Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (36): 7790-7796.doi: 10.12307/2025.566
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transcription factor NKX2.1 promotes differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into lung stem cells
Deng Li, Liu Yang, Wang Hui, Yang Qiu, Dong Mingqing
- Center for Medicine Research and Translation, Chengdu Fifth People’s Hospital, Chengdu 611130, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-05Accepted:2024-11-12Online:2025-12-28Published:2025-03-11 -
Contact:Dong Mingqing, MD, Professor, Center for Medicine Research and Translation, Chengdu Fifth People’s Hospital, Chengdu 611130, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Deng Li, PhD, Assistant researcher, Center for Medicine Research and Translation, Chengdu Fifth People’s Hospital, Chengdu 611130, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 2023NSFSC0531 (to DMQ); Chengdu High-Level Clinical Key Specialty Construction Project, No. KYJJ2021-27 (to DMQ); Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine “Xinglin Scholar” Hospital Special Project, No. XJ2023010001 (to DL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Li, Liu Yang, Wang Hui, Yang Qiu, Dong Mingqing. Transcription factor NKX2.1 promotes differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into lung stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7790-7796.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
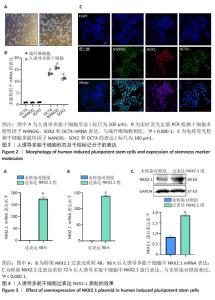
2.1 人诱导多能干细胞表型及干性标记分子的表达 如图2A所示,人诱导多能干细胞体外传代培养后,显微镜下观察细胞以紧密集结形成典型“干细胞簇”的表型,表明细胞状态良好。如图2B所示,人诱导多能干细胞中干性标记分子OCT4、NANOG和SOX2的mRNA表达水平较成纤维细胞显著增加(P < 0.000 1),表明人诱导多能干细胞干性维持良好。如图2C所示,免疫荧光检测人诱导多能干细胞中显著表达NANOG、SOX2和OCT4蛋白。 2.2 瞬时转染获得过表达NKX2.1的人诱导多能干细胞 通过Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂将NKX2.1过表达质粒瞬时转染入人诱导多能干细胞后,分别于48,96 h采用RT-qPCR检测NKX2.1 mRNA表达,72 h采用Western blot检测NKX2.1的蛋白表达,见图3。与未转染对照组相比,过表达NKX2.1组细胞中NKX2.1 mRNA和蛋白表达明显升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.000 1),提示成功转染NKX2.1过表达质粒。"

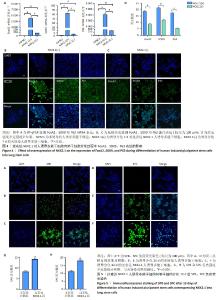
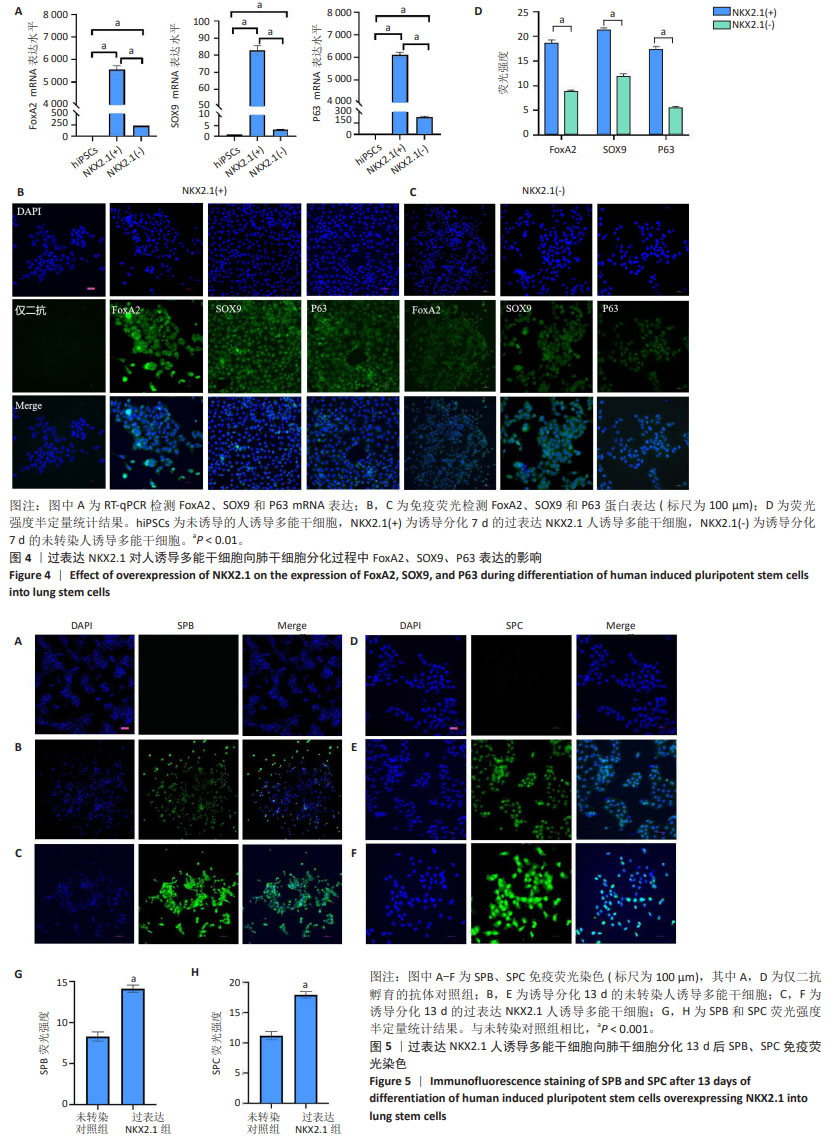
2.3 NKX2.1过表达对人诱导多能干细胞向肺干细胞分化的影响 人诱导多能干细胞向肺干细胞方向分化要经历定形内胚层、腹部前肠内胚层等阶段[29]。与正常的人诱导多能干细胞相比,诱导7 d后的未转染对照组和过表达NKX2.1组人诱导多能干细胞中均显著高表达肺干细胞相关标记物FoxA2、SOX9、P63(P < 0.000 1);与未转染对照组相比,过表达NKX2.1组FoxA2、SOX9、P63的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.000 1) ,见图4A。此外,免疫荧光染色显示,诱导7 d时过表达NKX2.1组细胞中显著表达FoxA2、SOX9和P63蛋白,见图4B-D。 2.4 NKX2.1过表达可促进人诱导多能干细胞向肺泡分化 为进一步证实NKX2.1过表达对人诱导多能干细胞向肺泡方向分化的影响,诱导分化13 d通过细胞免疫荧光检测肺泡细胞标记分子SPB和SPC的表达。如图5所示,与未转染对照组相比,NKX2.1过表达组SPB和SPC荧光强度明显升高,提示NKX2.1过表达可以显著促进人诱导多能干细胞向肺泡方向分化。 "
| [1] VAZQUEZ-ARMENDARIZ AI, TATA PR. Recent advances in lung organoid development and applications in disease modeling. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(22):e170500. [2] LEAVY OC, KAWANO-DOURADO L, STEWART ID, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a bidirectional Mendelian randomisation study. Thorax. 2024;79(6):538-544. [3] OLSON AL, SWIGRIS JJ, SPRUNGER DB, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease-associated mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183(3):372-378. [4] GENC AC, OZTURK Z, KARA AB, et al. Assessment of the clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung diseases: a retrospective evaluation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(18):8486-8493. [5] SOLOMON JJ, DANOFF SK, WOODHEAD FA, et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of pirfenidone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir Med. 2023;11(1):87-96. [6] PALOMÄKI A, FINNGEN RHEUMATOLOGY CLINICAL EXPERT GROUP, PALOTIE A, et al. Lifetime risk of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease in MUC5B mutation carriers. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(12):1530-1536. [7] ALYSANDRATOS KD, GARCIA-DE-ALBA C, YAO C, et al. Culture impact on the transcriptomic programs of primary and iPSC-derived human alveolar type 2 cells. JCI Insight. 2023;8(1):e158937. [8] DYE BR, DEDHIA PH, MILLER AJ, et al. A bioengineered niche promotes in vivo engraftment and maturation of pluripotent stem cell derived human lung organoids. Elife. 2016;5:e19732. [9] ANTONI D, BURCKEL H, JOSSET E, et al. Three-dimensional cell culture: a breakthrough in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(3):5517-5527. [10] KLEIN SG, SERCHI T, HOFFMANN L, et al. An improved 3D tetraculture system mimicking the cellular organisation at the alveolar barrier to study the potential toxic effects of particles on the lung. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013;10:31. [11] KÜHL L, GRAICHEN P, VON DAACKE N, et al. Human Lung Organoids-A Novel Experimental and Precision Medicine Approach. Cells. 2023; 12(16):2067. [12] SUN YL, HENNESSEY EE, HEINS H, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell modeling of alveolar type 2 cell dysfunction caused by ABCA3 mutations. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(2):e164274. [13] KITAMURA T, MISU M, YOSHIKAWA M, et al. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into lung-like cells using lung-derived matrix sheets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;686:149197. [14] LI T, SU X, LU P, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Dermcidin-Containing Migrasomes enhance LC3-Associated Phagocytosis of Pulmonary Macrophages and Protect against Post-Stroke Pneumonia. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(22):e2206432; [15] 李强,张明伟,李建明,等.miR-146b促进诱导多能干细胞向神经元样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(17):2711-2716. [16] 伟人悦,厉雪纯,李妍,等.无血清单层细胞诱导法培养猪诱导多能性干细胞定向分化为血管内皮细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(31):4971-4978. [17] ALBER AB, MARQUEZ HA, MA L, et al. Directed differentiation of mouse pluripotent stem cells into functional lung-specific mesenchyme. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3488. [18] KANAGAKI S, IKEO S, SUEZAWA T, et al. Directed induction of alveolar type I cells derived from pluripotent stem cells via Wnt signaling inhibition. Stem Cells. 2021;39(2):156-169. [19] HEIN RFC, CONCHOLA AS, FINE AS, et al. Stable iPSC-derived NKX2-1+ lung bud tip progenitor organoids give rise to airway and alveolar cell types. Development. 2022;149(20):dev200693. [20] LAZZARO D, PRICE M, DE FELICE M, et al. The transcription factor TTF-1 is expressed at the onset of thyroid and lung morphogenesis and in restricted regions of the foetal brain. Development. 1991;113(4): 1093-1104. [21] MINOO P, SU G, DRUM H, et al. Defects in tracheoesophageal and lung morphogenesis in Nkx2.1(-/-) mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1999; 209(1):60-71. [22] LITTLE DR, GERNER-MAURO KN, FLODBY P, et al. Transcriptional control of lung alveolar type 1 cell development and maintenance by NK homeobox 2-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(41): 20545-20555. [23] KUWAHARA A, LEWIS AE, COOMBES C, et al. Delineating the early transcriptional specification of the mammalian trachea and esophagus. Elife. 2020;9:e55526. [24] TOTH A, KANNAN P, SNOWBALL J, et al. Alveolar epithelial progenitor cells require Nkx2-1 to maintain progenitor-specific epigenomic state during lung homeostasis and regeneration. Nat Commun. 2023; 14(1):8452. [25] LITTLE DR, LYNCH AM, YAN Y, et al. Differential chromatin binding of the lung lineage transcription factor NKX2-1 resolves opposing murine alveolar cell fates in vivo. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2509. [26] OSTRIN EJ, LITTLE DR, GERNER-MAURO KN, et al. β-Catenin maintains lung epithelial progenitors after lung specification. Development. 2018;145(5):dev160788. [27] KUSAKABE T, KAWAGUCHI A, HOSHI N, et al. Thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein/NKX2.1 is required for the maintenance of ordered architecture and function of the differentiated thyroid. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20(8):1796-1809. [28] GHAEDI M, CALLE EA, MENDEZ JJ, et al. Human iPS cell-derived alveolar epithelium repopulates lung extracellular matrix. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(11):4950-4962. [29] YAMAMOTO Y, GOTOH S, KOROGI Y, et al. Long-term expansion of alveolar stem cells derived from human iPS cells in organoids. Nat Methods. 2017;14(11):1097-1106. [30] LIAKOULI V, CIANCIO A, DEL GALDO F, et al. Systemic sclerosis interstitial lung disease: unmet needs and potential solutions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024;20(1):21-32. [31] BEERS MF, MORRISEY EE. The three R’s of lung health and disease: repair, remodeling, and regeneration. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6): 2065-2073. [32] ALDER JK, BARKAUSKAS CE, LIMJUNYAWONG N, et al. Telomere dysfunction causes alveolar stem cell failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(16):5099-5104. [33] MATTHAY MA, ARABI Y, ARROLIGA AC, et al. A New Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(1):37-47. [34] MATTHAY MA, ZEMANS RL. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: pathogenesis and treatment. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:147-163. [35] 李福东,刘虹,陈亚君,等.肺干细胞向肺泡上皮分化在急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(6):21-24. [36] 张红蕾,聂宏光.干细胞治疗肺损伤的研究进展[J].生理科学进展, 2019,50(4):277-280. [37] MILLER AJ, HILL DR, NAGY MS, et al. In Vitro Induction and In Vivo Engraftment of Lung Bud Tip Progenitor Cells Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(1):101-119. [38] BEERS MF, MOODLEY Y. When Is an Alveolar Type 2 Cell an Alveolar Type 2 Cell? A Conundrum for Lung Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017;57(1):18-27. [39] ZHOU L, LIM L, COSTA RH, et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1, hepatocyte nuclear factor-3beta, surfactant protein B, C, and Clara cell secretory protein in developing mouse lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996;44(10):1183-1193. [40] MIURA A, SARMAH H, TANAKA J, et al. Conditional blastocyst complementation of a defective Foxa2 lineage efficiently promotes the generation of the whole lung. Elife. 2023;12:e86105. [41] WANG Y, MENG Z, LIU M, et al. Autologous transplantation of P63+ lung progenitor cells for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(734):eadi3360. [42] MCCAULEY KB, HAWKINS F, SERRA M, et al. Efficient Derivation of Functional Human Airway Epithelium from Pluripotent Stem Cells via Temporal Regulation of Wnt Signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(6): 844-857.e6. [43] KONISHI S, GOTOH S, TATEISHI K, et al. Directed Induction of Functional Multi-ciliated Cells in Proximal Airway Epithelial Spheroids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2016;6(1):18-25. |
| [1] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [2] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [3] | . Effect of miR-26b on neural and vascular differentiation in stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7769-7775. |
| [4] | Li Tingyue, Guo Qian, He Wenxi, Wu Jiayuan. Long noncoding RNA TP53TG1 promotes odontogenic and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7776-7782. |
| [5] | Zhang Min, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Li Zhuangzhuang, Wang Xue, Wang Huike. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosomes repair radiation-induced submandibular gland damage in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7804-7815. |
| [6] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [7] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [8] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [9] | Shao Xuekun, Shi Dianhua, Ding Zhiping, Qiu Zhuoya, Wang Ping, Wang Yi, Wang Cheng, Ding Xiaoyan, Sun Tiefeng. Calcined deer antler slices promote proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6601-6608. |
| [10] | Luo Dan, Ge Zhilin, Hou Yonghui, Wang Wanshun, Zhan Jiheng, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun, Chen Shudong. Extraction and subculture of neural stem cells from mouse embryonic spinal cord: comparison and analysis on advantages and disadvantages of three commonly used digestive enzymes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6609-6615. |
| [11] | Lin Shuqian, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Pan Xinghua, Li Zian, Ruan Guangping. Comparison of biological characteristics of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after interference and overexpression of telomere Cajal body protein-1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6616-6624. |
| [12] | Xiong Zhenghua, Zhou Jianghong, Shen Yi, Han Xuesong . Mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles in repair of endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6782-6791. |
| [13] | Zhong Min, Wang Cheng, Fan Zhenhai, Li Linyan, Yu Limei. Effect and mechanism of perinatal mesenchymal stem cells and their combination with hydrogels in treatment of intrauterine adhesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6792-6799. |
| [14] | Yuan Xiao, Liang Songlin, Xie Yanan, Guan Dongmei, Fan Longyu, Yin Xiaoxuan. Mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in treatment of inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6811-6820. |
| [15] | He Changliang, Wang Yan, Luo Ling, Liu Jian. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells thwart pyroptosis of lung tissue cells in septic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6642-6648. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||