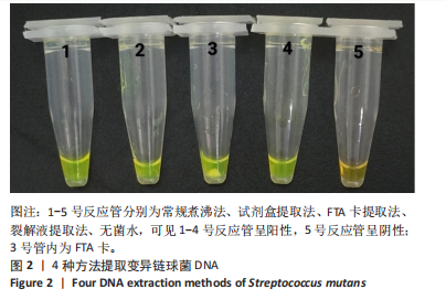
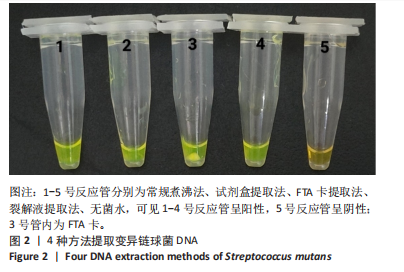
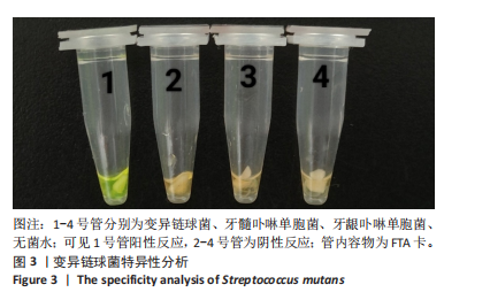
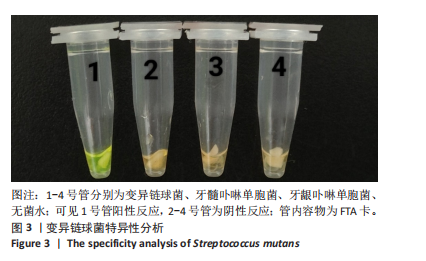
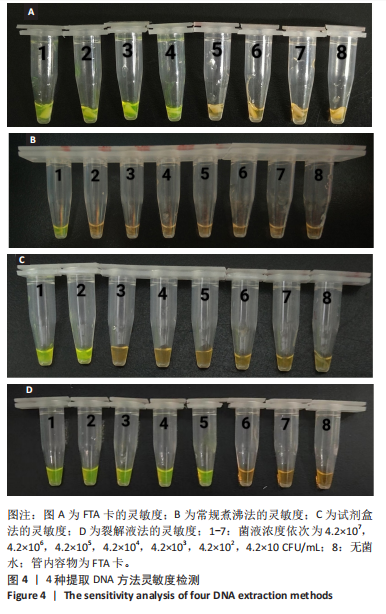
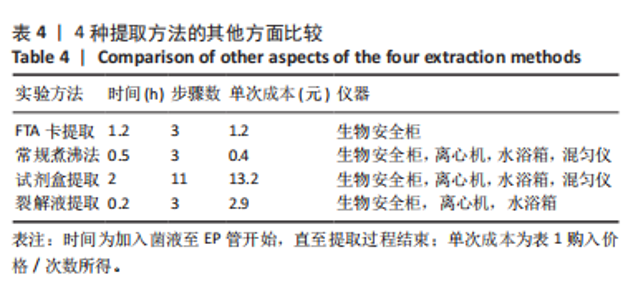
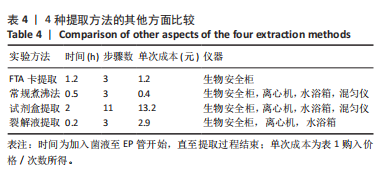
[1] LEMOS JA, PALMER SR, ZENG L, et al. The biology of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Spectr. 2019;7(1):10.
[2] 丁良,李芝香,汪慧渊,等.实时定量聚合酶螺旋反应定量检测变形链球菌方法的建立[J].生物技术通讯,2017,28(4):519-523.
[3] 黎凯歌,严冬,韩文睿,等.不同正畸方式对龈上菌斑中三种致龋菌的早期影响[J].北京口腔医学,2022,30(3):182-188.
[4] 王群,向瑶,赵茂吉,等.8种快速制备细菌基因组DNA方法的效果评价[J].现代预防医学,2017,44(16):3005-3009.
[5] 王瑞莲,林裕龙.细菌检测方法研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2014,35(16):2200-2201.
[6] 庄梦晴,张先舟,卢鑫,等.食品中沙门氏菌FTA膜结合跨越式滚环等温扩增检测方法的建立[J].现代食品科技,2021,37(4):275-283.
[7] STARK CR, GUSTAVSSON I, HORAL P, et al. Brush Samples of Oral Lesions to FTA Elute Card for High-risk Human Papilloma Virus Diagnosis.Anticancer Res. 2021;41(1):269-277.
[8] NOTOMI T, OKAYAMA H, MASUBUCHI H, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(12):E63.
[9] PARK SY, CHAE DS, LEE JS, et al. Point-of-Care Testing of the MTF1 Osteoarthritis Biomarker Using Phenolphthalein-Soaked Swabs.Biosensors (Basel). 2023;13(5):535.
[10] LONGHI SA, GARCÍA CASARES LJ, MUÑOZ-CALDERÓN AA, et al. Combination of ultra-rapid DNA purification (PURE) and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA in dried blood spots. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023;17(4): e0011290.
[11] CAMACHO MJ, ALBUQUERQUE DC, INÁCIO ML, et al. FTA-LAMP based biosensor for a rapid in-field detection of Globodera pallida—the pale potato cyst nematode. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1337879.
[12] 许立明,侯萌.变形链球菌密度感应系统研究新进展[J].口腔生物医学,2022,13(3):198-202.
[13] 胡丹阳,李兰,张锦龙,等.变形链球菌菌斑生物膜初期黏附机制研究进展[J].临床军医杂志,2022,50(8):878-880.
[14] LI Z, GONG T, WU Q, et al. Lysine lactylation regulates metabolic pathways and biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans. Sci Signal. 2023;16(801):eadg1849.
[15] LI Y, HUANG S, DU J, et al. Current and prospective therapeutic strategies: tackling Candida albicans and Streptococcus mutans cross-kingdom biofilm. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1106231.
[16] 潘一春,张丁,傅民魁.固定矫治器粘结前后牙齿颊面菌斑pH值和变形链球菌附着的改变[J].口腔正畸学,2003,10(1):23-26.
[17] 尹成芳,张瑞中,杨星民.基于龋病相关因素定量分析的儿童过敏性紫癜发病直线回归预测模型的研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2023, 39(1):33-37.
[18] MULLIS KB, FALOONA FA. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155: 335-350.
[19] YU J, XIE J, CAO Y, et al. A modified loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Anim Biotechnol. 2021;32(6):766-773.
[20] 冯润东,贾首前,王莉芳,等.中成药中沙门氏菌环介导等温扩增快速检测方法的建立及应用[J].中国药业,2023,32(5):83-87.
[21] SHIRSHIKOV FV, BESPYATYKH JA. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification: From Theory to Practice. Russ J Bioorg Chem. 2022; 48(6):1159-1174.
[22] SOROKA M, WASOWICZ B, RYMASZEWSKA A. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): the better sibling of PCR? Cells. 2021;10(8):1931.
[23] KÖSTER PC, BAILO B, DASHTI A, et al. Long-Term Preservation and Storage of Faecal Samples in Whatman® Cards for PCR Detection and Genoty** of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium hominis. Animals (Basel). 2021;11(5):1369.
[24] KRAMBRICH J, BRINGELAND E, HESSON JC, et al. Usage of FTA® Classic Cards for Safe Storage, Shipment, and Detection of Arboviruses.Microorganisms. 2022;10(7):1445.
[25] DAVIS EH, VELEZ JO, RUSSELL BJ, et al. Evaluation of Whatman FTA cards for the preservation of yellow fever virus RNA for use in molecular diagnostics. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022;16(6):e0010487.
[26] YUE N, JIA Z. Comparison between Whatman FTA Elute Cards and Conventional Swab for the Detection of Pathogenic Enteric Bacteria Using an RT-qPCR Assay. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021;2021: 9963047.
[27] STRINGER OW, BOSSÉ JT, LACOUTURE S, et al.Rapid detection and ty** of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serovars directly from clinical samples: Combining FTA® card technology with multiplex PCR.Front Vet Sci.2021;8:728660.
[28] GREEN H, TILLMAR A, PETTERSSON G, et al. The use of FTA cards to acquire DNA profiles from postmortem cases. Int J Legal Med. 2019; 133(6):1651-1657.
[29] LAMPEL KA, ORLANDI PA, KORNEGAY L. Improved template preparation for PCR-based assays for detection of food-borne bacterial pathogens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66(10):4539-4542.
[30] KATO H, CÁCERES AG, MIMORI T, et al. Use of FTA cards for direct sampling of patients’ lesions in the ecological study of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(10):3661-3665.
[31] NZELU CO, CÁCERES AG, GUERRERO-QUINCHO S, et al. A rapid molecular diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis by colorimetric malachite green-loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) combined with an FTA card as a direct sampling tool. Acta Tropica. 2016;153:116-119.
[32] MATOVU E, KUEPFER I, BOOBO A, et al. Comparative detection of trypanosomal DNA by loop-mediated isothermal amplification and PCR from flinders technology associates cards spotted with patient blood. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(6):2087-2090.
[33] 叶明亮,袁著忻,李晓娣,等.细菌随机扩增多态性DNA分析中模板提取方法的优化[J].军事医学科学院院刊,2001(2):100-102+106.
[34] 张艳,王金鸿,吕亚莉,等.六种试剂盒提取血液基因组DNA效果比较[J].中国草食动物科学,2014,34(2):9-12.
[35] KARTHIKEYAN K, SARANYA R, BHARATH R, et al. A simple filter paper-based method for transporting and storing Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei DNA from infected Litopenaeus vannamei tissues. J Invertebr Pathol. 2020;169:107305.
[36] MOEHLING TJ, CHOI G, DUGAN LC, et al. LAMP diagnostics at the point-of-care: emerging trends and perspectives for the developer community. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2021;21(1):43-61.
[37] 丁博文,段小红,张燕丽.牙菌斑检测技术及其应用[J].吉林医学, 2023,44(8):2323-2327.
[38] 江阿力•帕孜力别克,米热阿依克孜•马木提,赵莉,等.牙周源性牙周牙髓联合病变常见病原菌的分布及其意义[J].口腔疾病防治,2022,30(1):20-26.
[39] 魏华,孙立国,朱晶,等.不同的DNA提取法对两种常见医院感染菌ERIC-PCR鉴定的影响研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2007,17(9): 1044-1047.
[40] 贾霄,曹丹,王文雯,等.FTA卡采集和常温保存肋软骨组织的方法[J].刑事技术,2020,45(5):503-506.
[41] 连新宇,王秀华,李晨,等.FTA卡保存对虾传染性皮下和造血组织坏死病毒DNA洗脱方法的优化[J].渔业科学进展,2024(3):1-10. |