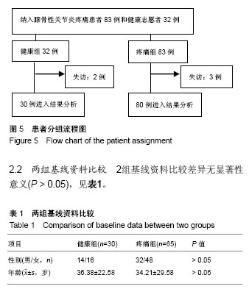
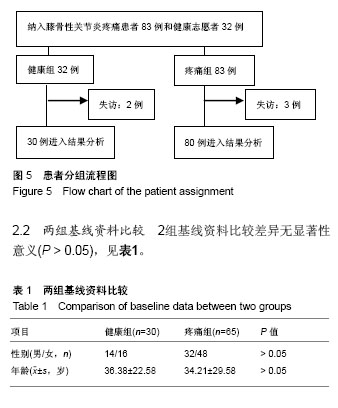
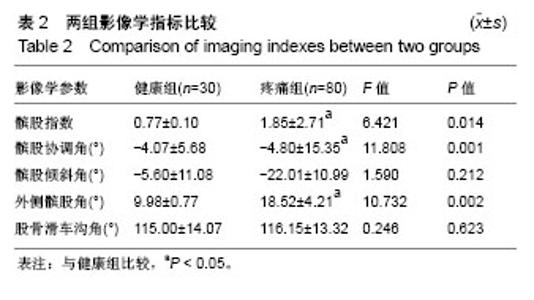
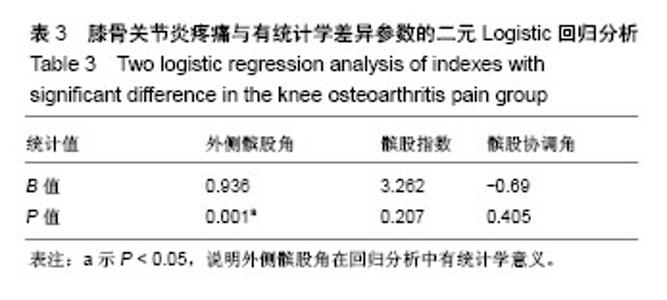
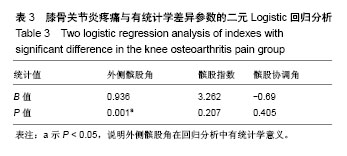
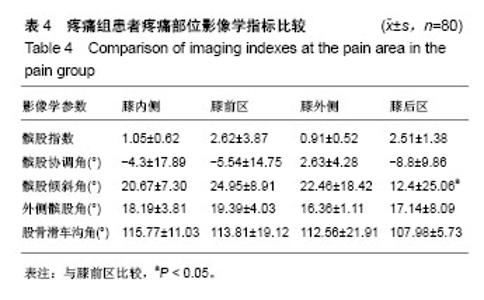
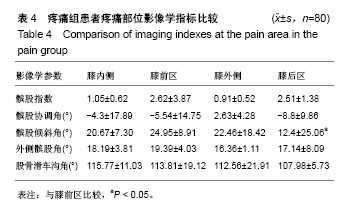
| [1] Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, et al. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology, 9th Edition. 2012. [2] Conaghan PG, Hunter DJ, Maillefert JF, et al. Summary and recommendations of the OARSI FDA osteoarthritis Assessment of Structural Change Working Group. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(5):606-610. [3] Conaghan P, D'Agostino M, Ravaud P, et al. EULAR report on the use of ultrasonography in painful knee osteoarthritis. Part 2: Exploring decision rules for clinical utility. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(12):1710. [4] Keen HI, Conaghan PG. Ultrasonography in osteoarthritis. Radiol Clin North Am. 2009;47(4):581-594. [5] Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJR, Agricola R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [6] Zhang W, Doherty M, Peat G, et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for the diagnosis of knee OA. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;69(3):483-489. [7] 谢平金,柴生颋.膝骨关节炎X线片观测指标及其应用进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(3):72-76.[8] 国家中医药管理局医政司.22个专业95个病种中医临床路径(合订本)[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2010:127-131.[9] Thome R, Augustsson J, Karlsson J. Patellofemoral pain syndrome sports injuries. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1999: 337-341. [10] Felson DT. Osteoarthritis of the knee. Curr Orthop. 2009; 4(2):77-78. [11] 阮培灿.探讨早期KOA患者髌周疼痛与髌股关节结构紊乱的相关性[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2014.[12] Caplan N, Kader DF. Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence classic papers in orthopaedics. Springer London, 2014:189-191. [13] 苏佳灿,李文锐,吴永发,等.髌骨临床治疗学[M].上海:第二军医大学出版社,2012.[14] 陈荣生,曾勇明,刘志宏,等.髌骨改良轴位的体位设计及临床应用[J].重庆医科大学学报,2010,35(6):920-922.[15] 马伟,董天华,姚飞荣,等.屈膝15°髌股关节轴位X线片在髌骨排列异常中的诊断价值[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(4):226-229.[16] 郭志良,郝晓光.初探髌骨135°轴位片在膝关节疼痛患者中的应用价值[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2015,2(18):3771-3772.[17] 马秀山,徐英杰,王利民,等.髌骨轴位X线摄片方法改进及多种测量方法综合评价的临床应用[J].中华放射学杂志, 2007,41(8): 862-864.[18] Weber KL, Jevsevar DS, Mcgrory BJ. AAOS clinical practice guideline: surgical management of osteoarthritis of the knee: evidence-based guideline. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016; 24(8):e94. [19] Hafezi-Nejad N, Demehri S, Guermazi A, et al. Osteoarthritis Year in Review 2017: Updates on Imaging Advancements. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018. [20] 张文贤.骨关节炎:膝关节骨性关节炎的病理研究与临床诊治[M].兰州:甘肃科学技术出版社,2008.[21] 蔡余力,王少山.膝关节骨性关节炎的X线测量与分析[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2006,4(5):358-361.[22] Baldini A, Anderson JA, Cerulli-Mariani P, et al. Patellofemoral evaluation after total knee arthroplasty. Validation of a new weight-bearing axial radiographic view. J Bone Joint Surg. 2007;89(8):1810-1817. [23] Katchburian MV, Bull AM, Shih YF, et al. Measurement of patellar tracking: assessment and analysis of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;412(412):241. [24] 隋金颇,葛帮荣,杨文锋,等.膝关节参数在膝前疼痛中的意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(9):1633-1640.[25] 王国良,孙艳,唐兆春,等.髌骨倾斜对兔髌骨关节软骨损害的实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(6):775-778.[26] 亓建洪,黄煌渊,陈世益,等.髌骨倾斜导致髌骨软骨软化实验研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,1999,18(1):15-17.[27] Tanamas SK, Teichtahl AJ, Wluka AE, et al. The associations between indices of patellofemoral geometry and knee pain and patella cartilage volume: A cross-sectional study. Bmc Musculoskelet Dis. 2010;11(1):87. |