Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 637-644.doi: 10.12307/2025.117
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification of core genes of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics
Zhu Xuekun, Liu Heng, Feng Hui, Gao Yunlong, Wen Lei, Cai Xiaosong, Zhao Ben, Zhong Min
- Army Seventy-One Army Group Hospital, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-16Accepted:2024-02-06Online:2025-01-28Published:2024-06-05 -
Contact:Liu Heng, Master, Attending physician, Army Seventy-One Army Group Hospital, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhu Xuekun, Master, Attending physician, Army Seventy-One Army Group Hospital, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Xuekun, Liu Heng, Feng Hui, Gao Yunlong, Wen Lei, Cai Xiaosong, Zhao Ben, Zhong Min. Identification of core genes of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 637-644.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
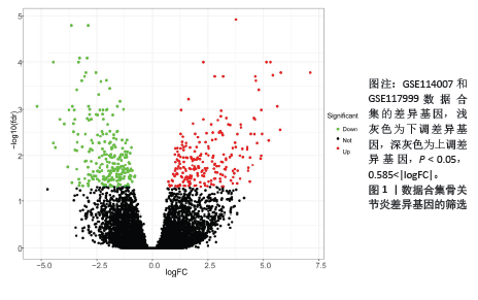
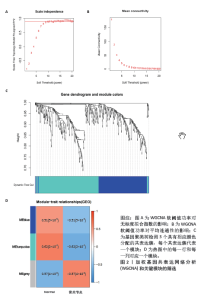
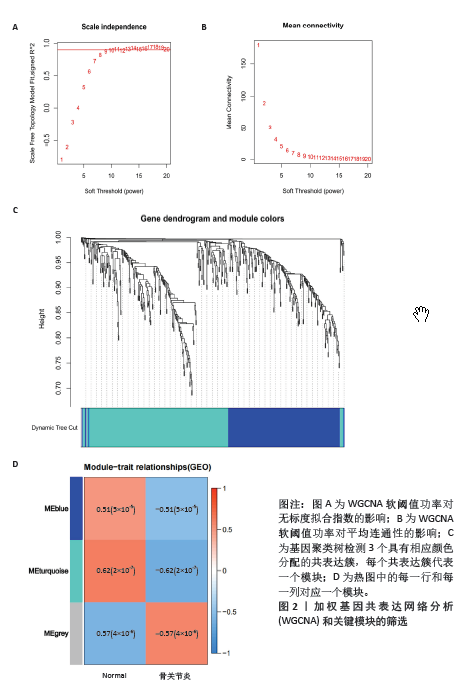
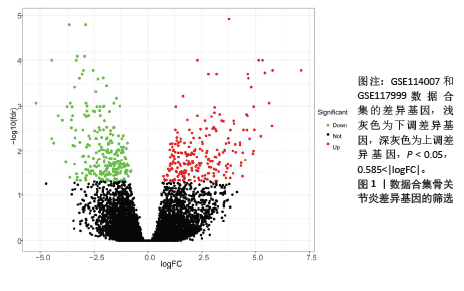
2.1 差异基因的筛选 数据合集包含28个正常软骨组织样本和30个骨关节炎软骨组织样本。根据条件设置P < 0.05,0.585<logFC或者logFC< -0.585,共筛选出477个差异基因,其中上调基因230个,下调基因247个(图1)。 2.2 加权基因共表达网络的构建和模块识别 为了进一步探索差异基因与骨关节炎的相关性,将差异基因与骨关节炎进行相关性分析。使用R软件WGCNA包pickSoftThreshold函自动数选取β最佳软阈值(图2A,B),建立了一种高效的共表达模块基因,并将表达模式相似的基因聚类(图2C),使用Pearson相关系数计算模块与骨关节炎之间的关联,并在热图中显示模块与疾病的相关性(图2D),获得了差异基因谱中的3个模块,其中模块“MEturquoise”与骨关节炎最相关(r=0.62,P < 0.001),此模块共聚集265个显著差异基因,并选择此模块进一步分析。"

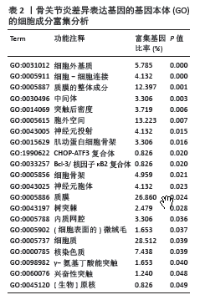
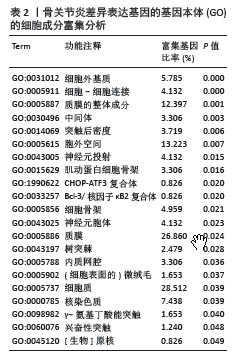
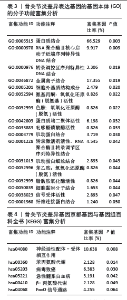
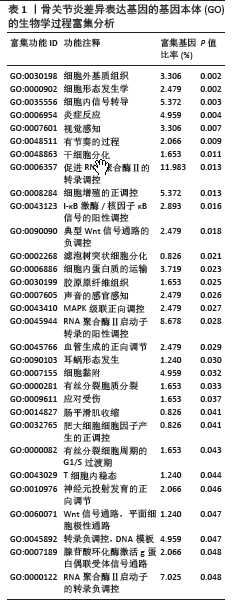
2.3 模块差异基因功能富集分析 为了更好地了解候选模块差异基因相关的生物过程和信号通路,利用公共DAVID数据库或者R软件进行了基因本体和KEGG分析。表1-3显示了富集模块差异基因在基因本体分析中生物学过程、细胞成分和分子功能的主要功能富集分析结果,结果显示差异基因在生物学过程中主要富集在RNA聚合酶Ⅱ的多项调控、细胞信号转导如核因子κB信号通路、MAPK信号通路的功能调控、炎症反应、细胞增殖和转录调控、细胞内蛋白质的运输、干细胞分化等多项生物学过程中,在细胞成分功能中富集有细胞外基质、Bcl-3/核因子κB2复合体、质膜的整体成分、细胞质等多项细胞成分发挥作用,在分子功能中富集有蛋白质结合、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ核心启动子近端序列特异性DNA结合、金属离子结合、细胞黏附分子结合等。而KEGG富集结果为神经活性配体-受体相互作用和一些氨基酸的代谢,而富集在FOXO信号通路上的P值> 0.05,差异并无统计学意义,见表4。"
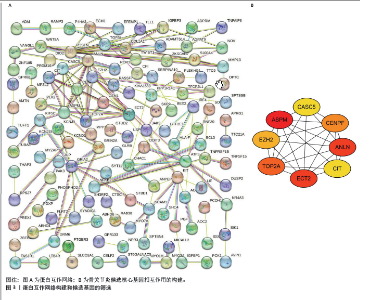
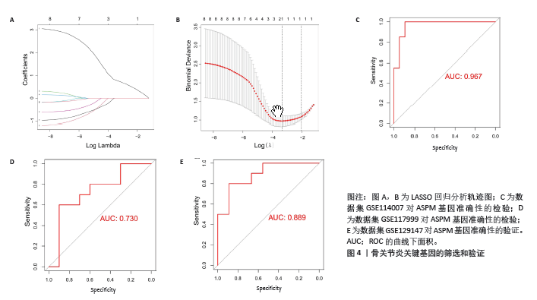
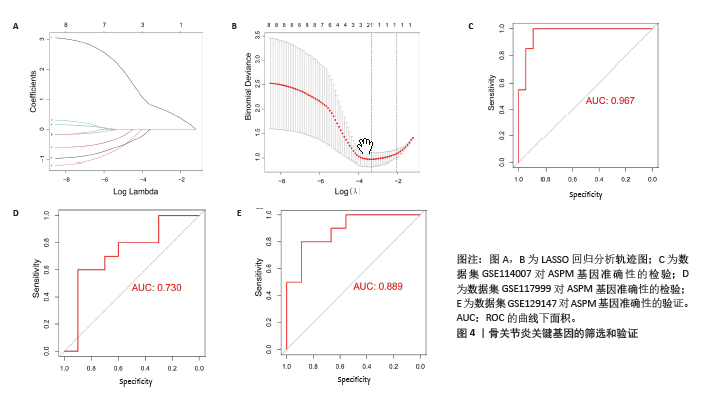
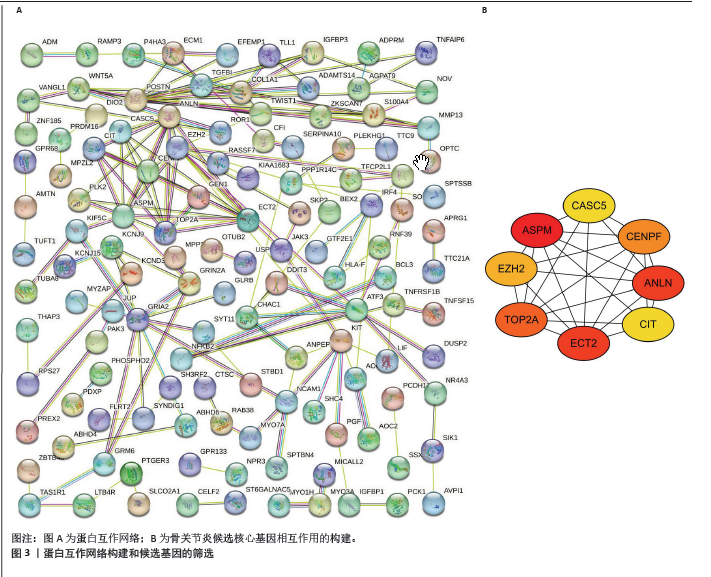
2.4 蛋白-蛋白互作网络的构建和候选核心基因的筛选 利用在线STRING数据库构建蛋白互作网络(图3A),并使用cytoscape软件进行蛋白互作网络可视化,并利用 Cytohubba插件MCC算法鉴定前8个候选基因,分别为ASPM、ANLN、ECT2、TOP2A、CENPF、 EZH2、CASC5、CIT基因(图3B)。 2.5 核心基因的检验和验证 通过LASSO回归分析和lambda值分析(图4A,B),在这些候选基因中筛选出差异基因ASPM与骨关节炎最为显著相关,随后对差异基因ASPM与骨关节炎相关性模型绘制ROC曲线图,结果显示GSE114007 ROC的曲线下面积值为0.967(图4C),GSE114007 ROC的曲线下面积值为0.730(图4D),并且外部数据集GSE129147验证了差异基因ASPM与骨关节炎显著相关的准确性,结果显示曲线下面积值为0.889(图4E),从而得出差异基因ASPM表达与骨关节炎显著相关。"
| [1] XIONG Y, MI BB, LIU MF, et al. Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2246-2256. [2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [3] MCKENZIE S, TORKINGTON A. Osteoarthritis - management options in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 2010;39(9):622-625. [4] VINCENT TL. Targeting mechanotransduction pathways in osteoarthritis: a focus on the pericellular matrix. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(3): 449-454. [5] SHEN S, WU Y, CHEN J, et al. CircSERPINE2 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(6):826-836. [6] SCHULZE-TANZIL G. Intraarticular Ligament Degeneration Is Interrelated with Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2019;8(9):990. [7] MEDVEDEVA EV, GREBENIK EA, GORNOSTAEVA SN, et al. Repair of Damaged Articular Cartilage: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(8):2366. [8] BHOSALE AM, RICHARDSON JB. Articular cartilage: structure, injuries and review of management. Br Med Bull. 2008;87: 77-95.[9] MOBASHERI A, RAYMAN MP, GUALILLO O, et al. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(5): 302-311. [10] JEON OH, KIM C, LABERGE RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775-781. [11] GAO X, JIANG S, DU Z, et al. KLF2 Protects against Osteoarthritis by Repressing Oxidative Response through Activation of Nrf2/ARE Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019: 8564681. [12] LU J, BI Y, ZHU Y, et al. CD3D, GZMK, and KLRB1 Are Potential Markers for Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Especially in Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody-Negative Patients. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12:726529. [13] WANG Z, CAO L, ZHOU S, et al. Construction and Validation of a Novel Pyroptosis-Related Four-lncRNA Prognostic Signature Related to Gastric Cancer and Immune Infiltration. Front Immunol. 2022;13:854785. [14] LI N, LI Y, HU J, et al. A Link Between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and the Immune Microenvironment of Salivary Glands in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Front Immunol. 2022;13:845209. [15] ZHAO Z, HE S, YU X, et al. Analysis and Experimental Validation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Innate Immunity Gene CYFIP2 and Pan-Cancer. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 954848. [16] TAN Y, LU L, LIANG X, et al. Identification of a pyroptosis-related lncRNA risk model for predicting prognosis and immune response in colon adenocarcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20(1):118. [17] CHEN M, ZHANG J, LIN X, et al. A pyroptosis-related prognosis model to predict survival in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2022;15(4):168-182. [18] LAFEBER FP, VAN SPIL WE. Osteoarthritis year 2013 in review: biomarkers; reflecting before moving forward, one step at a time. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(10): 1452-1464. [19] FISCH KM, GAMINI R, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, et al. Identification of transcription factors responsible for dysregulated networks in human osteoarthritis cartilage by global gene expression analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018; 26(11):1531-1538. [20] AŞIK MD, GÜRSOY S, AKKAYA M, et al. Microarray analysis of cartilage: comparison between damaged and non-weight-bearing healthy cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(5):456-464. [21] WANG J, FAN Q, YU T, et al. Identifying the Hub Genes and Immune Cell Infiltration in Synovial Tissue between Osteoarthritic and Rheumatoid Arthritic Patients by Bioinformatic Approach. Curr Pharm Des. 2022; 28(6):497-509. [22] CHEN Y, LIAO R, YAO Y, et al. Machine learning to identify immune-related biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis based on WGCNA network. Clin Rheumatol. 2022;41(4):1057-1068. [23] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559. [24] EMERY CA, WHITTAKER JL, MAHMOUDIAN A, et al. Establishing outcome measures in early knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(7):438-448. [25] GEYER M, SCHÖNFELD C. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):98-107. [26] JIANG C, LI Z, WU Z, et al. Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis of Hub Genes and Pathways Associated with a Compression Model of Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e927107. [27] STAHL D, GENTLES AJ, THIELE R, et al. Prognostic profiling of the immune cell microenvironment in Ewing´s Sarcoma Family of Tumors. Oncoimmunology. 2019;8(12):e1674113. [28] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84. [29] ZHANG Y, ZHU T, HE F, et al. Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Osteoarthritis via Bioinformatic Tools: An Updated Analysis. Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl):1457S-1464S. [30] JIANG F, ZHOU H, SHEN H. Identification of Critical Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on WGCNA and LASSO Algorithm. Front Immunol. 2022;13:925695. [31] ZHANG C, HUANG R, XI X. Comprehensive Analysis of Pyroptosis-Related Genes and Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration Characterization in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9: 871602. [32] CARBALLO CB, NAKAGAWA Y, SEKIYA I, et al. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage. Clin Sports Med. 2017;36(3):413-425. [33] DUNCAN-LEWIS C, HARTENIAN E, KING V, et al. Cytoplasmic mRNA decay represses RNA polymerase II transcription during early apoptosis. Elife. 2021:10:e58342. [34] WANG H, LIU H, ZHAO X, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-actin complex derived from extracellular vesicles facilitates proliferation and migration of human coronary artery endothelial cells by promoting RNA polymerase II transcription. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):11469-11486. [35] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU KA, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;132:90-100. [36] LU J, ZHANG H, PAN J, et al. Fargesin ameliorates osteoarthritis via macrophage reprogramming by downregulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):142. [37] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53. [38] CAO Y, TANG S, NIE X, et al. Decreased miR-214-3p activates NF-κB pathway and aggravates osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. 2021;65:103283. [39] QI Y, TANG R, SHI Z, et al. Wnt5a/Platelet-rich plasma synergistically inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory activity through NF-κB signaling pathway and prevents cartilage damage and promotes meniscus regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(7):612-624. [40] ZHANG K, LI Z, LU Y, et al. Silencing of Vangl2 attenuates the inflammation promoted by Wnt5a via MAPK and NF-κB pathway in chondrocytes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021; 16(1):136. [41] DENG Z, HU X, ALAHDAL M, et al. High expression of MAPK-14 promoting the death of chondrocytes is an important signal of osteoarthritis process. PeerJ. 2021;9:e10656. [42] SUTHON S, PERKINS RS, BRYJA V, et al. WNT5B in Physiology and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:667581. [43] 郑莉芳, 陈佩杰, 肖卫华. 骨骼肌质量控制信号通路[J]. 生理学报, 2019,71(4): 671-679. [44] LU HC, FORNILI A, FRATERNALI F. Protein-protein interaction networks studies and importance of 3D structure knowledge. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2013;10(6):511-520. [45] JONSSON PF, BATES PA. Global topological features of cancer proteins in the human interactome. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(18): 2291-2297. [46] RAMBALDI D, GIORGI FM, CAPUANI F, et al. Low duplicability and network fragility of cancer genes. Trends Genet. 2008;24(9): 427-430. [47] FRANCESCHINI A, SZKLARCZYK D, FRANKILD S, et al. STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D808-D815. [48] ZHANG Z, PAN J, CHENG D, et al. Expression of lactate-related signatures correlates with immunosuppressive microenvironment and prognostic prediction in ewing sarcoma. Front Genet. 2022;13:965126. [49] TIBSHIRANI R. The lasso method for variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med. 1997;16(4):385-395. [50] FENG Y, ZHANG C, WU Z, et al. Incorporation of liver chemistry score in predicting survival of liver-involved advanced gastric cancer patients who received palliative chemotherapy. Cancer Med. 2023;12(3):2831-2841. [51] OBUCHOWSKI NA, BULLEN JA. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves: review of methods with applications in diagnostic medicine. Phys Med Biol. 2018;63(7):07TR01. [52] WANG F, CHANG Y, LI J, et al. Strong correlation between ASPM gene expression and HCV cirrhosis progression identified by co-expression analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49(1):70-76. [53] SAFIEDDINE A, COLENO E, SALLOUM S, et al. A choreography of centrosomal mRNAs reveals a conserved localization mechanism involving active polysome transport. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1): 1352. [54] NASEER MI, ABDULKAREEM AA, MUTHAFFAR OY, et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies Three Novel Mutations in the ASPM Gene From Saudi Families Leading to Primary Microcephaly. Front Pediatr. 2020;8:627122. [55] TU Z, HE X, ZENG L, et al. Exploration of Prognostic Biomarkers for Lung Adenocarcinoma Through Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Genet. 2021;12:647521. |
| [1] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [2] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [7] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [8] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [9] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [10] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [11] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [12] | De Ji, Suo Langda, Wei Yuchen, Wang Bin, Awangcuoji, Renqingcuomu, Cui Jiuzeng, Zhang Lei, Ba Gui. Comprehensive analysis of genes related to endometrial receptivity and alternative splicing events in northwest Tibetan cashmere goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [14] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [15] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||