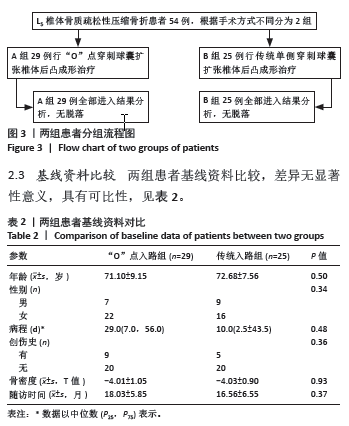
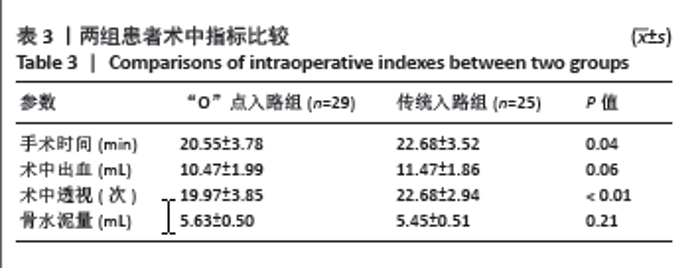
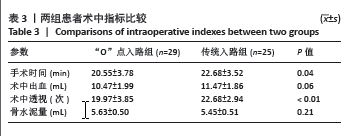
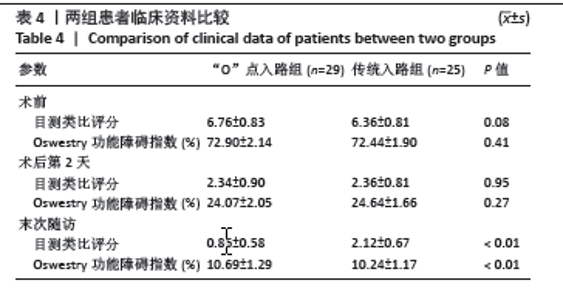
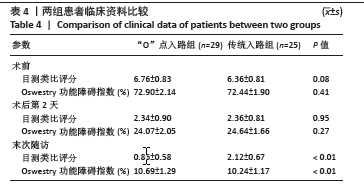
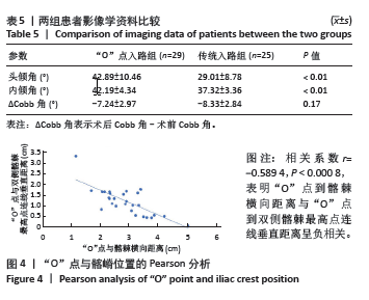
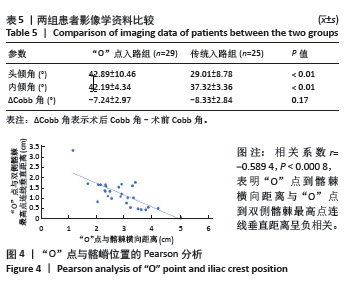
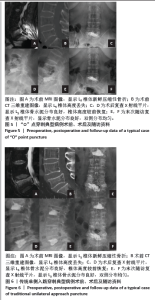
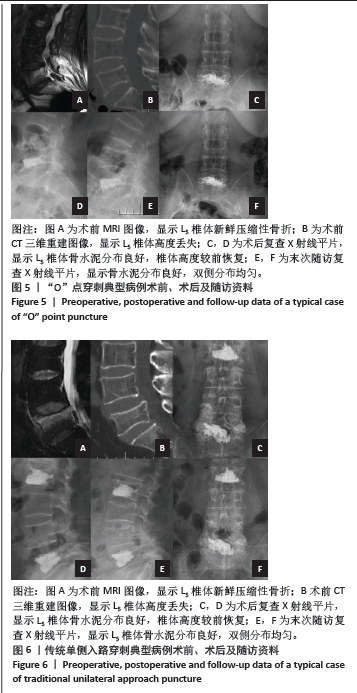
[1] LEE DG, PARK CK, PARK CJ, et al. Analysis of Risk Factors Causing New Symptomatic Vertebral Compression Fractures After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A 4-year Follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(10):E578-E583.
[2] HUANG J, YANG J, CHEN L, et al. A novel puncture approach via point “O” for percutaneous kyphoplasty in patients with L4 or L5 osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):18868.
[3] 刘瑞祯, 王望任, 郝晨, 等. 骨水泥分布对单侧穿刺经皮椎体成形治疗单节段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折后相邻椎体骨折的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(28):4498-4504.
[4] STEINMANN J, TINGEY CT, CRUZ G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(2): 201-205.
[5] 乔俊, 李松, 李刚, 等.单侧与双侧PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折临床疗效比较及骨水泥渗漏的危险因素分析[J].现代生物医学进展,2023,23(14): 2709-2713+2676.
[6] TAKAHASHI S, INOSE H, TAMAI K, et al. Risk of Revision After Vertebral Augmentation for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture: A Narrative Review. Neurospine. 2023;20(3): 852-862.
[7] HE H, TAN Y, YANG S, et al. Study of Unilateral Extrapedicular and Bilateral Pedicle Approach Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022;32(7):924-927.
[8] CHEN B, LI Y, XIE D, et al. Comparison of unipedicular and bipedicular kyphoplasty on the stiffness and biomechanical balance of compression fractured vertebrae. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(8):1272-1280.
[9] HUANG Z, WAN S, NING L, et al. Is unilateral kyphoplasty as effective and safe as bilateral kyphoplasties for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures? A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(9):2833-2842.
[10] CHEN H, TANG P, ZHAO Y, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Orthopedics. 2014;37(9):e828-e835.
[11] 陆兆华, 孙天泽, 张警, 等. 不同入路椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(36):5834-5839.
[12] 王延涛, 陈怡, 潘美均, 等. 单侧与双侧椎弓根入路注入骨水泥治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折有效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(10):1633-1640.
[13] ZHANG L, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. Bone cement distribution in the vertebral body affects chances of recompression after percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:431-436.
[14] 王松, 康建平, 冯大雄, 等. 经横突-椎弓根单侧穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折[J]. 山东医药,2012,52(32):20-22.
[15] 王松, 王清, 康建平, 等. 经横突-椎弓根单侧穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(7):622-626.
[16] 张帅, 王清, 王松, 等. 经横突-椎弓根入路单侧穿刺经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗腰椎骨质疏松性椎体骨折的疗效观察[J]. 华西医学,2020,35(10):1158-1163.
[17] 赵鹏, 慈元, 李志君, 等. 经椎间孔入路椎体成形术治疗Kümmell病的临床疗效[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(2):184-188.
[18] LIN HH, CHANG MC, CHOU PH, et al. Preoperative Planning of the Lateral Entry Point Is Necessary in Percutaneous L5 Vertebroplasty. World Neurosurg. 2017; 104:476-481.
[19] 李子祥, 李绍科, 刘丰春. 与经皮椎体成形术相关的L_5椎弓根影像解剖学研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(2):160-162.
[20] WANG S, WANG Q, KANG J, et al. An imaging anatomical study on percutaneous kyphoplasty for lumbar via a unilateral transverse process-pedicle approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(9):701-706.
[21] 王宇, 康建平, 王松, 等. 髂嵴-横突基底-椎体对角单侧穿刺L_5椎体后凸成形术[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(3):254-256.
[22] MENG H, LI Q, LIN J, et al. Intradiscal cement leakage (ICL) increases the stress on adjacent vertebrae after kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebra compression fracture (OVCF): a finite-element study. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):15984.
[23] DAI C, LIANG G, ZHANG Y, et al. Risk factors of vertebral re-fracture after PVP or PKP for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures, especially in Eastern Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1): 161.
[24] 詹子浩, 李然, 傅栋铭, 等. 单节段胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折经皮椎体后凸成形术后其他椎体新发骨折的影响因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022, 32(12):1095-1101.
[25] WARDLAW D, CUMMINGS SR, VAN MEIRHAEGHE J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9668):1016-1024.
[26] RINGER AJ, BHAMIDIPATY SV. Percutaneous access to the vertebral bodies: a video and fluoroscopic overview of access techniques for trans-, extra-, and infrapedicular approaches. World Neurosurg. 2013;80(3-4):428-435.
[27] 吴静晔, 韦祎, 李加宁, 等.结合术前CT规划及术中透视建立穿刺通道技术在老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折手术中的应用[J]. 实用老年医学,2019, 33(8):801-805.
[28] LIEN SB, LIOU NH, WU SS. Analysis of anatomic morphometry of the pedicles and the safe zone for through-pedicle procedures in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8):1215-1222.
[29] LIU L, CHENG S, WANG Q, et al. An anatomical study on lumbar arteries related to the extrapedicular approach applied during lumbar PVP (PKP). PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0213164.
[30] WANG H, HU P, WU D, et al. Anatomical feasibility study of unilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for lumbar through the conventional transpedicular approach: An observational study using 3D CT analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(37):e12314.
[31] ZHANG S, OUYANG J, PENG X, et al. CT observation of L5 pedicle screw fixation shielding by the iliac wing width and height. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;189:105637.
[32] TEZUKA F, SAKAI T, ABE M, et al. Anatomical considerations of the iliac crest on percutaneous endoscopic discectomy using a transforaminal approach. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1875-1880. |