Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 3091-3099.doi: 10.12307/2026.723
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of programmed cell death mediated by total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae
Han Yapeng, Gao Jun, Niu Yunwei, Deng Enjia
- Department of Chinese Orthopedics, Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-06Accepted:2025-08-21Online:2026-04-28Published:2025-09-30 -
Contact:Gao Jun, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Chinese Orthopedics, Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Han Yapeng, MS candidate, Department of Chinese Orthopedics, Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82374479 (to GJ); The Seventh Batch of National Senior Chinese Medicine Experts Academic Experience Inheritance Work Instructor and Successor Project, No. (2022)76 (to GJ); The Fourth Batch of Provincial Famous Old Chinese Medicine Experts Inheritance Studio Construction Project, No. (2021)7 (to GJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Yapeng, Gao Jun, Niu Yunwei, Deng Enjia. Mechanism of programmed cell death mediated by total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3091-3099.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
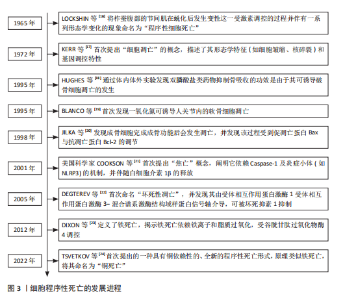
2.1 程序性死亡的发展进程 见图3。 2.2 骨碎补总黄酮调控骨相关细胞凋亡 细胞凋亡是一种受调节的细胞死亡途径,确保细胞以结构化的方式死亡,以防止对组织或生物体产生负面影响[25]。凋亡细胞的特征包括细胞及质膜的皱缩、浓缩和细胞核的破碎等[26]。作为细胞死亡最常见的机制之一,凋亡根据所接受刺激信号类型的不同被分为外源性、穿孔素颗粒酶和内源性3种途径[27]。与凋亡相关因子包括Bcl-2、核因子κB、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶等信号通路[28]。细胞凋亡对骨组织稳态十分重要,间充质干细胞的过度凋亡会导致它的成骨分化功能下降;在骨组织中,细胞凋亡是成骨细胞的主要命运,然而成骨细胞过度凋亡会影响骨形成和骨吸收的平衡,从而导致骨质流失、骨的微观结构被破坏和骨矿物质密度的降低[29];促进成熟破骨细胞的凋亡可有效降低骨吸收水平,改善骨质流失[30];软骨细胞凋亡水平的增加会促进关节软骨的炎症反应,从而导致骨关节炎的发生[31]。骨碎补总黄酮调控骨相关细胞凋亡的相关机制,见图4。 2.2.1 骨碎补总黄酮调控间充质干细胞凋亡 间充质干细胞是一种多能干细胞,在组织再生、创伤愈合和维持组织内环境稳定等方面发挥着重要作用[32]。间充质干细胞凋亡数量的增加会导致成骨细胞的生成减少,从而影响骨吸收-骨重建的平衡,最终导致新骨生成能力减弱、骨折愈合时间延长,因此,抑制间充质干细胞凋亡、提高其活力,对骨质疏松等疾病的治疗尤为关键。柚皮苷可拮抗酒精诱导的间充质干细胞内氧化应激水平提高,从而在一定程度上抑制间充质干细胞整体凋亡水平的增加,维持骨代谢的动态平衡,改善骨的微观结构的退化[33]。过氧化氢会使间充质干细胞内的氧化应激水平升高,诱导间充质干细胞凋亡,柚皮苷可通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路显著上调过氧化氢诱导的间充质干细"
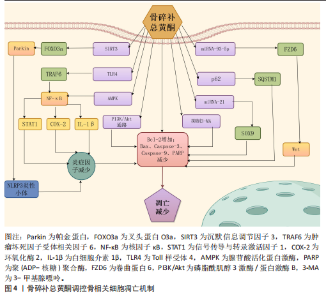
胞凋亡模型中抗凋亡分子Bcl-2的表达,同时下调促凋亡分子Bax和裂解的Caspase-3水平,降低细胞凋亡数量,进而提高间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的数量,促进成骨[34]。 2.2.2 骨碎补总黄酮调控成骨细胞凋亡 作为合成、分泌骨基质的主要细胞,成骨细胞分泌的胶原蛋白形成了骨的基本框架,为矿物质的沉积提供了场所。甲状旁腺素类似物如特立帕肽可促进成骨细胞增殖,治疗骨质疏松具有良好的疗效[35]。因此,促进成骨细胞增殖分化、减少成骨细胞凋亡数量对于预防、缓解骨质疏松等骨相关疾病十分重要。骨碎补总黄酮可以通过调控miRNA-93-5p/卷曲蛋白6/Wnt信号通路降低大鼠牙槽骨成骨细胞的凋亡率,提高成骨细胞中成骨标志物的表达,促进成骨细胞增殖与分化,从而促进种植体的骨整合[36]。有研究表明,柚皮苷可显著逆转3-甲基腺嘌呤诱导的成骨细胞凋亡率增加、促凋亡因子Bax升高和抗凋亡因子Bcl-2的降低,促进成骨细胞成骨分化及矿化[37]。骨碎补总黄酮可通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路降低活性氧水平、增加Bcl-2表达、降低Bax和Caspase-3的表达,从而抑制地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞凋亡,改善股骨头坏死大鼠的"
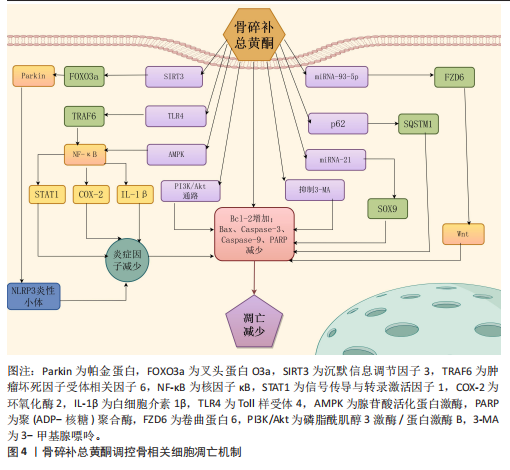
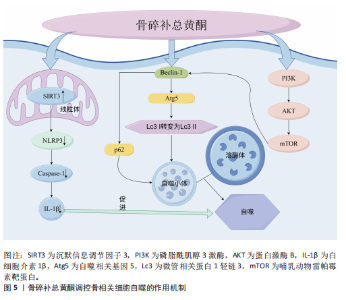
骨组织病理改变[38]。木犀草素可抑制地塞米松诱导的信号传导与转录激活因子1及Bax和细胞色素C表达升高,裂解Caspase-9等促凋亡因子,增加Bcl-2表达,减少成骨细胞凋亡,从而降低股骨头坏死大鼠股骨头空陷窝的比例[39]。过氧化氢引起的成骨细胞肿瘤坏死因子α升高可激活凋亡的死亡受体途径,木犀草素通过抑制核因子κB信号通路抑制过氧化氢诱导的成骨细胞凋亡[40]。 2.2.3 骨碎补总黄酮调控破骨细胞凋亡 破骨细胞是一种多核巨细胞,形成过程受到多种因子的精细调控。在骨的生长发育过程中,破骨细胞对骨骼的塑形起着不可或缺的作用,然而,破骨细胞的过度活跃会导致骨相关疾病的发生。在骨质疏松中,破骨细胞的活性增强,骨吸收超过骨形成,导致骨质减少。在骨肿瘤相关疾病中,肿瘤细胞分泌的因子可刺激破骨细胞,使破骨细胞异常活跃,造成骨质破坏。因此,促进破骨细胞凋亡对于维持骨稳态的平衡、减少骨质流失和抑制骨质破坏有着正向意义。柚皮苷不仅可以抑制成骨细胞的凋亡,也可以诱导破骨细胞的凋亡。李风波等[41]发现柚皮苷可降低破骨细胞数量和骨吸收能力,这可能与下调Bcl-2和基质金属蛋白酶9表达、上调Bax与Caspase-3表达、增加破骨细胞凋亡有关。山柰酚通过降解p62/选择性自噬接头蛋白1激活凋亡相关蛋白Caspase-9、Caspase-3和聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶诱导破骨细胞凋亡[42]。 2.2.4 骨碎补总黄酮调控软骨细胞凋亡 软骨细胞是软骨组织中唯一的细胞类型,对于软骨的形成、维持和修复起着关键作用。软骨细胞过度凋亡会导致软骨基质的过度降解,使得软骨磨损,最终出现关节疼痛和功能障碍等骨关节炎的典型表现,因此,骨关节炎患者软骨组织的软骨细胞凋亡率明显高于正常人软骨组织[43]。炎性小体的过度产生会以环境和细胞依赖的方式产生促炎环境,使软骨细胞凋亡增加,增加骨关节炎的患病风险。柚皮素通过抑制Toll样受体 4/肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6/核因子κB信号通路改善促炎因子白细胞介素1β对软骨细胞活力的抑制,减轻炎症反应、基质降解和细胞凋亡[44]。柚皮苷(柚皮素的糖苷形式)可以通过激活沉默信息调节因子3/叉头蛋白O3a/帕金蛋白途径抑制NLRP3炎性小体活化,保护软骨细胞免受氧化应激引发的凋亡和钙化,减轻细胞外基质的降解[45]。骨碎补总黄酮的另一有效单体成分山柰酚也对软骨细胞的凋亡有着抑制作用。研究表明,经脂多糖处理后软骨细胞凋亡增加,并且可检测到细胞中miRNA-21的高表达,山柰酚可以通过下调miRNA-21表达、上调SOX9表达减少软骨细胞凋亡[46]。米倚林等[47]发现经山柰酚干预后,小鼠软骨中Bax、Caspase-3蛋白表达降低而Bcl-2蛋白表达升高,表明山柰酚对软骨细胞凋亡具有抑制作用。骨碎补总黄酮还可以通过腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶/核因子κB信号通路抑制软骨细胞中促炎因子环氧化酶2的表达,阻断下游花生四烯酸代谢途径,保护软骨细胞免受凋亡,最终起到治疗骨关节炎的作用[48]。 2.2.5 骨碎补总黄酮调控其余骨相关细胞凋亡 除了对上述细胞凋亡的调控作用,骨碎补总黄酮也可介导其余骨相关细胞的凋亡,如骨细胞和骨肉瘤细胞。骨细胞是由陷在骨陷窝中的成骨细胞转化而成,借骨小管形成信息网络,这张网络可以监测并应对骨组织受到的机械应力改变,调节骨的重塑。骨细胞的过度凋亡会直接破坏骨的微观结构,打破骨稳态的平衡,最终导致骨质疏松等疾病的发生。柚皮苷可通过上调Wnt1信号通路提高大鼠骨细胞的Bcl-2 mRNA表达、降低Bax mRNA表达,降低骨细胞凋亡率,改善大鼠骨组织微观结构[49]。骨肉瘤是骨恶性肿瘤中最多见的一种,是从间充质干细胞发展而来。LEE等[50]研究发现,柚皮素通过线粒体功能障碍、活性氧产生和内质网应激信号通路诱导细胞凋亡、细胞周期阻滞和自噬,有助于柚皮素对骨肉瘤细胞的抗增殖作用。 2.3 骨碎补总黄酮调控骨相关细胞自噬的作用机制 自噬是一种高度保守的细胞内降解系统,是一种细胞通过降解和回收蛋白质和细胞器以维持细胞内稳态的过程[51],相关因子包括Beclin-1、p62和溶酶体关联膜蛋白1等蛋白以及磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B、腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶等信号通路。自噬可调节成骨细胞、骨细胞和破骨细胞的存活和功能,而异常的自噬会破坏骨的重塑平衡,使骨骼出现病理状态[52],因此,自噬对于维持骨骼稳态至关重要。骨碎补总黄酮调控骨相关细胞自噬的作用机制,见图5。 2.3.1 骨碎补总黄酮调控间充质干细胞自噬 间充质干细胞的自噬异常使得细胞无法清除老化受损的细胞器,影响它的分化功能,进而导致成骨细胞生成减少、骨量流失。与凋亡相似,酒精同样影响着间充质干细胞的自噬水平,柚皮苷可拮抗酒精诱导的自噬相关蛋白微管相关蛋白1轻链3表达水平增加,参与间充质干细胞自噬水平调控,使自噬趋于正常水平,保持间充质干细胞的成骨分化潜能[33]。 2.3.2 骨碎补总黄酮调控成骨细胞自噬 自噬参与骨形成的调节,抑制成骨细胞的凋亡,因此,通过增强成骨细胞自噬来促进成骨和抑制凋亡可能是一个有前途的途径[53]。柚皮苷通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路促进Beclin-1表达、抑制p62的表达、增加自噬体数量,诱导糖皮质激素性骨质疏松大鼠的成骨细胞自噬并促进其增殖[54]。吴泽钰[37]发现柚皮苷增加了成骨细胞自噬相关因子Beclin-1、自噬相关基因5的表达以及微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅰ向微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅱ的转化,逆转3-甲基腺嘌呤诱导的细胞凋亡增加,证实了柚皮苷介导的自噬能促进成骨分化、矿化。 2.3.3 骨碎补总黄酮调控破骨细胞自噬 破骨细胞中自噬的过度激活会导致细胞存活时间延长,从而过度吸收骨组织,使骨吸收强于骨重建,导致骨质疏松的发生。山柰酚可通过逆转核因子κB受体活化因子配体对破骨细胞中Beclin-1和p62/选择性自噬接头蛋白1等促自噬因子的mRNA水平的提高作用,抑制自噬功能,以促进破骨细胞凋亡水平,使得骨吸收减少,抑制骨质流失[42]。 2.3.4 骨碎补总黄酮调控软骨细胞自噬 软骨细胞的自噬障碍会使细胞内受损细胞器和异常蛋白累积,导致软"
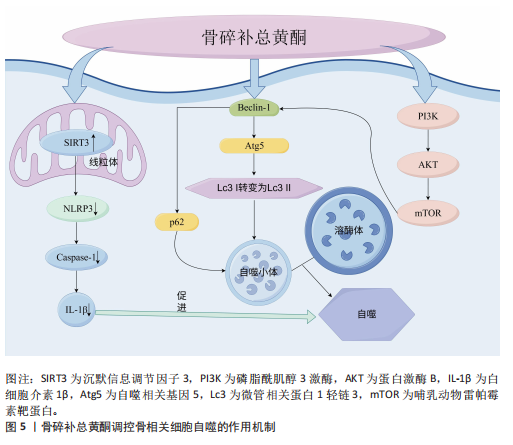
骨细胞凋亡、软骨基质降解甚至骨关节炎的发生。柚皮苷通过激活沉默信息调节因子3促进软骨细胞线粒体自噬,抑制NLRP3、Caspase-1和白细胞介素1β等炎症小体激活相关蛋白的表达,从而减轻过量的活性氧积累,使软骨细胞免于凋亡和退化,最终改善椎间盘退变的进展[45]。研究发现,经柚皮苷治疗后,软骨组织中Beclin-1表达增加、p62表达减少、自噬体数量增加[54]。木犀草素可增加软骨细胞中Beclin-1表达、微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅱ/微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅰ的比值并降低P62的表达,表明木犀草素可显著激活自噬信号通路;木犀草素还可提高软骨细胞中糖胺聚糖的表达,维持软骨细胞的合成代谢和分解代谢平衡[55]。 2.4 骨碎补总黄酮调控骨相关细胞焦亡的作用机制 2001年,COOKSON等[21]将鼠伤寒沙门氏菌感染的巨噬细胞中的程序性死亡模式正式定义为“焦亡”。与凋亡不同,焦亡的主要特征是细胞肿胀、细胞膜破裂,导致细胞内容物(如炎症递质)释放到细胞外,进而引发强烈的炎症反应。炎症小体和Caspase 蛋白家族以及炎症因子(如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18)是焦亡的主要相关因子,NLRP3可以激活蛋白酶Caspase-1诱导焦亡,并促进白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的释放[56],从而引发炎症反应,导致细胞焦亡的发生。对于骨相关细胞而言,炎症环境可显著降低间充质干细胞的活力和成骨分化能力,影响骨质流失[57],焦亡还会诱导成骨细胞凋亡增加,导致骨形成减少。 炎症小体可通过降低成骨细胞的骨形成能力、分化和增殖以及上调破骨细胞的生成能力,下调成骨细胞活性,甚至促进成骨细胞焦亡,从而减少新骨形成。微重力环境可引起炎症小体NLRP3的激活,同时诱导成骨细胞焦亡,焦亡的发生进一步导致成骨相关因子如骨桥蛋白、碱性磷酸酶表达水平降低,柚皮素可以激活激活核因子E2相关因子2/血红素氧化酶1信号通路控制细胞内活性氧的产生和纠正线粒体功能障碍,减弱细胞焦亡,促进成骨细胞分化[58]。过氧化氢同样被用于诱导细胞焦亡模型,木犀草素可减轻过氧化氢对成骨细胞中磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B轴和成骨作用的抑制以及成骨细胞焦亡,确保成骨细胞分化成骨;此外,木犀草素还可减轻细胞内活性氧的积累和线粒体功能障碍,降低成骨细胞自噬失衡的可能[59]。 2.5 骨碎补总黄酮调控骨相关细胞铁死亡的作用机制 2012年,DIXON等[23]首次提出铁死亡的概念,这是一种铁依赖性、非凋亡的细胞死亡模式,特征是细胞内铁离子超载和芬顿反应诱导的脂质过氧化物积累[60],铁死亡的细胞表现为线粒体收缩、膜密度增加、嵴减少甚至消失、外膜破裂等特点[61]。铁死亡与骨质疏松的发生发展密切相关,成骨细胞的铁死亡会破坏骨稳态,导致骨质疏松的发生。柚皮苷通过激活Wnt1信号通路降低骨组织内的铁沉积、转铁蛋白受体1的表达,提高膜转铁蛋白的表达,从而减少骨细胞内铁积累,降低骨细胞的铁死亡水平,抑制骨质疏松的进展[49]。柚皮素可通过上调软骨细胞中抗氧化基因核因子E2相关因子2和血红素加氧酶1表达减少软骨细胞中的铁积累,降低细胞中铁过载诱导产生的活性氧和氢过氧化物含量,逆转铁过载引起的软骨细胞活力降低,最终减轻铁过载下的软骨损伤[62]。 骨碎补总黄酮介导骨相关细胞程序性死亡的研究进展,见表1。 2.6 骨相关细胞其他程序性死亡的作用机制 除上述程序性死亡类型外,还有其他如铜死亡、坏死性凋亡等形式,研究骨相关细胞这些程序性死亡的作用机制对于治疗骨相关疾病十分重要。铜死亡是2022年由TSVETKOV等[24]首次提出的一种具有铜依赖性的、全新的程序性死亡形式,原理类似铁死亡,是一种由铜离子介导的细胞死亡方式。在铜死亡过程中,Cu2+通过与三羧酸循环的脂酰化组分结合而引起铜中毒,导致蛋白质聚集、铁硫簇蛋白丢失,进而导致蛋白毒性应"
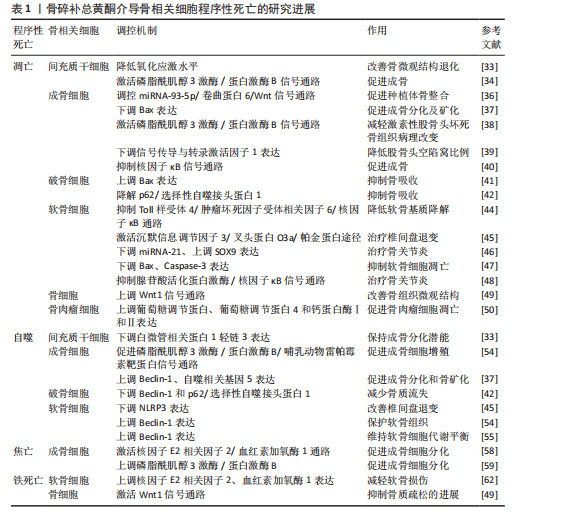
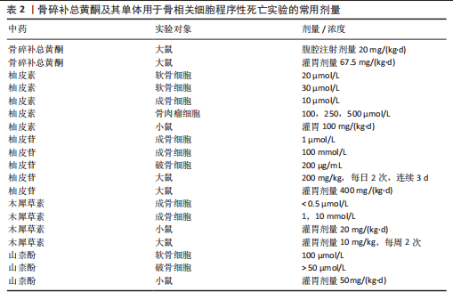
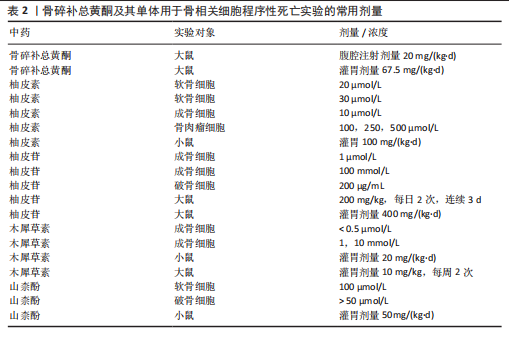
激而诱发细胞死亡[63]。研究表明,铜死亡相关基因PDHB可能是骨关节炎的风险因子,影响着免疫细胞在骨关节炎患者中的变化[64]。坏死性凋亡为一种非依赖Caspase活化且受调控的程序性死亡方式,主要特征为:①电子显微镜下细胞呈现典型的坏死形态学特征(如细胞肿胀、细胞膜破裂、细胞器肿胀和溶解等);②自噬小体形成和空泡现象;③线粒体膜电位缺失,活性氧自由基产生增多[22]。坏死性凋亡主要由受体相互作用蛋白激酶1和受体相互作用蛋白激酶 3以及混合谱系激酶结构域样蛋白等关键蛋白介导[65]。受体相互作用蛋白激酶 3表达的增加会使成骨细胞呈现坏死形态,而受体相互作用蛋白激酶 1的缺陷则会增加破骨细胞数量,从而使骨微结构紊乱,导致骨质疏松的发生[66]。不过,尚未查询到关于骨碎补总黄酮通过调控上述几种新型程序性死亡影响骨相关细胞的相关文献。 2.7 骨碎补总黄酮及其单体实验用法与临床应用 诸多实验及研究表明,骨碎补总黄酮及其单体的毒副作用很小,但缺乏具体的剂量及用法,因此,该文对前文所论述的实验部分进行总结概括,为骨碎补总黄酮及其单体用于以后的调控骨相关细胞程序性的实验提供参考,详见表2。就实验大鼠而言,药物灌胃剂量在10-400 mg/(kg·d)之间,小鼠灌胃剂量较大鼠减少,在20-100 mg/(kg·d)之间;细胞实验方面,对于成骨细胞、软骨细胞及破骨细胞等而言,骨碎补总黄酮及其单体的剂量大多在100 μmol/L以下,而对于骨肉瘤细胞则需要较大(100,250,500 μmol/L)的药物浓度。在临床试验中,以骨碎补总黄酮提取物为主要成分的强骨胶囊通常用于替代骨碎补总黄酮[67]。骨碎补总黄酮的单体之一柚皮苷具有水溶性差和溶解速率快等缺点,静脉给药时在血流中易降解[68],因此柚"

皮苷的临床应用受到限制,故载药系统是一个具有前景的选择。熊伟等[69]将柚皮苷负载于介孔生物玻璃微球(mesoporous bioactive glasses,MBG)获得载药微球,微球的载药率为(22.4±0.50)%,体外14 d的药物累计释放率达(60.4±0.8)%,对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌率为(56.0±1.7)%,较单体直接给药效果提升明显。柚皮素的载药研究也十分成熟,目前采用的纳米制剂(纳米乳剂、纳米载体、固体脂质纳米颗粒和纳米胶束)可以改善柚皮素的药代动力学特性,提高治疗效果[70]。另外,也有研究者制备出海藻酸钠/壳聚糖-山柰酚微胶囊和木犀草素磷脂复合物牛血清白蛋白纳米粒[71-72],这些载药系统显著提升了中药单体的生物利用度,改善了药物动力学,具有十分广阔的前景,展示了中药单体应用于临床的可能性。"

| [1] WANG S, DENG Z, MA Y, et al. The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders. Int J Biol Sci. 2020; 16(14):2675-2691. [2] TROMPET D, MELIS S, CHAGIN AS, et al. Skeletal stem and progenitor cells in bone development and repair. J Bone Miner Res. 2024;39(6):633-654. [3] LI Y, LING J, JIANG Q. Inflammasomes in Alveolar Bone Loss. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:691013. [4] STEGEN S, CARMELIET G. Metabolic regulation of skeletal cell fate and function. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024;20(7):399-413. [5] SUN Y, PENG ZL. Programmed cell death and cancer. Postgrad Med J. 2009;85(1001): 134-140. [6] 梁松林,成文翔,张鹏,等.成骨细胞程序性死亡的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(3):385-390. [7] CHEN L, YU C, XU W, et al. Dual-Targeted Nanodiscs Revealing the Cross-Talk between Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Macrophages. ACS Nano. 2023;17(3):3153-3167. [8] XIA Y, GE G, XIAO H, et al. REPIN1 regulates iron metabolism and osteoblast apoptosis in osteoporosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(9):631. [9] JIN Y, WU S, ZHANG L, et al. Artesunate inhibits osteoclast differentiation by inducing ferroptosis and prevents iron overload-induced bone loss. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023;132(2):144-153. [10] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1252-1261. [11] 谌顺清,梁伟,张雪妹,等.骨碎补化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2021,46(11):2737-2745. [12] RAVETTI S, GARRO AG, GAITÁN A, et al. Naringin: Nanotechnological Strategies for Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):863. [13] MOTALLEBI M, BHIA M, RAJANI HF, et al. Naringenin: A potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2022;305:120752. [14] YAN Z, ZHAN J, QI W, et al. The Protective Effect of Luteolin in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1195. [15] BANGAR SP, CHAUDHARY V, SHARMA N, et al. Kaempferol: A flavonoid with wider biological activities and its applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(28):9580-9604. [16] LOCKSHIN RA, WILLIAMS CM. PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH--I. cytology of degeneration in the intersegmental muscles of the pernyi silkmoth. j insect physiol. 1965;11:123-133. [17] KERR JF, WYLLIE AH, CURRIE AR. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972;26(4):239-257. [18] HUGHES DE, WRIGHT KR, UY HL, et al. Bisphosphonates promote apoptosis in murine osteoclasts in vitro and in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 1995;10(10):1478-1487. [19] BLANCO FJ, OCHS RL, SCHWARZ H, et al. Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am J Pathol. 1995;146(1):75-85. [20] JILKA RL, WEINSTEIN RS, BELLIDO T. Osteoblast programmed cell death (apoptosis): modulation by growth factors and cytokines. J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(5):793-802. [21] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114. [22] DEGTEREV A, HUANG Z, BOYCE M, et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005; 1(2):112-119. [23] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012; 149(5):1060-1072. [24] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261. [25] BOCK FJ, RILEY JS. When cell death goes wrong: inflammatory outcomes of failed apoptosis and mitotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(2):293-303. [26] Nagata S. Apoptosis and Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018; 36:489-517. [27] RODRÍGUEZ-GONZÁLEZ J, GUTIÉRREZ-KOBEH L. Apoptosis and its pathways as targets for intracellular pathogens to persist in cells. Parasitol Res. 2023;123(1):60. [28] ABOLFATHI H, ARABI M, SHEIKHPOUR M. A literature review of microRNA and gene signaling pathways involved in the apoptosis pathway of lung cancer. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):55. [29] LI W, JIANG WS, SU YR, et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy inhibits osteoblast apoptosis induced by advanced oxidation protein products. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(2):88. [30] LIU CL, HO TL, FANG SY, et al. Ugonin L inhibits osteoclast formation and promotes osteoclast apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;166:115392. [31] DING Y, WANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNA 93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting the TLR4/NF κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):779-790. [32] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147. [33] 申意伟,李雪,张晓峰,等.柚皮苷对酒精诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞氧化应激、自噬、凋亡和成骨成脂分化的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2022,40(5):36-39,263-265. [34] NAN LP, WANG F, RAN D, et al. Naringin alleviates H2O2-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(6):554-567. [35] 张艳杰,顾珊菱,赫子懿,等.治疗骨质疏松的药物对骨折愈合的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(18):4596-4599. [36] 申晓靖,刘海蓉,厉华,等.骨碎补总黄酮对口腔种植骨整合中牙槽骨成骨细胞增殖和凋亡的影响研究[J].口腔医学, 2023,43(8):679-685. [37] 吴泽钰.柚皮苷通过Akt/mTOR通路介导自噬促进牙槽骨成骨的作用及机制研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2023. [38] LV W, YU M, YANG Q, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae ameliorate steroid induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):345. [39] YAN Z, ZHAN J, QI W, et al. The Protective Effect of Luteolin in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1195. [40] PENG Z, ZHANG W, HONG H, et al. Effect of luteolin on oxidative stress and inflammation in the human osteoblast cell line hFOB1.19 in an inflammatory microenvironment. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024;25(1):40. [41] 李风波,孙晓雷,马剑雄,等.柚皮苷对破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(5):450-454. [42] KIM CJ, SHIN SH, KIM BJ, et al. The Effects of Kaempferol-Inhibited Autophagy on Osteoclast Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(1):125. [43] AKARAPHUTIPORN E, SUNAGA T, BWALYA EC, et al. An Insight into the Role of Apoptosis and Autophagy in Nitric Oxide-Induced Articular Chondrocyte Cell Death. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):826S-838S. [44] WANG Y, LI Z, WANG B, et alJ. Naringenin attenuates inflammation and apoptosis of osteoarthritic chondrocytes via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. PeerJ. 2023;11: e16307. [45] WANG J, JING X, LIU X, et al. Naringin safeguards vertebral endplate chondrocytes from apoptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through SIRT3-mediated mitophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024; 140:112801. [46] 丘志河,谢卫勇,黄刚,等.山奈酚通过调控miR-21/SOX9对骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J].中国药师,2022, 25(12):2073-2078. [47] 米倚林,易南星,许晓彤,等.山奈酚抑制软骨凋亡延缓小鼠膝骨关节炎的实验研究[J].海南医学院学报,2022,28(17): 1299-1306. [48] CHEN GY, LIU XY, YAN XE, et al. Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Treat Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Arachidonic Acid Metabolites Through AMPK/NFκB Pathway. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:4123-4140. [49] 兰双笠,向飞帆,邓光慧,等.柚皮苷抑制骨质疏松大鼠骨组织的铁沉积及细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(5): 888-898. [50] LEE CW, HUANG CC, CHI MC, et al. Naringenin Induces ROS-Mediated ER Stress, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Molecules. 2022; 27(2):373. [51] LIU S, YAO S, YANG H, et al. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(10):648. [52] TROJANI MC, SANTUCCI-DARMANIN S, BREUIL V, et al. Autophagy and bone diseases. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(3): 105301. [53] LIU Y, ZHAO L, HE X, et al. Jintiange proteins promote osteogenesis and inhibit apoptosis of osteoblasts by enhancing autophagy via PI3K/AKT and ER stress pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;311:116399. [54] GE X, ZHOU G. Protective effects of naringin on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2021; 13(6):6330-6341. [55] LI Y, DING Z, LIU F, et al. Luteolin regulating synthesis and catabolism of osteoarthritis chondrocytes via activating autophagy. Heliyon. 2024;10(11):e31028. [56] HUANG Y, XU W, ZHOU R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(9):2114-2127. [57] LI Z, LI D, CHEN R, et al. Cell death regulation: A new way for natural products to treat osteoporosis. Pharmacol Res. 2023; 187:106635. [58] CAO S, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Naringenin can Inhibit the Pyroptosis of Osteoblasts by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Alleviate the Differentiation Disorder of Osteoblasts Caused by Microgravity. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(46):25586-25600. [59] CHAI S, YANG Y, WEI L, et al. Luteolin rescues postmenopausal osteoporosis elicited by OVX through alleviating osteoblast pyroptosis via activating PI3K-AKT signaling. Phytomedicine. 2024;128:155516. [60] XIONG L, BIN ZHOU, YOUNG JL, et al. Exposure to low-dose cadmium induces testicular ferroptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;234:113373. [61] SEIBT TM, PRONETH B, CONRAD M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133: 144-152. [62] PAN Z, HE Q, ZENG J, et al. Naringenin protects against iron overload-induced osteoarthritis by suppressing oxidative stress. Phytomedicine. 2022;105:154330. [63] ZHAO J, GUO S, SCHRODI SJ, et al. Cuproptosis and cuproptosis-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis: Implication, prospects, and perspectives. Front Immunol. 2022;13:930278. [64] 王伟伟,欧志学,周毅,等.铜死亡基因在骨关节炎免疫浸润中的生物信息学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(11):1669-1676. [65] TIAN Q, QIN B, GU Y, et al. ROS-Mediated Necroptosis Is Involved in Iron Overload-Induced Osteoblastic Cell Death. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1295382. [66] 冉栋成,王槐骏,杨城,等.坏死性凋亡与骨质疏松症机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(5):745-750. [67] 余翔,黄志强,张鹏,等.骨碎补总黄酮干预骨质疏松性骨折愈合临床疗效机制研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2025,31(1):149-156. [68] RAVETTI S, Garro AG, Gaitán A, et al. Naringin: Nanotechnological Strategies for Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):863. [69] 熊伟,袁灵梅,王梁霞,等.黄连素-柚皮苷双重载药复合微球的制备及其抗菌-成骨性能评估研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(12):1505-1513. [70] MEHRANFARD N, GHASEMI M, RAJABIAN A, et al. Protective potential of naringenin and its nanoformulations in redox mechanisms of injury and disease. Heliyon. 2023;9(12):e22820. [71] 曲扬,刘振红.复合凝聚法制备山奈酚微胶囊及对剧烈运动所致氧化应激损伤保护作用[J].食品科技,2025,50(1):275-283. [72] 田莉,李伟宏,张付利.木犀草素磷脂复合物白蛋白纳米粒的制备及口服药动学评价[J].中草药,2024,55(10):3280-3290. |
| [1] | Chai Jinlian, Sun Tiefeng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Li Guangzheng, Zhou Zhongqi, Liang Xuezhen, Wang Ping. Therapeutic effect of Cornus Cervi Colla on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat models: fecal metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6187-6197. |
| [2] | Liu Ruojing, Zhao Xue, Zhu Yizhen, Fu Lingling, Zhu Junde. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in mice by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6219-6227. |
| [3] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [4] | Zhou Guanjin, Li Yanan, Li Tao. Neferine inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5624-5629. |
| [5] | Liu Ying, Liu Yalei, Liu Yu. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in adriamycin-induced myocardial injury antagonized with daisy leaf gentianone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4121-4128. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||