Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (15): 3290-3300.doi: 10.12307/2025.182
Visual analysis of research trends in pigmented villonodular synovitis
Xiong Binglang1, Cao Xuhan1, Zhang Cheng2, Guo Ziyan1, Sun Xudong1, Bai Zixing3, Sun Weidong1
- 1Second Department of Bone and Joint, 2Third Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100015, China; 3Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Shunyi Hospital of Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Beijing 101300, China
-
Received:2024-04-18Accepted:2024-05-25Online:2025-05-28Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Sun Weidong, MD, Chief physician, Second Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100015, China -
About author:Xiong Binglang, Doctoral candidate, Second Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100015, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81373802 (to SWD); Beijing Municipal Clinical Characteristic Applied Research Project, No. Z191100006619024 (to SWD); Special Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Evidence-based Research in the High-level Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Construction Project of Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, No. WJYY-XZKT-2023-18 (to SWD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiong Binglang, Cao Xuhan, Zhang Cheng, Guo Ziyan, Sun Xudong, Bai Zixing, Sun Weidong. Visual analysis of research trends in pigmented villonodular synovitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3290-3300.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
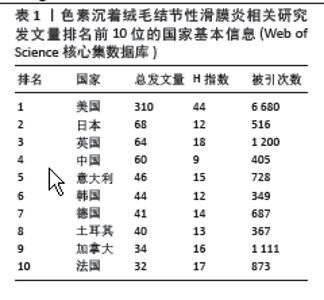
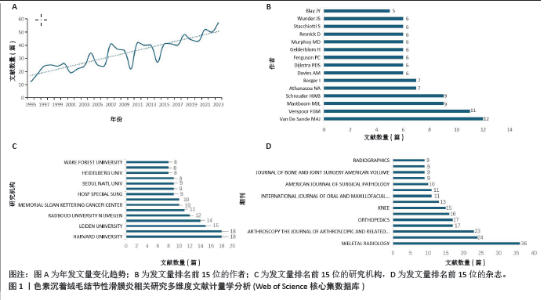
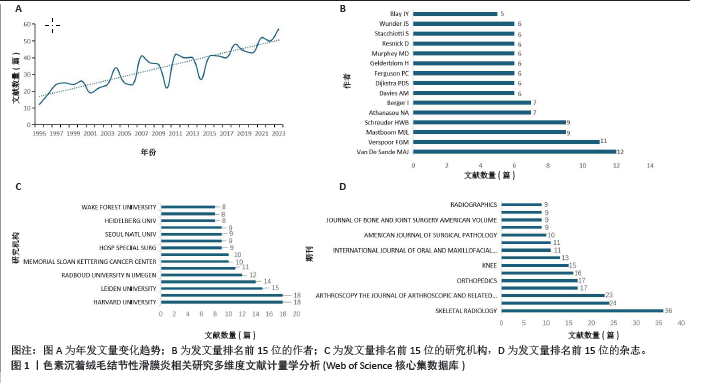
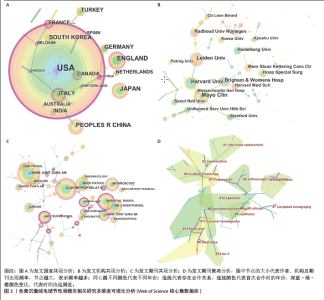
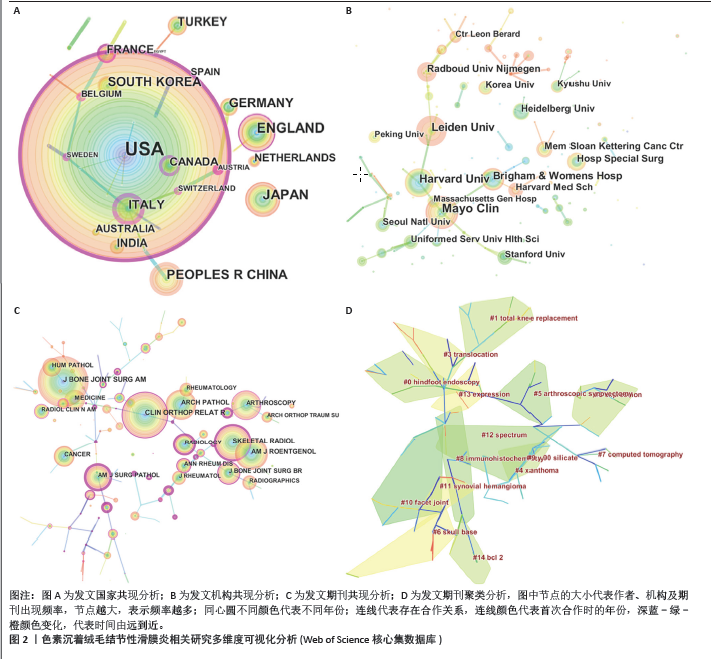
2.1 文献检索结果 制定正确的检索式,通过Web of Science核心合集数据库共检索出1 247篇出版物,排除会议摘要和信件等出版物后,共纳入文献986篇,其中涉及30个国家或地区,3 424位作者,1 041个研究机构,306个出版物来源,14 225篇被引文献。在1995-2023年色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎(色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎)相关研究总发文量大体呈波动式增长,其中近5年年发文量相对处于历史高位,均大于50篇,2023年最高,达57篇,见图1A,但每年的发文量相较其他疾病依然较低,可能由于色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎发病率较低,未能引起足够的重视有关。 2.2 发文国家分析 发文总量排名前5名的国家分别为:美国(310篇)、日本(68篇)、英国(64篇)、中国(60篇)、意大利(46篇)。H指数排名前5的国家分别为:美国(44篇)、英国(18篇)、法国(17篇)、加拿大(16篇)、意大利(15篇)。文献被引次数前5的国家分别为:美国(6 680次)、英国(1 200次)、加拿大(1 111次)、法国(873次)、意大利(728次),见表1。中心性排名前5名的国家有:澳大利亚(0.63)、意大利(0.6)、美国(0.53)、瑞士(0.51)、加拿大(0.46),见图2A,表1。中国的中心性只有0.01,H指数为9,在国际合作及发表文献质量方面仍需加强。美国在总发文量、H指数及被引次数等方面均占有绝对优势,证明美国在色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎研究方面处于领导地位。"

2.3 作者分析 Web of Science核心合集数据库中总发文排名前4位的作者分别为:VAN DE SANDE MAJ(12篇)、VERSPOOR FGM(11篇)、MASTBOOM MJL(11)、SCHREUDER HWB(9篇),见图1B。发文量排名前25位的作者总发文量只占总文献数的18.544%。且所有作者发文量均低于20篇。说明在色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎研究方面未形成鲜明的团队优势,未能出现行业的领军人物带动研究发展。但值得注意的是VAN DE SANDE MAJ、MASTBOOM MJL教授均来自于荷兰莱顿大学医学中心,VERSPOOR FGM与SCHREUDER HWB教授来自于荷兰内梅亨大学医学中心。这预示着虽然荷兰在总发文量方面未能突出,但依靠着这2个优秀团队,未来可能在色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎研究方面大有作为。图3展示了作者(左)、关键词(中)和作者国籍(右)之间的联系,矩形的面积与出版物的数量呈正比。由图可知排名靠前的作者与国家均涉及大部分研究领域,专注于某一方向的研究团队较少。中国发文排名前5位的作者分别为何伟、郭林、杨柳、李箭、张庆文。发文量最高的作者总发文量仅为6篇,说明中国对于色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎研究仍缺乏专一研究的团队,见表2。"

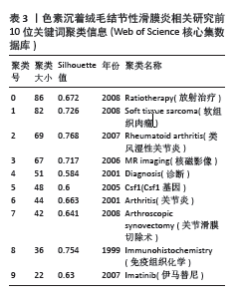
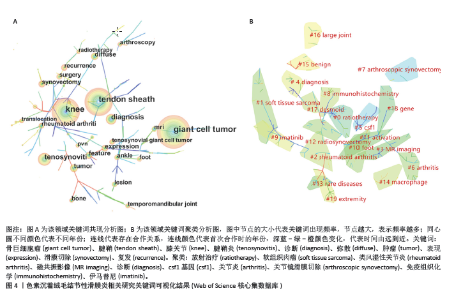
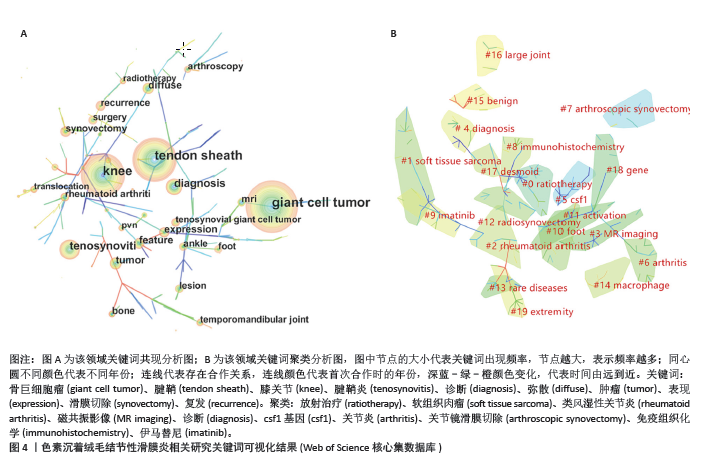
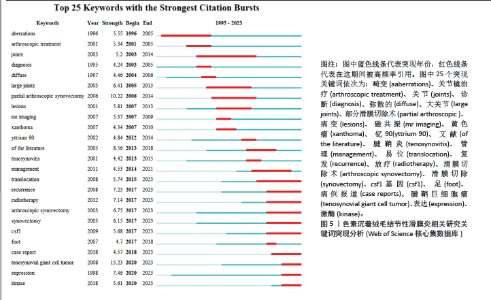
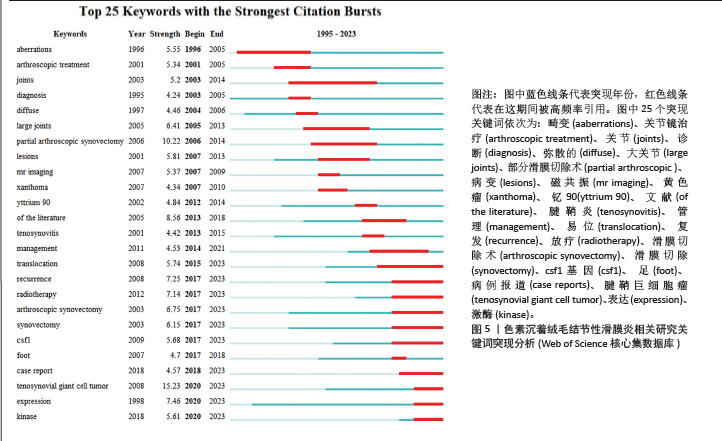
2.4 发文机构分析 Web of Science核心合集数据库中发文量排名前5的机构为:哈佛大学(18篇)、梅奥诊所(18篇)、莱顿大学(15篇)、布里格姆妇女医院(14篇)、内梅亨大学(12篇),见图1C。其中哈佛大学、梅奥诊所、布里格姆妇女医院均来自于美国,但其发文量只占全美国的16%。莱顿大学、内梅亨大学是荷兰两所知名学府,荷兰关于色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的相关研究几乎都产出于此。共现分析显示所有机构中心性均小于0.1,这说明机构间的交流合作不够,见图2B。而中国发文量排名前5位的单位分别为广州中医药大学第一附属医院、华中科技大学附属协和医院、第三军医大学第一附属医院、上海交通大学附属第六人民医院和北京大学第三医院,见表2。在广州中医药大学第一附属医院发表的11篇论文中仅有5篇为原创性研究,剩余均为病例报道或者文献二次研究,中国各研究机构仍缺乏高质量的原创性成果。 2.5 出版期刊分析 发文量前5位的期刊分别为:《SKELETAL RADIOLOGY》 (36篇,影响因子2.1)、《CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH》 (24篇,影响因子4.2)、《ARTHROSCOPY THE JOURNAL OF ARTHROSCOPIC AND RELATED SURGERY》(23篇,影响因子4.7)、《KNEE SURGERY SPORTS TRAUMATOLOGY ARTHROSCOPY》(17篇,影响因子3.8)、《ORTHOPEDICS》(17篇,影响因子 1.1),见如图1D及图2C。期刊共被引聚类分析显示,最大的5个聚类为:内镜检查、全膝关节置换、临床表现、染色体易位,细胞学,见图2D。该聚类Q值为0.872,Silhouette值为0.492。主题与这5大聚类相关的研究可能更受期刊青睐,更加容易发表。而中国有关色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的研究更容易在《中国矫形外科杂志》《中国骨伤》《医学影像学杂志》上发表,见表2。 2.6 关键词分析结果 Web of Science核心合集数据库中共现最多的10大关键词为:骨巨细胞瘤(231次)、腱鞘(196次)、膝关节(195次)、腱鞘炎(94次)、诊断(83次)、弥散(59次)、肿瘤(59次)、表现(54次)、滑膜切除(52次)、复发(49次),见图4A。关键词聚类排名前10位的聚类为:放射治疗、软组织肉瘤、类风湿性关节炎、磁共振影像、诊断、csf1、关节炎、关节镜滑膜切除、免疫组织化学、伊马替尼,见图4B和表3。该聚类Q值为0.918,Silhouette值为0.51。 关键词突现分析显示,关键词“突变”突现时间最长,从1996-2005年。持续突现至2023年的关键词有:CSF1、腱鞘巨细胞瘤、个案报道、染色体易位、放射治疗、表达、激酶,见图5。"
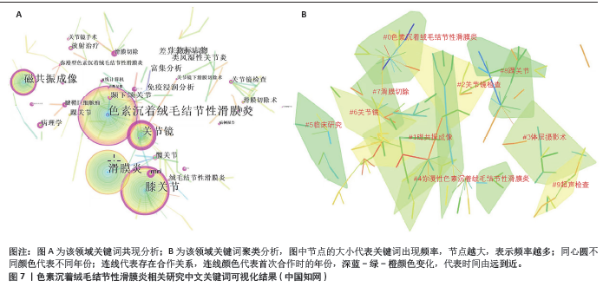
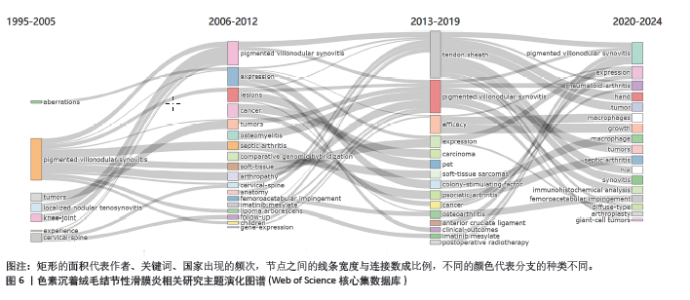
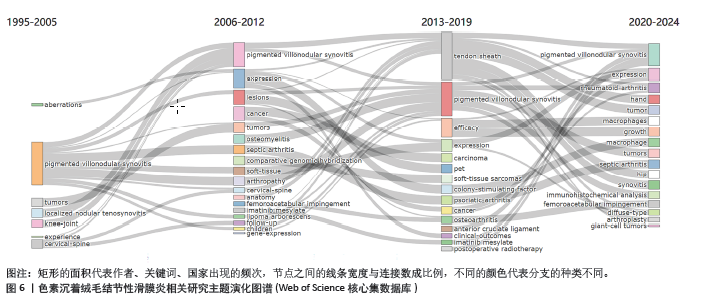
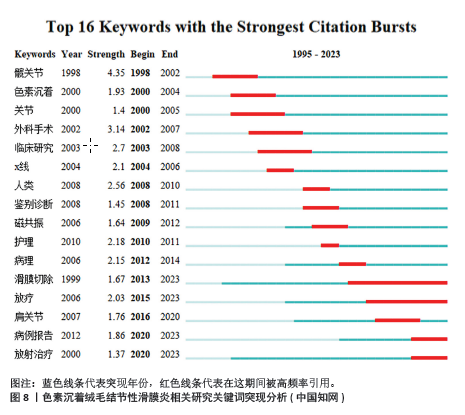
中国知网数据库中共现最多的10个关键词为:色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎(221次)、膝关节(168次)、滑膜炎(166次)、磁共振成像(93次)、关节镜(91次)、颞下颌关节(34次)、差异表达基因(28次)、生物标志物(28次)、类风湿性关节炎(28次)、免疫浸润分析(28次),见图7A。关键词聚类分析显示排名前10位的聚类为:色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎、磁共振成像、关节镜检查、体层摄影术、弥漫性色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎、临床研究、关节镜、滑膜切除、踝关节、超声检查,见表4和图7B。从分类可以看出,目前中国的研究热点主要为色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的诊断与临床治疗方面。中国的研究持续突现至2023年的关键词有:滑膜切除、放疗、病例报道、放射治疗,见图8,未来有关色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的滑膜切除与放射治疗是研究热点。"

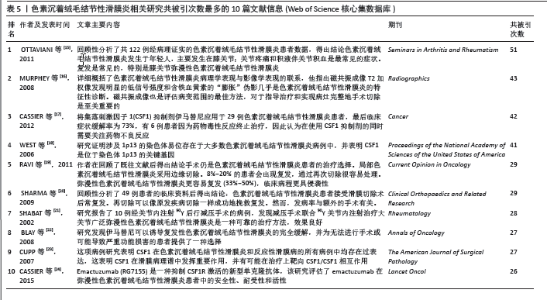
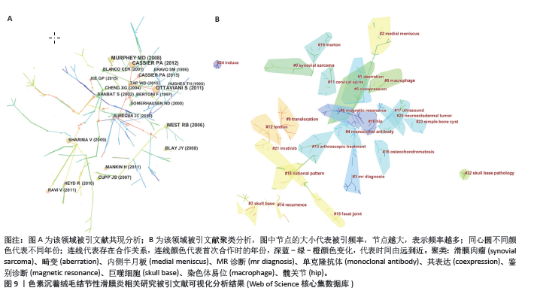
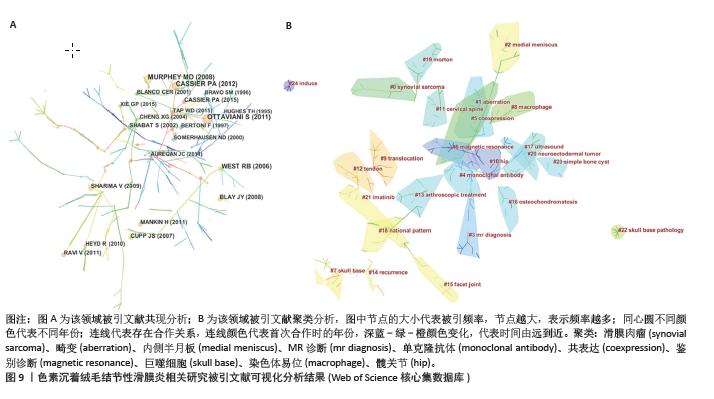
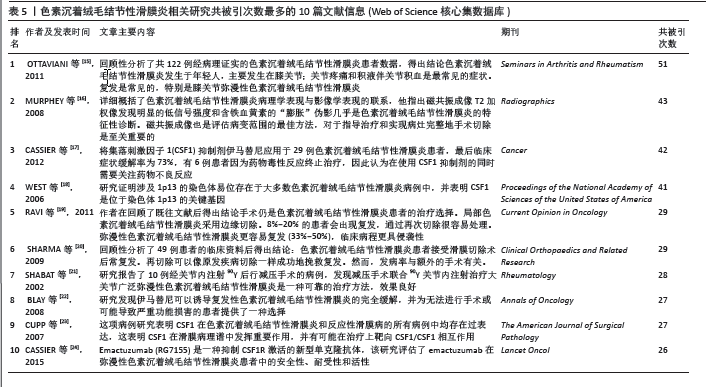
2.7 文献共被引分析结果 在1995-2023年,该领域共产生了14 225篇被引文献。文章整理了共被引次数最多的10篇文献信息[15-24],见表5和图9A。其中OTTAVIANI等[15]在2011年发表的一项回顾性研究共被引次数最多,他在分析了122例被诊断为色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎患者临床数据后,得出结论色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎好发于年轻人,主要累及膝关节,而关节疼痛与关节积液是最常见的临床症状,且治疗后易复发。MURPHEY等[16]在2008年发表的文献中详细概括了色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎病理学表现与影像学表现的联系,他指出磁共振成像T2加权像发现明显的低信号强度和含铁血黄素的“膨胀”伪影几乎是色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的特征性诊断。磁共振成像也是评估病变范围的最佳方法,对于指导治疗和实现病灶完整地手术切除是至关重要的。 在疾病治疗方面,WEST等[18]的一项基因研究发现涉及1p13的染色体易位存在于大多数色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎病例中,并表示CSF1是位于染色体1p13断点的基因,由此揭开了色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎基因靶向治疗的序幕。随后,CUPP等[23]开展一项病理研究表明CSF1在色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎患者的滑膜中过表达,这为色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎靶向药物的应用提供了基础。在这些高共被引文献的基础上,2008年, BLAY等[22]的临床研究发现CSF1抑制剂伊马替尼可以诱导复发性色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的完全缓解,并认为这为无法进行手术或可能导致严重功能损害的患者提供了一种选择。CASSIER等[17]将伊马替尼应用于29例色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎患者,最后临床症状缓解率为73%,有6例患者因为药物毒性反应终止治疗,因此在使用CSF1抑制剂的同时需要关注药物不良反应。在所有的高共被引文献中,有关CSF1的文献占到了4篇,这表明既往关于靶向CSF1的研究是绝对的研究热点。 剩余几篇高共被引文献均与色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎的手术治疗及术后复发情况相关。RAVI等[19]的统计发现8%-20%的色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎患者术后会出现复发,但是通过再次切除很容易应对。弥漫性色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎更容易复发(33%-50%),临床病程更具侵袭性。这提示区分局灶性还是弥漫性色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎对于疾病的预后与转归意义重大。SHABAT等[21]采用手术联合90Y关节内注射治疗弥漫性色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎,结果显示效果良好。据此可知,提升手术治疗效果与降低术后复发率依然是研究者关注的重点。 共被引文献聚类分析显示,排名前10位的聚类为:滑膜肉瘤、畸变、内侧半月板、MR诊断、单克隆抗体、共表达、鉴别诊断、巨噬细胞、染色体易位和髋关节,见图9B。该聚类Q值为0.930 2,Silhouette值为0.330 6。"
| [1] STEPHAN SR, SHALLOP B, LACKMAN R, et al. Pigmented villonodular synovitis: a comprehensive review and proposed treatment algorithm. JBJS Rev. 2016;4(7):e3. [2] SBARAGLIA M, BELLAN E, DEI TOS AP. The 2020 WHO Classification of soft tissue tumours: news and perspectives. Pathologica. 2021;113(2):70-84. [3] CHIANG ER, MA HL, WANG JP, et al. Multi-lineage differentiation and angiogenesis potentials of pigmented villonodular synovitis derived mesenchymal stem cells--pathological implication. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(3):395-403. [4] BERNTHAL NM, ISHMAEL CR, BURKE ZDC. Management of pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS): an orthopedic surgeon’s perspective. Curr Oncol Rep. 2020;22(6):63. [5] QUARESMA MB, PORTELA J, SOARES DO BRITO J. Open versus arthroscopic surgery for diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumours of the knee: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(6):339-346. [6] KAGER M, KAGER R, FAŁEK P, et al. Tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Folia Med Cracov. 2022;62(2):93-107. [7] DEGIRMENCI E, SAHIN AA, BULUM YE, et al. Diffuse-type giant cell tumor: pigmented villonodular synovitis of patellar fat pad. J Cancer Res Ther. 2022;18(4):1189-1191. [8] STAALS EL, FERRARI S, DONATI DM, et al. Diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumour: Current treatment concepts and future perspectives. Eur J Cancer. 2016;63:34-40. [9] PALMERINI E, STAALS EL. Treatment updates on tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Curr Opin Oncol. 2022;34(4):322-327. [10] BRAHMI M, VINCENEUX A, CASSIER PA. Current systemic treatment options for tenosynovial giant cell tumor/pigmented villonodular synovitis: targeting the CSF1/CSF1R axis. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016;17(2):10. [11] VERSPOOR FGM, MASTBOOM MJL, HANNINK G, et al. The effect of surgery in tenosynovial giant cell tumours as measured by patient-reported outcomes on quality of life and joint function. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(3):272-280. [12] CHEN C, DUBIN R, KIM MC. Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: a scientometric update (2000 -2014). Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14(9):1295-1317. [13] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究, 2015,33(2):242-253. [14] HIRSCH JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46): 16569-16572. [15] OTTAVIANI S, AYRAL X, DOUGADOS M, et al. Pigmented villonodular synovitis: a retrospective single-center study of 122 cases and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011;40(6):539-546. [16] MURPHEY MD, RHEE JH, LEWIS RB, et al. Pigmented villonodular synovitis: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2008;28(5):1493-1518. [17] CASSIER PA, GELDERBLOM H, STACCHIOTTI S, et al. Efficacy of imatinib mesylate for the treatment of locally advanced and/or metastatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor/pigmented villonodular synovitis. Cancer. 2012;118(6):1649-1655. [18] WEST RB, RUBIN BP, MILLER MA, et al. A landscape effect in tenosynovial giant-cell tumor from activation of CSF1 expression by a translocation in a minority of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(3): 690-695. [19] RAVI V, WANG WL, LEWIS VO. Treatment of tenosynovial giant cell tumor and pigmented villonodular synovitis. Curr Opin Oncol. 2011;23(4):361-366. [20] SHARMA V, CHENG EY. Outcomes after excision of pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467(11):2852-2858. [21] SHABAT S, KOLLENDER Y, MERIMSKY O, et al. The use of surgery and yttrium 90 in the management of extensive and diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis of large joints. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41(10):1113-1118. [22] BLAY JY, EL SAYADI H, THIESSE P, et al. Complete response to imatinib in relapsing pigmented villonodular synovitis/tenosynovial giant cell tumor (PVNS/TGCT). Ann Oncol. 2008;19(4):821-822. [23] CUPP JS, MILLER MA, MONTGOMERY KD, et al. Translocation and expression of CSF1 in pigmented villonodular synovitis, tenosynovial giant cell tumor, rheumatoid arthritis and other reactive synovitides. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31(6):970-976. [24] CASSIER PA, ITALIANO A, GOMEZ-ROCA CA, et al. CSF1R inhibition with emactuzumab in locally advanced diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumours of the soft tissue: a dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(8): 949-956. [25] MASTBOOM MJL, HOEK DM, BOVÉE JVMG, et al. Does CSF1 overexpression or rearrangement influence biological behaviour in tenosynovial giant cell tumours of the knee? Histopathology. 2019;74(2): 332-340. [26] DALE K, SMITH HJ, PAUS AC, et al. Dynamic MR-imaging in the diagnosis of pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000;29(5):336-339. [27] MYERS BW, MASI AT. Pigmented villonodular synovitis and tenosynovitis: a clinical epidemiologic study of 166 cases and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 1980;59(3):223-238. [28] GOUIN F, NOAILLES T. Localized and diffuse forms of tenosynovial giant cell tumor (formerly giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath and pigmented villonodular synovitis). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017; 103(1S):S91-S97. [29] XIE GP, JIANG N, LIANG CX, et al. Pigmented villonodular synovitis: a retrospective multicenter study of 237 cases. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121451. [30] FOTIADIS E, PAPADOPOULOS A, SVARNAS T, et al. Giant cell tumour of tendon sheath of the digits. A systematic review. Hand (N Y). 2011;6(3):244-249. [31] DAOUD J, AOUAD D, HASSAN Y, et al. Localized pigmented villonodular synovitis of the posterior knee compartment with popliteal vessel compression: a case report of arthroscopic resection using only anterior knee portals. Case Rep Orthop. 2018; 2018:7532358. [32] DINES JS, DEBERARDINO TM, WELLS JL, et al. Long-term follow-up of surgically treated localized pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(9):930-937. [33] GU HF, ZHANG SJ, ZHAO C, et al. A comparison of open and arthroscopic surgery for treatment of diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(11): 2830-2836. [34] MOLLON B, LEE A, BUSSE JW, et al, Theodoropoulos J. The effect of surgical synovectomy and radiotherapy on the rate of recurrence of pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee: an individual patient meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(4): 550-557. [35] GELDERBLOM H, DE SANDE MV. Pexidartinib: first approved systemic therapy for patients with tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Future Oncol. 2020;16(29): 2345-2356. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Ao Xiaojing, Li Kun, Liu Yuhang, Yang Xiaoxuan, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Ren Xiaoyan, Zhang Shaojie. Development and application of a three-dimensional digital visualization system for children’s neck acupoints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1834-1840. |
| [3] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [4] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [5] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [6] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [7] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [8] | Liu Yan, Wang Kai, Wu Min. Relationship between coronal angle fluctuation of ankle point and recovery of joint function after ankle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1820-1826. |
| [9] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [10] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [11] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [12] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [13] | Wang Yuehui, Shang Jin, Yang Chen, Fu Dongge, Cao Can, Zhang Xiaodong, Wang Jingfu. Evaluation of FTA-LAMP direct extraction method for extracting DNA from Streptococcus mutans [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1040-1049. |
| [14] | Li Huijun, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting. Physical activity and cognition in older adults: research hotspot and topic evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1073-1080. |
| [15] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||