Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 5943-5953.doi: 10.12307/2026.320
Previous Articles Next Articles
Traditional Chinese sports in the treatment of osteoporosis: potential biological mechanisms and clinical application progress
Du Xingbin1, Jiang Fugao2, Kong Jianda2
- 1General Education College of Shandong Huayu Institute of Technology, Dezhou 253034, Shandong Province, China; 2College of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 273165, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-27Accepted:2025-05-19Online:2026-08-18Published:2025-12-30 -
Contact:Kong Jianda, College of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 273165, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Du Xingbin, PhD candidate, Professor, General Education College of Shandong Huayu Institute of Technology, Dezhou 253034, Shandong Province, China Corresponding author: Du Xingbin, General Education College of Shandong Huayu Institute of Technology, Dezhou 253034, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Social Science Planning and Research Project in Shandong Province, No. 24CLYJ19 (to DXB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Du Xingbin, Jiang Fugao, Kong Jianda. Traditional Chinese sports in the treatment of osteoporosis: potential biological mechanisms and clinical application progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 5943-5953.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1 骨质疏松的病理机制 骨质疏松在老年人中的患病率极高[4-5],骨质疏松的发生与骨代谢紊乱存在密切联系,这主要是因为破骨细胞活性过高及成骨细胞功能缺失导致。骨组织通过成骨细胞、破骨细胞及骨细胞之间的精准信号调控以确保其动态平衡[6]。肠道菌群在骨代谢中的作用日益受到关注,特别是肠道菌群及其代谢产物(如短链脂肪酸以及硫化氢等)通过与免疫系统的相互作用能够对骨重塑产生重要影响,以调控骨密度及骨质量[7],虽然该机制是核心潜在机制,然而肠道菌群准确调控骨代谢的分子机制尚不清楚。另外,骨代谢与免疫系统的相关性也不可忽略,例如,在类风湿性关节炎等疾病中,辅助性T细胞17介导免疫反应的异常激活能够促使核因子κB受体活化因子配体依赖的破骨细胞产生,进而加速骨质流失[8],这说明免疫系统在骨质疏松的发病和进展机制中可能起关键作用。 除了上述病理表现,骨质疏松的另一个重要特征是骨吸收与骨形成不协调,从而造成骨密度降低以及骨小梁减少,进而产生骨折风险,其中破骨细胞过度活化和成骨细胞功能丧失是至关重要的过程。近年来,人们对肠道菌群、自噬、铁代谢平衡和细胞衰老等新的机制参与骨质疏松发生发展也有了更深入了解[9-10],这提升了骨质疏松机制研究的深度与广度,为探寻新型防治靶点开辟了创新路径;此外,雌激素分泌降低是骨质疏松发生的主要因素,尤其是绝经后女性雌激素的分泌减少造成骨代谢更加旺盛,骨吸收多于骨形成,因此造成骨质疏松[11]。但是骨质疏松的发生并不单单是由激素水平降低造成的,氧化应激、炎症反应、表观遗传等在骨代谢紊乱中也起到了关键作用[12],这些因素通过多途径协同作用:诱导破骨细胞增殖分化、增强破骨细胞活性,同时抑制成骨细胞功能,最终加速骨质疏松的进展。因此,通过维持骨代谢平衡、抑制破骨细胞过度生成及促进成骨细胞功能是防治骨质疏松的关键靶点。 骨质疏松的发生受到多方面因素的作用,包括遗传、生物学、激素水平以及生活方式等。其中,遗传易感性在骨质疏松预防中起到关键作用,特别是在来自有遗传倾向的家族个体中,特定基因的表达变化与变异情况可能显著影响疾病的发生发展[13]。另外,营养失衡、缺乏运动、吸烟及过度饮酒等生活方式均会对骨密度和骨质量产生显著影响,特别是中等到重度水平酒精摄入对骨健康的长期影响[14]。2型糖尿病和心血管疾病等慢性疾病对骨健康亦有不良影响。其中在长期的糖尿病患者中,特别是年龄较大、骨密度较低的患者,骨质疏松发生风险显著增加[15]。因此,针对该类易感因素,需进行早期筛查及干预,这对于骨质疏松的防治具有重要作用。 2.2 中国传统运动改善骨质疏松的潜在生物学机制 2.2.1 运动对骨代谢的效应机制 运动在骨代谢中发挥着关键作用,它的作用源于多种因素,其中机械负荷作为直接且基础性的因素,需对其作用于骨代谢的机制进行全面探究。运动对骨代谢的效应机制见图3。 机械负荷对骨代谢的效果:骨骼对运动中的机械负荷表现出高敏感性。在经受不同强度的运动时,骨组织的应力及应变会对骨细胞产生直接作用,刺激骨骼的重塑过程[16]。研究发现,进行有氧或抗阻训练(如跑步、举重等)能够显著增强骨密度及骨强度,特别是对下肢骨骼的作用尤其显著。运动负荷增加能够促使骨组织矿物质沉积,亦能够激活成骨细胞的合成,促进骨基质形成[17]。彭伟等[18]研究表明,骨骼系统对机械力信号(应力)的应变是骨骼适应性的核心因素,该类生物力学适应性对于骨密度的增加起着重要作用。CHOW等[19]研究也表明,运动负荷的增加能够显著促使骨量增加及骨结构的改善,特别是对下肢骨骼的效果尤为显著。运动负荷对破骨细胞的活性呈现出调控效应。适度的运动能通过增强骨折修复过程中的骨重建速度、降低过度骨吸收,具体来说,在运动过程中,骨髓中的前体细胞受到信号介导逐步分化为成骨细胞,进而促使骨生成[20]。研究发现,运动能够通过促进成骨细胞及破骨细胞的成长发育和活性来调控骨转换,亦能够调控骨重建进程,进而加快骨折修复速度[21]。骨骼中的成骨细胞及破骨细胞通过相互效应在骨生成及骨吸收之间保持稳态,使得骨骼能够伴随机体的成长与运动自我重塑,并具备修复功能[22]。 运动导致的骨细胞活性变化:骨细胞的活性是骨代谢的核心机制,运动通过直接调节成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞的活性来控制骨重塑过程。研究发现骨细胞通过分泌因子调控骨的稳态,从而影响其他器官的功能[22]。成骨细胞在机械负荷刺激下增殖、分化、合成骨基质,进而促使骨生成;而破骨细胞主要作用为骨吸收功能,它与成骨细胞的动态平衡直接决定骨代谢的健康状态[23]。然而,不同类型运动对骨细胞的效果亦呈现出差异,例如,高强度抗阻训练能够显著促使成骨细胞增生及功能呈现[19],有氧运动能够通过增强血液循环改善骨骼的营养供应,亦间接促进骨代谢过程[19]。另外,运动中的周期循环与负荷强度会对成骨细胞和破骨细胞的比例产生不同影响,主要表现为优化二者平衡、促进骨长期维持健康状态。 运动与激素水平的调控:研究表明,运动不仅能够促进骨形成,还能通过激活骨髓脂肪储存、维持骨基质合成,增强免疫系统功能,这说明了骨髓脂肪的效应,特别是在能量储存与淋巴细胞生成方面的核心效应,进一步印证了运动对骨代谢及免疫力提升的潜在意义[24-25],尤其为免疫相关性骨质疏松研究提供了新思路。另外,运动能够显著影响与骨代谢相关激素(如生长激素、胰岛素样生长因子1、雌激素以及睾酮等)的分泌,该类激素在促使骨生成以及维持骨密度中起到了关键作用,特别是在女性中,运动能够通过提升体内雌激素水平来缓解骨密度的下降[26]。男性睾酮水平对骨健康发挥着重要作用,睾酮能够维持骨密度并提升骨强度,而高强度规律性的运动能显著增强睾酮的分泌,进而提升骨密度和骨强度[27]。在绝经期女性群体中,由于雌激素水平自然下降,运动对骨骼健康的重要性更为凸显,其中规律运动可显著降低骨质疏松的发生风险,尤其在该群体中效果显著,能够通过调节激素水平增强骨强度[28]。 2.2.2 中国传统运动改善骨质疏松潜在生物学机制的研究进展 中国传统运动改善骨质疏松的生物学机制具有多层面性,并且各层面间密切相关。从提升骨密度及骨质的基础层面来看,中国传统运动能够通过机械负荷及内分泌调控等机制来改善骨质疏松。中国传统运动改善骨质疏松的生物学机制见图4。"
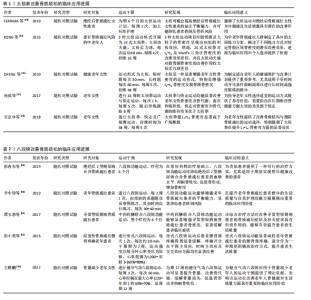
(1)提升骨密度以及骨质:中国传统运动在增强骨质疏松患者骨密度与骨质质量方面表现出多方面的生物学效应。通过刺激骨组织、调节骨代谢,运动能够有效提升骨密度、减缓骨质流失,显著促进了骨骼健康[5]。这类正向作用的关键在于对骨组织施加机械负荷,这一过程对提升骨密度极为重要。同时,通过调节雌激素、鸢尾素等内分泌系统的激素分泌,运动能够有效调控骨代谢,从而提高骨质、增加骨密度并减少骨质流失[29]。 中国传统运动对骨质疏松患者腰椎、股骨颈骨密度具有一定的改善作用。YAN等[30]的Meta分析表明,体疗可显著提升骨密度,证实传统体育运动疗法在预防骨质疏松方面具有积极作用与潜在应用价值。ZHANG等[31]研究发现,太极拳、八段锦等中国传统身心运动可显著提高腰椎、股骨颈骨密度,而抗阻运动则能有效增强髋部总骨密度。中国传统运动在促进骨质疏松患者骨健康方面的成效显著,不过具体效果或因运动种类与骨密度测量部位的差异而有所不同。另外,KONG等[32]分析24式太极拳、太极功夫扇及太极柔力球等各种太极拳形式对不同部位骨密度的影响,发现该类运动形式每周练习4次、持续18周可改善机体各部位骨密度,表明太极拳运动对骨质疏松高危个体具有适应性和显著效果[32]。中国传统运动的效果可能会根据运动类型及骨密度检测部位而改变,但总体而言,中国传统运动在骨质疏松防治中的作用已得到广泛认可。 (2)促使骨代谢平衡:太极拳及气功等中国传统运动能够平衡骨代谢,表明了中国传统运动改善骨健康的独特效果,然而,目前尚不明确这类传统运动的具体作用生物机制,仅有部分研究对相关机制进行了间接阐释。现有研究表明,特定传统运动方式的干预可显著调节肠道菌群发挥抗炎作用,平衡免疫应答,并通过雌激素等途径影响骨量[33],说明了肠-骨轴在骨质疏松防治中的核心作用。 除此之外,中国传统运动亦能够调控相关骨代谢标志物,如骨钙蛋白、N末端前骨胶原肽、血磷、碱性磷酸酶、血钙以及酸性磷酸酶等,特别是物理运动可能通过作用于骨代谢相关标志物有效提高腰椎和股骨颈骨密度,显著证实了运动对原发性骨质疏松的治疗作用[30]。另外,还有研究揭示了身心结合运动方式提升整体髋关节骨密度的潜在机制与作用[31],表明身心运动能够针对性地改善骨健康。KONG等[32]的Meta分析显示,中国传统运动在调节骨代谢和防治骨质疏松方面效果显著,进一步凸显了整体运动干预对骨健康的重要意义。 (3)改善血液循环以及内分泌功能:太极拳、八段锦、易筋经以及五禽戏等中国传统运动方式,因在促进血液循环和调节内分泌功能方面的重要作用而备受关注。LI等[33]开展的关于中国传统运动对心血管疾病影响的系统评价与 Meta 分析证实了这一点,该研究着重指出此类运动在改善血压、血脂水平等心血管健康指标方面具有积极作用。这些指标的改善不仅有益于心血管系统,还能间接促进骨骼健康,这对于营养物质的输送以及废物的排出具有重要作用。 研究发现八段锦等中国传统运动可改善血脂谱,能够通过调控总胆固醇、三酰甘油和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇等内分泌因素以及提升高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平调节信号通路,间接促进骨健康[34],表明中国传统运动对血脂谱的改善或许通过作用于参与骨代谢的内分泌因素与信号通路,进而间接影响骨骼健康。然而,该类机制的具体效应尚未完全明确。已有研究证实,包括中国传统运动在内的传统中医在促使骨再生以及治疗骨质疏松方面具有显著效果,尤其是通过刺激自然修复过程以及调控生化通路以增强骨的再生能力[35],表明中国传统运动以及传统中医能够直接促进受损组织修复及骨愈合,在防治骨折、骨质疏松及类风湿性关节炎等肌肉骨骼疾病方面展现出显著效果与长期有效性。然而,该类中国传统运动干预方式在促进骨健康方面的具体生物学机制依然是一个待研究的领域,因此,未来的研究应着重探讨该类运动如何通过改善血液循环及内分泌功能来具体发挥防治作用的。NIKANDER等[36]认为将中国传统运动纳入日常活动可成为一种高成本效益比、获取便捷的提升骨健康方式,进一步强调了中国传统运动在提升生活质量及预防疾病方面的重要作用,不仅体现在改善血液循环和内分泌功能方面,还体现在对心血管健康以及代谢调控中的积极影响[36]。 综上所述,太极拳、八段锦、易筋经以及五禽戏等中国传统运动方式能显著促进心血管健康、提升骨骼健康水平,该类运动可能通过改善血液循环、调控内分泌功能、影响内分泌因素及信号通路间接促进骨健康。中医以及中国传统运动在促使骨再生、治疗骨质疏松以及防治肌肉骨骼疾病方面均展现出显著效果与长期有效性。 (4)抗炎以及抗氧化效应:太极拳、八段锦以及气功等中国传统运动在抗炎和抗氧化方面的突出功效备受关注,这两种效应是改善骨健康及减轻骨质疏松影响的重要生物学机制。一项研究发现,该类运动方式能够显著降低体内炎症水平及氧化应激程度,而这2个因素与骨密度降低及骨质疏松导致的骨骼脆性增加密切相关[37]。这说明中国传统运动能够通过降低促炎细胞因子的分泌进而抑制破骨细胞的活性及骨吸收,该抗炎效果对于维持骨密度和骨健康具有重要作用。 中国传统运动通过中和活性氧发挥抗氧化作用,而活性氧与骨密度下降密切相关。研究发现,中国传统运动可通过抑制骨细胞的氧化损伤维持骨结构和功能的稳定[37]。亦有研究探究了太极拳及八段锦等中国传统运动对免疫系统及炎症反应的影响。OH等[38]的一项Meta分析表明,太极拳及气功等中国传统运动可显著提升免疫细胞水平,但在降低炎症水平方面的效果并不显著。太极拳对于增强老年人免疫功能亦有正向作用,相较于非练习者,太极拳练习者在免疫功能上获益显著,因太极拳练习能促进辅助性T细胞1的免疫反应,这与中年及老年妇女的免疫调控、自然杀伤细胞和树突细胞的协同作用紧密相关[39-40];此外,太极拳练习与改善功能移动性、增强CD4CD25调控性T细胞数量、降低炎症水平密切相关[39],而辅助性T细胞1、自然杀伤细胞、树突细胞以及CD4CD25调控性T细胞等方面的免疫反应与骨骼健康紧密相关[41]。因此,这或许有助于提升老年人的免疫功能以及整体健康状态,进而改善骨质疏松症状。 2.3 中国传统运动改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展 2.3.1 太极拳改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展 太极拳作为源于中国传统文化的运动方式,因具备显著防治骨质疏松的潜在功效备受关注。研究发现太极拳提升人体骨密度的水平有限,当骨密度达到一定水平后,即便持续运动后骨密度也不再增加,但可减缓骨质流失速度[5,42]。目前的研究表明,太极拳在提升骨密度、减轻骨质疏松相关疼痛以及改善患者总体生活质量等方面效果显著。一项Meta分析研究指出,在治疗骨质减退症及原发性骨质疏松时,太极拳在增强骨密度及减轻相关骨折风险上具有潜在作用[43]。可见太极拳在骨质疏松辅助性治疗中发挥核心作用,坚持练习太极拳能显著维持骨健康、降低骨折发生风险。 太极拳在提升骨密度及降低骨折风险方面具有积极作用,但其临床获益程度尚未完全明确。LEE等[44]的系统评价进一步证实了太极拳干预骨质疏松的优势,发现太极拳能够有效提升绝经后妇女骨密度。太极拳不仅对骨密度有积极作用,在改善平衡能力、降低跌倒风险方面也颇具优势,对预防骨质疏松相关骨折具有重要意义。太极拳对慢性疼痛、骨质疏松等方面的安全性及适用性亦在研究中得到验证。 关于太极拳改善骨质疏松患者骨密度的临床证据已有诸多报道。有研究发现,绝经后骨质疏松妇女进行6个月的太极拳训练后站立平衡功能得以改善[45]。尽管现有研究为太极拳治疗骨质疏松提供了有力依据,但仍需更高质量的研究深入探究其作用机制,特别是对比不同类型太极拳练习模式(如24式太极拳、太极功夫扇与太极柔力球等)在改善骨密度方面的差异。孔健达[3]研究表明,24式太极拳、太极功夫扇和太极柔力球均能提升骨密度,并且经过8周练习后24式太极拳对腰椎和Ward’s三角区骨密度表现出更大的改善,对存在骨质疏松风险的中老年人尤为有益。CHENG等[46]比较了以相同频率运动时间不同的太极拳运动对老年女性骨密度的影响,结果显示以每次30 min或60 min、每周5次、训练48周的太极拳运动能改善老年女性L2-L4骨密度和股骨颈骨密度,而不会改善股骨大转子和Ward’s三角区骨密度,太极拳对骨密度的改善效果并不会因运动时间延长而增强,表明不同太极拳运动模式对提高不同人群骨密度的效果存在差异。鉴于此,未来的研究需探究太极拳对不同人群(包括年龄、性别等因素)的影响,探寻最佳练习方式,并明确太极拳防治骨质疏松的作用机制。 有研究着重探讨了太极拳相较于其他运动方式所具备的显著潜在优势。其中一项研究发现,太极及快步走运动均能显著改善老年女性的骨密度以及骨代谢,但是在停止运动后太极拳对骨密度的改善效果不及快步走[47],说明如果选择太极拳作为增强骨密度的运动方式,需要坚持运动。宋京林等[48]对比了太极拳、快步走及广场舞运动48周后对老年女性的骨密度的效果,发现太极拳和广场舞对L2-L4骨密度的改善效果均优于快步走,说明太极拳和广场舞在长期改善骨密度方面具有优势,但该结果仅限于老年女性,目前尚不清楚是否同样适合老年男性与其他骨质疏松及其并发症患者。 综上,太极拳既能够增强骨密度、减轻骨量流失、降低骨折的风险,又能改善平衡功能、减少跌倒及骨折风险,还对减轻慢性疼痛和长期改善骨密度具有积极作用。然而,太极拳对增加人体骨密度的程度较为有限,并且不同模式太极运动在改善骨密度方面存在差异,因此,亟需深入探究太极拳对不同人群影响的核心作用。太极拳改善骨质疏的临床应用进展见表1。 2.3.2 八段锦改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展 八段锦作为中国传统气功运动,在临床应用于骨质疏松患者中已逐步展现出独特的治疗效果[5]。研究发现,对于绝经后2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松患者,在常规药物治疗的同时辅以八段锦功能性运动,既能显著降低血糖水平又能抑制骨吸收,促进骨形成,显著增加骨密度[49],这说明八段锦对改善骨代谢指标具有积极作用。不过,八段锦的具体作用机制尚未完全明确,因此后续研究应着重深入探讨其八段锦的作用机制。李中锋等[50]研究表明,八段锦能够增强老年骨质疏松患者的平衡能力,从而显著降低患者的跌倒风险,这一发现对于容易因跌倒导致骨折等严重后果的老年人群具有重要意义。 另一方面,中药药膳与八段锦功能运动相结合既能显著增强寻常型银屑病骨质疏松患者的骨密度,又能够显著缓解患者的临床症状,表明八段锦在综合治疗中的潜在意义[51]。另外,坐式八段锦运动在减轻老年骨质疏松患者腰背部疼痛方面也表现出显著效果[52],为运动功能受限的患者提供了一种切实可行的治疗方法。一项为期12周的研究探讨了八段锦气功对老年人骨密度、骨代谢及生活质量的影响,结果表明,八段锦可显著提升骨密度和代谢指标,显著缓解骨质流失,促进骨组织形成,明显改善参与者的生活质量[53],进一步证实了八段锦在提高生活质量方面的潜在作用。 综上所述,八段锦作为中国传统气功运动,在骨质疏松的治疗与预防中表现出广泛的应用价值,然而它的作用机制及更广泛的应用前景仍需进一步研究与验证。因此,后续研究应着重聚焦八段锦在骨质疏松及相关并发症治疗中的作用,同时探索如何优化其练习方式以满足不同患者群体的需求。八段锦改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展见表2。"
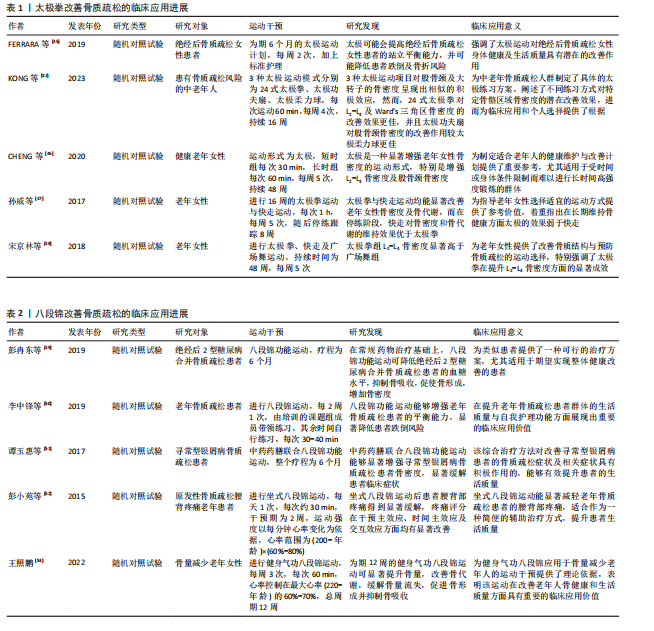
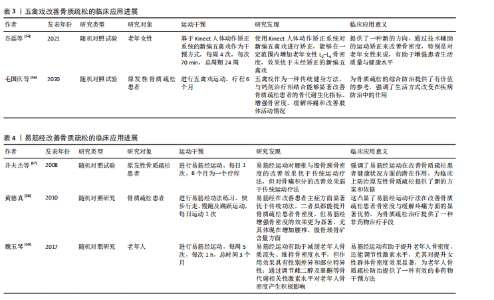
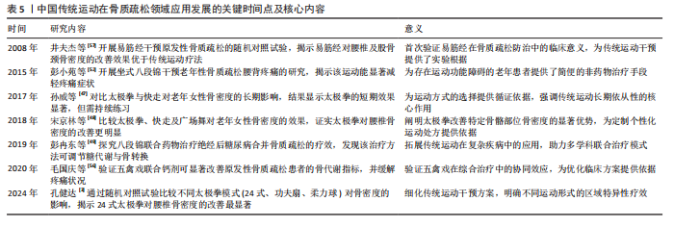
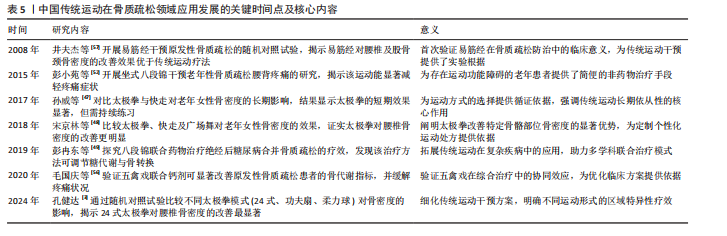
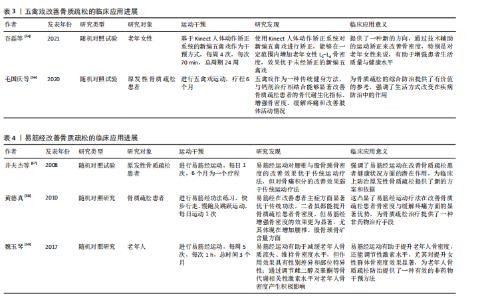
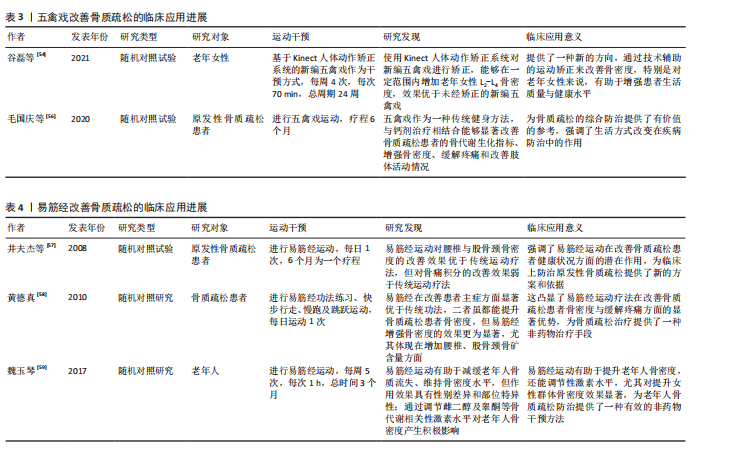
2.3.3 五禽戏改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展 五禽戏是中国传统的古老运动形式,通过模仿5种动物的动作来锻炼身体,并且随着研究的不断深入,五禽戏对提升健康状况,尤其是改善老年人骨质疏松与虚弱状态有着积极作用[5]。然而,这项运动对骨质疏松的直接效应仍未被充分记录,表明尽管五禽戏存在积极作用,但具体作用机制与确切疗效仍需进一步研究。 Kinect人体动作矫正系统的应用在一定范围内验证了五禽戏对特定骨骼健康指标改善的有效性。借助该系统矫正新编五禽戏,可显著提升老年女性L2-L4骨密度,并且效果优于未矫正练习,但对其他部位骨密度的改善并不明显[54],说明五禽戏在改善骨骼健康方面可能存在局限性。因此,未来研究应该重点关注如何增强五禽戏对全身骨骼健康的促进作用。CHENG等[55]开展的网状Meta分析指出,尽管五禽戏不能作为单独的预防手段,但将它融入临床治疗和日常体育活动中或许可成为降低老年人尤其是骨质疏松患者跌倒骨折风险的有效方案。研究表明,五禽戏能够优化骨质疏松患者骨代谢生化指标,增强骨密度,缓解疼痛并改善肢体活动状况,对骨质疏松具有良好的治疗效果[56]。关于五禽戏的具体作用机制是未来研究的重点方向。 总的来说,五禽戏作为一种整体疗法在骨质疏松治疗中表现出潜在价值。通过改善骨关节功能、增强体质及提高平衡能力,五禽戏或许能间接助力预防骨质疏松骨折,尽管目前直接证据有限,但五禽戏在骨质疏松治疗与预防中的潜作用值得深入研究,尤其是如何优化其运动形式并结合其他疗法以提升效果,是未来科研与临床实践的重点方向。五禽戏改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展见表3。 2.3.4 易筋经改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展 易筋经作为中国传统的身心运动方式,在改善骨质疏松方面的潜在积极作用正逐渐获得关注[5]。ZHANG等[31]开展的系统评价与网状Meta分析对比了不同运动干预对骨质疏松及骨量减少患者的疗效,结果显示,综合运动、抗阻训练、有氧运动以及易筋经等身心运动均能显著提升患者腰椎骨密度,特别是身心运动在提升股骨颈与腰椎骨密度方面的效果尤为突出,表明易筋经在提升骨质疏松患者骨密度方面的积极作用。井夫杰等[57]研究表明,易筋经可以作为防治原发性骨质疏松的有效方法,并且防治效果优于传统运动疗法,说明易筋经在临床应用中的潜在价值。黄德真[58]的研究同样佐证了这一观点,相较于常规运动方式,易筋经通过特定的练习方法能更显著提升骨质疏松患者骨密度,尤其在增加腰椎和股骨颈骨碳含量方面的效果更为显著。 魏玉琴[59]研究发现,易筋经练习不仅能显著降低骨质疏松诱发的骨折风险,还可通过增加骨血流量、促进骨形成及维持血液pH值稳定促进骨形成,能缓解老年人骨密度的流失,对骨密度的改善具有性别差异与部位特异性;可调节骨代谢相关激素水平,提高雌二醇以及睾酮含量,降低促卵泡激素与黄体产生素水平,增加女性群体骨密度。 因此,易筋经作为一种安全有效的运动方式,不仅能有效提升骨质疏松患者骨密度,还有助于降低骨折风险,改善老年人身体状况。然而,易筋经的具体作用机制与最佳练习方式仍需深入探究。因此,后续研究应围绕易筋经的练习方式、频率及对不同类型骨质疏松患者的影响展开,从而为临床应用提供更科学的指导。易筋经改善骨质疏松的临床应用进展见表4。 中国传统运动在骨质疏松领域应用发展的关键时间点及核心内容,见表5。"
| [1] SALARI N, DARVISHI N, BARTINA Y, et al. Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):669. [2] Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: the 2021 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2021; 28(9):973-997. [3] 孔健达.太极锻炼防治中老年人骨质疏松的元分析和实验研究[D].曲阜:曲阜师范大学,2024. [4] 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心,中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查报告[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2021. [5] 刘静,吴文忠,徐道明,等.传统功法治疗原发性骨质疏松症临床研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(12):1817-1820. [6] 任明诗,丁羽,李子涵,等.成骨细胞与破骨细胞相互调节作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):822-827. [7] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11): 696-711. [8] LYU Z, HU Y, GUO Y, et al. Modulation of bone remodeling by the gut microbiota: a new therapy for osteoporosis. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):31. [9] MAEDA K, YOSHIDA K, NISHIZAWA T, et al. Inflammation and Bone Metabolism in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Molecular Mechanisms of Joint Destruction and Pharmacological Treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2871. [10] THAPA S, NANDY A, RENDINA-RUEDY E. Endocrinal metabolic regulation on the skeletal system in post-menopausal women. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1052429. [11] LIANG B, BURLEY G, LIN S, et al. Osteoporosis pathogenesis and treatment: existing and emerging avenues. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27(1):72. [12] ZHIVODERNIKOV IV, KIRICHENKO TV, MARKINA YV, et al. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(21):15772. [13] SONG S, GUO Y, YANG Y, et al. Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2022; 237:108168. [14] POURESMAEILI F, KAMALIDEHGHAN B, KAMAREHEI M, et al. A comprehensive overview on osteoporosis and its risk factors. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14:2029-2049. [15] SAMPSON HW. Alcohol and other factors affecting osteoporosis risk in women. Alcohol Res Health. 2002;26(4):292-298. [16] SHIN B, KUPFERMAN J, SCHMIDT E, et al. Rac1 Inhibition Via Srgap2 Restrains Inflammatory Osteoclastogenesis and Limits the Clastokine, SLIT3. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(4):789-800. [17] ISHIKAWA S, KIM Y, KANG M, et al. Effects of weight-bearing exercise on bone health in girls: a meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2013; 43(9):875-892. [18] 彭伟,廖春晖,钟小龙,等.雌激素与机械张应力对骨重建相关因子的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(7):1141-1145. [19] CHOW KVC, O’LEARY C, PAXTON-HALL F, et al. Pembrolizumab-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis: case report. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2022;2022(3): omac025. [20] SHEN B, TASDOGAN A, UBELLACKER JM, et al. A mechanosensitive peri-arteriolar niche for osteogenesis and lymphopoiesis. Nature. 2021;591(7850):438-444. [21] 张玲莉,陈炳霖,邹军.运动影响骨转换:促进或抑制骨细胞/破骨细胞的发育和活性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(42):6838-6843. [22] HAN Y, YOU X, XING W, et al. Paracrine and endocrine actions of bone-the functions of secretory proteins from osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Bone Res. 2018;6:16. [23] SCHEINER S, PIVONKA P, HELLMICH C, et al. Mechanobiological regulation of bone remodeling--Theoretical development of a coupled systems biology-micromechanical approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1201.2488, 2012. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1201.2488v1 [24] 明霞,卞丽艳.运动对骨骼健康的益处[J].百科知识,2025(3):44-45. [25] PENG H, HU B, XIE LQ, et al. A mechanosensitive lipolytic factor in the bone marrow promotes osteogenesis and lymphopoiesis. Cell Metab. 2022;34(8): 1168-1182.e6. [26] 翁凯鸿,何玉婷,毛钰蘅,等.衰老相关分泌表型调控骨组织细胞功能的研究进展[J].生命科学,2024,36(12):1503-1513. [27] SHIGEHARA K, IZUMI K, KADONO Y, et al. Testosterone and Bone Health in Men: A Narrative Review. J Clin Med. 2021; 10(3):530. [28] CHANG CF, LEE JI, HUANG SP, et al. Regular Exercise Decreases the Risk of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women. Front Public Health. 2022;10: 897363. [29] SUN W, ZHANG XA, WANG Z. The role and regulation mechanism of Chinese traditional fitness exercises on the bone and cartilage tissue in patients with osteoporosis: A narrative review. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1071005. [30] YAN Y, TAN B, FU F, et al. Exercise vs Conventional Treatment for Treatment of Primary Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(5): 1474-1487. [31] ZHANG S, HUANG X, ZHAO X, et al. Effect of exercise on bone mineral density among patients with osteoporosis and osteopenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Clin Nurs. 2022;31(15-16):2100-2111. [32] KONG J, TIAN C, ZHU L. Effect of different types of Tai Chi exercise programs on the rate of change in bone mineral density in middle-aged adults at risk of osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):949. [33] LI K, JIANG Y, WANG N, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine in Osteoporosis Intervention and the Related Regulatory Mechanism of Gut Microbiome. Am J Chin Med. 2023;51(8):1957-1981. [34] MEI L, CHEN Q, GE L, et al. Systematic review of chinese traditional exercise baduanjin modulating the blood lipid metabolism. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:282131. [35] PENG Z, XU R, YOU Q. Role of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Bone Regeneration and Osteoporosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:911326. [36] NIKANDER R, SIEVÄNEN H, HEINONEN A, et al. Targeted exercise against osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis for optimising bone strength throughout life. BMC Med. 2010;8:47. [37] LI Q, TIAN C, LIU X, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant traditional Chinese Medicine in treatment and prevention of osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14:1203767. [38] OH B, BAE K, LAMOURY G, et al. The Effects of Tai Chi and Qigong on Immune Responses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicines (Basel). 2020; 7(7):39. [39] YEH SH, CHUANG H, LIN LW, et al. Regular tai chi chuan exercise enhances functional mobility and CD4CD25 regulatory T cells. Br J Sports Med. 2006;40(3):239-243. [40] SU Z, ZHAO J. Comparative Study of the Effects of Tai Chi and Square Dance on Immune Function, Physical Health, and Life Satisfaction in Urban Empty-Nest Older Adults. Front Physiol. 2021;12:721758. [41] WANG H, FANG K, YAN W, et al. T-Cell Immune Imbalance in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Associated with Alterations in NK Cells and NK-Like T Cells Expressing CD38. J Innate Immun. 2022;14(2):148-166. [42] 李文龙,范铜钢.太极拳改善骨质疏松研究进展[J].中医药导报,2020,26(14):105-110. [43] ZHANG Y, CHAI Y, PAN X, et al. Tai chi for treating osteopenia and primary osteoporosis: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:91-104. [44] LEE MS, PITTLER MH, SHIN BC, et al. Tai chi for osteoporosis: a systematic review. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(2):139-146. [45] FERRARA PE, SALINI S, MAGGI L, et al. Evaluation of quality of life and static balance in postmenopausal osteoporosis women after Tai Chi Chuan practice: an observational randomized case control study. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019; 33(2 Suppl. 1):163-169. [46] CHENG L, BA H. Effect of Tai Chi exercise with the same frequency and different exercise duration on the bone mineral density of older women. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020;60(10):1396-1400. [47] 孙威,王疆娜,杨春荣,等.太极拳和快走练习对老年女性骨密度和骨代谢影响的跟踪研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017,23(8):1034-1040. [48] 宋京林,程亮,常书婉.48周太极拳、快走和广场舞运动对老年女性骨密度的影响[J].山东体育学院学报,2018,34(6): 105-108. [49] 彭冉东,邓强,李中锋,等.八段锦对绝经后2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松症患者糖、骨代谢指标的影响[J].中医药导报,2019, 25(23):53-56. [50] 李中锋,邓强,张彦军,等.八段锦改善老年骨质疏松患者平衡能力及跌倒风险的疗效观察[J].西部中医药,2019,32(9):62-65. [51] 谭玉惠,阚丽君,李丽楠,等.中药药膳联合八段锦改善寻常型银屑病骨质疏松症状的临床观察[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017,23(1):107-111. [52] 彭小苑,李巧萍,黎小霞.坐式八段锦锻炼对老年性骨质疏松患者腰背疼痛的影响[J].护理学杂志,2015,30(21):4-6. [53] 王照鹏.健身气功八段锦对骨量减少老年人骨密度、骨代谢及生活质量的影响[D].上海:上海师范大学,2022. [54] 谷磊,刘毅.健身功法新编五禽戏对老年女性骨密度的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2021,41(1):79-82. [55] CHENG M, WANG Y, WANG S, et al. Network meta-analysis of the efficacy of four traditional Chinese physical exercise therapies on the prevention of falls in the elderly. Front Public Health. 2022;10:1096599. [56] 毛国庆,陈世洲,孙玉明,等.五禽戏联合钙剂治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].上海中医药杂志,2020,54(1):60-63. [57] 井夫杰,张静.易筋经锻炼对原发性骨质疏松症患者骨密度的影响[J].中国体育科技,2008,44(2):88-90,102. [58] 黄德真.健身气功—易筋经防治骨质疏松症的临床和机理研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2010. [59] 魏玉琴.易筋经运动对老年人骨密度与性激素的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院, 2017. |
| [1] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [2] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [3] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [4] | Wang Yan, Lyu Hao, Hu Zhimu, Zhou Yao, Liu Qiang, Yang Yuxiang, Yi Hairu, Wang Jiuxiang, Jiang Ting. Intervention with Compound Kidney-Invigorating Granules in a mouse model of osteoporosis: role of the TRIB3/beta-catenin axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6142-6149. |
| [5] | Jiang Chao, Che Yanjun. Biological mechanisms and future research trends of cartilaginous endplate degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 5915-5924. |
| [6] | Yin Xingxiao, Jiang Yang, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Shen Zhen, Li Yanqi, Song Yueyu, Peng Hao, Chen Qigang. Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis: a genome-wide data analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6030-6039. |
| [7] | Wu Lingjie, Zheng Kaiyuan, Wang Guangrong, Yin Chong . Strategies for the application of miRNA-targeted therapy in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5792-5803. |
| [8] | Wang Siwei, Yao Xiaosheng, Qi Xiaonan, Wang Yu, Cui Haijian, Zhao Jiaxuan. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 mediates mitophagy to regulate osteogenesis and myogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4557-4567. |
| [9] | Fu Jingyue, Zhou Qinfeng, Li Muzhe, Ma Yong, Pan Yalan, Sun Jie, Huang Xiangyang, Guo Yang. Preparation and evaluation of an animal model of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis comorbidity in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4299-4308. |
| [10] | Zhou Jiajun, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Li Yang, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Assessing distribution characteristics and clinical significance of vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis based on whole spine MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1883-1889. |
| [11] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [12] | Liu Chenchen, Liu Ruize, Bao Mengmeng, Fang Li, Cao Liquan, Wu Jiangbo. Blood flow restriction training intervention in the elderly with sarcopenic obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6963-6970. |
| [13] | Wang Runzheng, Fu Su, Dong Chao, Li Dongzhe, Wang Yongkui. Relationship between bone mineral density and lumbar disc degeneration in middle-aged and elderly men and postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5079-5085. |
| [14] | Qiao Zhengji, Chai Niubing, Zheng Luyao, Gao Yunna, Wang Yang. Effect of whole‑body vibration training on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a meta‑analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5195-5202. |
| [15] | Liu Kedi, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haibiao, Guo Shenghui, Qin Zhongshe, Meng Juewei, Cui Shanlin, Fan Junhong. Causal relationship between peripheral blood cells and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2605-2613. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||