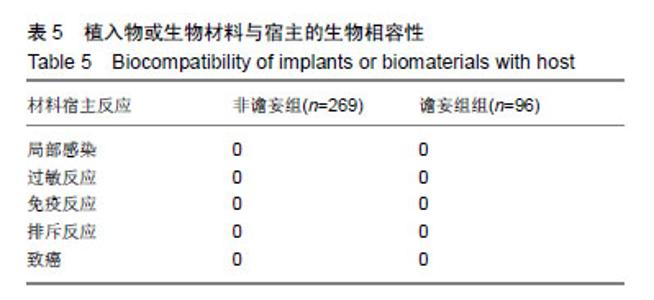
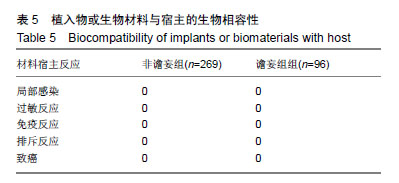
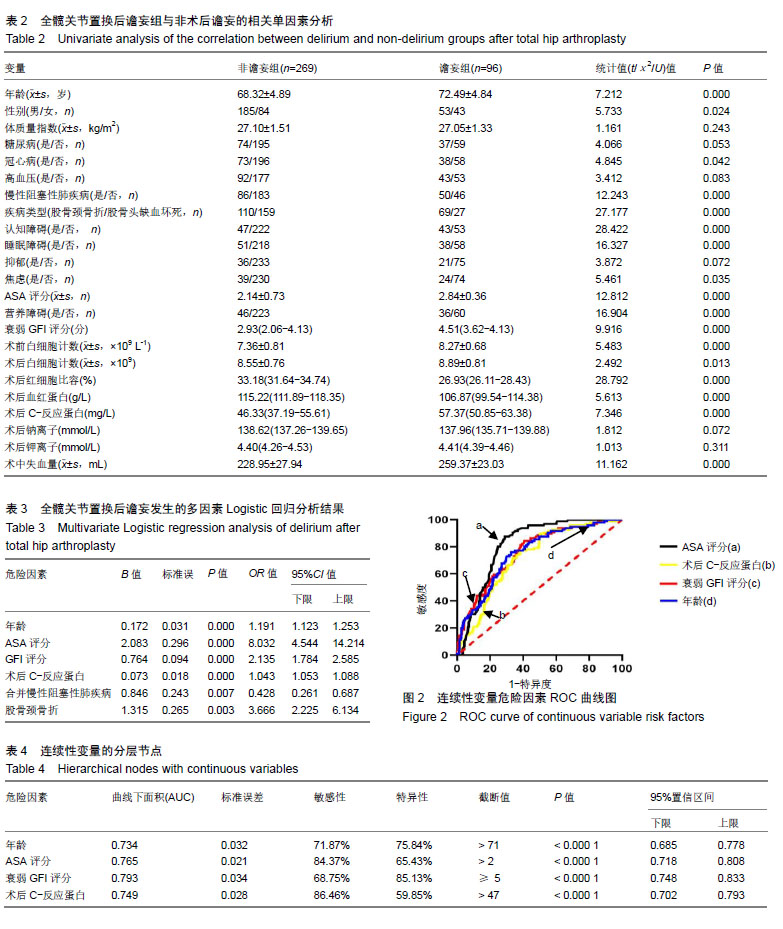
2.2 全髋关节置换后谵妄组与非术后谵妄组相关因素比较 术前通过比较发现两组患者在年龄、性别、合并冠心病、合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病、疾病类型、认知障碍、睡眠障碍、焦虑、ASA评分、营养障碍、衰弱GFI指数、术前及术后白细胞计数、术后红细胞比容、术后血红蛋白水平、术后C-反应蛋白水平及术中失血量方面有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而在体质量指数、合并糖尿病、合并高血压、抑郁、术后钠、钾离子水平方面差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 2.3 全髋关节置换后谵妄组发生的多因素Logistic回归分析 多因素Logistic回归分析以术后是否发生谵妄为因变量,上述因素分析中统计值P < 0.1的相关因素为自变量进行多因素Logistic回归分析显示:年龄、ASA评分、GFI评分、术后C-反应蛋白、合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病、股骨颈骨折行全髋关节置换是老年行全髋关节置换后发生术后谵妄的高危因素,见表3。 2.4 全髋关节置换后发生术后谵妄危险因素连续性变量的ROC曲线下面积 将危险因素连续性变量通过MedCalc 15.8软件绘制ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别找出年龄、ASA评分、GFI评分、术后C-反应蛋白的截断值;研究发现:年龄>71岁、ASA评分>2分、衰弱GFI评分≥5分、术后C-反应蛋白> 47 mmol/L时全髋关节置换后发生术后谵妄的风险越高,具有较好的特异性和灵敏性,见表4及图2。 2.5 植入物与宿主的生物相容性 见表5。"
| [1]Simon ST, Gomes B, Koeskeroglu P, et al. Population, mortality and place of death in Germany (1950-2050)-implications for end-of-life care in the future. Public Health. 2012;126(11):937-946. [2]Hoorntje A, Janssen KY, Sbt B, et al. The effect of total hip arthroplasty on sports and work participation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2018;48(6):1-32. [3]Capone A, Bienati F, Torchia S, et al. Short stem total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients 60 years or younger: a 3- to 10-year follow-up study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):301. [4]Barbosa FT, Da CR, Pinto AL. Postoperative delirium in the elderly. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2008;58(58):665-670. [5]Saczynski JS, Marcantonio ER, Quach L, et al. Cognitive Trajectories after Postoperative Delirium. New Engl J Med. 2012,367(1):30-39.[6]Jones CA, Jhangri GS, Feeny DH, et al. Cognitive status at hospital admission: postoperative trajectory of functional recovery for hip fracture. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(1):61-67. [7]Watt J, Tricco AC, Talbot-Hamon C, et al. Identifying older adults at risk of delirium following elective surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;16(1):1-10. [8]Gleason LJ, Schmitt EM, Kosar CM, et al. Effect of delirium and other major complications on outcomes after elective surgery in older adults. JAMA Surg. 2015;150(12):1134-1140. [9]Hamilton GM, Wheeler K, Michele JD, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the impact of incident postoperative delirium on mortality. Anesthesiology. 2017;127(1):78-88.[10]Schenning KJ, Deiner SG. Postoperative delirium in the geriatric patient. Anesthesiol Clin. 2015;33(3):505-516. [11]Organization WH. World Health Organization launches new initiative to address health needs of a rapidly ageing population. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2004;12(4):210-216.[12]Hooijer C, Dinkgreve M, Jonker C, et al. Short screening tests for dementia in the elderly population. I. A comparison between AMTS, MMSE, MSQ and SPMSQ. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1992;7(8): 559-571. [13]李建明.睡眠状况自评量表(SRSS)简介[J].中国健康心理学杂志,2012, 20(12):1851-1851.[14]Zung WW. Factors influencing the self-rating depression scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1967;16(5):543.[15]Jegede RO. Psychometric attributes of the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale. Psychol Rep. 1977;40(1):303-306. [16]Rubenstein LZ, Harker JO, Salvà A, et al. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice: developing the short-form mini-nutritional assessment (MNA-SF). J Gerontol. 2001;56(6): M366-M372. [17]Steverink N, Slaets JPJ, Schuurmans H, et al. Measuring frailty: developing and testing the gfi (groningen frailty indicator). Gerontologist. 2001;41(Special Issue 1):236-237. [18]Wei LA, Fearing MA, Sternberg EJ, et al. The Confusion Assessment Method: a systematic review of current usage. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;56(5):823-830. [19]Pollard C, Fitzgerald M, Ford K. Delirium: The lived experience of older people who are delirious post-orthopaedic surgery. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2015;24(3):213-221. [20]Wang LH, Xu DJ, Wei XJ, et al. Electrolyte disorders and aging: risk factors for delirium in patients undergoing orthopedic surgeries. BMC Psychiatry. 2016;16(1):418. [21]Raats JW, Eijsden WAV, Crolla RMPH, et al. Risk factors and outcomes for postoperative delirium after major surgery in elderly patients. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136071. [22]Brown CH 4th, Max L, LaFlam A, et al. The association between preoperative frailty and postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2016;123(2):430-435. [23]Jung P, Pereira MA, Hiebert B, et al. The impact of frailty on postoperative delirium in cardiac surgery patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;149(3):869-875. [24]Soysal P, Stubbs B, Lucato P, et al. Inflammation and frailty in the elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2016;31:1-8.[25]Alsop DC, Fearing MA, Johnson K, et al. The role of neuroimaging in elucidating delirium pathophysiology. J Gerontol. 2006;61(12): 1287-1293. [26]Alsop DC, Fearing MA, Johnson K, et al. Review article the role of neuroimaging in elucidating delirium pathophysiology. J Gerontol. 2006;61(12):1287-1293. [27]Vcon Gool WA, van de Beek D, Eikelenboom P. Systemic infection and delirium: when cytokines and acetylcholine collide. Lancet. 2010;375(9716):773-775. [28]Lakstygal A, Kolesnikova T, Khatsko S, et al. DARK classics in chemical neuroscience: atropine, scopolamine and other anticholinergic deliriant hallucinogens. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2018. DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00615.[29]李呈凯,白树财,宋秀钢,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄相关危险因素的回顾性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(4):250-256. [30]Brouquet A, Cudennec T, Benoist S, et al. Impaired mobility, ASA status and administration of tramadol are risk factors for postoperative delirium in patients aged 75 years or more after major abdominal surgery. Ann Surg. 2010;251(4):759-765. [31]Chen CC, Lin MT, Liang JT, et al. Pre-surgical geriatric syndromes, frailty, and risks for postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery: prevalence and red flags. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;19(5):927-934. [32]Leung JM, Tsai TL, Sands LP. Preoperative frailty in older surgical patients is associated with early postoperative delirium. Anesth Analg. 2011;112(5):1199-1201. [33]Van-Munster B, Korevaar JC, Zwinderman AH, et al. Time-course of cytokines during delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;56(9):1704-1709. [34]Dillon ST, Vasunilashorn SM, Ngo L, et al. Higher c-reactive protein levels predict postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing major elective surgery: a longitudinal nested case-control study. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;81(2):145-153.[35]Jakub K, Andrzej B, Joanna L, et al. Raised IL-2 and TNF-α concentrations are associated with postoperative delirium in patients undergoing coronary-artery bypass graft surgery. Int Psychogeriatr. 2014;26(5):845-855.[36]Pol RA, van Leeuwen BL, Izaks GJ, et al. C-reactive protein predicts postoperative delirium following vascular surgery. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28(8):1923-1930.[37]Björkelund KB, Hommel A, Thorngren KG, et al. Reducing delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture: a multi-factorial intervention study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010;54(6):678-688. [38]Wei W, Hong-Liang L, Dong-Xin W, et al. Haloperidol prophylaxis decreases delirium incidence in elderly patients after noncardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 2012;40(3): 731-739. |
| [1] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [4] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Su Baotong, Wang Hanyu, Xu Yilang, Xie Yajuan, Cheng Zhian. Construction of a Nomogram prediction model for postoperative delirium after hip fracture in the elderly based on medical records from a hospital [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3844-3849. |
| [9] | Li Haifeng, Liu Yu, Yin Qudong, Sun Zhenzhong, Rui Yongjun, Gu Sanjun. Risk of complications of early postoperative weight-bearing after internal fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2875-2880. |
| [10] | Yang Kun, Fei Chen, Wang Pengfei, Zhang Binfei, Yang Na, Tian Ding, Zhuang Yan, Zhang Kun . Meta-analysis of the efficacy of robot-assisted and traditional manual implantation of cannulated screws in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2938-2944. |
| [11] | Song Kaikai, Du Gangqiang, Li Peng, Jiang Shengyuan, Gong Zhihao, Zhang Zhiwei, Zhang Kai . Application of head-neck ratio in the treatment of femoral neck fracture in aged patients with artificial femoral head replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2805-2809. |
| [12] | Fan Zhirong, Su Haitao, Zhou Lin, Huang Huida, Zhou Junde, Jiang Tao, Liu Zitao. Finite element analysis of novel femoral neck system for unstable femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2321-2328. |
| [13] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [14] | Li Yonghe, Wang Xiankang, Meng Yu, Liu Lu, Zhang Chunqiu, Ye Jinduo . Mechanical analysis on the position difference of short-stemmed prosthesis in hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2394-2399. |
| [15] | Gao Ziqing, Ruan Sibei, Li Li, Ling Feng, Tang Xiaoqin, Kang Qingmei, Luo Siyi, Luo Jing, Tang Yaping, Tang Mingxi . Identification and survival analysis of tTA/tetO-CCKR-2 double transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1682-1687. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||